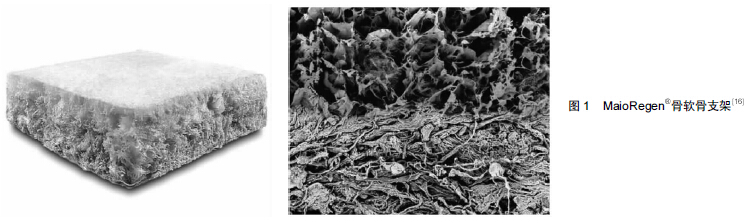
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (43): 7017-7022.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.43.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
Calcium phosphate as a scaffold for repair of osteochondral defects
Cai Zhu-yun, Peng Fan, Zi Yun-peng, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong
- Department of Joint Surgery, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University of PLA, Shanghai 200003, China
-
Received:2015-08-14Online:2015-10-15Published:2015-10-15 -
Contact:Qian Qi-rong, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Joint Surgery, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University of PLA, Shanghai 200003, China -
About author:Cai Zhu-yun, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Joint Surgery, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University of PLA, Shanghai 200003, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai, No. 09ZR1410100; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81171727
Cite this article
Cai Zhu-yun, Peng Fan, Zi Yun-peng, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong . Calcium phosphate as a scaffold for repair of osteochondral defects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(43): 7017-7022.
share this article
|
[1] Seo SJ,Mahapatra C,Singh RK,et al.Strategies for osteochondral repair: Focus on scaffolds.J Tissue Eng. 2014;5:2041731414541850.
[2] 许荣耀,张寿.组织工程化软骨修复关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(41):7747-7750.
[3] Varga I,Zamborský R,Böhmer D.The tissue engineering of articular cartilage: cells, scaffolds and stimulating factors.Exp Biol Med (Maywood).2012;237(1):10-17.
[4] Chen F, Zhu YJ. Multifunctional Calcium Phosphate Nanostructured Materials and Biomedical Applications.Curr Nanosci.2014;10(4):465-485.
[5] Dorozhkin SV.Biocomposites and hybrid biomaterials based on calcium orthophosphates. Biomatter.2011;1(1):3-56.
[6] Dorozhkin SV.Calcium orthophosphates in nature, biology and medicine. Materials.2009; 2(2): 399-498.
[7] Gomoll A H,Madry H,Knutsen G,et al.The subchondral bone in articular cartilage repair: current problems in the surgical management. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18(4):434-447.
[8] Ignjatovic NL,Ajdukovic ZR,Savic VP,et al.Size effect of calcium phosphate coated with poly-DL-lactide-co-glycolide on healing processes in bone reconstruction.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2010;94(1):108-117.
[9] Wu G,Wang YJ,Lu H D,et al.Application of Multilayer Collagen/HA Scaffold in Cartilage Tissue Engineering.Key EngMater.2007;336:1549-1552.
[10] Zhou J,Xu C,Wu G,et al.In vitro generation of osteochondral differentiation of human marrow mesenchymal stem cells in novel collagen–hydroxyapatite layered scaffolds. Acta Biomaterialia.2011;7(11):3999-4006.
[11] 刘兴漠,项禹诚,麦海民,等.关节软骨-骨一体化修复体修复全层关节软骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(4): 365-371.
[12] 刘兴漠,项禹诚,潘滔,等.胶原/羟基磷灰石一体化支架修复关节软骨缺损的机制研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2012,18(1): 37-40.
[13] Wang X,Grogan SP,Rieser F,et al.Tissue engineering of biphasic cartilage constructs using various biodegradable scaffolds: an in vitro study.Biomaterials.2004;25(17): 3681-3688.
[14] Kon E,Delcogliano M,Filardo G,et al.Orderly osteochondral regeneration in a sheep model using a novel nano-composite multilayered biomaterial.J Orthop Res.2010;28(1):116-124.
[15] Kon E,Delcogliano M,Filardo G,et al.A novel nano-composite multi-layered biomaterial for treatment of osteochondral lesions: technique note and an early stability pilot clinical trial.Injury.2010;41(7):693-701.
[16] Kon E,Delcogliano M,Filardo G,et al.Novel nano-composite multilayered biomaterial for osteochondral regeneration a pilot clinical trial.Am J Sports Med.2011;39(6):1180-1190.
[17] Kon E,Filardo G,Di Martino A,et al.Clinical results and MRI evolution of a nano-composite multilayered biomaterial for osteochondral regeneration at 5 years.Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(1):158-165.
[18] Ding X, Zhu M, Xu B,et al.Integrated trilayered silk fibroin scaffold for osteochondral differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2014;6(19): 16696- 16705.
[19] 王文良,张华亮,初殿伟,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞复合壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石支架修复兔膝骨软骨缺损[J].中华骨科杂志,2009, 29(1):61-64.
[20] 张华亮,王文良,关静,等.双层壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石复合支架的制备及性能研究[J].医疗卫生装备,2008,29(9):4-11.
[21] Lee CH,Cook JL,Mendelson A,et al.Regeneration of the articular surface of the rabbit synovial joint by cell homing: a proof of concept study.Lancet.2010;376(9739):440-448.
