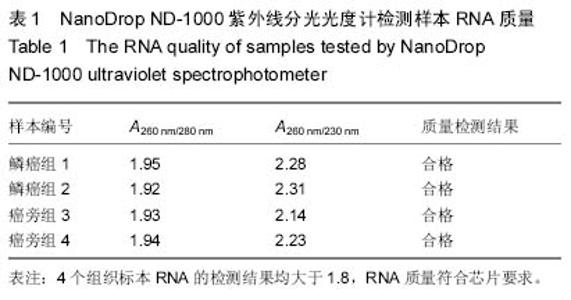
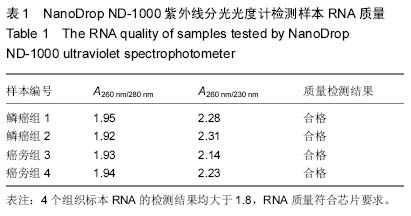
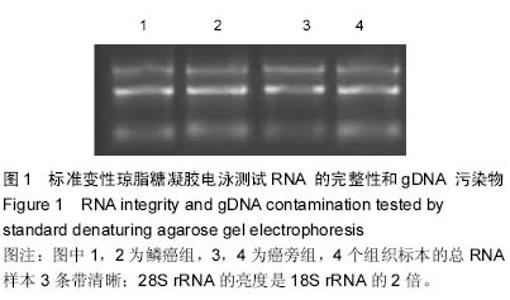
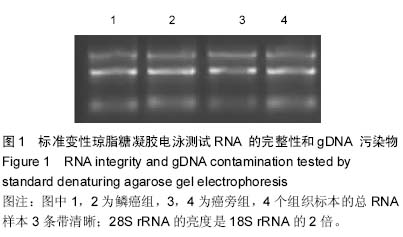
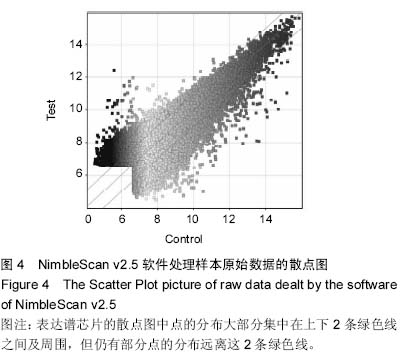
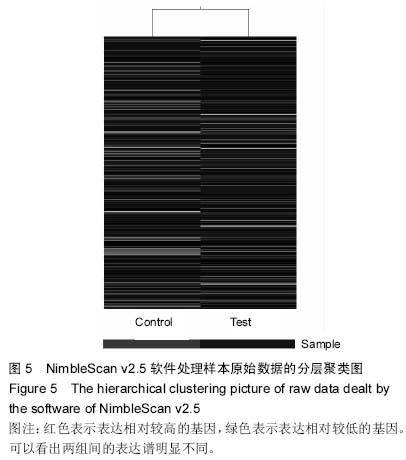
| [1] |
Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi.
Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323.
|
| [2] |
Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin.
Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339.
|
| [3] |
Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng.
Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255.
|
| [4] |
Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua.
Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289.
|
| [5] |
Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua.
Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108.
|
| [6] |
Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli.
Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128.
|
| [7] |
Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei.
In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141.
|
| [8] |
Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian.
The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812.
|
| [9] |
Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui.
Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569.
|
| [10] |
Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han.
Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606.
|
| [11] |
Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He.
Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620.
|
| [12] |
Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei.
Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631.
|
| [13] |
Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia.
Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643.
|
| [14] |
Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian.
Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650.
|
| [15] |
He Jie, Chang Qi.
Biological reconstruction of large bone defects after resection of malignant tumor of extremities
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 420-425.
|