Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (2): 296-302.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1425
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of physical activity and exercise on metabolic syndrome
Tian Lu, Liu Bin
- School of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
-
Received:2019-03-22Revised:2019-03-30Accepted:2019-05-05Online:2020-01-18Published:2019-12-25 -
About author:Tian Lu, Master candidate, School of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China -
Supported by:the Research Project of Chongqing Sports Bureau, No. B2017022
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Lu, Liu Bin. Effects of physical activity and exercise on metabolic syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 296-302.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
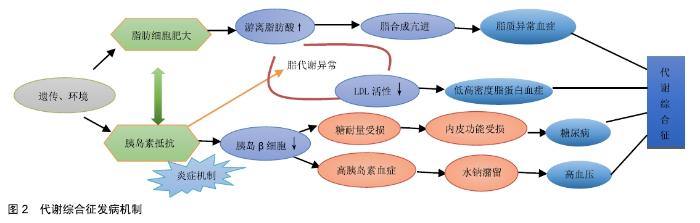
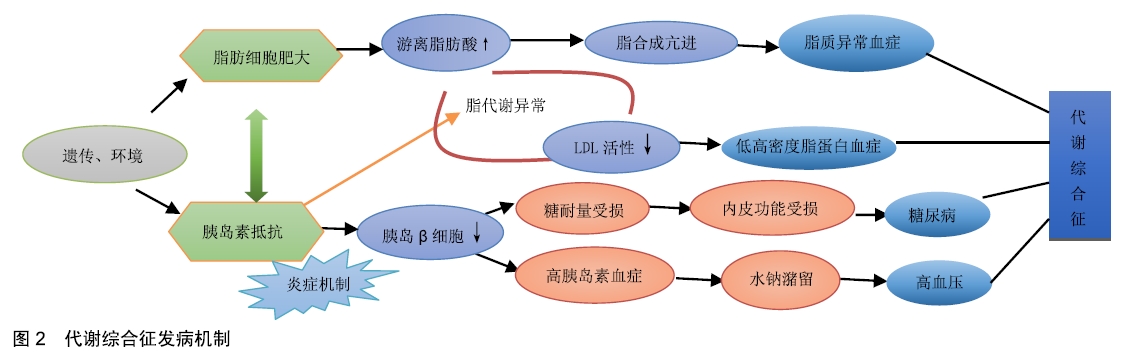
2.1 代谢综合征发病机制 美国心肺及血液研究所和心脏协会共同指出代谢综合征的病理机制主要是由肥胖分布异常、胰岛素抵抗等多种独立因素的共同作用的结果[8](见图2)。遗传和环境因素共同引起机体肥胖和胰岛素抵抗。肥胖因子的堆积使游离脂肪酸(fundus fluorescein angiography,FFA)升高,游离脂肪酸异位沉积激发其非氧化途径,引起肝脏脂合成亢进与异化屏障,形成脂质异常血症。胰岛素抵抗的出现使肝糖原合成和肌肉对葡萄糖的摄取减弱,促使葡萄糖堆积血糖升高,使胰岛β细胞功能代偿性减弱,导致糖耐量异常和高胰岛素血症。其中糖耐量异常导致葡糖糖自身氧化等系统及代谢激活,造成使血管内皮细胞功能受损,促进了糖尿病的发生;由于高胰岛素血症增加交感神经活性,活性增强通过刺激肾小管对钠离子的重吸收,引起去甲肾上腺素潴留,血容量增大导致高血压。另外胰岛素抵抗产生后游离脂肪酸等危险因素又会进一步加重,引起脂肪利用储存障碍,脂肪组织异位聚集导致脂质代谢异常,脂蛋白脂肪酶活性降低使高密度脂蛋白浓度生成下降,即低高密度脂蛋白血症。并且胰岛素抵抗与炎症密切相关,且常伴随炎性因子的上升而产生。内脏性肥胖与低水平的慢性炎症反应有关,提示炎症也可能是致胰岛素抵抗的机制。总之,肥胖和胰岛素抵抗相辅相成,互为因果,共同形成代谢综合征。 "

