Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (18): 2939-2945.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0874
Previous Articles Next Articles
Progress in the repair of osteoporotic bone defects: scaffold implantation and local drug delivery
Li Zu-hao, Wang Chen-yu, Wang Zhong-han, Gao Chao-hua, Shi Chen-yu, Yang Fan, Liu He, Wang Jin-cheng
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2018-03-22Online:2018-06-28Published:2018-06-28 -
Contact:Wang Jin-cheng, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Li Zu-hao, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81671804, 81772456, 81771681; the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province, No. 20160101109JC, 20150414006GH, 20150312028ZG, 20130206060GX; Ph.D. Outstanding Talent Cultivation Program of Norman Bethune Health Science Center of Jilin University, No. YB201501; the Innovation Research Program for Postgraduates in Jilin University, No. 2017032
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zu-hao, Wang Chen-yu, Wang Zhong-han, Gao Chao-hua, Shi Chen-yu, Yang Fan, Liu He, Wang Jin-cheng. Progress in the repair of osteoporotic bone defects: scaffold implantation and local drug delivery[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(18): 2939-2945.
share this article
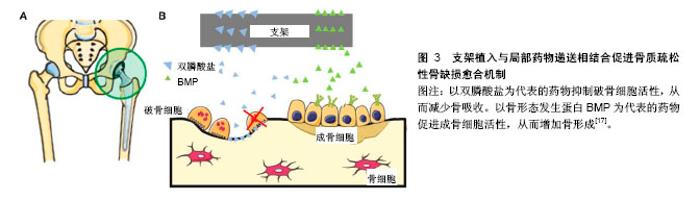
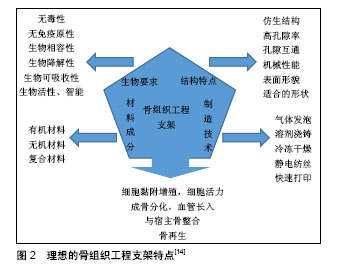
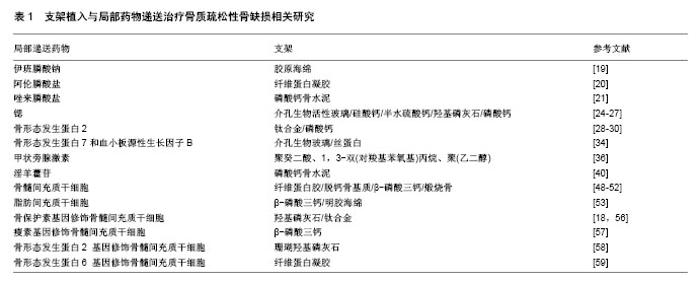
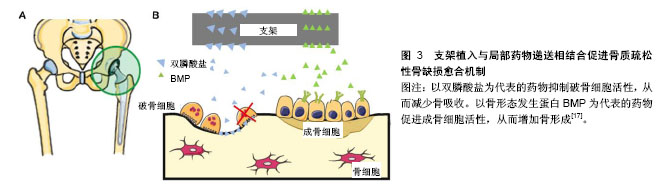
2.1.2 骨组织工程支架的特性 近年来,随着材料合成学和骨组织工程学的快速发展,骨支架材料日益成为骨科学及材料学研究的热点。应用于骨组织工程的支架材料应具备下列特性:①良好的生物相容性:支架利于骨形成相关细胞的黏附、增殖,且无抗原性、无毒,不引起体内排斥反应;②合适的生物降解速率:支架的降解速率应与骨组织再生速率相协调,材料降解时间应能根据骨组织再生情况进行有效调控;③表面活性:材料应为骨再生相关细胞在其表面黏附、增殖和分泌基质提供适宜的微环境,能激活特异性成骨基因的表达;④可塑性:便于加工成与骨缺损相匹配的形状;⑤力学强度:具有较好的力学性能,再植入体内一段时间内仍可保持其形状,填充骨缺损的同时起到力学支撑作用;⑥孔隙结构:支架应具有多孔结构,高孔隙率支架内部表面积大,这样有利于营养物质的进入、细胞的黏附、骨组织的长入,以及代谢产物的排出[15-16]。 骨质疏松性骨缺损的支架不仅需要满足以上一般骨组织工程支架要求,还需要更佳的骨整合能力来应对骨质疏松状态下较差的骨质和量情况。对此,文章主要介绍具有促进骨再生功能的新型支架及与药物递送相结合,来促进骨质疏松性骨缺损的愈合。 2.2 支架植入与局部药物递送相结合促进骨质疏松性骨缺损愈合 治疗骨质疏松的药物主要分为抑制骨吸收与促进骨形成两大类。骨吸收抑制剂包括双膦酸盐、组织蛋白酶K抑制剂、受体激活NF-κB配体抑制剂、雷奈酸锶、降钙素和选择性雌激素受体调节剂等;促进骨形成药物主要有甲状旁腺激素片段和类似物、硬化蛋白抑制剂及一些生长因子等[17]。近年来,随着分子生物学的发展,中药成分和干细胞也逐渐被纳入支架材料中[18]。支架植入与局部药物递送相结合促进骨质疏松性骨缺损愈合的机制,见图3,其相关研究见表1。 2.2.1 支架结合骨吸收抑制剂 双膦酸盐是应用最为广泛的一种抗骨质疏松药物。Guo等[19]将伊班膦酸钠/胶原海绵局部应用来促进去卵巢大鼠股骨骨折愈合,伊班膦酸钠局部给药促进骨痂形成、改善骨微结构和力学性能。将阿伦膦酸盐纳入市售的纤维蛋白凝胶中,体外研究显示其可促进人源间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化,在家兔骨缺损模型中证明具有良好的成骨能力[20]。唑来膦酸盐作为另一种临床常用的双膦酸盐类药物,将其纳入磷酸钙骨水泥后植入去卵巢大鼠体内,能明显降低骨转换率,改善骨微观结构[21]。经唑来膦酸盐和锶修饰过的泡沫铁支架,可促进骨质疏松性骨折愈合,该复合体通过上调骨形态发生蛋白2表达,抑制受体激活NF-κB配体/骨保护素表达来促进成骨、抑制破骨活性[22]。 锶是一种碱土金属,目前用于治疗骨质疏松症的锶类药物主要是雷奈酸锶[23]。锶对抑制骨吸收有明显作用,近年来的研究表明锶还有一定的成骨能力。Zhang 等[24]研究表明搭载锶的介孔生物活性玻璃在体外能促进成骨细胞分化,在体内可加速骨质疏松性骨缺损的骨再生。Lin等[25]制备的多孔锶取代硅酸钙支架,其提取物能促进骨质疏松大鼠来源骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化和人脐静脉内皮细胞向成血管分化,体内实验表明该复合支架极大地促进去卵巢大鼠颅骨缺损模型骨再生和血管生成。