Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (22): 3595-3601.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.22.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
Non-biodegradable and biodegradable long-term subdermal contraceptive implants: advances in theoretical research and application
- 1Liaoning Research Institute of Family Planning, Key Laboratory of Reproductive Health and Medical Genetics, National Health and Family Planning Commission, Shenyang 110031, Liaoning Province, China; 2Zhengzhou Shuqing Medical College, Zhengzhou 450064, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2017-02-17Online:2017-08-08Published:2017-09-01 -
Contact:Yang Li-qun, M.D., Associate researcher, Liaoning Research Institute of Family Planning, Key Laboratory of Reproductive Health and Medical Genetics, National Health and Family Planning Commission, Shenyang 110031, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jin-zhe, Assistant researcher, Liaoning Research Institute of Family Planning, Key Laboratory of Reproductive Health and Medical Genetics, National Health and Family Planning Commission, Shenyang 110031, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51503093; the Public Welfare Fund for Science and Technology Research in Liaoning Province, No. 2015001007; the Doctoral Fund of Liaoning Province, No. 201501116; the Science and Technology Research Project of Shenyang, No. F16-205-1-37
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jin-zhe, Zhou Qun-hua, Yang Li-qun, Zhang Wei, Li Jian-xin, Jin Ying, Yi Dong-xu.
share this article
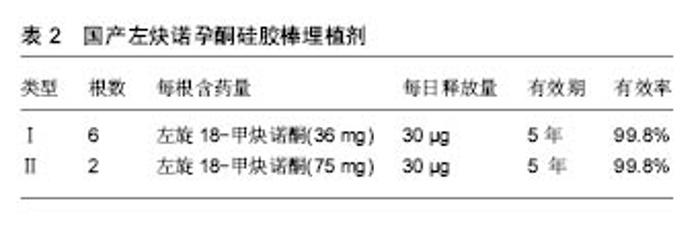
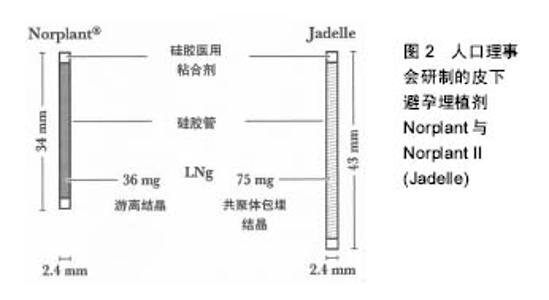
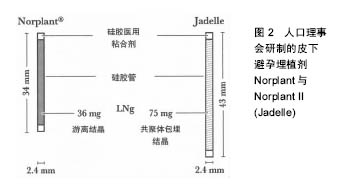
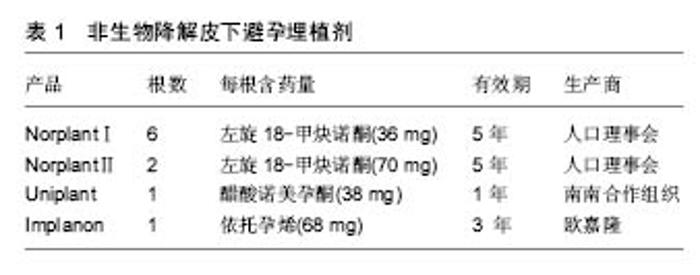
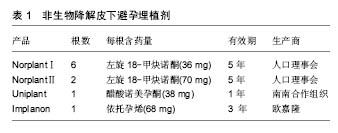
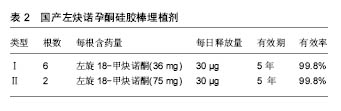
Norplant为美国人口理事会研制,是目前世界上使用时间最长、范围最广的皮下避孕埋植剂[14],其剂型采用长34 mm、直径2.4 mm的硅橡胶管,内装36 mg左旋18-甲炔诺酮(LNG),两端封闭。于月经来潮7 d内,在严格消毒条件下,一般埋入前臂部位,一次埋植6根,埋植24 h后发挥避孕作用。对Norplant的实验室研究从1966年开始,现已基本完成有关的试验。1974年开始陆续在各国进行皮下埋植胶囊的临床试验,证实了它的延长激素效应,并探讨了埋植有效期限及最适宜的埋植剂数量。1981年Croxatot等做了较长期的观察,埋植后的5年内左旋18-甲炔诺酮平均浓度稳定于0.29-0.35 μg/L,受抑制的排卵周期占半数以上,药物总释放率开始为 68 μg/d,1年后下降至40 μg/d,5年后为30 μg/d。Norplant埋植临床试验已超过50 000例妇女,妊娠率在开始3年内与绝育术可以相比,每年均未超过0.5/100,5年时累积妊娠率为2.7/100,整个5年期间的平均妊娠率为0.5/100,其妊娠率显著低于宫内节育器,可有效使用5年。