2.2 身体活动与运动对代谢综合征的影响 2.2.1 身体活动对儿童青少年代谢综合征的影响 随着社会高速发展,过于舒适的生活环境使儿童青少年形成不良生活方式。身体活动过于缺乏,长此已久静坐少动的生活习惯是其形成肥胖致代谢综合征并发症逐渐增多的元凶之一。充足的身体活动是儿童青少年代谢综合征的保护独立因素,改善胰岛素敏感度以及中心性肥胖是其重要机制[9]。张晨[10]对193名儿童青少年采用佩戴客观加速传感器测量体力活动水平,结果显示假期看电视、上网时间的长短与代谢综合征的流行概率具有显著关系,并且随着年龄的增长身体活动强度及时间出现下降趋势,正常组活动量显著高于代谢综合征组,代谢异常者普遍静坐时间过长,能量消耗过低。OKOSUN等[11]对美国青少年的体质量指数、休闲身体活动时间及代谢综合征危险评分中发现,当休闲运动方式由静态转为动态时机体代谢水平显著升高,体质量指数呈下降趋势,代谢综合征的平均危险评分降低4倍。并且KAMATH等[12]分析表明,减少久坐的生活方式,与青少年相比儿童效果更佳。 此外,叶萍[13]指出遗传因素与身体活动具有相关性,研究显示脂联素的11377C/G位点是代谢综合征的一大危险因素,身体活动不足与此基因位点产生交互作用,促使儿童患代谢综合征风险。同时王凯风等[14]对114例对照组与实验组研究指出,身体活动也与此基因型存在交互作用,并证实充分的身体活动水平能有效降低其危险因素。出生时低体质量的人也会出现高胰岛素血症,这类患儿都有久坐的不良习惯,但保持每周>25 min的身体活动则不会出现这种关联[15]。由此可见减少长时间静坐,改变日常生活方式可降低体质量与患代谢综合征危险性,因此对于长期静坐以及肥胖儿童需进行生活方式的转变,建议增加课余时间、节假日的体育锻炼和各种户外活动来完成这种转变。 2.2.2 运动对儿童青少年代谢综合征的影响 儿童、青少年是中国成人慢性疾病的强大“后备军”,遏制“源头”是一大重要举措。国外学者发现低水平运动是儿童代谢综合征早发风险因素,长期缺少运动儿童与经常参加体育锻炼儿童相比患代谢综合征风险的概率更高,并且成年后患代谢综合征概率比正常人群高出5.16倍和6.08倍,儿童期的肥胖增加了成年后代谢综合征及其他慢性疾病发病率[16]。儿童青少年肥胖与代谢综合征关系密切,是导致其发病的关键,故预防肥胖是儿童青少年代谢综合征发生的核心机制。机体内脂肪细胞代谢十分活跃,不断分泌大量脂联素、内脏脂肪素及胰岛素抵抗素等炎症因子。据研究显示,肥胖儿童青少年血清中C-反应蛋白、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8等指标水平显著高于正常组[17]。所激发的炎症因子可直接损伤机体内血管内皮细胞,使血管活性下降,致血管血压上升。并且大量脂肪细胞所分泌的炎症因子极大扰乱机体正常代谢系统,进一步加快病情发展。 阳玉晶[18]指出心外膜脂肪是内脏脂肪的重要部分,是导致代谢综合征及心脑血管疾病的一大因素,经3个月对47名肥胖青少年有氧运动干预,能有效降低青少年腹部肥胖及心外膜脂肪厚度。有证据显示运动能够改善脂肪因子及氧化应激水平,儿童在体质量未减轻状态下有氧运动仍能直接改善炎症标志物和脂肪因子,降低代谢综合征发病率[19]。吴海英等[20]指出儿童患代谢综合征会使心脏结构和功能受常,研究证实饮食及有氧运动综合干预能改善患儿左心室舒张、肥大及心脏结构与功能的多种异常代谢水平,减少成年后心脏病和心血管疾病的发病风险。 世界卫生组织建议儿童青少年每日进行不低于 60 min的中等强度运动[21]。关尚一等[22]对801名青少年持续1周的身体运动量与代谢综合征风险“剂量与效应”的关系中研究显示,每日运动60 min相比30 min运动使患代谢综合征风险下降水平更显著。但大部分都无法达到该时间水平,经全国学生体质与健康测试调查显示,儿童青少年人群每天仅有22.7%保持60 min以上的体育运动[23]。