Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (22): 3498-3505.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0917
Previous Articles Next Articles
Sodium alginate/podophyllotoxin drug delivery system: preparation, release and anti-colon cancer effects
Wang Jiang1, Wang Qing-feng2, Jiang Yi-xin3, Chen Na1, Chu Zheng4
- 1Department of Chinese Herbs, 4Department of Pharmacy, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Region, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China; 2Food School of Shenyang Normal University, Shenyang 110032, Liaoning Province, China; 3Liaoning Vocational Technical College, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2018-05-01Online:2018-08-08Published:2018-08-08 -
Contact:Chu Zheng, Pharmacist in charge, Department of Pharmacy, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Region, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Jiang, Master, Pharmacist-in-charge, Department of Chinese Herbs, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Region, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, No. 20170540601; the Science and Technology Research Project of Shenyang, No. 18-013-0-44
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jiang, Wang Qing-feng, Jiang Yi-xin, Chen Na, Chu Zheng. Sodium alginate/podophyllotoxin drug delivery system: preparation, release and anti-colon cancer effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(22): 3498-3505.
share this article
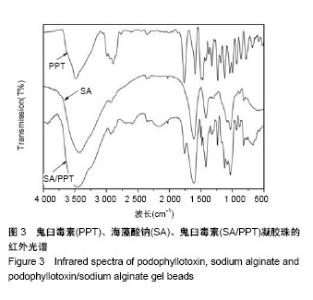
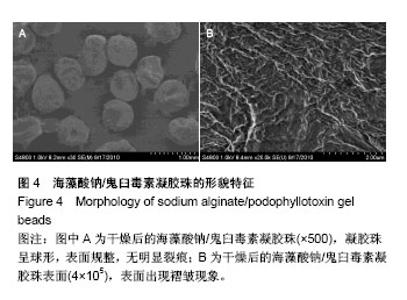
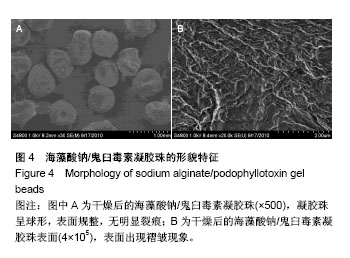
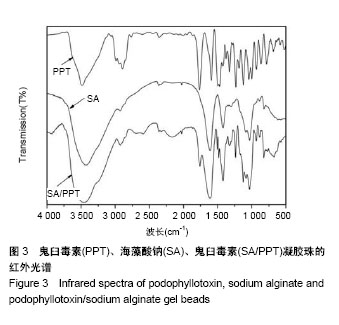
2.2 海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素凝胶珠的傅里叶变换红外光谱和扫描电镜分析 从图3同时看出海藻酸钠、鬼臼毒素、海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素的红外光谱特征[27]。分析海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素的红外光谱图可得:1 770 cm-1的特征峰是C=O的伸缩振动引起的,且1 507 cm-1和1 484 cm-1的特征吸收是C=C的振动引起的,这几个特征峰体现了鬼臼毒素芳香环的结构特征[28];1 236,1 128,1 033 cm-1的特征峰,是由鬼臼毒素和海藻酸钠分子的-C-O振动引起的;1 613 cm-1和 1 423 cm-1的特征峰,是海藻酸钠的-COOH振动引起 的[29-30]。