此外,Norplant具有较高的可接受性,一般健康妇女均可选用Norplant。因其为单纯孕激素避孕剂,适用于哺乳妇女及有使用雌激素禁忌证而不宜采用复方口服避孕药的妇女。同时,Norplant使用方便为其最突出优点,放置后不必经常求医,局部无需特殊护理且避孕高度有效。 NorplantⅡ(Jadelle)含有2根载药硅胶棒,每个硅胶棒长44 mm,每支含左旋18-甲炔诺酮75 mg,共 150 mg,其左旋18-甲炔诺酮释放率和血药浓度与Norplant相似,日释放左旋18-甲炔诺酮量高于Norplant,可有效避孕5年。研究认为,Jedelle与Norplant有相似的避孕效果,但取出术所需时间明显缩短。 Implanon植入剂由FDA于2006年7月18日批准上市,由荷兰欧加农(Organon)公司生产的一种非生物降解的单根纯孕激素皮下埋植剂,具有高效、长效、可逆、使用方便、取放容易等特点。Implanon植入剂单根含依托孕烯68 mg,大小与火柴相似,可以通过手术植入女性上臂内侧皮下,无创伤。植入体内后可以连续3年持续稳定释放低剂量的依托孕烯,不受患者自身状况的影响。患者根据需要随时取出植入剂后,生育能力可以很快得到恢复。与纯孕激素避孕方法一样,Implanon的作用机制也是通过抑制排卵,使宫颈黏液稠厚、阻止精子穿透,进而实现避孕目的。 Uniplant埋植剂由南-南合作组织发展的单根埋植剂,含合成孕酮(醋酸诺美孕酮),有很强孕激素活性而无雄激素活性,其子宫流血模式与正常周期相似,抑制排卵是其主要的作用机制。 2.1.2 国内研究现状 国产皮埋剂共有2种类型产品上市,分别称为国产Ⅰ型和国产Ⅱ型(表2)。其中,国产Ⅰ型皮埋剂由6根硅橡胶药囊组成,每根长3.4 cm,直径0.24 cm,含左旋18-甲炔诺酮36 mg,6根共计含药 216 mg,可避孕有效期5-7年,由丹东鸭绿江制药厂于20世纪90年代初期生产。国产Ⅱ型由2根左旋-18甲基炔诺酮和硅橡胶混匀制成的药棒组成,每根长4.4 cm,直径0.24 cm,含左旋18-甲炔诺酮75 mg,2根共计含药150 mg,是20世纪80年代开发的单纯孕激素皮下埋植缓释剂。因其具有长期、高效、安全、方便、可逆等优点,对于采取其他避孕措施失败的育龄妇女提供了较好的避孕方法,深受广大育龄妇女欢迎。 国产皮埋剂率先在北京、上海、天津、沈阳等城市使用,同时为了解国产皮埋剂的有效性和安全性,有关部门已在全国建立多个皮下埋植剂临床试验中心,进行皮下埋植避孕法手术,以观察国产皮下埋植剂避孕效果、副反应、续用率等情况。1993年开始在全国的11个分中心对国产两型埋植剂进行了19 673例的多中心研究,其中Ⅰ型9 739例,Ⅱ型9 934例,根据有关资料统计,2年内妊娠率仅为0.1%,3年内妊娠率为0.24%,证明了左旋炔诺孕酮硅胶棒安全高效的避孕效果。其不良反应的发生率Ⅰ型为38.42%,Ⅱ型为36.42%,90%以上为月经失调。研究表明,国产皮下埋植剂的避孕效果和不良反应与Norplant相似,可以替代Norplant。国产Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型埋植剂价格便宜,显著节约了费用,在临床上使用广泛,目前中国主要使用国产Ⅱ型埋植剂。 2.1.3 优点 经临床研究证实, 皮下埋植避孕法是一种高效、安全、可逆、接受性高的长效避孕方法,具有下列优点:①避孕效果好,避孕有效率达99%以上[15-16];②避孕作用长,一次埋植可避孕5年[17-21];③药物反应小,这种避孕剂中只有孕激素,不含雌激素,不良反应较小;④避免口服给药的肝脏“首过效应”[22],亦避免了注射针剂或口服给药时血浓度峰值的波动与剂量大等缺点,血液中无蓄积作用,对机体代谢影响小;⑤具有可复性,将硅胶囊管取出后可以很快恢复生育能力[23-24];⑥使用方便,只需在局部麻醉下用一套管将硅胶棒扇形植于皮下即可,手术简单易学,便于推广,且手术损伤组织少,对妇女身心健康和婴儿发育无影响[25-26]。 2.1.4 缺点 皮下避孕埋植剂也具有一些缺点,主要不良反应为干扰正常月经、不规则出血及月经期延长最为普遍[27],少数有闭经现象。月经失调可能与干扰某些内分泌及对生殖道局部作用有关。这种失调一般都能耐受,并会随时间延长而减轻[28-29]。除月经问题之外,其他不良反应包括使用纯孕激素避孕伴发的典型症状,其中以头痛及体质量增加最为常见[30];同时可见食欲改变、嗜睡、抑郁、情绪改变、神经质和焦虑、痤疮、色素沉着等症状以及因埋植剂引起的局部不适等[31]。但因左炔诺孕酮采用缓释系统,保持恒定而较低的血药浓度。因此,除有月经问题外,上述其他不良反应发生率低、症状轻,绝大部分在使用早期即可消失[32]。 除上述问题之外,传统皮下避孕埋植剂所采用的药物缓释载体为非可生物降解的硅橡胶(图2)。众所周知,因其非降解特性,硅橡胶在体内不能降解为小分子化合物并被机体吸收或代谢,放置有效期满后需要二次手术取出。由于取出手术要比植入手术困难的多,不但增加了使用成本、给使用者带来不必要的痛苦,而且难于保证所有使用者均能按期取出,从而增加避孕失败的危险。 2.2 生物降解型长效皮下避孕埋植剂 生物降解型药物缓控释体系的研究始于世界卫生组织(WHO)和美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)。