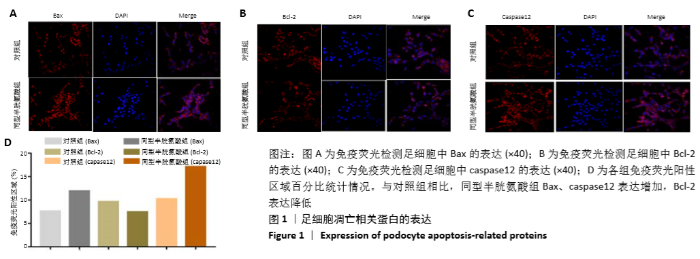
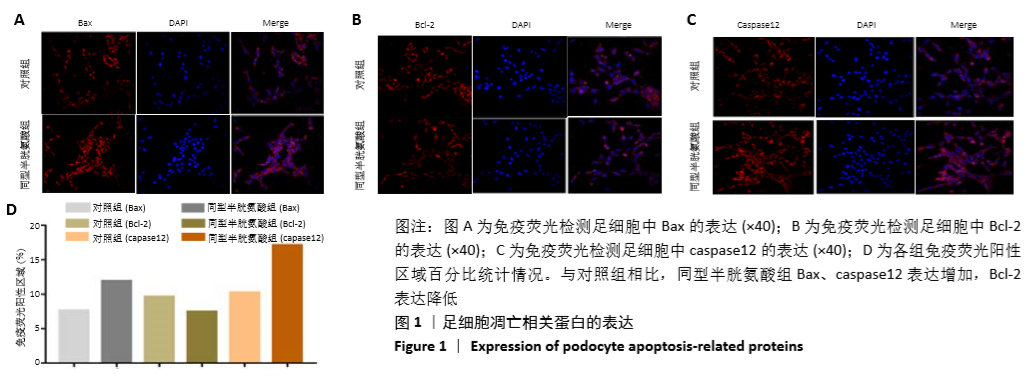
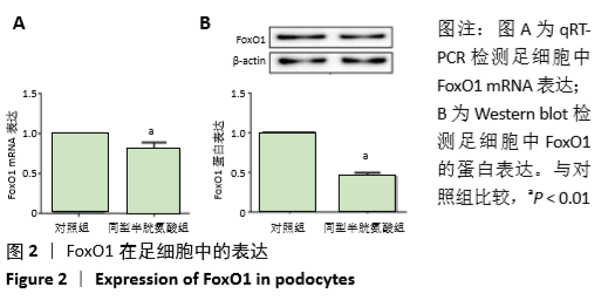
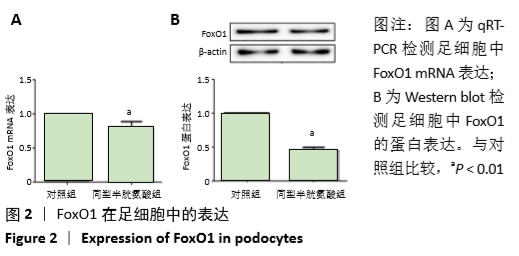
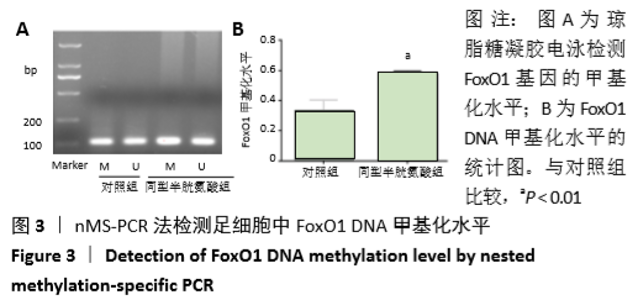
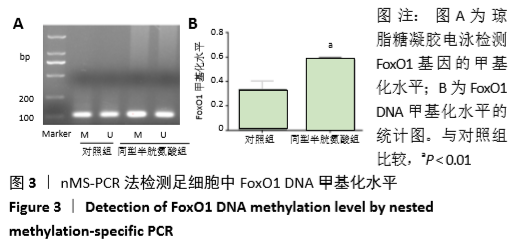
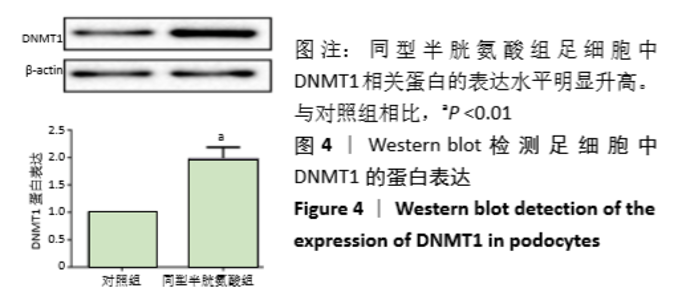
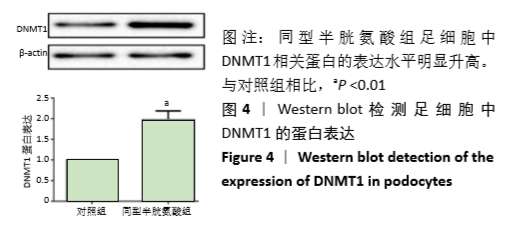
[1] OSTRAKHOVITCH EA, TABIBZADEH S. Homocysteine in Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv Clin Chem. 2015;72:77-106.