另外,海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素的1 770,1 507, 1 484 cm−1的特征峰比其在鬼臼毒素中的弱。综上,鬼臼毒素被包裹在海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素凝胶珠中。 海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素凝胶珠的形貌特征见图4。如图4A干燥的海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素凝胶珠为500 μm左右的球形,所获得的凝胶珠表面规整,无明显裂痕,药物包埋完整。而如图4B所示,干燥的凝胶珠表面出现褶皱现象,这是由于带负电的海藻酸钠分子与带正电的Ca2+通过静电作用形成“蛋盒”结构而形成了外膜。该结果说明,所获得的凝胶珠结构完整,并对药物进行了有效的包埋,可以用于后续的药理学研究。"
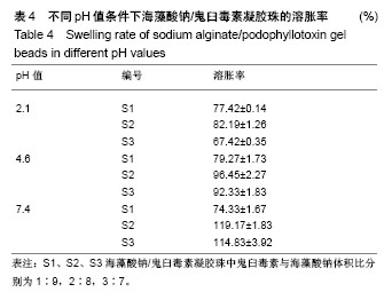
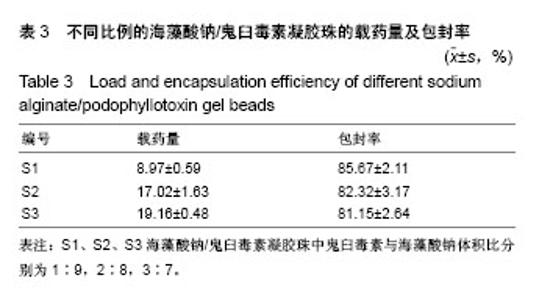
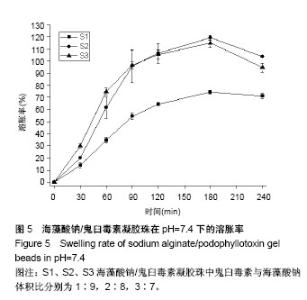
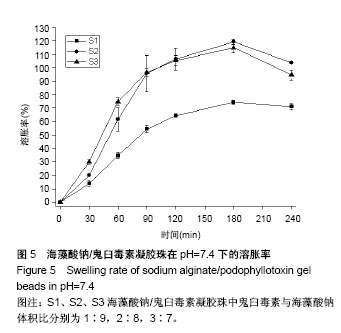
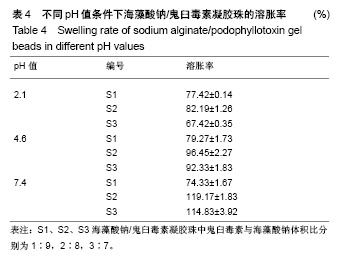
2.3 海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素凝胶珠在不同pH值下的溶胀性能 由表4可知,180 min后,3个样品都达到了最大溶胀率,且随PPT的增加,海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素的溶胀速度也增加。由于大量PO43-阴离子存于pH=7.4的PBS中,可以和海藻酸钠的-COO-1竞争与Ca2+结合,导致海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素溶胀。且随着时间增加,海藻酸钠溶解于PBS中,引起海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素在pH=7.4的溶胀率下降。在pH=2.1和 pH=4.6时,海藻酸钠分子的-COO-转化为-COOH,海藻酸钠变为不溶于水的大分子,因此较低的溶胀率是由表面海藻酸钠的水化导致的。以上表明:海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素凝胶珠可在胃中保持稳定,将药物输送到肠中,可作为肠靶向载药体系。 图5为海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素凝胶珠在pH=7.4下的溶胀性能,可以看出,整个凝胶珠体系在180 min处获得了最大的溶胀率。然而,由于壁材的原因,其在240 min处,溶胀率出现下降。该结果显示,制备的海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素凝胶珠在pH=7.4的条件下,可以充分溶胀,并有助于后续药物的缓释。"
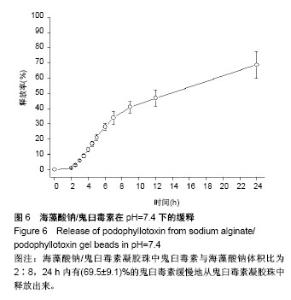
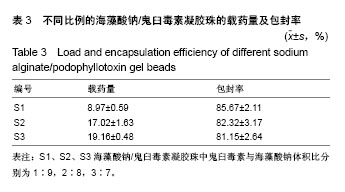
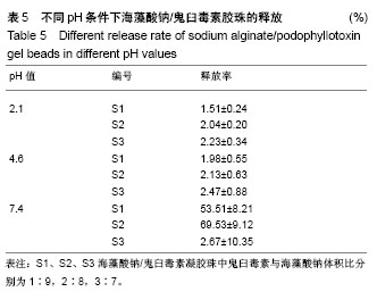
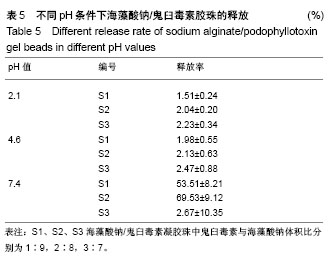
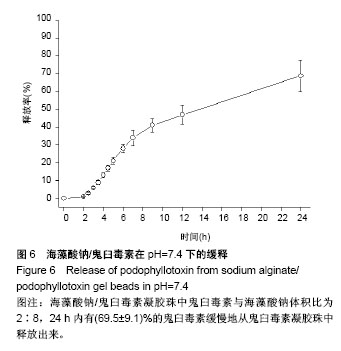
2.4 海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素凝胶珠在体外不同pH值下的释药行为 如图6所示,以样本S2为模型,在pH=7.4的模拟肠液中,24 h内有(69.5±9.1)%的鬼臼毒素缓慢地从鬼臼毒素凝胶珠中释放出来;在pH=2.1和pH=4.6的模拟胃液中(表5),24 h只有(2.0±0.2)%和(2.1±0.6)%的鬼臼毒素释放。由于模拟胃液中(pH=2.1和pH=4.6)鬼臼毒素凝胶珠几乎不溶胀,只有表面吸附的鬼臼毒素溶解到了介质中,而在模拟肠液中(pH=7.4),凝胶珠中的鬼臼毒素随时间被释放到介质中。