20世纪70年代中后期,有关生物降解型避孕埋植剂的研究逐渐开展起来,由聚丙交酯(PLA)或聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物(PLGA)与分散在其中的孕酮类药物所制备的基质型埋植剂和可注射微型胶囊实现了6个月的避孕效果[33-35]。然而,由于孕酮的释放行为受到扩散和降解双重因素控制,导致此类埋植剂的释放动力学比较复杂,难以达到恒速释放,因而阻碍了其推广应用。 2.2.1 Capronor 美国北卡三角研究院以降解性能良好,生物相容性优异的生物可降解聚己内酯(PCL)胶囊为缓释载体[36-42],内装左旋-18甲基炔诺酮,制成贮库型左炔诺孕酮长效埋植剂Capronor。其特点是左旋-18甲基炔诺酮全部释放完毕后载体材料才开始发生变形、失重和降解,在整个药物释放过程中药物的扩散不受载体材料降解的影响。该机制符合零级释放动力学,可实现药物的恒速释放[38]。研究证实聚己内酯对载体药物的透过性可与硅橡胶媲美[37],而Capronor埋植剂内含乙基油酸酯,可以增加药物的释放速度,由此导致Capronor埋植剂释放左旋-18甲基炔诺酮的速率比Norplant埋植剂快10倍。因此,单根Capronor埋植剂的有效释药量与6根Norplant埋植剂相当[29]。研究表明,Capronor埋植剂的体外释放率为20 μg/(d•cm),而其体内平均释放率为15-20 μg/(d•cm)[39],临床研究证明植入1根可安全避孕至少1年[43-44]。 经多年的基础研究及动物实验研究,并结合实际临床需求,研究人员最终确定的Capronor埋植剂有2种规格:直径均为2.41 mm,长度分别为2.5 cm和4.0 cm,左旋-18甲基炔诺酮含量分别为12.0 mg和21.6 mg,分别标记为Capronor(2.5)与Capronor(4.0)。2种规格的Capronor埋植剂都经历了一期临床和二期临床研究。二期临床研究结果表明,尽管Capronor(2.5)与Capronor(4.0)的避孕机制均与Norplant相似,但是Capronor(2.5)不能提供有效避孕血药浓度,而Capronor (4.0)的血药浓度与Norplant接近,可以实现有效避孕。因此,4.0 cm长度是Capronor实现有效避孕所需的最低极限长度。由印度医学研究委员会提供的印度Capronor(4.0)二期临床研究报告表明,Capronor(4.0)可有效避孕1年[43]。值得注意的是Capronor(4.0)在体内放置1年以后,仍可以释放少量、无避孕作用的左旋-18甲基炔诺酮,该释放量对人体无害[42]。此时,Capronor (4.0)埋植剂仍保持完整结构,并且周围没有纤维组织沉淀[41, 43],可根据需要随时将其取出,且取出术相对Norplant的取出更容易进行。 Capronor(4.0)埋植剂的避孕效果、安全性、可接受性及不良反应与Norplant相似[45],释放率和左旋-18甲基炔诺酮的血药浓度也与Norplant相似。与Norplant相比,Capronor(4.0)埋植剂为单根型给药系统,易于埋植;更主要的是Capronor(4.0)埋植剂在体内可被降解吸收,不需要手术取出,易于使用者接受。即使是需要取出时,Capronor埋植剂的取出也比Norplant埋植剂取出更为容易。但Capronor(4.0)埋植剂的有效避孕时间不及Norplant,只能适用于短期避孕需求的使用者。此外,Capronor为了促进左旋-18甲基炔诺酮释放而使用了液态分散介质乙基油酸酯,在保存中存在渗漏和引起泄漏物氧化的现象[42],增加了埋植剂贮藏的难度并影响药效,因此尚需进一步的研究和改进才能继续更大范围的临床试用。 2.2.2 CaproF 针对Capronor埋植剂中液态分散介质导致的渗漏问题,中国医学科学院生物医学工程研究所在Capronor基础上改变了缓释胶囊的配方,即在聚己内酯中加入10% Pluronic-F68® (F68)作为增释剂,制成长效抗生育埋植剂CaproF。F68在体液中被溶出后形成多微孔结构,使CaproF的药物释放速率比Capronor提高了30%。体外和动物体内药物释放研究表明,CaproF具有零级释放动力学,可在体内长期维持稳定的药物释放量,每2根CaproF埋植剂(总长为6 cm,总装药量为30 mg)的左旋-18甲基炔诺酮体内释放速率约为42 μg/d,可达到人类抗生育的有效剂量[42],且具有长期稳定释放药物的作用。此外,CaproF埋植剂在体内降解2年后仍能保持结构完整,预期一次植入2根可有效避孕2年[45-51]。 临床初步研究结果表明,CaproF的不良反应与Capronor及Norplant相似,主要为月经紊乱。同时,埋植CaproF后,受试者出血、滴血天数增加,但月经失血量呈降低趋势。放置CaproF后其他副反应少见,受试者血压无变化,体质量略增加(P > 0.05)[52]。Ⅰ期临床结果表明2根CaproF埋植剂(3 cm,15 mg/根)的左旋-18甲基炔诺酮释放量不能完全抑制排卵,但血药浓度可影响宫颈黏液、内膜、排卵管,可使卵泡处于发育不良和黄体功能不完全状态,起到避孕作用[53]。10例志愿者,无一例受孕。除1例不规则出血外,其他受试者对本理植剂的可接受性、耐受性均良好,无不良反应发生。 