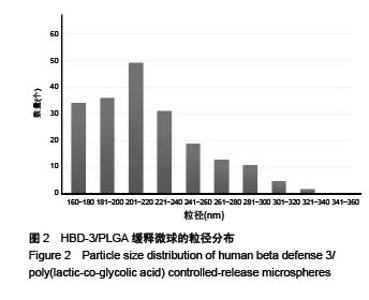
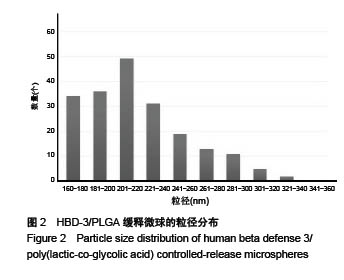
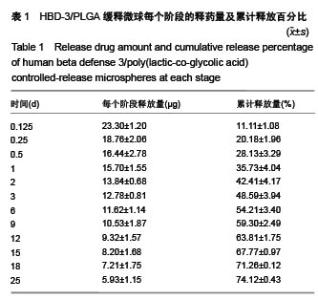
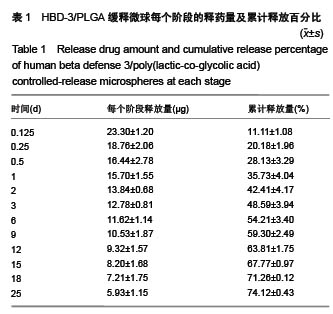
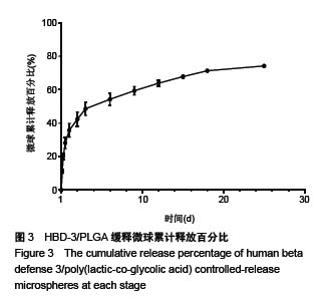
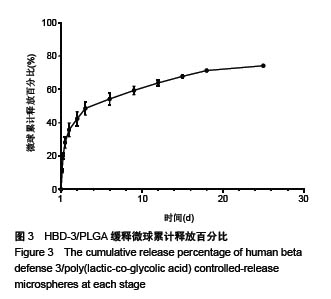
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (10): 1514-1519.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.10.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human beta defense 3/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) controlled-release microspheres: preparation and in vitro releasing performance
Sun Zhi-bang, Zhou Yi-qin, Chen Song, Wu Hai-shan
- Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University of PLA, Shanghai 200003, China
-
Received:2017-02-13Online:2017-04-08Published:2017-05-08 -
Contact:Wu Hai-shan, M.D., Professor, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University of PLA, Shanghai 200003, China -
About author:Sun Zhi-bang, Studying for master’s degree, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University of PLA, Shanghai 200003, China -
Supported by:the Project of Shanghai Health Bureau, No. 2012353
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Zhi-bang, Zhou Yi-qin, Chen Song, Wu Hai-shan. Human beta defense 3/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) controlled-release microspheres: preparation and in vitro releasing performance[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(10): 1514-1519.
share this article
| [1]吴宇黎,王继芳.感染人工关节周围生物膜对细菌影响的研究[J].中华外科杂志,1997,35(8):469-471.[2]吴宇黎,李晓华,钱齐荣,等.感染性人工关节生物膜中细胞外多粘质物质对抗生素的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2002,9(10): 980-981.[3]Esteban J, Molina-Manso D, Spiliopoulou I,et al. Biofilm development by clinical isolates of Staphylococcus spp. from retrieved orthopedic prostheses.Acta Orthop. 2010;81(6): 674-679.[4]Al-Ahmad A, Wiedmann-Al-Ahmad M, Faust J, et al. Biofilm formation and composition on different implant materials in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;95(1): 101-109.[5]吴宇黎,王继芳,卢世璧,等.大剂量灌注冲洗对感染性假体表面生物膜中细胞外多粘质物质(ESS)的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2001,8(8):791-792.[6]吴宇黎,王继芳,卢世璧,等.假体表面感染性生物膜中细胞外多粘质物质对淋巴细胞和多形核白细胞功能的影响[J].第二军医大学学报,2001,22(z1): 37-39.[7]Bruellhoff K, Fiedler J, Möller M, et al. Surface coating strategies to prevent biofilm formation on implant surfaces. Int J Artif Organs. 2010;33(9):646-653.[8]Zanger P, Holzer J, Schleucher R, et al. Severity of Staphylococcus aureus infection of the skin is associated with inducibility of human beta-defensin 3 but not human beta-defensin 2. Infect Immun. 2010;78(7):3112-3117.[9]Hirsch T, Spielmann M, Zuhaili B, et al. Human beta-defensin-3 promotes wound healing in infected diabetic wounds. J Gene Med. 2009;11(3):220-228.[10]Reichel M, Heisig A, Heisig P, et al. Skin bacteria after chlorhexidine exposure-is there a difference in response to human beta-Defensin-3. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010; 29(6):623-632.[11]李冠楠,夏雪娟,隆耀航,等.抗菌肽的研究进展及其应用[J]. 动物营养学报,2014,26(1):17-25.[12]Warnke PH, Springer IN, Russo PA, et al. Innate immunity in human bone. Bone. 2006;38(3):400-408.[13]Dhople V, Krukemeyer A, Ramamoorthy A. The human beta-defensin-3, an antibacterial peptide with multiple biological functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1758(9): 1499-1512.[14]韩敏,苏秀霞,李仲谨.载药微球制剂的研究进展[J].应用化工, 2007,36(5):493-495.[15]Karal-Y?lmaz O, Serhatl? M, Baysal K, et al. Preparation and in vitro characterization of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-loaded poly(D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres using a double emulsion/solvent evaporation technique. J Microencapsul. 2011;28(1):46-54.[16]罗字燕,张永明,吴传斌. 一种聚乳酸聚乙醇酸缓释微球的制备工艺[J].中国医院药学杂志,2011,31(11) :875-878 .[17]罗宇燕,李姝瑾,张永明.聚乳酸聚乙醇酸微球体外突释的影响因素的研究[J].今日药学,2011,21(4):207-210 .[18]Yang F, Song FL, Pan YF, et al. Preparation and characteristics of interferon-alpha poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres. J Microencapsul. 