[22] 苏保,李吉东,蒋电明,等.聚氨酯/纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66股骨髁修复犬骨软骨缺损的实验研究[J].功能材料,2013,4(44): 493-497.
[23] Tanaka T,Komaki H,Chazono M,et al. Use of a biphasic graft constructed with chondrocytes overlying a β-tricalcium phosphate block in the treatment of rabbit osteochondral defects. Tissue Eng.2005;11(1-2):331-339.
[24] Zou C,Weng W,Deng X,et al.Preparation and characterization of porous β-tricalcium phosphate/collagen composites with an integrated structure.Biomaterials.2005;26(26): 5276-5284.
[25] 陈竹生,吕玉明,张兵.纳米β-磷酸三钙/Ⅰ、Ⅱ型胶原层状支架复合骨髓间充质干细胞修复膝关节骨软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2010,14(42):7797-7801.
[26] 査国庆,廖威明,王迎军,等.胶原复合梯度TCP修复关节软骨的形态学观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(8):989-992.
[27] Liu S,Wu J,Liu X,et al.Osteochondral regeneration using an oriented nanofiber yarn‐collagen type I/hyaluronate hybrid/TCP biphasic scaffold.JBiomedMater Res Part A.2015; 103(2):581-592.
[28] Shao X,Goh JCH,Hutmacher DW,et al.Repair of large articular osteochondral defects using hybrid scaffolds and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit model.Tissue Eng.2006;12(6):1539-1551.
[29] Zhang W,Lian Q,Li D,et al.The effect of interface microstructure on interfacial shear strength for osteochondral scaffolds based on biomimetic design and 3D printing.Mater Sci EngC.2015;46:10-15.
[30] Otani Y,Komura M,Komura H,et al.Optimal Amount of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor in Gelatin Sponges Incorporating β-Tricalcium Phosphate with Chondrocytes.Tissue Eng Part A.2015;21(3-4):627-636.
[31] 任强,孙水,张磊,等.应用生物反应器体外培养骨软骨复合体修复犬关节软骨损伤[J].中华创伤杂志,2010,26(4):361-365.
[32] Park EK,Lee E,Choi JY,et al.Cellular biocompatibility and stimulatory effects of calcium metaphosphate on osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived stromal cells. Biomaterials.2004;25(17):3403-3411.
[33] Waldman SD,Grynpas MD,Pilliar RM,et al.Characterization of cartilagenous tissue formed on calcium polyphosphate substrates in vitro.J Biomeical Mater Res.2002; 62(3): 323-330.
[34] Kandel RA,Grynpas M,Pilliar R,et al.Repair of osteochondral defects with biphasic cartilage-calcium polyphosphate constructs in a sheep model.Biomaterials.2006;27(22): 4120-4131.
[35] St-Pierre JP,Pilliar RM,Grynpas MD,et al.Calcification of cartilage formed in vitro on calcium polyphosphate bone substitutes is regulated by inorganic polyphosphate.Acta Biomaterialia.2010;6(8):3302-3309.
[36] St-Pierre JP,Gan L,Wang J,et al.The incorporation of a zone of calcified cartilage improves the interfacial shear strength between in vitro-formed cartilage and the underlying substrate. Acta Biomaterialia.2012;8(4):1603-1615.
[37] Gao J,Dennis JE,Solchaga LA,et al.Repair of osteochondral defect with tissue-engineered two-phase composite material of injectable calcium phosphate and hyaluronan sponge. Tissue Eng.2002;8(5):827-837.
[38] Huang X,Yang D,Yan W,et al.Osteochondral repair using the combination of fibroblast growth factor and amorphous calcium phosphate/poly (L-lactic acid) hybrid materials. Biomaterials.2007;28(20):3091-3100.
[39] Hsu S,Huang TB,Cheng SJ,et al.Chondrogenesis from human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A.2011;17(11-12):1549-1560.
[40] Hu X,Zhu J,Li X,et al.Dextran-coated fluorapatite crystals doped with Yb 3+/Ho 3+ for labeling and tracking chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo.Biomaterials.2015;52:441-451.
[41] Yan LP,Silva-CorreiaJ,Oliveira MB,et al.Bilayered silk/silk-nanoCaP scaffolds for osteochondral tissue engineering: In vitro and in vivo assessment of biological performance.Acta Biomaterialia.2015;12227-12241.
[42] Arcaute K,Mann B,Wicker R.Stereolithography of spatially controlled multi-material bioactive poly (ethylene glycol) scaffolds. Acta Biomaterialia.2010;6(3):1047-1054.
[43] Inzana JA,Olvera D,Fuller SM,et al.3D printing of composite calcium phosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration.Biomaterials.2014;35(13):4026-4034.
[44] Zhang W,Lian Q,Li D,et al.The effect of interface microstructure on interfacial shear strength for osteochondral scaffolds based on biomimetic design and 3D printing. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2015;46:10-15.
|
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [4] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [6] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [7] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [8] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [9] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [10] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [11] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [12] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [13] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [14] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||