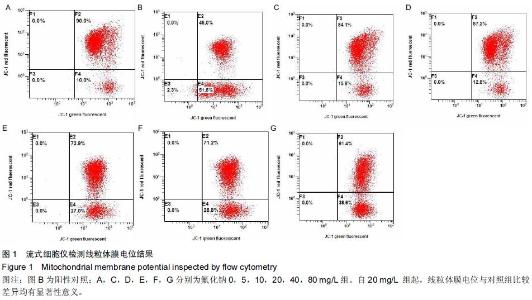
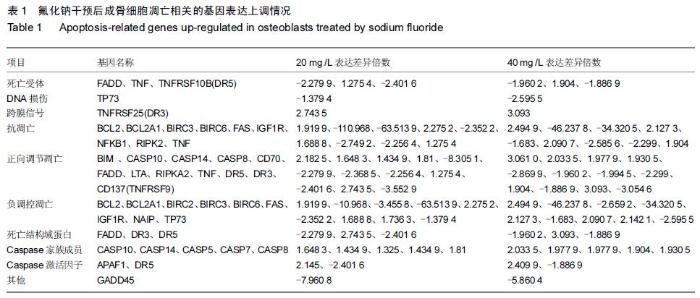
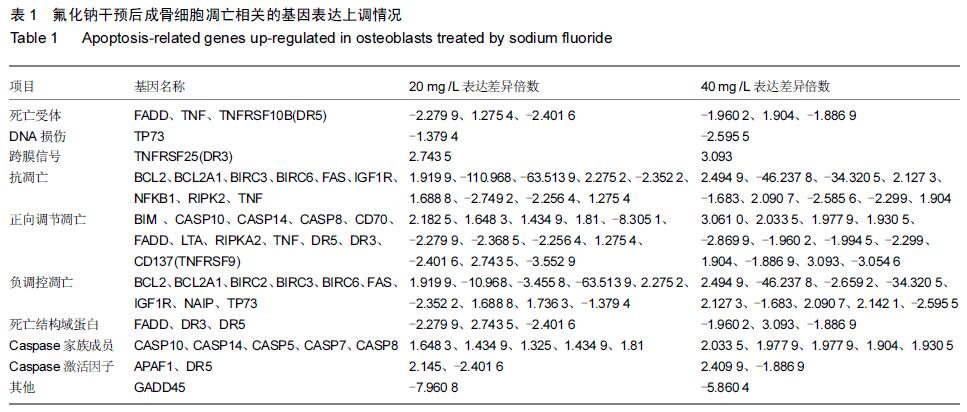
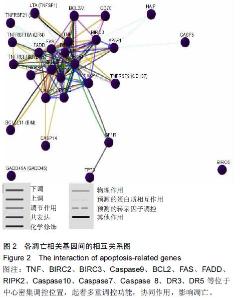
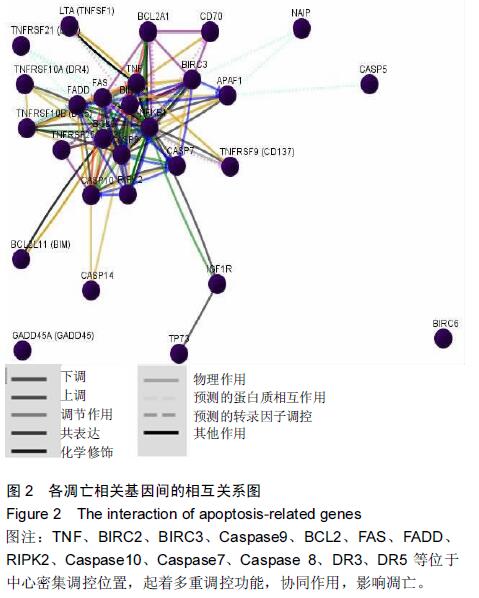
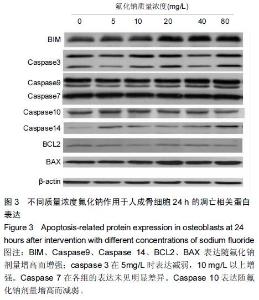
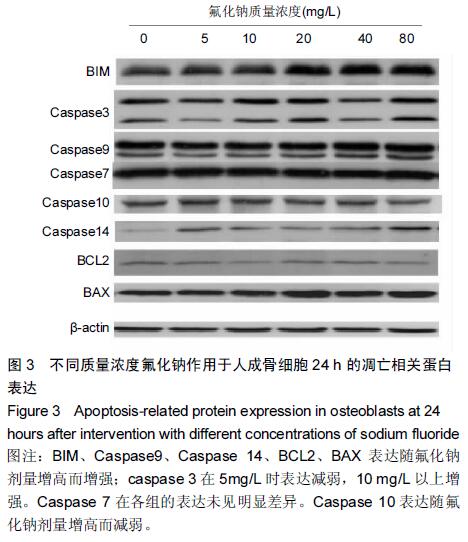
|
[1] 官志忠.关注地方性氟中毒发病机制研究的重要性和热点问题[J].中华地方病学杂志,2014,33(2):119-120.
