Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (34): 5540-5546.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0972
Previous Articles Next Articles
Polymethylmethacrylate bone cement loaded with antituberculosis drugs: combined drug-loading program and anti-tuberculosis effects
Yuan Hucheng1, Shi Shiyuan2, Ma Wenxin3, Li Xusheng3, Liu Zhen1, Ma Xuehua1
- 1Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Red Cross Hospital of Hangzhou, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310003, Zhejiang Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2018-06-25Online:2018-12-08Published:2018-12-08 -
Contact:Ma Wenxin, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yuan Hucheng, Master candidate, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, No. NZ17145; the Youth Scientific and Technological Talent Lifting Project of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yuan Hucheng, Shi Shiyuan, Ma Wenxin, Li Xusheng, Liu Zhen, Ma Xuehua. Polymethylmethacrylate bone cement loaded with antituberculosis drugs: combined drug-loading program and anti-tuberculosis effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(34): 5540-5546.
share this article

2.1 载抗结核药物骨水泥研究现状及抗结核药物的选择 目前,由于流动人口的增加,免疫缺陷性疾病的流行,结核分枝杆菌的变异、耐药菌的出现,不规范使用抗结核药物等原因,致使结核病在全球死灰复燃,尤其在发展中国家更为严重,成为一个严重的卫生和社会问题,已是严重危害人类健康和生存的最危险因素之一。作为常见的肺外结核之一的骨关节结核,严重影响人们的关节功能。沿用过去老的、传统的治疗方法势必陷入困境,根本无法避免相当一部分患者的结核不愈及复发现状。从另一层面讲,迁延不愈、复发患者必定成为耐药菌株的携带者与传播者,造成区域性范围内耐药结核菌的流行,增加了疾病的治疗难度。究其原因,其一,病灶局部形成致密的硬化壁,成为抗结核药物进入病灶的屏障,使病灶内难以达到有效的抗菌浓度,使病灶迁延不愈或者复发[8-13]。这也被作者所在团队的系列基础研究所证实:骨关节结核骨性病灶硬化者占70%以上;结构致密、无血管结构的硬化壁及其所包裹的中央病灶中,异烟肼、利福平、吡嗪酰胺的药物浓度检测不到或达不到最低抑菌浓度,但其中结核分枝杆菌DNA扩增检测阳性率高达88.9%;而硬化壁外围的“亚正常骨”中上述药物浓度可达杀菌浓度,但其中结核分枝杆菌DNA扩增检测阳性率仅有16.7%[14-15],这亦被其他作者的研究所证实[16],说明病灶组织中极低的药物浓度难以杀灭其中的结核菌群。其二,骨关节结核引起的大范围骨缺损需予以手术修复,现行的植骨材料来源有限,尚缺乏临床行之有效的人工植骨材料,故研制有效的人工材料亦是该领域重要的科学问题。如何解决上述两大难题,改变骨关节结核的治疗方法,提高治疗效果?局部缓释植骨材料可将上述两大难题有机地结合起来统一解决:载抗结核药物人工缓释材料,既具备在病变局部持续缓慢释放抗结核药物、使病变部位药物浓度升高、有效杀灭局部结核杆菌、全身血药浓度低、不良反应小的作用,又兼备病变局部植骨修复的成骨效果、更快地修复结核病变引起骨缺损的作用。因此,除术中彻底切除病灶硬化壁外,亟需一种通过提高病灶局部抗结核药物浓度的方法来提高治疗效果,局部药物缓释系统—载抗结核药物骨水泥即具备此种性能。因而,尝试开发出高效、无或低毒副作用的载抗结核药物骨水泥,推动人工关节置换在全关节结核病治疗中的普遍应用,具有重要的学术价值和社会意义。 2.1.1 载抗结核药物骨水泥的研究现状及各自优缺点 见表1。"