因此应多鼓励儿童青少年在课余时间参加体育锻炼,尤其是有氧运动,从而预防代谢综合征及心血管疾病的发生。 此外,运动对青少年的心理健康有一定的积极影响。代谢综合征对青少年大脑海马体细胞健康相关因子及认知功能产生负面作用,对其学习心理均产生不利影响。张磊等[24]研究发现代谢综合征青少年认知领域评分显著低于正常组,实验证明对48组实验对照组进行为期8周的有氧运动+抗阻运动干预后,大脑海马代谢水平得以显著提高,对青少年身心认知功能得到改善。还有研究指出有敌意情绪的儿童和青少年更易患代谢综合征,有氧运动是减轻超重儿童暴躁情绪以由此引发攻击行为的有效策略[25]。提示运动对代谢综合征所引起的紧张、焦虑、愤怒等神经障碍表现有所缓解,轻松愉悦情绪显著增加,达到缓解代谢综合征作用。 2.3 身体活动与运动对中老年人代谢综合征的影响 2.3.1 身体活动对中老年人代谢综合征的影响 身体活动能够有效提高中老年人的健康水平,而缺乏足够的身体活动是成为其失去健康的主要原因之一。国外研究报道显示,对生活方式型身体活动的转变是防治中老年代谢综合征最可行可靠的举措[26]。虽然规律运动对代谢综合征有很大益处,但对于中老年患者长期坚持存在很大难度。调查显示,推荐公众健康的日常生活方式可提高参与程度,相比传统的有氧耐力运动干预具有更好的坚持率[27]。KI-WOL[28]对老年患者进行10个月的持续观察,通过激活仪器加速器和血液检测收集了关于日常身体活动和生化变量数据,结果表明随着日常生活中身体活动水平的增高患者各项机体危险水平随之降低。相关研究指出,散步联合饮食治疗使胰岛素水平下降,胰岛素敏感度增加了基线的77%,而单纯饮食治疗对胰岛素水平没有改善,由此可见身体活动是改善胰岛素敏感度的重要决定因素[29]。谢文娟等[30]研究表明日常工作步行上下班和工作性质与代谢综合征密切相关,每日上班步行每增加10 min,患高血压的风险则下降12%。日常家务活动量与多种慢性疾病也具有相关性。例如,糖尿病患者家务劳动的变量系数与患病率呈负相关关系,每增加一个家务劳动的PASE分值就会降低糖尿病0.4%患病率,随着家务活动水平的提高,患肥胖病、高血压、动脉硬化等疾病和患病总数量的风险程度呈显著下降趋势[31]。 长期静坐也是中老年人独立于体力活动患代谢综合征风险的危险因素。资料显示静坐时间随着年龄的增大而增加,减少静坐时间或增加静坐中断次数对代谢综合征的防治具有积极作用[32]。ARSHAD等[33]通过问卷对200名中老年患者的每日身体活动水平调查研究得出结论,81.7%的男性及83.3%女性每日步行距离低于1.6 km,长期低水平的身体活动是患代谢综合征的重要因素。对于老年患者步行是最主要身体活动方式,多数研究建议中老人患者每日步行30 min左右及类似身体活动[34]。但有研究指出由于老年患者体内分泌功能下降和机体的衰退,长期大量的步行后期效果明显低于前期,并且出现肌肉减轻情况,使老年人肌肉分解造成关节过度磨损[35]。提示对于老年患者在身体活动过程中把握好强度及时间十分重要,不宜过度步行。由此可见倡导全民健身活动,减少久坐少动的不良习惯,鼓励低碳健康的上下班方式,推荐健康生活方式的转变是防治中老年代谢综合征的重要举措。 2.3.2 运动对中老年人代谢综合征的影响 有氧运动因运动强度小、安全性高,在减少体脂和降血压方面较其他运动更为显著,并且仅有氧运动能降低代谢综合征的炎症反应,故认为是防治中老年人代谢综合征的主要运动方式[36]。动物研究指出代谢综合征大鼠具有严重炎症反应及伴随着心血管保护因子诱导型一氧化氮合酶降低,极大促使心血管疾病的发生。而有氧运动能缓解代谢综合征大鼠炎症反应以及促进诱导型一氧化氮合酶因子增加,并加速大鼠糖脂代谢,游离脂肪酸和低密度脂蛋白的上升激发了M-PPARamRNA表达增加,启动抗炎反应并增加心血管保护因子[37]。