此外,锶改性半水硫酸钙支架同样能促进去卵巢大鼠颅骨缺损处血管与骨的再生[26]。总之,无论是羟基磷灰石支架还是磷酸钙支架,经锶改性后植入骨质疏松性骨缺损中都能有效促进骨再生[27]。 2.2.2 支架结合骨形成促进剂 骨形态发生蛋白2具有促进骨形成的作用,将骨形态发生蛋白2用于骨质疏松的治疗始于2005年,将非糖基化骨形态发生蛋白2涂层的羟基磷灰石钛支架植入骨质疏松山羊胫骨,为期20周的观察表明骨形态发生蛋白2能够促进骨形成,改善骨的力学性能,促进骨质疏松性骨缺损的骨整合[28]。相似的,在去卵巢大鼠胫骨缺损处植入支架表面连接骨形态发生蛋白2的Ti6Al4V支架,体外研究表明4周后有20%的活性骨形态发生蛋白2释放,同样取得了较好的骨整合效果[29]。将含有骨形态发生蛋白2和降钙素的壳聚糖/明胶膜沉积到Ti6Al4V支架,将其促进骨整合效果在骨质疏松兔股骨缺损模型中进行验证,发现骨形态发生蛋白2和降钙素可诱导骨质疏松症模型的新骨形成,提高骨缺损愈合的稳定性[30]。Li等[31]制备了明胶微球包载骨形态发生蛋白2与磷酸钙的一种可注射复合材料,将其用于修复去卵巢山羊椎体临界骨缺损,早期结果显示(45 d)这种骨形态发生蛋白2缓释体系具有更快的骨形成速度与更好的力学强度,长期结果(140 d)力学强度明显优于对照组。除了骨形态发生蛋白2,骨形态发生蛋白家族的骨形态发生蛋白7、骨形态发生蛋白9也能促进骨质疏松性骨缺损的再生[32-33]。含将有骨形态发生蛋白7和血小板源性生长因子B的介孔生物玻璃/丝蛋白支架植入去卵巢大鼠股骨缺损处,生长因子的持续释放有利于间充质干细胞的募集,增加缺损处Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、骨桥蛋白和骨唾液酸蛋白表达,加速骨转换/重塑[34]。 甲状旁腺激素是目前FDA批准的唯一一种治疗骨质疏松症的合成代谢药物。特立帕肽是人甲状旁腺激素的氨基酸片段,通过促进血管形成加速骨再生[35]。聚癸二酸、1,3-双(对羧基苯氧基)丙烷和聚(乙二醇)组成的聚合物,作为一个可生物降解的新型药物输送系统,将甲状旁腺激素纳入其中可脉冲式稳定释放达21 d,将这个药物输送系统与无细胞仿生纳米纤维支架结合植入小鼠骨缺损局部,在促进缺损处骨再生的同时未见明显全身不良反应,且再生骨的质和量优于甲状旁腺激素骨缺损局部连续释放和标准化全身注射给药[36]。 2.2.3 支架结合中药成分 考虑到一些西药的不良反应较大,治疗效果不彻底,加快了对中药治疗骨质疏松的研究。随着近年对中药研究的不断深入,运用中药诱导成骨细胞增殖逐渐得到证实,并在细胞分子水平证实了中药治疗骨质疏松的分子生物学依据[37-38]。抗骨质疏松中药主要包括淫羊藿苷、杜仲、骨碎补总黄酮和人工虎骨粉等。近年来,随着生物材料合成的发展,研究者将中药纳入骨组织工程支架中促进骨质疏松性骨缺损的愈合。淫羊藿苷具有促进骨形成,抑制骨吸收的作 用[39]。Wu等[40]构建了含淫羊藿苷的磷酸钙骨水泥支架,并在去卵巢大鼠体内评估复合材料的成骨和成血管能力,结果表明淫羊藿苷能上调骨髓间充质干细胞成骨和成血管基因的表达,破骨细胞的形成受到抑制,磷酸钙骨水泥可作为淫羊藿苷合适的缓释系统,来促进骨质疏松性骨缺损内骨与血管的再生。 2.2.4 支架结合细胞治疗 干细胞拥有自我更新和多向分化潜能,常用于促进受损组织的再生研究,其中,间充质干细胞具有多向分化潜能,可分化为成骨细胞、软骨细胞、肌细胞、脂肪细胞和成纤维细胞,且免疫原性低,不易引起排斥反应[41-42],故而间充质干细胞被认为是细胞替代疗法治疗骨科疾病的理想细胞来源。间充质干细胞修复组织的应用正逐渐发展,将这种细胞介导治疗用于促进生理愈合能力低下机体的骨再生[43]。 具有良好生物相容性组织工程的支架,能够为骨缺损修复相关细胞的附着、增殖和发挥功能提供一个有利的局部微环境,促进骨缺损愈合的同时不引起多余的不良反应。虽然许多与干细胞相关的支架被用于骨缺损的治疗,但它们在骨质疏松性骨缺损治疗方面的研究尚不深入[44-45]。骨组织工程支架复合间充质干细胞的思路,为骨质疏松性骨缺损治疗提供了一个有效解决途径。 对骨质疏松症患者和动物模型来源的骨髓间充质干细胞研究发现,骨质疏松常与骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化能力退化有关[46]。局部注射正常骨髓间充质干细胞可改善骨质疏松部位的骨结构[47]。将搭载骨髓间充质干细胞的纤维蛋白胶三维生物支架植入骨质疏松大鼠股骨远端5 mm局限性骨缺损处,结果表明无毒的纤维蛋白胶支架搭载骨髓间充质干细胞,可诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞系分化,明显促进股骨远端缺损的再生[48]。Wang等[49]将骨髓间充质干细胞在体外成骨诱导培养之后复合脱钙骨基质支架(decalcified bone matrix,DBM),植入骨质疏松性家兔桡骨中段骨缺损中,X射线平片、Micro-CT和组织形态学检查结果显示,脱钙骨基质支架复合骨髓间充质干细胞治疗组形成了致密的骨组织,对骨缺损产生了较好的修复效果,免疫组化结果表明缺损处成骨活性增强,与单纯脱钙骨基质支架治疗相比显著提高了骨再生。此外,间充质干细胞来源的外泌体可促进去卵巢来源骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化,复合β-磷酸三钙支架后通过促进血管生成和成骨加速骨质疏松性骨缺损愈合[50]。在骨质疏松性骨缺损动物模型中,β-磷酸三钙支架与自体浓缩骨髓间充质干细胞复合体或煅烧骨包裹同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞复合体都具有加速骨再生的能力[51-52]。脂肪间充质干细胞比骨髓间充质干细胞更容易获取且来源丰富,具有成骨分化能力的同时,还可通过激活骨形态发生蛋白2和骨形态发生蛋白受体IB基因信号通路,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨作用和抑制脂肪生成,最终达到促进骨质疏松性骨缺损的再生[53]。将β-磷酸三钙/明胶海绵搭载骨质疏松家兔自体脂肪间充质干细胞植入胫骨骨缺损中,研究表明搭载脂肪间充质干细胞的复合支架比单独β-磷酸三钙/明胶海绵支架有更好的骨修复能力,且新生骨具有更好的力学性能[54]。 2.2.5 支架结合基因工程治疗 随着分子生物学的发展,经基因修饰的干细胞引起了研究者极大的兴趣。基因治疗虽然最初是用来纠正有缺陷的基因,但现已被应用于治疗多种疾病,基因转移被用作一种药物传递系统。