[2] KARMIN O, SIOW YL. Metabolic Imbalance of Homocysteine and Hydrogen Sulfide in Kidney Disease. Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(3): 367-377.
[3] 叶增纯,黎燕,张俊,等.原发性肾小球肾炎患者高同型半胱氨酸血症的发生率及与靶器官损害之间的关系[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2016,37(6):869-874+880.
[4] CHEN X, ZHAO L, XING Y, et al. Down-regulation of microRNA-21 reduces inflammation and podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy by relieving the repression of TIMP3 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 108:7-14.
[5] 蒲道静,郑府,徐先顺,等.萝卜硫素干预纳米细菌诱导肾小管上皮细胞凋亡及线粒体自噬相关蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(34):5503-5507.
[6] WEI X, YANG X, WANG B, et al. LncRNA MBNL1-AS1 represses cell proliferation and enhances cell apoptosis via targeting miR-135a-5p/PHLPP2/FoxO1 axis in bladder cancer. Cancer Med. 2019 Nov 25.
[7] XING YQ, LI A, YANG Y, et al. The regulation of FoxO1 and it is role in disease progression. Life Sci. 2018;193:124-131.
[8] 谢琳,丁宁,徐灵博,等.FoxO1 DNA甲基化在同型半胱氨酸致肝细胞凋亡中的作用[J].实用医学杂志,2018,34(16):2659-2662+2669.
[9] HISHIKAWA A, HAYASHI K, ABE T, et al. Decreased KAT5 Expression Impairs DNA Repair and Induces Altered DNA Methylation in Kidney Podocytes. Cell Rep. 2019;26(5):1318-1332.e4.
[10] LASSEIGNE BN,BROOKS JD.The Role of DNA Methylation in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Mol Diagn Ther. 2018;22(4):431-442.
[11] 丁宁,郭凤英,谢琳,等.miR-30a在同型半胱氨酸致足细胞凋亡中的作用[J].广东医学,2019,40(6):762-766.
[12] 李金红,陶建瓴,李航.足细胞损伤与糖尿病肾病的研究现状[J].中国医学科学院学报,2010,32(5):590-596.
[13] WU CC, ZHENG CM, LIN YF, et al. Role of homocysteine in end-stage renal disease. Clin Biochem. 2012; 45(16-17):1286-94.
[14] ZHOU YF, GUAN YF. [Hyperhomocysteinemia and kidney diseases]. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2018;70(6):607-611.
[15] CIANCIOLO G,DE PASCALIS A,DI LULLO L,et al. Folic Acid and Homocysteine in Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease Progression: Which Comes First? Cardiorenal Med. 2017;7(4):255-266.
[16] FAN Y, ZHANG J, XIAO W, et al. Rtn1a-Mediated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Podocyte Injury and Diabetic Nephropathy. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1): 323.
[17] WANG Y, LI H, SONG SP. β-Arrestin 1/2 Aggravates Podocyte Apoptosis of Diabetic Nephropathy via Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:1724-1732.
[18] WANG L, SCOTT I, ZHU L, et al. GCN5L1 modulates cross-talk between mitochondria and cell signaling to regulate FoxO1 stability and gluconeogenesis. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):523.
[19] 贺东黎.姜黄素通过ATK/FoxM1信号通路调控胃癌干细胞增殖及凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(32):4731-4737.
[20] CHAE YC, KIM JY, PARK JW, et al. FoxO1 degradation via G9a-mediated methylation promotes cell proliferation in colon cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(4):1692-1705.
[21] 张扬,吴朝蒙,雷博涵,等.PI3K/AKT/FoxO1信号通路参与复方中药CFF-1诱导的前列腺癌细胞凋亡和周期阻滞[J].中华男科学杂志,2017,23(09):828-837
[22] LIU Z, REN YA, PANGAS SA, et al. FOXO1/3 and PTEN Depletion in Granulosa Cells Promotes Ovarian Granulosa Cell Tumor Development. Mol Endocrinol. 2015; 29(7):1006-1024.
[23] TIRADO-MAGALLANES R, REBBANI K, LIM R, et al. Whole genome DNA methylation: beyond genes silencing. Oncotarget. 2017;8(3): 5629-5637.
[24] ZHANG L,ZHANG Q,LIU S,et al.DNA methyltransferases 1 may be a therapy target for attenuating diabetic nephropathy and podocyte injury. Kidney Int. 2017;92(1):140-153.
[25] 尹树慧,闫少春,周立社,等.肾细胞癌患者组织中RASSF1A、hMLH1及ALU甲基化水平的分析[J].临床检验杂志,2016,34(1): 31-34.
[26] 吴元,张文涛,马文超,等.SOX7启动子甲基化对膀胱癌增殖及凋亡的影响[J].医学研究生学报,2019,32(12):1285-1290.
[27] KIM M, COSTELLO J. DNA methylation: an epigenetic mark of cellular memory. Exp Mol Med. 2017 Apr 28;49(4):e322.
[28] MOORE LD, LE T, FAN G. DNA methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;38(1):23-38.
[29] AL-JAMAL HA,MAT JUSOH SA,HASSAN R,et al.Enhancing SHP-1 expression with 5-azacytidine may inhibit STAT3 activation and confer sensitivity in lestaurtinib (CEP-701)-resistant FLT3-ITD positive acute myeloid leukemia. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:869.
[30] 田平平,刘忠强,孔静,等.DNA甲基转移酶及分泌型卷曲相关蛋白1在糖尿病肾脏疾病大鼠肾组织中的表达研究[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2018,26(7):594-598. |