尽管CaproF解决了Capronor中液态分散介质的渗漏问题,提高了埋植剂的稳定性,在临床实际应用表现出一定的应用前景,但是由于其贮库式的载药方式,随着载体材料的降解,缓释胶囊的管壁一旦破裂,将会导致大量孕激素类药物溢出,造成体内药量骤增,给使用者带来极大的不良反应甚至生命危险。因此,设计与开发基质型恒速缓控释给药体系对生物降解型皮下避孕埋植剂的临床推广应用尤为重要。 2.2.3 基质型降解避孕埋植剂 为了开发一类能恒速释放类固醇类避孕药的基质型药物恒速释放体系,song等[54]采用活性聚合的方法合成了可生物降解CL-LA嵌段共聚物,并以其为药物缓释载体,制备了基质型左 旋-18甲基炔诺酮控制释放体系。结果表明,CL-LA嵌段共聚物包埋膜对左旋-18甲基炔诺酮有缓释作用。在体外4 d后,左旋-18甲基炔诺酮的释放速度相对恒定。通过嵌段共聚物的组成可调控左旋-18甲基炔诺酮的释放速率。 顾忠伟等[55]在冯新德的研究基础上,进一步以CL/DLLA=85/15的嵌段共聚物为载体制备左旋-18甲基炔诺酮长效避孕埋植剂。体外及体内长期埋植实验等结果表明生物降解左旋-18甲基炔诺酮长效埋植剂避孕无任何毒副作用,具有良好生物相容性[56-57]。体外释放实验证明基于CL/DLLA嵌段共聚物的左旋-18甲基炔诺酮长效避孕埋植剂具有显著的缓控释作用,7 d后释放量基本趋于平稳,释放量在10个月内基本处于20-25 μg之间[56]。同时,左旋-18甲基炔诺酮长效避孕埋植剂具有显著的抗生育效果[57]。抗生育时间与埋植剂的含药量呈正相关,长度为0.8 cm的左旋-18甲基炔诺酮长效避孕埋植剂(含药13 mg,日释放量为25 μg/cm)即可产生完全的抗生育效果。上述研究结果表明,这种埋植剂有可能成为有临床应用前景的、能恒速释放左旋-18甲基炔诺酮的长效避孕埋植剂;同时,上述研究为进一步研究左旋-18甲基炔诺酮长效避孕埋植剂的药效学提高了必要的数据,同时也为研究长期埋植后抗生育效果及生育能力的恢复打下良好的实验基础。 此外,正在研究的生物降解型皮下埋植避孕剂还有以聚原酸酯为基质制成左旋-18甲基炔诺酮植入棒(Chronormer®)以及以PLGA (LA∶GA=90∶10)为药物缓释载体的左旋-18甲基炔诺酮棒状埋植剂[58-59],并已在动物体内进行了长期观察。 "
| [1]Mascarenhas L. Long acting methods of contraception. BMJ. 1994;308(6935):991-992.[2]Darney PD. Hormonal implants: contraception for a new century. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;170(5 Pt 2):1536-1543.[3]Sivin I, Alvarez F, Mishell DR Jr, et al. Contraception with two levonorgestrel rod implants. A 5-year study in the United States and Dominican Republic. Contraception. 1998;58(5):275-282.[4]Segal SJ, Croxatto HB. Single administration of hormones for long-term control of reproductive function. Washington DC:Proceedings of the 23rd Meeting of the American Fertility Society, 1967.[5]Segal SJ. Contraceptive subdermal implants. In: Mishell DR Jr, edits. Advances in Fertility Research. New York: Raven Press, 1982:117-127.[6]黄婷,曾佳,相琳,等. 烯诺孕酮制剂研究进展[J]. 中国新药杂志, 2015, 24(4):409-414.[7]Feldblum PJ, Hanitriniaina O, Lendvay A, et al. Performance of Sino-implant (II) in routine service delivery in Madagascar. Contraception. 2013;88(1):103-108.[8]Trussell J. The Essentials of Contraception: Efficacy, Safety, and Personal considerations. In: Hatcher RA, Trussell J, Nelson AL, Cates W, Stewart FH, Kowal D, edits, Contraceptive Technology. New York: Ardent Media, 2007: 343-349.[9]WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee.Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use.5th edition. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2015.[10]郭延玲,傅正英.可复性输卵管避孕材料应用进展[J].医疗卫生装备,2011,32(6):85-87.[11]杨丹.第三代口服避孕药的药代动力学和对代谢的影响[J]. 实用妇产科杂志, 2001, 17(6): 32-325.[12]张翀,杨丹,孟舒,等. 生物可降解高分子材料在避孕领域中的应用进展[J].塑料,2011,40 (1):49-51.[13]汤谷平, 陈启琪. 可生物降解的高分子材料在控释出体避孕药中的应用[J]. 生殖与避孕, 1997,17(5):259-261.[14]钱翠凤,黄紫蓉. 皮下埋植避孕剂的研究进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2013,32(2):107-110.[15]Townsend S. Norplant: safe and highly effective. Netw Res Triangle Park N C. 1990;11(4):6-8.[16]Trussell J, Hatcher RA, Cates W Jr, et al. Contraceptive failure in the United States: an update. Stud Fam Plann. 1990;21(1):51-54.[17]Chetri M, Bhatta A, Amatya RN, et al. Five-year evaluation of safety, efficacy and acceptability of Norplant implants in Nepal. Adv Contracept. 1996;12(3):187-199.[18]Sivin I, Mishell DR Jr, Darney P, et al. Levonorgestrel capsule implants in the United States: a 5-year study. Obstet Gynecol. 1998;92(3):337-344.[19]Gu S, Sivin I, Du M, et al. Effectiveness of Norplant implants through seven years: a large-scale study in China. Contraception. 1995;52(2):99-103.[20]Sivin I. International experience with NORPLANT and NORPLANT-2 contraceptives. Stud Fam Plann. 1988;19(2):81-94.[21]Diaz S, Pavez M, Miranda P, et al. A five-year clinical trial of levonorgestrel silastic implants (Norplant TM). Contraception. 1982;25(5):447-456.[22]张倩,姚小东,宁美英,等. 女性避孕药物制剂的研究进展[J]. 中国计划生育学杂志,2015, 23(7):501-504.[23]Croxatto HB, Díaz S, Pavez M, et al. Clearance of levonorgestrel from the circulation following removal of NORPLANT subdermal implants. Contraception. 1988;38(5):509-523.[24]李明英. 放置皮下埋植剂238例避孕效果[J]. 中国生育健康杂志, 2008, 19(2): 121,124.[25]Tu P, Qiu S, Fang H, et al. Acceptance, efficacy, and side effects of Norplant implants in four counties in north China. Stud Fam Plann. 1997;28(2):122-131.[26]Díaz S, Herreros C, Juez G, et al. Fertility regulation in nursing women: VII. Influence of NORPLANT levonorgestrel implants upon lactation and infant growth.Contraception. 1985;32(1):53-74.[27]Shaaban MM, Salem HT, Abdullah KA. Influence of levonorgestrel contraceptive implants, NORPLANT, initiated early postpartum upon lactation and infant growth. Contraception. 1985;32(6):623-635.[28]The Piopulation Councile. Norplant-a summary of scientific data. New York: The Population Council, 1990: 1-26.