将海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素在pH=7.4下的释放曲线用R%= ktn(power law model)拟合。经过拟合得出鬼臼毒素的拟合曲方程式为:y=0.051 0×t0.83,n为0.83,属于控制扩散和溶胀释放机制。 另进一步对各组的缓释情况对比可知,其他两组在 24 h处的缓释趋势同其他两组基本相同。组间对比并无显著性区别(P > 0.05),可以肯定制备的凝胶珠效果稳定且在强酸性环境pH=2.1及弱酸性pH=4.6环境下均表现出一定的稳定性,而在pH=7.4的弱碱性条件下则可缓慢的释放,其24 h释放率同添加的鬼臼毒素质量浓度呈正比,但组间并无显著区别(P > 0.05)。该结果显示在该条件下,所获得的凝胶珠性质稳定,可满足临床的实际需要。"
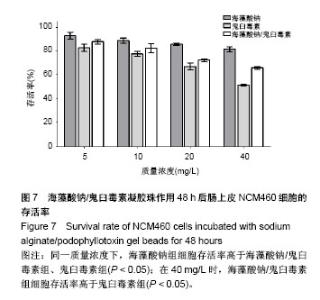
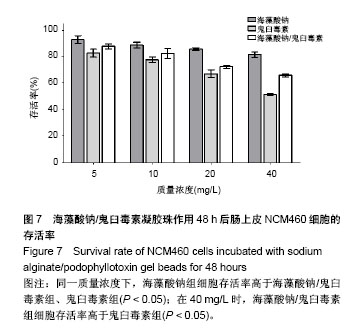
2.5 海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素凝胶珠对正常细胞及结肠癌SW480细胞的作用 2.5.1 对正常细胞的毒性 图7显示了不同物质在各浓度下对正常细胞的毒性,可以看出随着质量浓度增加,NCM460细胞存活率均逐步下降。其中,海藻酸钠组各个浓度下细胞存活率都高于80%,说明海藻酸钠有很好的安全性,5 mg/L组对比其他3组的细胞存活率差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);而10 mg/L同20 mg/L组、20 mg/L同40 mg/L组相比差异无显著性意义(P >0.05)。与之对应,鬼臼毒素组的细胞存活率则呈现一个显著性下降趋势,随着质量浓度的不断增加,组内的细胞存活率也随之下降,且各组间对比差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。结果表明,单独使用鬼臼毒素投入到人体体内会直接杀伤结肠细胞,带来相应的细胞毒性,其并不适合直接应用于临床。 海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素组的NCM460细胞亦随着其质量浓度的不断上升而死亡,且同鬼臼毒素组类似,随着质量浓度的不断增加,海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素组内的NCM460细胞的存活率也随之下降,且各组间对比差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.01),但其趋势较鬼臼毒素组明显放缓。组间对比,在质量浓度分别为5,10,20 mg/L时,虽然海藻酸钠也可通过对鬼臼毒素的包埋起到保护细胞的作用,但海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素组与鬼臼毒素组的细胞存活率对比无显著性意义(P > 0.05);当质量浓度上升至40 mg/L时,海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素组的细胞存活率为(65.85±1.10)%,相比于海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素的(51.22±0.85)%差异显著(P < 0.05)。该结果进一步证明海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素体系能降低药物对正常细胞的毒性。"
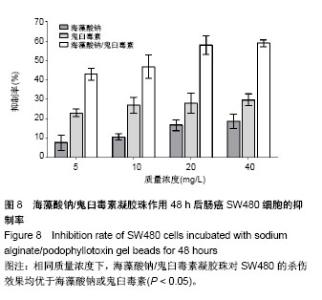
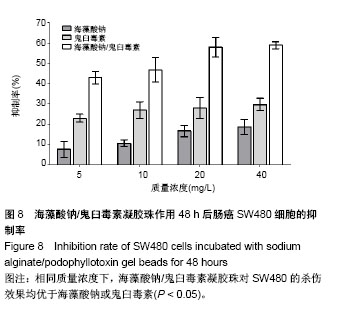
2.5.2 对肠癌细胞的杀伤作用 海藻酸钠、鬼臼毒素和海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素对SW480结肠癌细胞的抑制实验表明,随3者质量浓度的增加,SW480细胞的抑制率有提高(图8)。在实验质量浓度下,鬼臼毒素组出现了不同程度的抑制。单纯提高海藻酸钠的质量浓度,对SW480细胞的抑制作用有限,当海藻酸钠浓度提升至40 mg/L时,相比于5 mg/L组杀伤率仅提升了59.2%;另5 mg/L组同10 mg/L组、 20 mg/L组同40 mg/L组相比差异不显著(P > 0.05)。 相比于海藻酸钠,鬼臼毒素对SW480的杀伤率有提升,在鬼臼毒素作用下,5 mg/L组同10 mg/L组、20 mg/L细胞抑制率相比差异不显著(P > 0.05),40 mg/L组与 5 mg/L组细胞抑制率相比差异显著(P < 0.05),10 mg/L组与40 mg/L组细胞抑制率相比差异不显著(P > 0.05)。 相同质量浓度下,海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素凝胶珠对SW480的杀伤效果均优于海藻酸钠或鬼臼毒素(P < 0.05)。在当海藻酸钠/鬼臼毒素作用下,20 mg/L组细胞抑制率高于 5 mg/L组(P < 0.05),40 mg/L组与20 mg/L组细胞抑制率相比未进一步上升(P > 0.05),仅提升了2%。"
