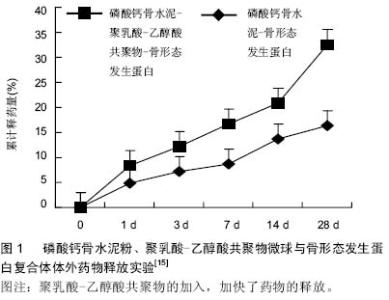
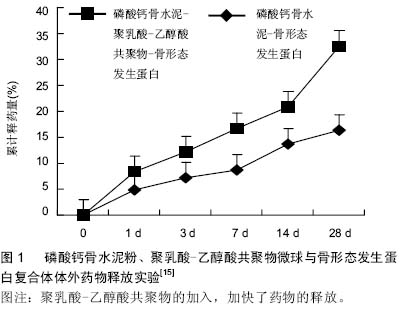
| [1] Sia IG,Wieland ML.Current Concepts in the Management of Tuberculosis.Mayo Clin Proc.2011;86(4):348-361.
[2] Gao Y,Zuo J,Bou-Chacra N,et al.In vitro release kinetics of antituberculosis drugs from nanoparticles assessed using a modified dissolution apparatus.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013: 136590.
[3] Gelperina S,Kisich K,Iseman MD,et al.The potential advantages of nanoparticle drug delivery systems in chemotherapy of tuberculosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172(12):1487-1490.
[4] Seeherman H.The influence of delivery vehicles and their properties on the repair of segmental defects and fractures with osteogenic factors.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2001;83(suppl 1):61-79
[5] 陈安民,王泰仪,孙淑珍,等.利福平—陶瓷人工骨核(R-PHA)治疗骨结核的实验研究与临床应用[J].中华骨科杂志,1992,12(1): 1218-1221.
[6] 孟志斌,孙材江,邹学农.结合利福平的珊瑚人工骨预防骨感染的实验研究[J].中华创伤杂志,1996,12(6):388-389.
[7] 邹学农,孙材江,廖龙元,等.利福平一珊瑚羟磷灰石复合物预防骨感染的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1998,18(10):610-614.
[8] 钱志松,黄山虎,刘志礼,等.乙胺丁醇一磷酸钙骨水泥复合体药物缓释的研究[J].江西医药,2009,44(7):465-467.
[9] 邢辉,陈晓明.磷酸钙骨水泥的研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2005,28(3):46-50.
[10] 苗军,王继芳,赵斌,等.磷酸钙水泥降解成骨机制的研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2005,13(5):365-367.
[11] Bohner M.New hydraulic cements based on alpha-tricalcium phosphate-calcium sulfate dihydrate mixtures. Biomaterials. 2004;25:741-749.
[12] Bigi A,Bracci B,Panzavolta S.Effect of added gelatin on the properties of calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials.2004; 25:2893-2899.
[13] Xu HH,Quinn JB,Takagi S,et al.Synergistic reinforcement of in situ hardening calcium phosphate composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials. 2004;25:1029-1037.
[14] Simon CG Jr,Khatri CA,Wight SA,et al.Preliminary report on the biocompatibility of a moldable, resorbable, composite bone graft consisting of calcium phosphate cement and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres.J Orthop Res.2002; 20:473-482.
[15] Fei Z, Hu Y, Wu D,et al. Preparation and property of a novel bone graft composite consisting of rhBMP-2 loaded PLGA microspheres and calcium phosphate cement.J Mater Sci Med.2008;19(3):1109-1116.
[16] 费正奇,胡蕴玉,张德志,等.携载rhBMP-2微球的新型复合人工骨的释药及成骨活性研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2006,23(2): 151-155.
[17] 李良,李国明,黎茂荣,等.利福平/聚乳酸微球的制备研究[J].华南师范大学学报:自然科学版,2003,8(3):103-107.
[18] 杨亚楠,娄玲,梁奇志,等.生物降解聚酯包埋利福平缓释微球的制备及释放行为[J].高等学校化学学报,2004,25(1):162-165.
[19] 王丹,姜航航.聚巍酸共聚物复合缓释药物的材料特征实验应[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(8):1473-1479.