[29]Darney PD, Klaisle CM, Tanner S. Sustained-release contraceptives. Current Problems in Obstetrics Gynecology & Fertility. 1990; 13(3): 95-125. [30]杜娟,雷贞武. 单纯孕激素长效避孕剂安全性研究进展[J]. 实用妇产科杂志,2014,30(7):485-488.[31]雷贞武,周静. 皮下埋植避孕剂出血不良反应及安全性的研究进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志,2011,30(6):425-428.[32]高瞰秀,聂垚. 基于各类型材料的宫内节育器、皮下避孕埋植剂及输卵管节育器[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(52):8503-8508.[33]Jackanicz TM, Nash HA, Wise DL, et al. Polylactic acid as a biodegradable carrier for contraceptive steroids. Contraception. 1973; 8(3): 227-234.[34]Beck LR, Cowsar DR, Lewis DH, et al. New long-acting injectable microcapsule contraceptive system. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1979;135(3):419-426.[35]Hahn DW, Mcguire JL, Cohn RM, et al. Development of microencapsulated norgestimate as a long-acting contraceptive. In: Zatuchni GL, edits, Long-Acting Contraceptive Delivery Systems. Philadelphia: Harpen and Row, 1984: 96-112.[36]Sun H, Mei L, Song C, et al. The in vivo degradation, absorption and excretion of PCL-based implant. Biomaterials. 2006;27(9):1735-1740.[37]Pitt CG, Chasalow FI, Hibionada YM, et al. Aliphatic polyesters. I. The degradation of poly(ε-caprolactone) in vivo. Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 1981; 26(11): 3779-3787.[38]武莉,孙洪范,杨菁,等. 医用聚已内酯长期毒性动物实验研究[J]. 天津医药, 2008, 36(2): 126-129.[39]Sinha VR, Bansal K, Kaushik R, et al. Poly-epsilon- caprolactone microspheres and nanospheres: an overview. Int J Pharm. 2004;278(1):1-23.[40]Baker R. Controlled release of biologically active agents. Menlo Park, California: Membrane Technology and Research Inc, 1984: 89.[41]Pitt CG, Gratzl MM, Jeffcoat AR, et al. Sustained drug delivery systems II: Factors affecting release rates from poly(epsilon-caprolactone) and related biodegradable polyesters. J Pharm Sci. 1979;68(12):1534-1538. [42]Pitt CG, Schindler A. Capronor: A biodegradable delivery system for levonorgestrel. In: Zatuchni GI, Goldsmith A, Shelton JD, Sciarra JJ, edits. Long-Acting contraceptive delivery systems. Philadelphia: Harper and Row, 1984: 48-63.[43]Darney PD, Monroe SE, Klaisle CM, et al. Clinical evaluation of the Capronor contraceptive implant: preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989;160(5 Pt 2):1292-1295.