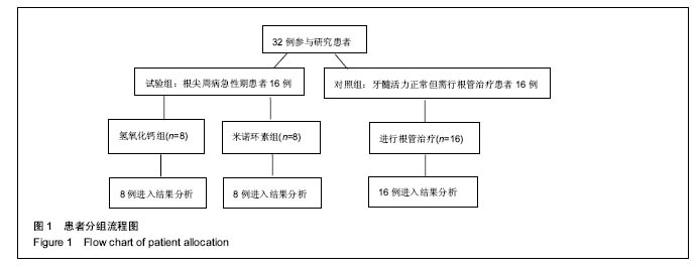
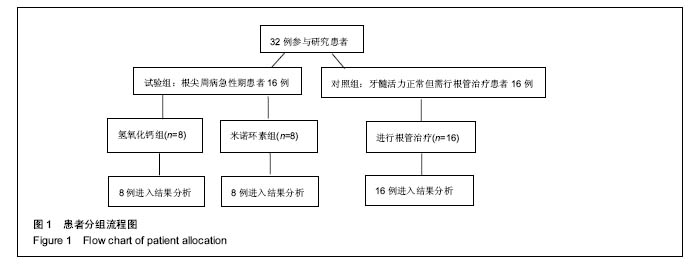
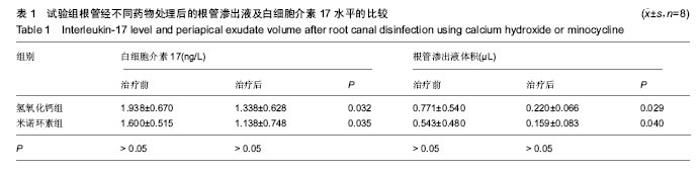
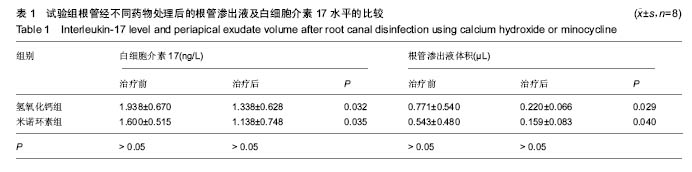
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
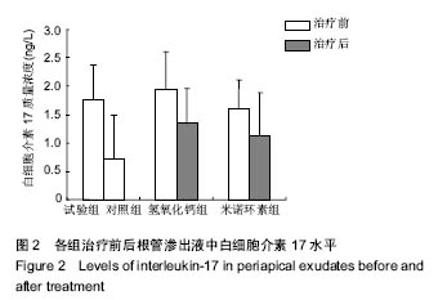
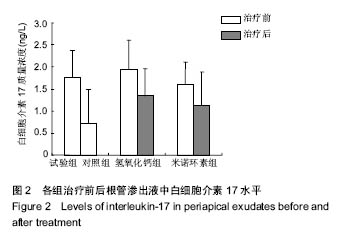
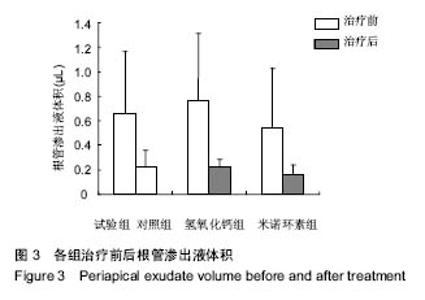
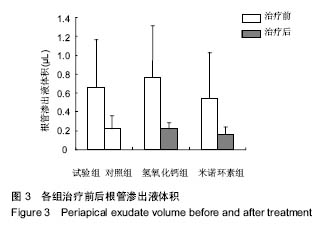
Interleukin-17 in apical exudates of periapical periodontitis treated with minocycline controlled-release formulation
Jia Zhi, Du Yu, Du Yuan, Jiang Chen
- Department of Endodontics, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China
-
Received:2017-02-04Online:2017-04-08Published:2017-05-08 -
Contact:Jia Zhi, Associate professor, Department of Endodontics, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China -
About author:Jia Zhi, Associate professor, Department of Endodontics, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China -
Supported by:the Application Foundation and Frontier Technology Research Program of Tianjin, No. 15JCYBJC50200
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jia Zhi, Du Yu, Du Yuan, Jiang Chen. Interleukin-17 in apical exudates of periapical periodontitis treated with minocycline controlled-release formulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.10.006.