干细胞疗法与基因治疗相结合,使间充质干细胞对某些成骨相关生长因子过量表达已成为干细胞治疗的一个新思路。骨保护素作为一种已知的治疗剂,可抑制破骨细胞的分化,已被用于慢性骨吸收性疾病的治 疗[55]。将骨保护素基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞接种于羟基磷灰石支架上,可促进去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠下颌骨缺损的再生。这种新型骨保护素-骨髓间充质干细胞-羟基磷灰石结构,被证明能够很好地调节骨髓间充质干细胞的骨形成和破骨细胞的骨吸收,在骨质疏松相关骨缺损重建中有着很好的应用潜力[18]。与此相似,Yin等[56]将携带人源性骨保护素的腺病毒载体导入骨髓间充质干细胞中,体外研究显示其可明显抑制破骨细胞前体(RAW264.7细胞)的分化和功能,将其与钛合金内植物复合植入去卵巢大鼠骨缺损处,可加速钛合金假体与宿主骨的整合效果。 Zheng等[57]将腺病毒携带的人瘦素基因转染到大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中,然后种植在β-磷酸三钙支架上,同样促进了骨质疏松大鼠骨缺损处的新骨形成。骨形态发生蛋白是一种广为研究的成骨相关因子,将人源性骨形态发生蛋白2基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞-珊瑚羟基磷灰石复合支架[58]、异基因骨形态发生蛋白6修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞-纤维蛋白凝胶复合支架[59],植入骨质疏松性骨缺损后均取得较好的骨修复效果。 总之,在骨质疏松性骨缺损局部植入复合干细胞的三维支架治疗方法,可能成为未来的治疗策略之一。 2.2.6 支架结合其他治疗 除上述常规几大类抗骨质疏松药物及干细胞疗法治疗骨质疏松性骨缺损,研究者还将理疗和一些其他类型的药物纳入支架中植入骨质疏松性骨缺损。 低强度激光治疗可增加成骨细胞活性、胶原纤维的分布和刺激植入部位的血流,从而促进新骨形成,此外还有抗菌和免疫效果[60]。将多孔钛合金支架植入去卵巢大鼠骨缺损之后,局部使用低强度激光治疗2周和6周可见骨再生明显加速[61]。低氧模拟剂去铁胺可促进间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,将其纳入聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物中,可极大地刺激骨质疏松大鼠股骨缺损的骨形成和血管生成[62]。介孔生物玻璃在成骨细胞分化和矿化中发挥重要作用[63],Wu等[64]将介孔生物玻璃溶液与去卵巢大鼠来源骨髓间充质干细胞共培养,可上调成骨基因的表达,促进成骨的同时还可抑制脂肪形成。 "
| [1] Rachner TD,Khosla S,Hofbauer LC.Osteoporosis: now and the future.Lancet. 2011;37(9773):1276-1287.[2] Teitelbaum SL.Stem Cells and Osteoporosis Therapy.Cell Stem Cell.2010;7(5):553-554.[3] Hemmeler C,Morell S,Amsler F,et al.Screening for osteoporosis following non-vertebral fractures in patients aged 50 and older independently of gender or level of trauma energy-a Swiss trauma center approach.Arch Osteoporos. 2017;12(1):38.[4] Mirsaidi A,Genelin K,Vetsch JR,et al.Therapeutic potential of adipose-derived stromal cells in age-related osteoporosis. Biomaterials. 2014;35(26):7326-7335.[5] Reichert JC,Saifzadeh S,Wullschleger ME,et al.The challenge of establishing preclinical models for segmental bone defect research. Biomaterials.2009;30(12):2149-2163.[6] Egermann M,Schneider E,Evans CH,et al.The potential of gene therapy for fracture healing in osteoporosis. Osteoporosis Int. 2005; 16:S120-S128.[7] Agarwal R,Garcia AJ.Biomaterial strategies for engineering implants for enhanced osseointegration and bone repair.Adv Drug Del Rev. 2015;94(12):53-62.[8] Gruskin E,Doll BA,Futrell FW,et al.Demineralized bone matrix in bone repair: History and use.Adv Drug Del Rev. 2012;64(12):1063-1077.[9] Schilcher J,Michaelsson K,Aspenberg P.Bisphosphonate Use and Atypical Fractures of the Femoral Shaft.New Engl J Med. 2011;364(18): 1728-1737.[10] Black DM,Kelly MP,Genant HK,et al.Bisphosphonates and Fractures of the Subtrochanteric or Diaphyseal Femur.New Engl J Med. 2010;362 (19):1761-1771.