Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (2): 274-280.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2952
Previous Articles Next Articles
Maxing Xiongting Mixture regulates factors relevant to lung reshaping and vascular remodeling of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension rats
Li Songtao, Li Xinyi, Song Yunfeng, Ning Jiayin, Ren Qiang, Yang Renxu, Peng Bo
- Affiliated Hospital / Clinical Medical College of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2020-01-09Revised:2020-01-14Accepted:2020-03-07Online:2021-01-18Published:2020-11-21 -
Contact:Peng Bo, MD, Associate professor, Affiliated Hospital / Clinical Medical College of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Li Songtao, Affiliated Hospital / Clinical Medical College of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Seed Engineering Plan of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. 2018RZ0126; “Xinglin Scholar” Discipline Talent Culture Program of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. QNXZ2019042; the Fund of the Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 18PY15
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Songtao, Li Xinyi, Song Yunfeng, Ning Jiayin, Ren Qiang, Yang Renxu, Peng Bo. Maxing Xiongting Mixture regulates factors relevant to lung reshaping and vascular remodeling of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 274-280.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
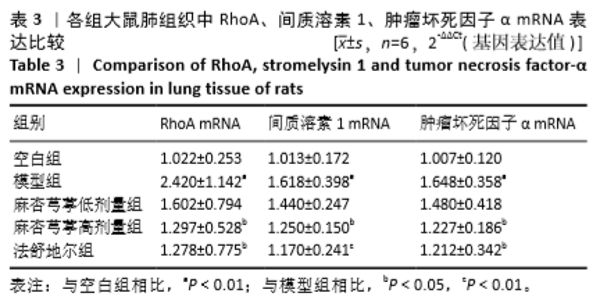
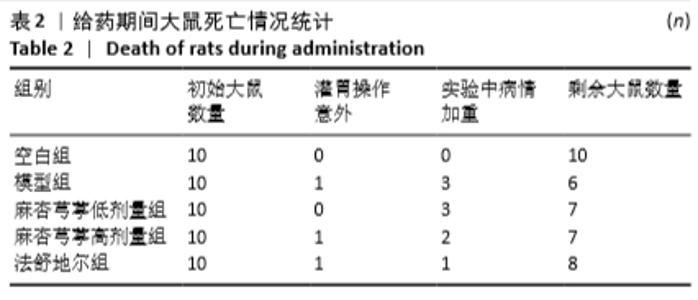
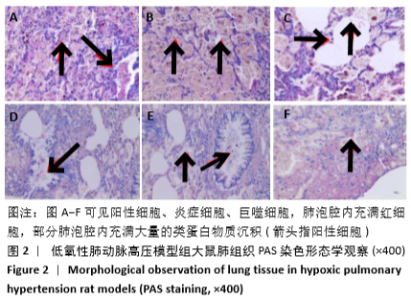
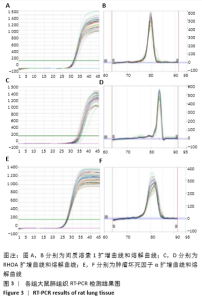
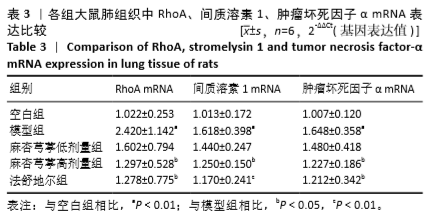
2.3.1 各组大鼠肺组织中RhoA基因表达比较 与空白组相比,模型组大鼠肺组织中RhoA基因表达明显升高(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,麻杏芎葶低剂量组大鼠肺组织中RhoA基因表达无明显差异;与模型组相比,麻杏芎葶高剂量组、法舒地尔组大鼠肺组织中RhoA基因表达降低P < 0.05);麻杏芎葶高剂量组与法舒地尔组相比RhoA mRNA表达差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。见表3。 2.3.2 各组大鼠肺组织中间质溶素1基因表达比较 与空白组相比,模型组大鼠肺组织中间质溶素1基因表达明显升高 (P < 0.01);与模型组相比,麻杏芎葶高剂量组大鼠肺组织中间质溶素1基因表达降低(P < 0.05),法舒地尔组大鼠肺组织中间质溶素1基因表达明显降低(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,麻杏芎葶低剂量组大鼠肺组织中间质溶素1基因表达无明显差异;麻杏芎葶高剂量组与法舒地尔组相比,间质溶素1基因表达差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。见表3。 2.3.3 各组大鼠肺组织中肿瘤坏死因子α基因表达比较 与空白组相比,模型组大鼠肺组织中肿瘤坏死因子α表达明显升高(P < 0.01)。与模型组相比,麻杏芎葶低剂量组大鼠肺组织中肿瘤坏死因子α基因表达差异无显著性意义;与模型组相比,麻杏芎葶高剂量组、法舒地尔组大鼠肺组织中肿瘤坏死因子α基因表达降低P < 0.05);麻杏芎葶高剂量组与法舒地尔组相比肿瘤坏死因子α基因表达无明显差异(P > 0.05)。见表3。 "
| [1] SARODE R, BALLAS SK, GARCIA A, et al. Red blood cell exchange: 2015 American Society for Apheresis consensus conference on the management of patients with sickle cell disease. J Clin Apher. 2017; 32(5): 342-367. [2] 郑莉莉,王婕琼,李泽庚.“肺络微型癥瘕”与慢性阻塞性肺疾病肺血管重构的相关性[J].长春中医药大学学报, 2017,33(1): 7-9. [3] 李泽庚,王传博,彭波,等.慢性阻塞性肺疾病痰瘀阻肺证大鼠模型的建立[J].天津中医药,2010,27(1): 43-45. [4] 李俊山, 龙超良, 崔文玉,等.野百合碱诱导大鼠肺动脉高压及肺源性心脏病的病理生理特征[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志, 2012, 28(3):193-196. [5] IKEDA S, SATOH K, KIKUCHI N, et al. Crucial role of rho-kinase in pressure overload-induced right ventricular hypertrophy and dysfunction in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2014;34(6): 1260-1671. [6] LIU WH, XU XH, LUO Q, et al. Inhibition of the RhoA/Rho-associated, coiled-coil-containing protein kinase-1 pathway is involved in the therapeutic effects of simvastatin on pulmonary arterial hypertension.Clin Exp Hypertens.2018;40(3): 224-230. [7] WU F, YAO W, YANG J, et al. Protective effects of aloperin on monocroline-induced pulmonary hypertension via regulation of Rho A/Rho kinsase pathway in rats. Biomed Pharmacother.2017;95: 1161-1168. [8] CHEN IC, TAN MS, WU BN, et al. Statins ameliorate pulmonary hypertension secondary to left ventricular dysfunction through the Rho-kinase pathway and NADPH oxidase. Pediatr Pulmonol.2017;52(4): 443-457. [9] GIEN J, TSENG N, SEEDORF G, et al. Endothelin-1-Rho kinase interactions impair lung structure and cause pulmonary hypertension after bleomycin exposure in neonatal rat pups.