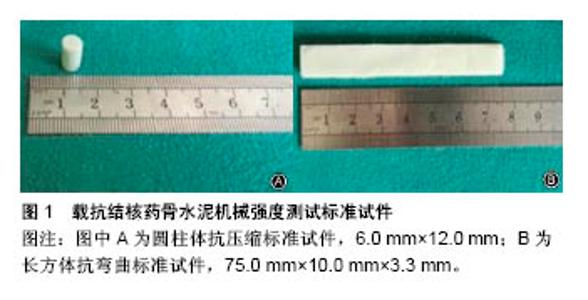
为解决植骨支撑和缓释的双重难题,人们尝试将羟基磷灰石、硫酸钙、磷酸钙等可降解高分子生物材料与抗结核药物混合,用于骨关节结核骨缺损的替代治疗,取得了良好疗效[17-18]。乔永杰[19]在3D打印β-磷酸三钙骨组织工程支架负载异烟肼、利福平/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物缓释微球治疗感染性骨缺损的实验研究中,发现3D打印β-磷酸三钙骨组织工程支架负载异烟肼、利福平/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物缓释微球对慢性骨髓炎的治疗效果良好,不仅生物相容性及生物力学性能令人满意,而且具有局部抗菌与成骨修复的双重优势,对未来骨髓炎的临床治疗提供了有力实验依据。李坤[20]通过对载药抗结核复合骨支架的构建与特性研究发现,载药抗结核复合骨支架无显著细胞毒性,且生物相容性及安全性好,对细胞的毒性评估符合生物材料使用标准。此外,载药抗结核复合骨支架诱导成骨的能力较强,将其应用于骨关节结核术后骨缺损的治疗,可促进骨缺损的愈合。上述生物材料解决了当前脊柱结核疗程长、复发率高的难题,为缩短疗程、提高治愈率、降低术后复发率及减少耐药菌株的发生提供了一种新的治疗途径。该材料可使结核病灶局部药物浓度达到有效治疗浓度并能维持数月,同时使脊柱结核的修复重建富于生物活性特性,使愈合的过程更快、更有效,提高脊柱结核疗效,填补了国内外在此方面对脊柱结核治疗的空白,这对于推动国内外脊柱结核专业的快速发展具有重要科学意义。然而,成为该材料应用于骨关节结核治疗最大阻碍的是:其机械强度差,且均属于可降解生物材料,无论在体外模拟体液中、模拟动物体内,还是人体内其终将降解,虽然达到了短时间内在病灶局部抗菌与成骨修复的双重作用,但无法起到长期植骨支撑的作用,尤其对于骨缺损较大的病灶,可降解植骨材料将无法起到预期的填充效果。 1987年,Galibert等首次报道将PMMA骨水泥用于椎体血管瘤的治疗,该技术被称为经皮椎体成形。此后,随着该项技术的不断发展,人们逐渐将其用于骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折、椎体转移瘤等的治疗中,临床效果可靠。近年来,PMMA骨水泥治疗骨缺损的应用越来越多。为此,人们探索将载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥作为骨关节结核相关生物材料的研究。然而,迄今为止,国内外有关载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥的研究十分有限,检索CNKI、万方数据库、PubMed数据库,国内外尚无规范的此类研究;国外在临床尝试方面仅有零星的个案报 道[21-23];在抗生素骨水泥治疗和预防开放性骨折、骨髓炎的研究中,国内外均报道了载利福平骨水泥珠链的研究且获得了良好效果[24]。2013年Han等[25]首次针对脊柱结核治疗进行了载异烟肼、利福平骨水泥缓释性能与抗菌活性的体外实验,是迄今为止对于载抗结核药物骨水泥研究最为深入的。但该研究仅选择了1种骨水泥与2种抗结核药物,且无力学性能、安全性的研究;更为重要的是未进行体内实验研究,故其研究结果及结论较为局限。尽管如此,此科学问题已在国际上开始被少数专业人士所关注。Kim等[26]对1950至2012年间活动性髋关节结核行人工关节置换的文献进行了系统评价,该研究结果肯定了这种治疗方法;在分析了复发原因后指出,目前骨水泥复合抗结核药物的研究太少,强调要进行毒性小、洗脱性能好的载抗结核药物骨水泥研究。因而进行载抗结核药物骨水泥的实验与临床研究十分必要。马文鑫等[7]分别将抗结核药物利福平、异烟肼、吡嗪酰胺、莫西沙星与PMMA骨水泥Palacos R混合,制备载抗结核药物骨水泥标准试件,并进行了物理性能、机械强度及缓释性能研究,结果发现载吡嗪酰胺、莫西沙星骨水泥具有良好的物理性能及机械强度,且释药周期长;而载利福平、异烟肼骨水泥的上述性能均较差。与可降解生物材料相比,PMMA骨水泥最大的优点在于其属于不可降解生物材料,在体内存留时间长。研究表明,PMMA骨水泥聚合时产生的平均最高温度在75 ℃左右,且持续时间较长[27],温度的高低与注入椎体骨水泥的剂量和在椎体内的体积相关,其热效应可破坏周围组织内的神经末梢,缓解疼痛,但聚合过程并不影响抗生素活性[28]。 2.1.2 载抗结核药物骨水泥中抗结核药物的选择 在载抗结核药物骨水泥制备中,抗结核药物选择的基本原则是:不影响骨水泥的物理性能;有良好的化学稳定性和热稳定性;抗菌谱广;不易耐药;释药持久、稳定;无过敏性,毒副作用小[29-30],且必须兼顾对抗结核杆菌与一般感染细菌引起的复发及二重感染两方面。然而目前并没有抗结核药物能够完全满足上述要求。临床常用一线抗结核药物有异烟肼、利福平、吡嗪酰胺、乙胺丁醇、链霉素等,其全身抗结核效果良好,仍为临床首选。杨彦君等[31]将利福平与PMMA骨水泥混合,结果表明混合物具有良好的生物相容性,且无细胞毒性。