[11] Ruggiero SL,Mehrotra B,Rosenberg TJ,et al.Osteonecrosis of the jaws associated with the use of bisphosphonates: A review of 63 cases.J Oral Maxil Surg.2004;62(5):527-534.[12] Bolland MJ,Avenell A,Baron JA,et al.Effect of calcium supplements on risk of myocardial infarction and cardiovascular events: meta-analysis. Bmj-Brit Med J. 2010;341(7767):289-289.[13] Liu H,Webster TJ.Ceramic/polymer nanocomposites with tunable drug delivery capability at specific disease sites.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93(3):1180-1192.[14] 何春耒,王大平,马经野.骨组织工程支架材料的种类及发展趋势[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(25):4905-4908.[15] 梁卫东,王宏伟,王志强.不同骨组织工程支架材料的生物安全性及性能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(34):6385-6388.[16] 朱伟民,王大平,熊建义骨组织工程支架材料的生物学特性及临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(48):9781-9784.[17] Luhmann T,Germershaus O,Groll J,et al.Bone targeting for the treatment of osteoporosis. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society. 2012;161(2):198-213.[18] Liu X,Bao C,Xu HHK,et al.Osteoprotegerin gene-modified BMSCs with hydroxyapatite scaffold for treating critical-sized mandibular defects in ovariectomized osteoporotic rats.Acta Biomater. 2016;42:378-388.[19] Guo JL,Zhang Q,Li J,et al.Local application of an ibandronate/collagen sponge improves femoral fracture healing in ovariectomized rats.Plos One. 2017;12(11):e0187683.[20] Kim BS,Shkembi F,Lee J.In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Commercially Available Fibrin Gel as a Carrier of Alendronate for Bone Tissue Engineering.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017(3):6434169.[21] Wu CC,Wang CC,Lu DH,et al.Calcium phosphate cement delivering zoledronate decreases bone turnover rate and restores bone architecture in ovariectomized rats.Biomed Mater. 2012;7(3):035009.[22] Ray S,Thormann U,Eichelroth M,et al.Strontium and bisphosphonate coated iron foam scaffolds for osteoporotic fracture defect healing. Biomaterials.2018;157:1-16.[23] Kargozar S,Lotfibakhshaiesh N,Ai J,et al.Strontium- and cobalt-substituted bioactive glasses seeded with human umbilical cord perivascular cells to promote bone regeneration via enhanced osteogenic and angiogenic activities.Acta Biomater. 2017;58: 502-514.[24] Zhang Q,Chen XH,Geng SN,et al.Nanogel-based scaffolds fabricated for bone regeneration with mesoporous bioactive glass and strontium: In vitro and in vivo characterization. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017; 105(4):1175-1183.[25] Lin K,Xia L,Li H,et al.Enhanced osteoporotic bone regeneration by strontium-substituted calcium silicate bioactive ceramics. Biomaterials. 2013;34(38):10028-10042.[26] Yang S,Wang L,Feng S,et al.Enhanced bone formation by strontium modified calcium sulfate hemihydrate in ovariectomized rat critical-size calvarial defects.Biomed Mater. 2017;12(3):035004.