share this article
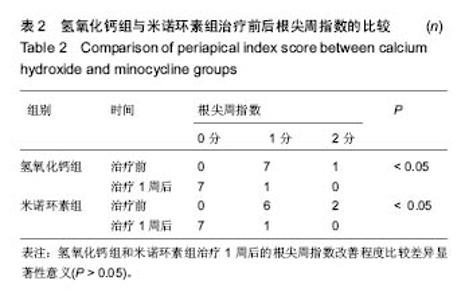
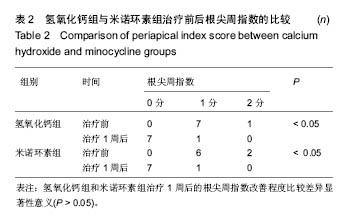
| [1]Siqueira JF Jr,Rôças IN.Distinctive features of the microbiota associated with different forms of apical periodontitis.J Oral Microbiol.2009;1. [2]Dutta A,Smith-Jack F,Saunders WP.Prevalence of periradicular periodontitis in a Scottish subpopulation found on CBCT images.Int Endod J.2014;47(9):854-863.[3]Fukunaga T,Zou W,Warren JT,et al.Vinculin regulates osteoclast function.J Biol Chem. 2014;289(19):13554-13564. [4]Ren Y,Vissink A.Cytokines in crevicular fluid and orthodontic tooth movement.Eur J Oral Sci.2008;116(2):89-97.[5]Basaran G,Ozer T,Kaya FA,et al.Interleukins 2, 6, and 8 levels in human gingival sulcus during orthodontic treatment.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2006;130(1): 7 e1-6.[6]Kapoor P,Kharbanda OP,Monga N,et al.Effect of orthodontic forces on cytokine and receptor levels in gingival crevicular fluid: a systematic review.Prog Orthod.2014;15:65.[7]Pacifici R.The Role of IL-17 and TH17 Cells in the Bone Catabolic Activity of PTH. Front Immunol.2016;7:57.[8]Ibáñez L,Abou-Ezzi G,Ciucci T,et al.Inflammatory Osteoclasts Prime TNFα-Producing CD4+ T Cells and Express CX3 CR1.J Bone Miner Res.2016;31(10):1899-1908.[9]Uluçkan Ö,Jimenez M,Karbach S,et al.Chronic skin inflammation leads to bone loss by IL-17-mediated inhibition of Wnt signaling in osteoblasts.Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(330): 330ra37. [10]Vera J,Siqueira JF Jr,Ricucci D,et al.One- versus two-visit endodontic treatment of teeth with apical periodontitis: a histobacteriologic study.J Endod.2012;38(8):1040-1052.[11]Law A,Messer H.An evidence-based analysis of the antibacterial effectiveness of intracanal medicaments.J Endod.2004;30(10):689-694.[12]Menakaya IN,Adegbulugbe IC,Oderinu OH,et al.The Efficacy of Calcium Hydroxide Powder mixed with 0.2% Chlorhexidine Digluconate or mixed with Normal Saline as Intracanal Medicament in the Treatment of Apical Periodontitis.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2015;16(8):657-664.[13]McHugh CP,Zhang P,Michalek S,et al.pH required to kill Enterococcus faecalis in vitro.J Endod.2004;30(4):218-219.[14]Dahlan AA,Haveman CW,Ramage G,et al.Sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidine gluconate, and commercial denture cleansers as disinfecting agents against Candida albicans: An in vitro comparison study.Gen Dent.2011; 59(6): e224-229.[15]耿素芳,曹采方,陈智滨,等.盐酸米诺四环素软膏对龈沟液中胶原酶的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2000,35(5):15-18.[16]李向阳,李妞.盐酸米诺环素软膏与氢氧化钙糊剂治疗窦道型根尖周炎疗效分析[J].中国当代医药,2016,23(20):118-119,131.[17]罗焕娣,缪小青,李静,等.盐酸米诺环素软膏应用时机对超声龈下刮治治疗慢性牙周炎效果的影响[J].中国医药科学,2016,6(2): 203-205.[18]李宝奎,张辉.盐酸米诺环素辅助根管治疗在牙周牙髓联合病变中的应用效果评价[J].临床医学研究与实践,2016,1(26):25-26.[19]Takashiba S,Ohyama H,Oyaizu K,et al. HLA genetics for diagnosis of susceptibility to early-onset periodontitis.J Periodontal Res.1999;34(7):374-378.[20]Bettelli E,Korn T,Oukka M,et al.Induction and effector functions of T(H)17 cells. Nature.2008;453(7198):1051-1057.[21]Xiong H,Wei L,Peng B.Immunohistochemical localization of IL-17 in induced rat periapical lesions.J Endod.2009;35(2): 216-220.[22]卫书盛,川岛伸之,铃木规元,等.Th17相关细胞因子在大鼠实验性根尖周炎表达的研究[J]. 北京口腔医学,2010,18(1):21-24.