许多研究将异烟肼、利福平、吡嗪酰胺3药联合进行体外缓释性能研究,效果良好,但均未进行体内研究[32-33]。二线抗结核药物有阿米卡星、卷曲霉素、莫西沙星、对氨基水杨酸钠、利福喷丁、环丝氨酸、丙硫异烟胺等。周晓东等[34]对10例中心型单椎体结核患者进行经皮链霉素骨水泥注射椎体成形治疗,连续规范随访6个月,结果发现术后1-3个月全身结核中毒症状明显好转;术后6个月血沉、C-反应蛋白恢复正常者4例,接近正常者6例,腰背部疼痛症状明显缓解,X射线片及CT、MRI检查均未见复发征象。钱志松等[35]以白兔为研究对象,将乙胺丁醇-磷酸钙复合体植入兔臀大肌和股骨髓腔中,用质谱法测定其中血药浓度,结果显示乙胺丁醇-磷酸钙复合体能够缓慢、持久释放乙胺丁醇。还有人用载利福喷丁微球磷酸钙骨水泥治疗骨结核,效果良好。但这些研究并未将PMMA骨水泥作为抗结核药物的载体。目前尚无将阿米卡星、卷曲霉素、丙硫异烟胺与PMMA骨水泥混合用于人工关节置换后感染与复发治疗的研究报道。研究表明,载抗结核药物骨水泥在病灶局部缓慢释药,并不经过肝脏的“首过消除”作用;同时,释放出来的药物极少进入全身血液循环系统,对人体的毒副作用很小,亦或无毒副作用[36-37]。因此,其释放出来的药物是原药,并非各药的代谢产物,局部应用可提高局部药物浓度。 2.2 PMMA骨水泥的选择、释药机制及缓释性能影响因素 自从1958年Charney首次应用骨水泥固定股骨假体成功施行全髋关节置换以来,骨水泥己被广泛应用于骨科临床。目前临床使用的骨水泥主要有两大类,一类是临床最常用的骨水泥,占所有骨水泥的84%以上,即不降解PMMA骨水泥,PMMA骨水泥是一种不降解、机械性能强、临床应用广泛的高分子生物材料;另一类为可降解材料,由于其在体内可降解,起不到长久植骨支撑的作用,故临床应用较少。关于PMMA骨水泥的结构,Kuehn等[38]用扫描电镜观察发现,PMMA横截面为孔径30-100 μm不等的孔状结构。在骨水泥中加入抗生素后可观察到抗生素颗粒,且骨水泥孔径增大为40-250 μm。PMMA中药物的释放可能是通过骨水泥表面、裂缝、空隙中药物浓度梯度的弥散作用来完成的,上述结构是载抗结核药PMMA骨水泥能够载药与释药的结构基础。Drognitz等[39]认为骨水泥中抗生素的释放可能是通过浓度梯度的弥散作用完成的,释放浓度随时间逐渐降低,故抗生素的含量越高抗生素越容易释放。也有人认为在体外的抗生素骨水泥模型中,庆大霉素主要通过表面弥散和模型的裂缝释放。 抗结核药能够稳定、持久地在局部释放,并能达到最小有效抑菌浓度,是载抗结核药PMMA骨水泥在骨科临床应用的基础。研究发现,影响载抗结核药PMMA骨水泥缓释性能的因素主要有以下几点:①不同品牌的骨水泥与不同的抗生素混合后缓释性能各异,这是由其结构所决定的,且已被众多研究结果公认,如庆大霉素 168 h的释放量,Palamed骨水泥为17.0%、Palacos R骨水泥为8.4%、CMW骨水泥为3.8%-5.5%[40]。在众多骨水泥中,Palacos品牌骨水泥被认为是缓释性能最佳的骨水泥,Wahlig[41]首次证明,Palacos品牌骨水泥和庆大霉素分别在骨水泥和抗生素中具有最佳的药代动力学特性;②有学者在载多联药物骨水泥缓释性能的研究中发现,药物间的相互作用有3种不同的现象,即相互促进、相互抑制、互不影响。Han等[25]研究发现异烟肼联合利福平与骨水泥混合后,利福平可抑制异烟肼的缓释性能。为了充分发挥抗结核药物相互促进的作用,避免相互抑制现象的发生,在抗结核药物的选择上应引起高度重视;③此外,还有研究表明,低频超声刺激[42]、多抗生素联合使用、添加增孔剂(可降解物质、亲水性物质、表面活性剂等)[43]、不同混合比例与搅拌方式[44]、不同室温均会影响骨水泥的缓释性能。 2.3 抗结核药对骨水泥物理性能及机械性能的影响 骨水泥机械强度的评价有ISO 5833与ASTMF 451两个标准。只有当骨水泥满足压缩强度≥70 MPa、弯曲强度≥50 MPa、弯曲模量≥1 800 MPa时,方可用于人工关节置换中假体的固定。药物对骨水泥的影响主要体现在以下2个方面:第一,混合后骨水泥聚合延迟或不聚合,表现为聚合过程中混合物产热反应低、松散、柔软、嗅之有气味、机械强度低。有研究表明,利福平、异烟肼与Palacos R骨水泥混合后均会阻碍骨水泥的聚合,且利福平或异烟肼与其他抗结核药联合后,与单药时一样也影响骨水泥的聚合,故不适于制作载抗结核药PMMA骨水泥[7,25]见图1。 而吡嗪酰胺、莫西沙星与上述骨水泥混合后,均不影响骨水泥的聚合,这可能与上述药物的理化性质和结构有关;第二,影响其机械强度,表现为药物与骨水泥混合后骨水泥已聚合,但其机械强度仍达不到ISO 5833标准。有研究还表明,上述药物同样会影响骨水泥的机械强度,且随药物添加剂量的增大,骨水泥的机械强度也相应降低。目前较为公认的比例是在 40 g骨水泥中加入1.0-2.0 g抗生素为宜,此比例虽可降低骨水泥的机械强度,但测定值仍符合ISO 5833标准,故可安全地用于人工关节置换中假体的固定[45-46],在载多联药物骨水泥的研究中,此添加比例仍可适用,并且推荐两种药物联合最好,而超过4 g,则使骨水泥的机械强度明显低于ISO 5833标准。 