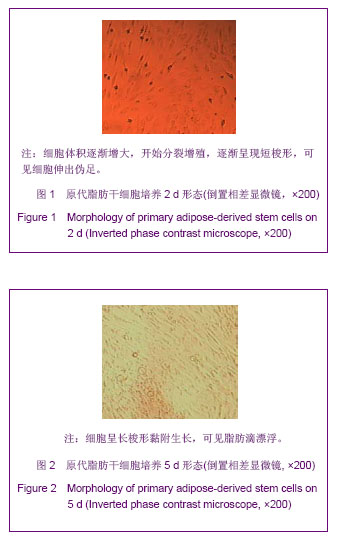
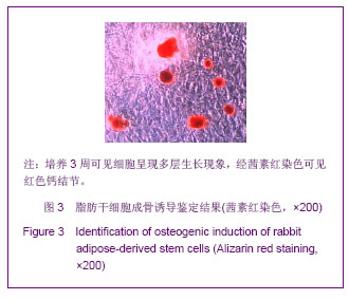
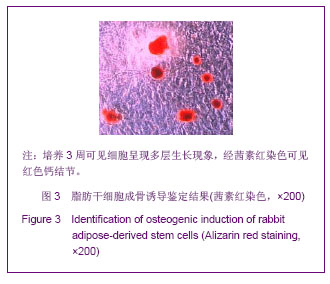
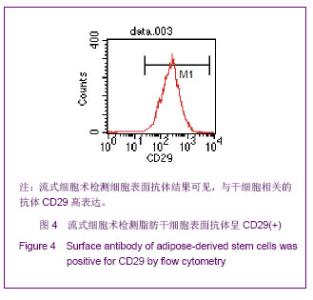
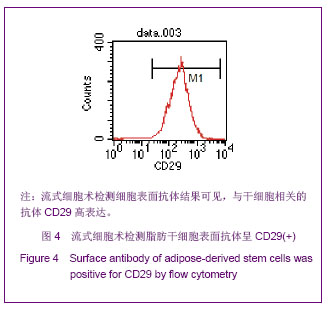
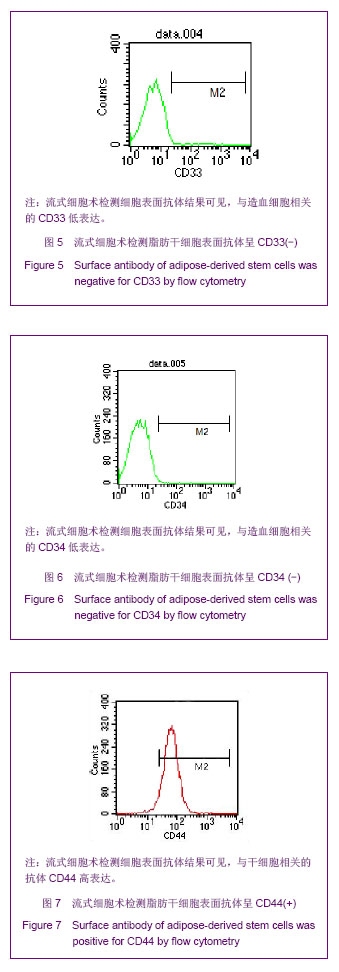
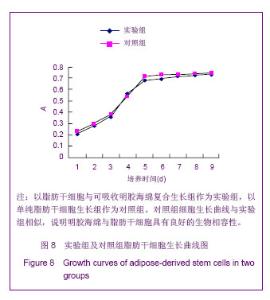
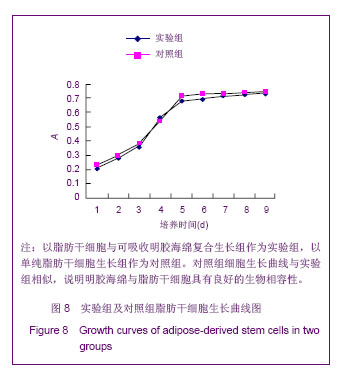
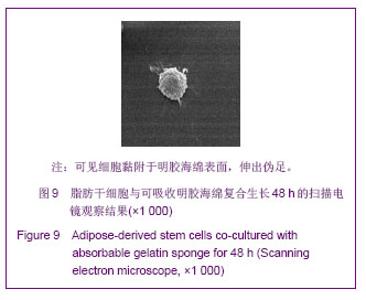
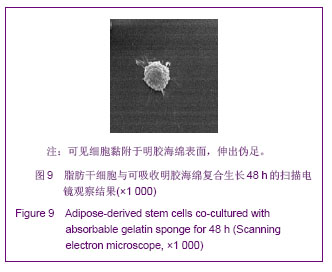
| [1]Huang SJ,Fu RH,Shyu WC,et al.Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Isolation, Characterization and Differentiation Potential,Cell Transplant.2012; [Epub ahead of print]
[2]Zhu Y, Liu T, Song K, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell: a better stem cell than BMSC. Cell Biochem Funct. 2008;6(6):664- 675.
[3]Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue:Implication for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-238.
[4]Zuk PA. The Adipose-derived Stem Cell: Looking Back and Looking Ahead. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21(11): 1783-1787.
[5]Pak J.Autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cells induce persistent bone-like tissue in osteonecrotic femoral heads.Pain Physician. 2012;15(1):75-85.