[27] Neves N,Linhares D,Costa G,et al.In vivo and clinical application of strontium-enriched biomaterials for bone regeneration: A systematic review.Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(6):366-375.[28] Sachse A,Wagner A,Keller M,et al.Osteointegration of hydroxyapatite-titanium implants coated with nonglycosylated recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) in aged sheep. Bone.2005;37(5):699-710.[29] Wolfle JV,Fiedler J,Durselen L,et al.Improved Anchorage of Ti6Al4V Orthopaedic Bone Implants through Oligonucleotide Mediated Immobilization of BMP-2 in Osteoporotic Rats.Plos One. 2014;9(1): e86151.[30] Huang L,Luo Z,Hu Y,et al.Enhancement of local bone remodeling in osteoporotic rabbits by biomimic multilayered structures on Ti6Al4V implants.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(6):1437-1451.[31] Li M,Liu X,Liu X,et al.Calcium phosphate cement with BMP-2-loaded gelatin microspheres enhances bone healing in osteoporosis: a pilot study.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(7):1978-1985.[32] Kim HK,Lee JS,Kim JH,et al.Bone-forming peptide-2 derived from BMP-7 enhances osteoblast differentiation from multipotent bone marrow stromal cells and bone formation. Exp Mol Med. 2017; 49(5):e328.[33] Wang X,Huang J,Huang F,et al.Bone morphogenetic protein 9 stimulates callus formation in osteoporotic rats during fracture healing.Mol Med Rep.2017;15(5):2537-2545.[34] Zhang Y,Cheng N,Miron R,et al.Delivery of PDGF-B and BMP-7 by mesoporous bioglass/silk fibrin scaffolds for the repair of osteoporotic defects.Biomaterials. 2012;33(28):6698-6708.[35] Xie ZJ,Weng SJ,Li H,et al.Teriparatide promotes healing of critical size femur defect through accelerating angiogenesis and degradation of beta-TCP in OVX osteoporotic rat model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;96:960-7.[36] Dang M,Koh AJ,Jin XB,et al.Local pulsatile PTH delivery regenerates bone defects via enhanced bone remodeling in a cell-free scaffold. Biomaterials.2017;114:1-9.[37] Wang Q,Cao LY,Liu Y,et al.Evaluation of synergistic osteogenesis between icariin and BMP2 through a micro/meso hierarchical porous delivery system.Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:7721-7735.[38] Chen R,Qi QL,Wang MT,et al.Therapeutic potential of naringin: an overview.Pharm Biol. 2016;54(12):3203-3210.[39] Chen SH,Zheng LZ,Zhang JY,et al.A novel bone targeting delivery system carrying phytomolecule icaritin for prevention of steroid-associated osteonecrosis in rats.Bone. 2018;106:52-60.[40] Wu Y,Cao L,Xia L,et al.Evaluation of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis of Icariin in Local Controlled Release and Systemic Delivery for Calvarial Defect in Ovariectomized Rats. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5077.[41] Clines GA.Prospects for osteoprogenitor stem cells in fracture repair and osteoporosis. Curr Opin Organ Tran. 2010;15(1):73-78.