2.4 载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥抗结核性能 载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥抗菌活性的评价指标有很多,但主要集中在以下2个方面:①抗菌性能的变化:有学者发现,按前述药物选择要求所选取的抗生素与骨水泥混合后,并不改变药物的抗菌活性[47-48]。有研究也表明,利福平、异烟肼、吡嗪酰胺、莫西沙星与PAMA骨水泥Palacos R混合后其释药浓度不受影响,均在最低抑菌浓度范围内,但并未进行抗菌活性的体内外实验,上述药物与Palacos R骨水泥混合后抗菌活性是否受影响,尚需进一步研究。刘海涛等[49]在涂饰聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物的载三联抗结核药HRZ硫酸钙/聚氨基酸人工骨的研究中发现,异烟肼第19周的检测浓度、利福平第18周的检测浓度、吡嗪酰胺第12周的检测浓度仍在其最低抑菌浓度的10倍以上。何胤等[50-51]经复合三联抗结核药人工缓释材料体外抗结核性能的研究中发现,载药人工缓释材料第4周浸提液中的异烟肼、利福平、吡嗪酰胺浓度均高于其最低杀菌浓度;第8周载药人工缓释材料浸提液中异烟肼、利福平仍显著高于其最低杀菌浓度,然而吡嗪酰胺虽然高于其最低杀菌浓度,但是差距不大;第12周载药人工缓释材料浸提液中异烟肼浓度高于其最低杀菌浓度,吡嗪酰胺浓度明显低于其最低杀菌浓度,利福平浓度已测不到;②生物膜:近年研究发现,结核分枝杆菌能够以生物膜的形式存在,生物膜也是细菌的重要耐药机制之一[52]。载抗生素骨水泥可有效抑制生物膜的形成,且多药联合抗生素骨水泥的抑菌效果优于单一药物,因此抑制生物膜的形成程度是评价抗菌活性的指标之一。故对结核分枝杆菌生物膜形成机制与抗结核药物对生物膜抑制作用的研究显得十分重要。然而,截止目前,该方面的研究尚处于空白。 2.5 载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥的安全性 载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥在病灶局部高浓度、长期、持续的释放药物,是否会引起全身和局部组织的毒副作用,是载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥研究中值得关注的另一重要课题。载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥对机体的低或无毒副作用非常重要,一旦发生毒副作用,就要将其从结核病灶中取出,否则会引起严重的不良反应,甚至危及患者生命。然而将其取出又有一定的困难,故选择低或无毒副作用的抗结核药物与骨水泥显得尤为重要。载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥的安全性主要从以下2个方面进行评估:①全身毒副作用及过敏反应:载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥中的抗结核药一般对机体正常组织损害较小,因为研究中载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥的抗结核药物剂量均属预防剂量,与治疗人工关节感染的占位器相比,其载药量较低,属于低剂量,且载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥在局部高效、持久地释药时并不引起全身血药浓度的升高。目前尚无低剂量抗生素骨水泥中药物释放引起全身毒性反应的报道;其最常见的不良反应为过敏反应,但发生率极低,文献已有过报道[53]。许多研究认为抗生素骨水泥低剂量的持续释放,可导致耐药的发生,但Sader等[54]从欧盟44个多中心的研究证实,在初次置换中常规使用,并没有增加耐药性的发生;②局部组织毒性作用:尽管目前尚无有关低剂量药物浓度下成骨细胞活性受影响的研究报道,但在高剂量药物浓度体外实验条件下,可致碱性磷酸酶减少、DNA总数减少[55]。但对载抗结核药物骨水泥来说,上述均未进行过相关研究,这是载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥研究需进一步探索的课题。 载抗结核药物骨水泥的不良反应及毒副作用除了上述2个方面,主要还是抗结核药物本身的不良反应。有关抗结核药物的研究发现,利福平不良反应较多,主要有肝肾毒性与过敏反应,表现为肝功能减退、发热、皮疹、急性肾衰竭、流感样综合征、溶血性贫血及血小板减少等[56],与异烟肼联合应用时其肝毒性发生的危险性增加[57]。乙胺丁醇常见视神经损害,如球后视神经炎等。链霉素耳毒性、肾毒性强。莫西沙星有较强的抗结核性能,且易穿过血脑屏障,维持较高的药物浓度,在脑脊液中发挥作用,生物利用度达90%以上,不良反应小[58],与吡嗪酰胺联用对杀灭巨噬细胞内结核杆菌有协同作用。一项关于利福喷丁与利福平治疗肺结核总有效率的研究发现,利福喷丁的抗结核菌作用较利福平强2-10倍,利福喷丁治疗肺结核的总有效率高于利福平组(P < 0.05),且利福喷丁组降低白细胞及胃肠道反应发生率低于利福平组(P < 0.05)[59]。由于载抗结核药物PMMA骨水泥的释药量少,且一般仅作用于病灶局部,很少进入血液循环系统,故不良反应小,上述药物的毒副作用不足以引起全身毒副作用。 "