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2016;311(6): L1090-L1100. [10] WALKER J, UNDEM C, YUN X, et al. Role of Rho kinase and Na+/H+ exchange in hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration.Physiol Rep. 2016;4(6). pii: e12702. [11] FUKUMOTO Y, YAMADA N, MATSUBARA H, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial with a rho-kinase inhibitor in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Circ J.2013;77(10): 2619-2625. [12] Storck EM, Wojciak-Stothard B. Rho GTPases in pulmonary vascular dysfunction. Vascul Pharmacol.2013; 58(3): 202-210. [13] CHEN XY, DUN JN, MIAO QF, et al. Fasudil hydrochloride hydrate, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, suppresses 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation via JNK and ERK1/2 pathway. Pharmacology.2009;83(2): 67-79. [14] Wang XY, Mo D, Tian W, et al. Inhibition of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway ameliorates hypoxic pulmonary hypertension via HIF-1α-dependent functional TRPC channels, Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019;369:60-72. [15] Fediuk J, Gutsol A, Nolette N, Dakshinamurti S. Thromboxane-induced actin polymerization in hypoxic pulmonary artery is independent of Rho.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2012;302(1): L13-26. [16] Sun XZ, Li SY, Tian XY, et al. Effect of Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil on the expression ET-1 and NO in rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension.Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2019;71(1):3-8. [17] Wojciak-Stothard B. New drug targets for pulmonary hypertension: Rho GTPases in pulmonary vascular remodelling.Postgrad Med J. 2008; 84(993):348-353. [18] Mair KM, MacLean MR, Morecroft I,et al.Novel interactions between the 5-HT transporter, 5-HT1B receptors and Rho kinase in vivo and in pulmonary fibroblasts.Br J Pharmacol.2008;155(4): 606-616. [19] 张俊志,李涵葳,张中军,等.TNF-α在先天性体-肺分流性肺动脉高压大鼠中的表达变化[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2018,47(4): 445-449. [20] FUJITA M, MASON RJ, COOL C, et al. Pulmonary hypertension in TNF-alpha-overexpressing mice is associated with decreased VEGF gene expression. J Appl Physiol (1985).2002;93(6): 2162-2170. [21] LEI Y, ZHEN J, MING XL,et al. Induction of higher expression of IL-beta and TNF-alpha, lower expression of IL-10 and cyclic guanosine monophosphate by pulmonary arterial hypertension following cardiopulmonary bypass.Asian J Surg.2002;25(3): 203-208. [22] WETZL V, TIEDE SL, FAERBER L,et al.Plasma MMP2/TIMP4 Ratio at Follow-up Assessment Predicts Disease Progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Lung.2017;195(4): 489-496. [23] WANG JJ, ZUO XR, XU J, et al.Evaluation and Treatment of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress in Right Ventricular Dysfunction during Monocrotaline-Induced Rat Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther.2016;30(6): 587-598. [24] HOFFMANN J, MARSH LM, PIEPER M, et al.Compartment-specific expression of collagens and their processing enzymes in intrapulmonary arteries of IPAH patients. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015;308(10): L1002-1013. [25] KAUR G, SINGH N, LINGESHWAR P, et al. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1: an emerging target in right ventricle dysfunction associated with pulmonary hypertension.Pulm Pharmacol Ther.2015; 30: 66-79. [26] BIASIN V, MARSH LM, EGEMNAZAROV B, et al. Meprin β, a novel mediator of vascular remodelling underlying pulmonary hypertension.J Pathol.2014;233(1): 7-17. [27] TIEDE SL, WASSENBERG M, CHRIST K, et al. Biomarkers of tissue remodeling predict survival in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Int J Cardiol. 2016. 223: 821-826. [28] YASUDA T, TADA Y, TANABE N, et al.R ho-kinase inhibition alleviates pulmonary hypertension in transgenic mice expressing a dominant-negative type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor gene. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. 301(5): L667-1674. [29] 王筠默.中药药理学[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,1985:25-27. [30] 刘兴隆,贾波,黄绣深,等.苦杏仁药理研究概况[J].江苏中医药, 2005,26(7):59. [31] 丁东宁,谭延华,刘俊儒,等.镇原苦杏仁化学成分的研究[J].西北药学杂志,1990,5(3):21-23. [32] 周英,郜文.苦杏仁的生理功能和保健饮料的研制[J].食品工业科技,2000,21(5):19-50. [33] 甘露.大鼠 pEGFP-N1-BKβ1真核表达载体的构建及苦杏仁苷对支气管平滑肌细胞增殖的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2007:28-30. [34] 孙明月,郭春雨,王景尚,等.铁调素高表达与内皮损伤的相关性及川芎嗪的干预作用[J].中草药,2015,46( 15) : 2265-2269 [35] 李海刚,胡晒平,周意,等.川芎主要药理活性成分药理研究进展[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2018,23(11):1302-1308. [36] LV L, JIANG SS, XU J, et al. Protective effect of ligustrazine against myocardial ischaemia reperfusion inrats: the role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.2012;39( 1) : 20-27. [37] SONG S, ZHANG M, YI Z, et al. The role of PDGF-B/TGF-β1/neprilysin network in regulating endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary artery remodeling.Cell Signal.2016;28(10): 1489-501. [38] 苏琛,杨仁旭.麻杏芎葶合剂对低氧性肺动脉高压大鼠的干预作用及分子机制研究[J].四川中医,2015,33(9):37-39. |
| [1] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | Li Guijun, Fang Xiaohui, Kong Weifeng, Yuan Xiaoqing, Jin Rongzhong, Yang Jun. Finite element analysis of the treatment of hallux valgus deformity by microplate combined with super strong suture elastic fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 938-942. |
| [4] | Fan Jianchao, Xu Paidi, Han Yongli, Wen Caiyuzhu, Zhang Hongxing, Pan Xiaoli. Effects of electroacupuncture at Zusanli acupoint on visceral hypersensitivity in rats with functional dyspepsia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 663-668. |
| [5] | Dong Miaomiao, Lai Han, Li Manling, Xu Xiuhong, Luo Meng, Wang Wenhao, Zhou Guoping. Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3/cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1 in rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 749-755. |
| [6] | Huang Shibo, Xie Hui, Wang Zongpu, Wang Weidan, Qin Kairong, Zhao Dewei. Application of degradable high-purity magnesium screw in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 493-498. |
| [7] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [8] | Wang Ruanbin, Cheng Liqian, Chen Kai. Application and value of polymer materials in three-dimensional printing biological bones and scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 610-616. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Liu Yubo, Zhang Huizeng, Zhang Tongrun, Sui Gengyi, Ma Nan, Cheng Xu, Gao Xupeng, Xu Jing, Wang Chaoliang. Correlation analysis between the morphological changes of ankle acupoints and the ankle function after ankle fracture surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 440-445. |
| [11] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Huanan, Chen Feng, Chai Yuan, Gan Bin, Li Song, Chen Dingpeng. Potential molecular mechanism of Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Decoction in the treatment of gouty arthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 245-252. |
| [12] | Sun Xinzheng, Chen Xiaoke, Wang Chenghao, He Hui. Exercise improves pain induced by sciatic nerve injury in animal models: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 321-328. |
| [13] | Li Wanhai, Dong Yuhang, Shi Chao, Jiang Yiyao, Liu Ge, Diao Wenjie, Wu Zhen. Ligustrazine furoxan complex protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 205-210. |
| [14] | Li Shulun, Hao Peng, Hao Fei, Duan Hongmei, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Chaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Pathological changes in rats with ischemic stroke induced by improved photochemical embolization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 218-224. |
| [15] | Kang Yue, Liu Jie. Biological function of circular RNAs in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 106-111. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||