| [1] Canel C,Moraes RM,Dayan FE,et al. Podophyllotoxin. Phytochemistry. 2000;54(2):115-120.[2] 李楠,赵阳,魏菲,等.鬼臼毒素脲类衍生物的合成和体外抗癌活性的研究[J].天津医科大学学报,2016, 22(3):199-203.[3] Gordaliza M,García PA,Del corral JM,et al.Podophyllotoxin: Distribution, Sources, Applications and New Cytotoxic Derivatives. Toxicon.2004;44(4):441-459.[4] 种树彬,王小婕,陈如大,等.鬼臼毒素二元醇质体体外抗宫颈HPV感染的研究[J].中国实用医药,2017, 12(1):1-4.[5] Han HW,Qiu HY,Hu C, et al. Design, Synthesis and Anti-cancer Activity Evaluation of Podophyllotoxin-norcantharidin Hybrid Drugs. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.2016;26(14): 3237-3242.[6] 成伟华,陈虹,邹忠梅.鬼臼毒素的结构修饰及抗肿瘤活性研究进展[J].中国医药工业杂志,2017,48(5):644-650.[7] 程冀,季宇彬,王向涛.正交试验法优选鬼臼毒素新型脂质体的制备工艺[J].黑龙江大学自然科学学报, 2009,26(6):795-798.[8] Qin L,Xue M,Wang W,et al.The in Vitro and in Vivo Anti-tumor Effect of Layered Double Hydroxides Nanoparticles as Delivery for Podophyllotoxin. Int J Pharm. 2010;388(1): 223.[9] Fan L,Wu H,Zhang H, et al. Ph‐sensitive Podophyllotoxin Carrier for Cancer Cells Specific Delivery. Polymer Composites.2010; 31(1):51-59.[10] 高鹏.鬼臼毒素的聚乙二醇-聚己内酯胶束的制备[J].江西中医药, 2010,41(2):57-59.[11] 朱雄,吴葆金,罗厚蔚,等.去氧鬼臼毒素-磺丁基醚-β-环糊精包合物的制备及抗肿瘤作用[J].中国药科大学学报, 2010,41(5):447-450.[12] 邓亚利,蔡鑫剑,姚淑娴.羧基化碳纳米管负载鬼臼毒素的制备及透皮性能研究[J].中国药学杂志, 2017,52(12):1049-1055.[13] 程浩.1,2-顺式otobain-podophyllotoxin杂化物的合成及其抑制肿瘤活性研究[D].上海:华东师范大学,2016.[14] 梁华丽.紫杉醇纳米颗粒制备和应用[J].亚太传统医药, 2016,12(7): 52-53.[15] 高昊辰,汪沛,曹志中,等.载米诺环素纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合体的体外释放及抑菌性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(8):1118-1125.[16] 李瑞端,张建军.聚乳酸-羟基乙酸聚合物载入羟基喜树碱载药纳米粒子的制备及表征[J].化学反应工程与工艺, 2016,32(6):542-546.[17] 黄妍瑜.生物大分子纳米载药体系的功能化设计及其在肿瘤诊疗中的研究[D].广州:暨南大学,2016.[18] 宋一凡,柴云,张普玉.刺激响应性聚合物载药纳米胶束研究进展[J].化学研究,2016,27(5):655-659.[19] 董丽艳,李晓华,焦晓雯,等.他克莫司载药胶束的制备与制剂学性质[J].