| [1] Hardinge K,Williams D,Etienne A,et al.Conversion of fusion hips to low friction arthroplast.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1977; 59(4):385-392.[2] Johnson R,Barnes KL,Owen R.Reactivation of tuberculosis after total hip replacement.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979;61(2): 148-150.[3] Habaxi KK,Wang L,Miao XG,et al.Total knee arthroplasty treatment of active tuberculosis of the knee:a review of 10 cases.Eur Rev Med.2014;18(23):3587-3592.[4] 宋向伟,王骞,施建党,等.脊柱结核彻底病灶清除术后3-4.5个月超短程化疗方案的疗效观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2017,27(4): 326-332.[5] Buchholz HW,Engelbrecht H.Depot effects of various antibiotics mixed with Palacos resins. Chirurg. 1970;41(11): 511-515. [6] Randelli P,Evola FR,Cabitza P,et al.Prophylactic use of antibiotic-loaded bone cement in primary total knee replacement.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18(2):181-186.[7] 马文鑫,金卫东,王骞,等.载利福平、异烟肼、吡嗪酰胺、莫西沙星骨水泥物理性能及洗脱性能的体外研究[J].中华骨科杂志, 2016,36(11):735-744.[8] 虢剑,王骞,马文鑫,等.32例脊柱内固定术后急性感染的临床分析[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2016,38(12):1458-1461.[9] 马文鑫,王骞,王自立,等.脊柱内固定术后感染的治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(15):1357-1362.[10] Oga M,Arizono T,Takasita M,et al.Evaluation of the risk of instrumentation as a foreign body in spinal tuberculosis.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1993;18(13):1890-1894.[11] 王骞,马文鑫.骨关节结核:骨病灶药物分布特点及缓释材料[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(48):7859-7859.[12] 施建党,刘园园,王骞,等.病椎固定治疗胸、腰椎结核的疗效分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(11):681-690.[13] Jin W,Wang Q,Wang Z,et al.Complete debridement for treatment of thoracolumbarspinal tuberculosis:a clinical curative effect observation.Spine J.2014;14(6):964-970.[14] Si J,Geng G,Wang Z.Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA in the sclerotic spinal wall.Orthopedics. 