[42] Berglund AK,Fortier LA,Antczak DF,et al.Immunoprivileged no more: measuring the immunogenicity of allogeneic adult mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Res ther.2017;8:288.[43] Vilquin JT,Rosset P.Mesenchymal stem cells in bone and cartilage repair: current status. Regen Med. 2006;1(4):589-604.[44] Ben-Ari A,Rivkin R,Frishman M,et al.Isolation and implantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells with fibrin micro beads to repair a critical-size bone defect in mice.Tissue Eng Part A. 2009; 15(9):2537-2546.[45] Langenbach F,Naujoks C,Laser A,et al.Improvement of the cell-loading efficiency of biomaterials by inoculation with stem cell-based microspheres, in osteogenesis.J Biomater Appl. 2012;26(5):549-564.[46] Pountos I,Georgouli T,Henshaw K,et al.The Effect of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2, Bone Morphogenetic Protein-7, Parathyroid Hormone, and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor on the Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived From Osteoporotic Bone.J Orthop Trauma.2010;24(9):552-556.[47] Ocarino ND,Boeloni JN,Jorgetti V,et al.Intra-bone marrow injection of mesenchymal stem cells improves the femur bone mass of osteoporotic female rats.Connect Tissue Res. 2010;51(6):426-433.[48] Orsi PR, Landim-Alvarenga FC, Justulin LA, et al. A unique heterologous fibrin sealant (HFS) as a candidate biological scaffold for mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporotic rats.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017; 8(1):205.[49] Wang ZX,Chen C,Zhou Q,et al.The Treatment Efficacy of Bone Tissue Engineering Strategy for Repairing Segmental Bone Defects Under Osteoporotic Conditions.Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(17-18): 2346-2355.[50] Qi X,Zhang J,Yuan H,et al.Exosomes Secreted by Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Critical-Sized Bone Defects through Enhanced Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats.Int J Biol sci.2016;12(7):836-849.[51] Cao L,Liu GW,Gan YK,et al.The use of autologous enriched bone marrow MSCs to enhance osteoporotic bone defect repair in long-term estrogen deficient goats.Biomaterials. 2012;33(20):5076-5084.[52] Liu YH,Min LG,Luo HL,et al.Integration of a calcined bovine bone and BMSC-sheet 3D scaffold and the promotion of bone regeneration in large defects.Biomaterials. 2013;34(38):9998-10006.[53] Ye X,Zhang P,Xue S,et al.Adipose-derived stem cells alleviate osteoporosis by enhancing osteogenesis and inhibiting adipogenesis in a rabbit model.Cytotherapy. 2014;16(12):1643-1655.[54] Kikuta S,Tanaka N,Kazama T,et al.Osteogenic effects of dedifferentiated fat cell transplantation in rabbit models of bone defect and ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19 (15-16):1792-1802.