[6]邓春华,孙祥宙,高勇,等.大鼠脂肪组织来源干细胞的分离、培养和生物学特性的研究[J].中华男科学杂志,2008,14(2):99-105.
[7]Du Y, Roh DS, Funderburgh ML, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells differentiate to keratocytes in vitro. Mol vis.2010;16: 2680-2689.
[8]田霖,孙筱放,刘海波,等.人脂肪干细胞的分离培养与生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(32):5946-5952.
[9]Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human Adipose Tissue Is a Source of Multipotent Stem Cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13:(12): 4279-4295.
[10]鞠晓东,娄思权,田华,等.脂肪间充质干细胞的基本生物学特性及向成骨细胞诱导分化的实验研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2004, 21(6):654-656.
[11]李晓峰,赵劲民,苏伟,等.大鼠成骨细胞的原代培养和鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(6):990-994.
[12]殷小雪,陈仲强,郭昭庆,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞定向诱导分化为成骨细胞及其鉴定[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2004,18(2): 88-91.
[13]项鹏,张丽蓉,陈振光,等.成人骨髓间质干细胞定向诱导为脂肪细胞的研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2001,17(7):598-601.
[14]凌宏艳,文格波,胡弼,等.小鼠间充质干细胞诱导分化成脂肪细胞miRNA表达的变化[J].中国应用生理学杂志, 2011,27(4): 391-395.
[15]余方圆,卢世璧,袁玫,等.脂肪干细胞向软骨细胞方向诱导的初步研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2004,5(12):2042-2043.
[16]Yarak S, Okamoto OK. Human adipose-derived stem cells: current challenges and clinical perspectives. An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85(5):647-656.
[17]路坦,李小伟,张江峰,等.多聚赖氨酸对脂肪来源干细胞三维立体条件下生物学特性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(40):7489-7492.
[18]刘彦春,王炜,曹谊林,等.卵磷脂、多聚赖氨酸和PLA包埋PGA与软骨细胞体外培养的实验研究[J].实用美容整形外科杂志,1997, 10(8):225-228.
[19]郝新保,张利朝,殷缨,等.MTT比色法测定细胞生长曲线[J].第四军医大学学报,1997,8(4):390-391.
[20]张云松,高建华,鲁峰,等.Ⅰ型胶原支架材料与人脂肪干细胞体外生物相容性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2007,27(2):223.
[21]聂绪强,陈怀红,唐宁,等.脂肪干细胞的共培养及其分化应用概述[J].生物工程学报, 2011, 27(8):1121-1131.
[22]郭翔,管欣,赵珩,等.脂肪干细胞与三维支架体内外培养构建的组织工程化气管[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(41):7658-7663.
[23]张端珍,盖鲁粤,刘宏伟,等.脂肪干细胞与间充质干细胞体外诱导分化为心肌细胞的差别[J].生理学报,2008,60(3):341-347.
[24]方丽茹,翁文剑,沈鸽,等.骨组织工程支架及生物材料研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2003,20(1):148-152.
[25]Sasai Y,Eiraku M,Suga H,et al.In vitro organogenesis in three dimensions: self-organising stem cells. Development. 2012; 139(22):4111-4121.
[26]燕卫东,吴春华.胚胎干细胞的研究进展[J].赤峰学院学报:自然科学版, 2010,26(2):27-28.
[27]董效信,任晓敏,董雅妮,等.胚胎干细胞研究的伦理和心理学问题[J].中国组织工程研究, 2011,15(49):9303-9306.
[28]邴丽娟,付蓉.间充质干细胞的研究进展[J].临床血液学杂志, 2012, 25(6):750-753.
[29]Baglioni S, Francalanci M, Squecco R, et al. Charaterization of human adult stem-cell populations isolated from visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue. FASEB J. 2009;23: 3494-3505.
[30]Zuk PA. The adipose-derived stem cell:Looking back and looking ahead. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21:1783-1787.
[31]韩长杰,杨向群,张传森,等.脂肪干细胞的免疫学性质[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(27):5095-5098.
[32]De Ugarte DA, Morizono K, Elbarbary A, et al. Comparison of multi-lineage cells form human adipose tissue and bone marrow. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174:101-109.
[33]Qing W, Guang-Xing C, Lin G, et al.The osteogenic study of tissue engineering bone with BMP2 and BMP7 gene-modified rat adipose-derived stem cell. J Biomed Biotechnol.2012; 2012: 410879.
[34]毛天球,陈富林,杨维东,等.骨组织工程的研究进展[J].中国临床康复, 2001,5(16):5-7.
[35]樊国栋,陈佑宁,张光华,等.医用聚乳酸类高分子材料的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(18):3617-3620.
[36]王彦平,朱凌云,张红梅,等.聚磷酸钙纤维/羟基磷灰石/明胶软骨组织工程支架材料的制备及性能[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(43):8005-8008.
[37]王新,刘玲蓉,张其清,等.纳米羟基磷灰石-壳聚糖骨组织工程支架的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(2):120-124.
[38]郝伟,胡蕴玉,魏义勇,等.脂肪干细胞/Ⅰ型胶原凝胶复合体的构建及其体内外成骨分化研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2007,24(6): 659-661.
[39]王海燕,苏冠方.可吸收明胶海绵载体与骨髓间充质干细胞的相容性[J].眼科研究, 2009,27(9):743-746.
[40]何艳新,刘超.可吸收材料生物蛋白胶及明胶海绵在肝部分切除的应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012;16(12):2180-2182. |