[44]Phase II--clinical trial with biodegradable subdermal contraceptive implant Capronor (4.0-cm single implant). Indian Council of Medical Research Task Force on Hormonal Contraception. Contraception. 1991;44(4):409-417.[45]Darney PD, Klaisle CM, Monroe SE, et al. Evaluation of a 1-year levonorgestrel-releasing contraceptive implant: side effects, release rates, and biodegradability. Fertil Steril. 1992; 58(1):137-143.[46]Ma G, Song C, Sun H, et al. A biodegradable levonorgestrel-releasing implant made of PCL/F68 compound as tested in rats and dogs. Contraception. 2006;74(2):141-147.[47]施化莲,孙洪范,武莉. 可降解长效抗生育埋植剂(Capro-F)的大白鼠抗生育作用[J]. 中国计划生育杂志, 1998(6): 254-255.[48]王彭延,宋存先,施化莲,等. 可降解长效抗生育埋植剂的研究[J]. 生物医学工程与临床, 1997(1): 23-26.[49]宋存先,杨菁,孙洪范,等. 左炔诺孕酮长效缓释埋植剂 I. 结构特征的研究和体内外药物释放的长期观察[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报,1999,18(1):22-29.[50]Wang PY, Song CX, Sun HF, et al. A biodegradable long-term contraceptive implant developed in China. Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference of the ZEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. 1998; 20(6): 2901-2904.[51]唐丽娜,孙洪范,宋存先,等. 长效抗生育埋植剂CaproF体内药物释放的研究[J]. 生物医学工程与临床, 2007,11(1): 17-19.[52]刘春海, 钱丽娟. 可生物降解皮下埋植剂CaproF的临床初步研究[J].中国计划生育杂志, 2000(3): 108-111.[53]王彭延, 存先,施化莲,等. 可降解长效抗生育埋植剂及I期临床结果[C].21世纪医学工程学术研讨会论文摘要汇编, 2001:58.[54]Song CX, Chen HY, Feng XD. Preparation of block coplymer of ε-caprolactone and DL-lactide and their evaluation as carrier for biodegradable sustained drug delivery. Acta Polymerica Sinica. 1983; 1(3): 177-183.[55]顾忠伟,杨纪元,杜福胜,等. 生物降解左旋-18甲长效避孕埋植剂的研制及其体外释放研究[J]. 中国计划生育学杂志,1997(2): 70-73.[56]顾忠伟,丁训诚,杨纪元,等. 生物降解左旋-18基长效避孕埋植剂载体材料的生物相容性研究[J]. 中国计划生育学杂志, 1997(3): 135-141.[57]王英,顾忠伟,王红,等. 左旋-18甲基炔诺酮生物降解长效避孕埋植剂抗生育作用的研究[J]. 中国计划生育学杂志,1999(1): 11-13.[58]Heller J, Penhale DW, Fritzinger BK, et al. Controlled release of contraceptive steroids from biodegradable poly (ortho esters). Contracept Deliv Syst. 1983;4(1):43-53.[59]Gresser JD, Wise DL, Beck LR, et al. Biodegradable cylindrical implants for fertility regulation. In: Hafez ES, Van Os WA, edits, Biodegradables and delivery systems for contraception. Boston, Massachusetts: G.K. Hall Publishers, 1980: 83-95.[60]李坤, 刘晓君,陈庆华, 等. 可生物降解长效注射给药系统的研究进展[J]. 中国医药工业杂志,2012,43(3):214-221.