2012;35(3): 409-413. [15] Ge Z,Wang Z,Wei M.Measurement of the concentration of three antituberculosis drugs in the focus of spinal tuberculosis.Eur Spine J.2008;17(11):1482-1487. [16] Liu P,Zhu Q,Jiang J.Distribution of three antituberculous drugs and their metabolites in different parts of pathological vertebrae with spinal tuberculosis.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(20):1290-1295.[17] Ha KY,Chung YG,Ryoo SJ.Adherence and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis on various spinal implants.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):38-43.[18] Dale H,Fenstad AM,Hallan G,et al.Increasing risk of prosthetic joint infection after total hip arthroplasty.Acta Orthop. 2012; 83(5):449-458.[19] 乔永杰.3D打印β-TCP骨组织工程支架负载异烟肼、利福平/ PLGA缓释微球治疗感染性骨缺损的实验研究[D].兰州:兰州大学, 2017.[20] 李坤.基于三维打印技术的载药抗结核骨支架的构建与特性研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2016.[21] Leclere LE,Sechriest VF,Holley KG,et al.Tuberculous arthritis of the knee treated with two-stage total knee arthroplasty.A case report.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2009;91(1):186-191.[22] Masri BA,Duncan CP,Jewesson P,et al.Streptomycin-loaded bone cement in the treatment of tuberculous osteomyelitis:an adjunct to conventional therapy.Can J Surg.1995;38(1):64-68.[23] Su JY,Huang TL,Lin SY.Total knee arthroplasty in tuberculous arthritis.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1996;(323):181-187. [24] Anguita-Alonso P,Rouse MS,Piper KE,et al.Comparative study of antimicrobial release kinetics from polymethylmethacrylate.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;445 (445):239-244.[25] Han CD,Oh T,Cho SN.Isoniazid could be used for antibiotic-loaded bone cement for musculoskeletal tuberculosis: an in vitro study.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471(7):2400-2406.[26] Kim SJ,Postigo R,Koo S,et al.Total hip replacement for patients with active tuberculosis of the hip:a systematic review and pooled analysis.Bone Joint J.2013;95(5):578-582.[27] 孙强,郑加法,刘德南.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥作为抗肿瘤药物缓释载体的实验研究[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2010,17(11): 823-826.[28] Urabe K,Naruse K,Hattori H,et al.In vitro comparison of elution characteristics of vancomycin from calcium phosphate cement and polymethy lmethacrylate.J Orthop Sci.2009;14(6): 784-793. [29] 胡汉,刘欣伟,田竞,等.