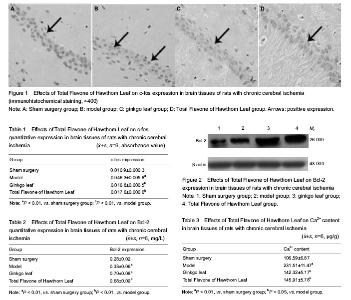
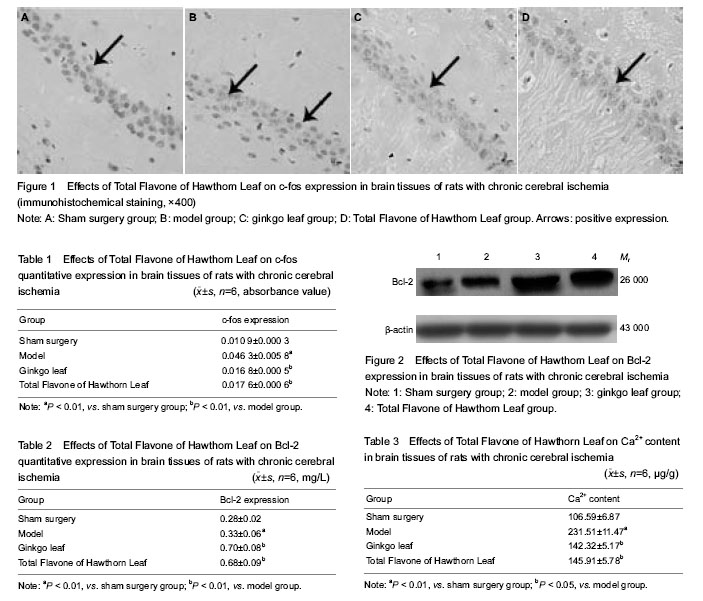
| [1] Tu YH, Hu CL. Discussion on the early rehabilitation of stroke treatment with acute symptoms worsen. Chongqing Yixue. 2007;36(16):1666-1667.
[2] Tai WJ, Ye X, Bao XQ, et al. Study of microglia and cerebral ischemia relationship.Yaoxue Xuebao.2012;47(3): 346-353.
[3] Khodagholi F, Ashabi G. Dietary supplementation with Salvia sahendica attenuates memory deficits, modulates CREB and its down-stream molecules and decreases apoptosis in amyloid beta-injected rats. Behav Brain Res. 2013;15(241):62-69.
[4] Zhao L, Wu XG, Du LY, et al. The influence of hawthorn leaves flavonoids on vascular dementia(vd) rat hippocampul glutamate and NMDA receptor expression. Guangdong Yixue. 2014;35(3):353-356.
[5] Miao GX, Mao XX, Wu XG, et al. Impact of total flavone of hawthorn leaf on learning and memory ability and intracephalic cholinergic activity in rats with vascular dementia. Jiepou Xue Zazhi. 2014;37(2):192-196.
[6] Ni J, Ohta H, Matsumoto K, et al. Progressive cognitive impairment following chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced by permanent occlusion of bilateral carotid arteries in rats. Brain Res. 1994;653(1-2):231-236.
[7] Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.
[8] Shivaraju A, Yu C, Kattan MW, et al. Temporal trends in percutaneous coronary intervention-associated acute cerebrovascular accident (from the 1998 to 2008 Nationwide Inpatient Sample Database). Am J Cardiol. 2014;114(2):206-213.
[9] Killander F, Anderson H, Kjellén E, et al. Increased cardio and cerebrovascular mortality in breast cancer patients treated with postmastectomy radiotherapy-25 year follow-up of a randomised trial from the South Sweden Breast Cancer Group. Eur J Cancer. 2014. in press.
[10] Takasusuki T, Yamaguchi S, Hamaguchi S, et al. Effects of general anesthetics on substance P release and c-Fos expression in the spinal dorsal horn. Anesthesiology. 2013;119(2):433-442.
[11] Naseer MI, Ullah I, Rasool M, et al. Erratum to: Downregulation of dopamine D1 receptors and increased neuronal apoptosis upon ethanol and PTZ exposure in prenatal rat cortical and hippocampal neurons. Neurol Sci. 2014. in press.
[12] Abdelli S, Papas KK, Mueller KR, et al. Regulation of the JNK3 Signaling Pathway during Islet Isolation: JNK3 and c-fos as New Markers of Islet Quality for Transplantation. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e99796.
[13] Sayin A, Derinöz O, Yüksel N, et al. The effects of the estrus cycle and citalopram on anxiety-like behaviors and c-fos expression in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2014; 124C:180-187.
[14] Hendrickx A, Pierrot N, Tasiaux B, et al. Epigenetic regulations of immediate early genes expression involved in memory formation by the amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer disease. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e99467.
[15] Lee SY, Lee KS, Yi SH, et al. Acteoside suppresses RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting c-Fos induction and NF-κB pathway and attenuating ROS production. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e80873.
[16] Zhang L, He Q, Wang Q, et al. Intracellular Ca2+ overload induced by extracellular Ca2+ entry plays an important role in acute heart dysfunction by tentacle extract from the Jellyfish Cyanea capillata. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2014. in press.
[17] Liang YG, Jorgensen AG, Kaestel CG, et al. Bcl-2, Bax, and c-Fos expression correlates to RPE cell apoptosis induced by UV-light and daunorubicin. Curr Eye Res. 2000;20(1): 25-34.
[18] Ouyang YB, Giffard RG. microRNAs affect BCL-2 family proteins in the setting of cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Int. 2013. in press. |