2010;27(2):133-141.[19]Thomes B, Murray P, Bouchier-Hayes D. Development of resistant strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis on gentamicin-loaded bone cement in vivo. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(5):758-760.[20]Wilmes M, Cammue BP, Sahl HG, et al. Antibiotic activities of host defense peptides: more to it than lipid bilayer perturbation. Nat Prod Rep. 2011;28(8):1350-1358.[21]Schibli DJ, Hunter HN, Aseyev V, et al. The solution structures of the human beta-defensins lead to a better understanding of the potent bactericidal activity of HBD3 against Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(10): 8279-8289.[22]Levón J, Al-Samadi A, Mackiewicz Z, et al. Human beta-defensin-3 producing cells in septic implant loosening. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(2):98.[23]Ford Versypt AN, Pack DW, Braatz RD. Mathematical modeling of drug delivery from autocatalytically degradable PLGA microspheres--a review. J Control Release. 2013; 165(1): 29-37.[24]Qi F, Wu J, Fan Q, et al. Preparation of uniform-sized exenatide-loaded PLGA microspheres as long-effective release system with high encapsulation efficiency and bio-stability. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;112:492-498.[25]Wang Y, Li P, Kong L. Chitosan-modified PLGA nanoparticles with versatile surface for improved drug delivery. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2013;14(2):585-592.[26]李卫红,司鹏,雷文.药用合成高分子缓、控释材料研究进展[J].高分子通报,2015(1):56-59.[27]Astete CE, Sabliov CM. Synthesis and characterization of PLGA nanoparticles. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2006;17(3): 247-289.[28]高飞,赵燕.重组人β防御素-3抗菌活性及影响因素的研究[J].生物学通报, 2016,51(6):53-56.[29]钱婷玉,崔爱军,彭松,等.聚乳酸-羟基乙酸(PLGA)及其载药微球的制备研究[J].化工新型材料,2015,43(12):143-145.[30]孙美丽,班俊峰,黄思玉,等.PLGA微球的载药量和包封率的影响因素及控制[J].广东药学院学报,2011,27(6):644-648.[31]罗宇燕,麦海燕 ,黎呐,等.复乳法及其改良法制备的干扰素PLGA微球载药释药特性的对比[J].中山大学学报:自然科学版, 2014 ,53(3):110-114.[32]Qian F, Ni N, Burton LS, et al. Sustained release subcutaneous delivery of BMS-686117, a GLP-1 receptor peptide agonist, via a zinc adduct. Int J Pharm. 2009;374 (1-2):46-52.[33]Xuan J, Lin Y, Huang J, et al. Exenatide-loaded PLGA microspheres with improved glycemic control: in vitro bioactivity and in vivo pharmacokinetic profiles after subcutaneous administration to SD rats. Peptides. 2013;46: 172-179.[34]Zaky A, Elbakry A, Ehmer A, et al. The mechanism of protein release from triglyceride microspheres. J Control Release. 2010;147(2):202-210.[35]Wang Y, Gu B, Burgess DJ. Microspheres prepared with PLGA blends for delivery of dexamethasone for implantable medical devices. Pharm Res. 2014;31(2):373-381. [36]Gu B, Burgess DJ.Prediction of dexamethasone release from PLGA microspheres prepared with polymer blends using a design of experiment approach.Int J Pharm. 2015; 495(1): 393-403. [37]Zolnik BS, Burgess DJ.Evaluation of in vivo-in vitro release of dexamethasone from PLGA microspheres.J Control Release. 2008; 127(2):137-145.[38]Zolnik BS, Leary PE, Burgess DJ.Elevated temperature accelerated release testing of PLGA microspheres.J Control Release. 2006; 112(3):293-300. [39]Liu B, Dong Q, Wang M, et al.Preparation, characterization, and pharmacodynamics of exenatide-loaded poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2010; 58(11):1474-1479.[40]Lim SM, Eom HN, Jiang HH, et al. Evaluation of PEGylated exendin-4 released from poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres for antidiabetic therapy.J Pharm Sci. 2015; 104(1):72-80. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Li Xuan, Sun Yimin, Li Longbiao, Wang Zhenming, Yang Jing, Wang Chenglin, Ye Ling. Manufacturing of nano-modified polycaprolactone microspheres and its biological effects in dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1530-1536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||