[2] Huo L, Liu K, Pei J, et al. Fluoride promotes viability and differentiation of osteoblast-like Saos-2 cells via BMP/Smads signaling pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013;155(1): 142-149.
[3] Mitsui N, Suzuki N, Maeno M, et al. Optimal compressive force induces bone formation via increasing bone morphogenetic proteins production and decreasing their antagonists production by Saos-2 cells. Life Sci. 2006;78(23): 2697-2706.
[4] Degasne I, Basle MF, Demais V, et al. Effects of roughness, fibronectin and vitronectin on attachment, spreading, and proliferation of human osteoblast-like cells (Saos-2) on titanium surfaces. Calcif Tissue Int.1999;64(6):499-507.
[5] Huang Y, Dai H, Guo QN. TSSC3 overexpression reduces stemness and induces apoptosis of osteosarcoma tumor-initiating cells. Apoptosis.2012;17(8):749-761.
[6] Tsutsui H, Kinugawa S, Matsushima S. Mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction in myocardial remodelling. Cardiovasc Res.2009;81(3):449-456.
[7] Joseph B, Marchetti P, Formstecher P, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction is an essential step for killing of non-small cell lung carcinomas resistant to conventional treatment. Oncogene.2002;21(1):65-77.
[8] Sugiyama T, Shimizu S, Matsuoka Y, et al. Activation of mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel by apro-apoptotic of BH3-only protein Bim. Oncogene. 2002; 21(32):4944-4956.
[9] 张亚楼,孙小娜,冯树梅,等.过量氟引起成骨细胞内质网应激信号通路的基因差异表达[J].重庆医学,2014,43(33): 4425-4427.
[10] 郭晓东,杨茂伟,梁单,等.氟诱导成骨细胞MC3T3-E1自噬与凋亡及其相互作用分析[J].中国地方病防治杂志,2012,27(3): 165-168.
[11] 陈燕平,王长松,刘家骝,等.不同浓度氟对兔成骨细胞细胞周期及凋亡的影响[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(32):7124-7126.
[12] Yang S, Wang Z, Farguharson C, et al. Sodium fluoride induces apoptosis and alters bcl-2 family protein expression in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2011;410(4):910-915.
[13] 王军舰,王海彬.氟对人成骨样细胞株凋亡的影响[J].中国公共卫生,2005,21(12):1453-1455.
[14] Crowder RN, El-Deiry WS. Caspase-8 regulation of TRAIL-mediated cell death. Exp Oncol. 2012;34(3): 160-164.
[15] Ryter SW, Mizumura K, Choi AM. The impact of autophagy on cell death modalities. Int J Cell Biol.2014;2014:502676.
[16] Liu XL, Li CC, Liu KJ, et al. The Influence of Fluoride on the Expression of Inhibitors of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Rat Skin Fibroblast Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012; 148(1): 117-121.
[17] 宋秀祖,相文忠,许爱娥.Caspase-14在表皮终末分化及皮肤屏障中的作用[J].中国中西医结合皮肤性病学杂志,2009,8(1):65-67.
[18] Lu P, Li X, Ruan L, et al. Effect of siRNA PERK on fluoride-induced osteoblastic differentiation in OS732 cells. Biol Trace Elem Res.2014;159 (1-3):434-439.
[19] Sun F, Li X, Yang C, et al. A role for PERK in the mechanism underlying fluoride-induced bone turnover. Toxicology.2014; 325:52-66.
|