[61]Gentile P, Chiono V, Carmagnola I, et al. An overview of poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA)-based biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):3640-3659. [62]Sachlos E, Czernuszka JT. Making tissue engineering scaffolds work. Review: the application of solid freeform fabrication technology to the production of tissue engineering scaffolds. Eur Cell Mater. 2003;5:29-39.[63]Karp JM, Shoichet MS, Davies JE. Bone formation on two-dimensional poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) films and three-dimensional PLGA tissue engineering scaffolds in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003;64(2):388-396.[64]Yang L, Li J, Li M, et al. The in vitro and in vivo degradation of cross-linked poly(trimethylene carbonate)-based networks. Polymers. 2016; 8 (4): 151. [65]Yang L, Li J, Zhang W,et al. The degradation of poly(trimethylene carbonate) implants: the role of molecular weight and enzymes. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2015; 122: 77-87. [66]Yang L, Li J, Jin Y, et al. In vitro enzymatic degradation of the cross-linked poly(ε-caprolactone) implants. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2015; 112: 10-19.[67]Yang L, Li J, Jin Y, et al. Highly efficient cross-Linking of poly(trimethylene carbonate) via bis(trimethylene carbonate) or bis(ε-caprolactone). Polymer. 2014; 55(26): 6686-6695. [68]Yang L, Li J, Meng S, et al. The in vitro and in vivo degradation behavior of poly (trimethylene carbonate-co-ε-caprolactone) implants. Polymer. 2014; 55(20): 5111-5124. [69]Yang L, He B, Meng S, et al. Biodegradable cross-linked poly(trimethylene carbonate) networks for implant applications: synthesis and properties. Polymer. 2013; 54(11): 2668-2675.[70]Yang LQ, Yang D, Guan YM, et al. Random copolymers based on trimethylene carbonate and ε-caprolactone for implant applications: synthesis and properties. Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 2012; 124(5): 3714-3720. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Fang Xiaoyang, Tang Tian, Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Repair and regenerative therapies of the annulus fibrosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1582-1587. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||