[23]OuYang Q,Pan Y,Luo H,et al.MAD ointment ameliorates Imiquimod-induced psoriasiform dermatitis by inhibiting the IL-23/IL-17 axis in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016;39: 369-376. [24]Costerton W,Veeh R,Shirtliff M,et al.The application of biofilm science to the study and control of chronic bacterial infections.J Clin Invest. 2003;112(10):1466-1477.[25]高守红,温燕,邬蓉,等.注射用盐酸米诺环素在健康人体的药物动力学[J].药学实践杂志, 2009,27(3):193-194,200.[26]van Steenberghe D,Rosling B,Soder PO,et al.A 15-month evaluation of the effects of repeated subgingival minocycline in chronic adult periodontitis. J Periodontol.1999;70(6): 657-667.[27]赵宁民,王睿,梁蓓蓓,等.米诺环素文献循证计量分析[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2010,26(12):942-946.[28]Holmgren C,Esplin MS,Hamblin S,et al.Evaluation of the use of anti-TNF-alpha in an LPS-induced murine model.J Reprod Immunol.2008;78(2):134-139.[29]Rathnayake N,Gustafsson A,Norhammar A,et al.Salivary Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 and -9 and Myeloperoxidase in Relation to Coronary Heart and Periodontal Diseases: A Subgroup Report from the PAROKRANK Study (Periodontitis and Its Relation to Coronary Artery Disease).PLoS One.2015; 10(7):e0126370.[30]Choi DH,Moon IS,Choi BK,et al.Effects of sub-antimicrobial dose doxycycline therapy on crevicular fluid MMP-8, and gingival tissue MMP-9, TIMP-1 and IL-6 levels in chronic periodontitis.J Periodontal Res.2004;39(1):20-26.[31]Golub LM,Goodson JM,Lee HM,et al.Tetracyclines inhibit tissue collagenases. Effects of ingested low-dose and local delivery systems.J Periodontol.1985;56(11 Suppl):93-97.[32]Gul SS,Douglas CW,Griffiths GS,et al.A pilot study of active enzyme levels in gingival crevicular fluid of patients with chronic periodontal disease.J Clin Periodontol.2016;43(8): 629-636.[33]邹萍,莫其农,薛明惠,等.盐酸米诺环素缓释剂对慢性牙周炎龈沟液弹性蛋白酶水平的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2008,24(7): 404-406.[34]耿素芳,曹采方,陈智滨,等.盐酸米诺四环素软膏对龈沟液中胶原酶的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2000,35(5):336-339.[35]Frantz B,Polson A.Tissue interactions with dentin specimens after demineralization using tetracycline.J Periodontol.1988; 59(11):714-721.[36]张文怡,刘洪臣,吴霞,等.米诺环素对体外培养的成年大鼠牙槽骨成骨细胞生物活性的影响[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2007,5(3): 173-176.[37]Akcay M,Arslan H,Topcuoglu HS,et al.Effect of calcium hydroxide and double and triple antibiotic pastes on the bond strength of epoxy resin-based sealer to root canal dentin.J Endod.2014;40(10):1663-1667.[38]Zhao J,Di T,Wang Y,et al.Multi-glycoside of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. ameliorates imiquimod-induced skin lesions through a STAT3-dependent mechanism involving the inhibition of Th17-mediated inflammatory responses.Int J Mol Med.2016;38(3):747-757.[39]Nikodemova M,Watters JJ,Jackson SJ,et al.Minocycline down-regulates MHC II expression in microglia and macrophages through inhibition of IRF-1 and protein kinase C(PKC)alpha/betaII.J Biol Chem.2007;282(20):15208-15216. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Fang Xiaoyang, Tang Tian, Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Repair and regenerative therapies of the annulus fibrosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1582-1587. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||