沈阳药科大学学报,2016,33(9):679-685.[20] 何思良.水凝胶/微球/淫羊藿苷复合载药体系的制备及性能研究[D].湘潭:湖南科技大学,2015.[21] 熊露.基于超分子聚合物前药的可注射载药水凝胶[D].杭州:浙江大学, 2016.[22] Podual† K,Iii FD,Peppas NA.Modeling of Water Transport in and Release From Glucose-sensitive Swelling-controlled Release Systems Based on Poly(diethylaminoethyl Methacrylate-g- ethylene Glycol).Ind Eng Chem Res. 2004;43(23):7510-7512.[23] 杨继荣,严文伟,肖勇翔,等.不同聚合物配方的硝苯地平缓释片体外释放差异研究[J].中国药业,2016, 25(18):43-47.[24] 吴叶,刘袖洞,王云红,等.海藻酸钠纳米粒制备的研究进展[J].材料导报, 2016,30(5):7-11.[25] 宋丽敏,李明,倪雅欣,等.高效氯氰菊酯/海藻酸钠/壳聚糖凝胶微球的制备[J].应用化工,2016,45(11): 2118-2120.[26] 赵睿.海藻酸钠基复合凝胶的制备与性能研究[D].武汉:武汉工程大学, 2016.[27] Liu Y,Yang L,Liu Y,et al.Synthesis and Insecticidal Activities of Novel Derivatives of Podophyllotoxin.Nat Prod Res. 2007;21(11) 967-974.[28] 王盈盈. CS/PAA@TPGS/PLGA纳米核递药系统逆转肺癌细胞多药耐药的效应及机制研究[D].南京:南京师范大学,2016.[29] Xie S,Luo J,Liu Q,et al.Adsorption Characteristics and Mechanism of Hydroxyethyl Cellulose/sodium Alginate Blend Films for Uranium(vi). Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica.2015; 32(1):268-275.[30] Hong C,Li M,Xin M,et al.Synthesis and Drug Release Performance of Chitosan Immobilized Cyclodextrin-sodium Alginate.Chin J Mater Res.2011;25(2):135-140.[31] Wang L,Yang F,Yang X,et al.Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New 4β-anilino-4′- O -demethyl-4-desoxypodophyllotoxin Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents.Eur J Med Chem.2011; 46(1):285-296.[32] 江中洪,曾抗,李国锋,等.鬼臼毒素纳米脂质载体的制备及质量考察[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(6):1039-1042.[33] 成伟华,牛聪,孙强稳,等.呋喃鬼臼毒素衍生物及其抗肿瘤活性研究[J].天津医科大学学报,2016, 22(5):381-385.[34] Li P,Dai YN,Zhang JP,et al.Chitosan-alginate Nanoparticles as a Novel Drug Delivery System for Nifedipine.Int J Biomed Sci. 2008; 4(3):8-221.[35] 肖潇.4-邻氨基酚-4'去甲表鬼臼醚抑制人舌鱗癌细胞增殖、黏附、迁移和侵袭[D].兰州大学,2013.[36] 孙如宁,熊晔蓉,涂家生.去氧鬼臼毒素mPEG-PDLLA聚合物胶束的制备及其性质的研究[J].海峡药学, 2016,28(4):26-30.[37] 李亚瑜,毛晓颖,汪凌,等. PLA-PEG-PLA的微波合成工艺及其在鬼臼毒素载药微球中的应用[J].化工新型材料, 2012,40(3):127-130. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||