抗生素PMMA骨水泥研究进展[J].创伤与急危重病医学,2016,4(4):253-256.[30] 刘斌,王骞,王自立.PCR-SSCP快速检测脊柱结核耐药基因[J].宁夏医学杂志,2010,32(9):795-796.[31] 杨彦君,熊屹,易洪城,等.载利福平-骨水泥复合物的生物相容性研究[J].贵阳中医学院学报,2014,36(1):27-30.[32] 王骞,刘海涛,施建党,等.聚乳酸/聚乙醇酸共聚物涂饰载三联抗结核药人工骨体外释药对比[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(6): 911-916.[33] 刘海涛,施建党,王自立,等.硫酸钙/聚氨基酸复合三联抗痨药人工缓释材料的制备及物理性能测定[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015, 23(21):1984-1988.[34] 周晓东,高玉盛,牟瑜瑜,等.链霉素骨水泥椎体成形术治疗中心型单椎体结核疗效观察[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2016,30(9): 928-930.[35] 钱志松,黄山虎,刘志礼,等.乙胺丁醇-磷酸钙骨水泥复合体药物缓释的研究[J].江西医药,2009,44(7):657-659.[36] 闫军法,王骞,王自立,等.涂饰PLGA载三联抗痨药人工骨的体外释药研究[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2015,37(6):661-664.[37] 何胤,杨宗强,王骞,等.复合三联抗结核药聚乳酸-羟基乙酸缓释微球的制备及体外释药特性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2015,25(5): 456-461.[38] Kuehn KD,Ege W,Copp U.Acrylic bone cements:composition and properties.Orthop Clin North Am.2005;36(1):17-28.[39] Drognitz O,Thorn D,Krüger T,et al.Release of vancomycin and teicoplanin from a plasticized and resorbable gelatin sponge: in vitro investigation of a new antibiotic delivery systemwith glycopeptides.Infection.2006;34(1):29-34.[40] Neut D,van de Belt H,van Horn JR,et al.The effect of mixing on gentamicin release from polymethylmethacrylate bone cements.Acta Orthop Scand.2003;74(6):670-676.[41] Wahlig H,Kinetics of the liberation of antibiotics from bone cements results of comparative studies in vitro and in vivo.Aktuelle Probl Chir Orthop.1987;31:221-226.[42] Cai XZ,Chen XZ,Yan SG,et al.Intermittent watt-level ultrasonication facilitates vancomycin release from therapeutic acrylic bone cement.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2009;90(1):11-17.[43] Miller RB,McLaren AC,Leon CM,et al.Surfactant-stabilized emulsion increases gentamicin elution from bone cement.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2011;469(11):2995-3001.[44] 杨骐宁,蔡迅梓,严世贵.抗生素骨水泥的药释特性和增效思路[J].中华关节外科杂志,2011,5(3):369-373.[45] Persson C,Baleani M,Guandalini L,et al.Mechanical effects of the use of vancomycin and meropenem in acrylic bone cement.Acta Orthop.2006;77(4):617-621.