[20] 叶向阳,孙湘,贾会文,等.利福平/聚乳酸-聚羟基乙酸缓释微球的制备及特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(51): 9608-9612.
[21] 刘江涛,王永清,夏侃,等.异烟肼聚乳酸缓释体的制备及体内外释药特性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008,18(4):290-293.
[22] 伍卫刚,郑启新,郭晓东.利福平-异烟肼-控释型载药人工骨的实验研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2010,29(1):137-143.
[23] Ruckh TT, Oldinski RA, Carroll DA. Antimicrobial effects of nanofiber poly(caprolactone) tissue scaffolds releasing rifampicin.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2012; 23(6):1411-1420.
[24] 邹冰,曲向华,梁娟.聚乙二醇(PEG)羟乙酸与羟丁酸共聚物(PHBHHx)共混膜的细胞亲水研究[J].中国生物工程杂志, 2006, 26(9):43-50.
[25] 刘彦春,王炜,曹谊林,等.卵磷脂、多聚赖氨酸和PLA包埋PGA与软骨细胞体外培养的实验研究[J].实用美容整形外科杂志, 1997, 8(5):225-227.
[26] Yang XB,Roach HI,Clarke NM,et al. Human osteoprogenitor growth and differentiation on synthetic biodegradable structures after surface modification.Bone. 2001;29:523-531.
[27] Fahmy TM,Samstein RM,Harness CC,et al.Surface modification of biodegradable polyesters with fatty acid conjugates for improved drug targeting. Biomaterials. 2005; 26:5727-5736.
[28] Yao J,Radin S,SLeboy P,et al.The effect of bioactive glass content on synthesis and bioactivity of composite poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)/bioactive glass substrate for tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2005;26:1935-1943.
[29] Chen G,Ushida T,Tateishi T.A biodegradable hybrid sponge nested with collagen microsponges.J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51:273-279.
[30] Jaganathan KS,Rao YU,Singh P,et al.Development of a single dose tetanus toxoid formulation based on polymeric microspheres: a comparative study of poly(D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) versus chitosan microspheres.Int J Pharm. 2005;294:23-32.
[31] 崔一民,鲁云兰.利福平白蛋白微球的研制[J].中国医院药学杂志,1999,19(3):131-134.
[32] 李怀芬,蓝文正,牛惠生,等.骨结核手术治疗辅助药异烟肼明腔海绵缓释作用的研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1992,12(6):444-447.
[33] 孟晓林,时和同.缓释抗结核药佐治脊柱结核合并巨大冷脓肿[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2001,26(2):148-152.
[34] 史朝晖,王东凯,王晓艳,等.利福平明胶微球制剂及体内外释药特性的研究[J].中华临床医药,2004,5(14):7-9.
[35] 刘利萍,李苹,吴泽志,等.肺靶向利福平壳聚糖磁微球的构建[J].化学世界,2003,44(4):200-202.
[36] 王心静,王巍,黎立,等.口服利福平海藻酸钠微球的制备[J].医药导报,2007,26(l2):1486-1488.
[37] 王心静,王巍,黎立,等.大鼠口服利福平海藻酸钠微球的体内药动学研究[J].中国预防医学杂志,2007,8(5):594-597.
[38] 冯会成,胡明,马远征,等.异体脱钙骨基质-利福平明胶复合材料治疗修复兔桡骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2009, 15(6):529-531.
[39] 崔旭,马远征,李大伟.磷酸三钙、聚乳酸-聚乙醇酸、异烟肼、左氧氟沙星缓释材料的成骨检测[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(3):381-317.
[40] Dutt M,Khuller GK.Chemotherapy of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections in mice with a combination of isoniazid and rifampicin entrapped in Poly ( DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microparticles.J Antimicrob Chemother.2001;47(6):829-835.
[41] 郑治,王剑龙,肖飞,等.磷酸钙骨水泥/聚乳酸-聚羟基乙酸生物复合材料的实验研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2005,15(8): 1152-1154.
[42] du Toit LC, Pillay V, Danckwerts MP.Tuberculosis chemotherapy: current drug delivery approaches. Respir Res. 2006;7:118-122.
[43] 鲍玉成,张文龙,王勇,等.长效缓释双药物人工骨的制备及缓释特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(38):7215-7130. |