[55] Kearns AE,Khosla S,Kostenuik PJ.Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin regulation of bone remodeling in health and disease.Endocr Rev. 2008;29(2):155-192.[56] Yin G,Chen J,Wei S,et al.Adenoviral vectormediated overexpression of osteoprotegerin accelerates osteointegration of titanium implants in ovariectomized rats.Gene Ther.2015;22(8):636-664.[57] Zheng B,Jiang J,Chen Y,et al.Leptin Overexpression in Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Promotes Periodontal Regeneration in a Rat Model of Osteoporosis.J Periodontol. 2017;88(8):808-818.[58] Tang Y,Tang W,Lin Y,et al.Combination of bone tissue engineering and BMP-2 gene transfection promotes bone healing in osteoporotic rats. Cell Biol Int. 2008;32(9):1150-1157.[59] Pelled G,Sheyn D,Tawackoli W,et al.BMP6-Engineered MSCs Induce Vertebral Bone Repair in a Pig Model: A Pilot Study. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:6530624.[60] Boldrini C,de Almeida JM,et al.Biomechanical effect of one session of low-level laser on the bone-titanium implant interface.Laser Med Sci. 2013;28(1):349-352.[61] de Vasconcellos LM,Barbara MA,Rovai ES,et al.Titanium scaffold osteogenesis in healthy and osteoporotic rats is improved by the use of low-level laser therapy (GaAlAs). Laser Med Sci. 2016;31(5): 899-905.[62] Jia P,Chen H,Kang H,et al.Deferoxamine released from poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) promotes healing of osteoporotic bone defect via enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis.J Biomed Mater Res A.2016;104(10):2515-2527.[63] Cheng N,Wang Y,Zhang Y,et al.The osteogenic potential of mesoporous bioglasses/silk and non-mesoporous bioglasses/silk scaffolds in ovariectomized rats: in vitro and in vivo evaluation.Plos One.2013;8(11):e81014.[64] Wu T,Cheng N,Xu C,et al.The effect of mesoporous bioglass on osteogenesis and adipogenesis of osteoporotic BMSCs.J Biomed Mater Res A.2016;104(12):3004-3014. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [3] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [6] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [7] | Xiao Fangjun, Chen Shudong, Luan Jiyao, Hou Yu, He Kun, Lin Dingkun. An insight into the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza intervention on osteoporosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 772-778. |
| [8] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [9] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [10] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [11] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [12] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [13] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [14] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [15] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||