[46] Dunne N,Hill J,McAfee P,et al.In vitro study of the efficacy of acrylic bone cement loaded with supplementary amounts of gentamicin:effect on mechanical properties,antibiotic release,andbiofilm formation.Acta Orthop. 2007;78(6): 774-785.[47] Gálvez-López R,Peña-Monje A,Antelo-Lorenzo R,et al.Elution kinetics,antimicrobial activity,and mechanical properties of 11 different antibiotic loaded acrylic bone cement. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis.2014;78(1):70-74.[48] Chang Y,Tai CL,Hsieh PH,et al.Gentamicin in bone cement:A potentially more effective prophylactic measure of infectionin joint arthroplasty.Bone Joint Res.2013;2(10):220-226.[49] 刘海涛,施建党,王骞,等.载三联抗结核药物硫酸钙/聚氨基酸人工材料体外缓释性能的观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2015,25(3): 239-244.[50] 何胤,杨宗强,王骞,等.复合三联抗结核药聚乳酸-羟基乙酸缓释微球的制备及体外释药特性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2015,25(5): 456-461.[51] 闫军法,王骞,施建党,等.涂饰PLGA载三联抗痨药人工骨的体外释药研究[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2015,37(6):661-664.[52] Ojha AK,Trivelli X,Guerardel Y,et al.Enzymatic hydrolysis of trehalose dimycolate releases free mycolic acids during mycobacteria growth in biofilms.J Biol Chem. 2010;285(23): 17380-17389.[53] Eben R,Dietrich KA,Nerz C,et al.Contact allergy to metals and bone cement components in patients with intolerance of arthro plasty.Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2010;135(29): 1418-1422.[54] Sader H,Fritsche T,Stilwell M,et al.10 years of surveillance of bloodstream infections in European medical centres by the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (1997-2006).Int J Antimicrob Agents.2007;29(2):78.[55] Isefuku S,Joyner CJ,Simpson AH.Gentamicin may have an adverse effect on osteogenesis.J Orthop Trauma. 2003;17(3): 212-216.[56] 武丽娟,梁建琴.利福平过敏机制研究进展[J].中国临床医生杂志, 2017,45(5):17-20.[57] 何雪,宋育林,王莉,等.激活PPARγ抑制异烟肼与利福平合用致大鼠肝损伤及HMGB1水平上调[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2017,26(2):129-133.[58] 潘静.莫西沙星与抗结核药物联用治疗难治性结核性脑膜炎的疗效观察[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2017,20(05):104-106.[59] 陈利,肖兰春.利福喷丁与利福平治疗肺结核临床效果[J].中国医药科学,2017,7(5):56-58. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||