代谢综合征与心脑血管死亡密切相关,代谢综合征增加心脑血管疾病的发病率,符合代谢综合征标准是中老年人发生心脑血管急症的不良预测因素[38]。有证据显示64名中老年代谢综合征患者进行每日30-60 min,每周三四次的有氧运动,结果显示6个月后患者空腹血糖及餐后2 h血糖、胰岛素水平显著下降[39]。中老年患者三酰甘油、总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白的升高是导致心血管疾病发病率极大增高的危险因子,高水平的抗冠心病因子可有效预防心血管疾病的发生,而高密度脂蛋白胆固醇是唯一与冠心病的发生呈负相关的脂蛋白。研究表明有氧运动增加了脂蛋白脂肪酶活性[40],运动时与运动后脂肪组织分解,同时也促使了三酰甘油表面成分向低密度脂蛋白转移,促进高密度脂蛋白活性升高与形成,从而纠正脂代谢紊乱,改善血脂水平,减轻糖调节受损,降低中老年人心脑血管疾病的发病风险。 随着人们认识的深入,对骨骼肌产生积极影响的抗阻运动受到研究者的关注。抗阻运动是美国心脏联盟等机构所推崇预防心血管疾病的方式之一[41]。较有氧运动在提高基础代谢率、改善胰岛素抵抗、促进葡萄糖转运和摄取,增加骨密度和肌肉力量方面的效果更佳[42-43]。骨骼肌是决定胰岛素敏感度的重要因素,人体衰老骨骼肌的减退与胰岛素降低有关。运动时骨骼肌以游离脂肪酸氧化为主要的能量来源,伴随运动中游离脂肪酸大量利用,血清三酰甘油分解代谢增加,浓度降低,利于减缓脂质沉积以及血管硬化。抗阻训练能更有效改善骨骼肌的糖代谢和分泌功能,刺激骨骼肌蛋白质的合成,使肌肉含量增长进一步改善患者葡萄糖负荷引起的胰岛素的应激反应,提高胰岛素敏感度[44]。有研究报道,老年人接受10周(2次/周)以上的抗阻训练骨骼肌可增7.4%-10.0%,对由于老龄性的瘦体质量流失和安静时代谢下降具有良好的效果,运动的结束后肌肉和肝脏还会摄取血中大量葡萄糖补充肝糖原和肌糖原的消耗,使血糖进一步下降[45]。同时,有报道指出,即使采取较低负荷的抗阻练习对血糖控制能力及胰岛敏感度的提高也有显著效果。可能由于主要运动肌结合血流限制使体脂率显著降低的同时,也增加了肌肉体积及力量,使机体脂肪组织三酰甘油和脂肪细胞体积下降,提高了体内最主要的糖类吸收组织——骨骼肌含量,提示低负荷抗阻运动可作为针对中老年患者的运动处方[46]。近年还有学者发现,鸢尾素健康水平与否与胰岛素抵抗的发生密切相关。 HUH等[47]研究指出,鸢尾素可能是在急性运动时产生的调节性应激因子,血液循环中的鸢尾素在开始运动后则急速提升,并与有氧运动相比进行抗阻运动时其水平提升更显著。 因此有学者提出,联合进行有氧与抗阻运动较单一运动形式可获得更大程度的代谢改善,推荐采用有氧为主抗阻为辅的结合,针对中心性肥胖和心脑血管疾病等危险因素可获得更大收益[35]。陈宝宜等[48]研究证实老年患者经有氧联合抗阻训练使肌肉反复收缩,起到降低血糖及增加肌肉含量的双重作用。同时,石劢[49]指出两者联合干预使脂代谢、糖、糖原异生等各种途径都可发挥对血糖的控制,激活肝脏细胞内糖原的形成,血液中的葡萄糖可被肝脏利用而合成糖原,即便在运动停止后仍能使血糖浓度维持较低水平。综上,身体状况允许的中老年人群可选择适量抗阻与有氧运动相结合,以获得更大的收益。何江山[50]研究表明老年人代谢综合征患抑郁状态明显高于正常组,组分中肥胖和高三酰甘油血症与抑郁状态密切相关。证据显示,进行适量运动可促进交感神经兴奋,提高肾上腺素刺激内啡肽分泌,从而摆脱因代谢综合征所引起的抑郁负面情绪,改善心理健康,有益于更高效率的改善病情[51]。并且刘海明[52]指出代谢综合征老年患者伴有认知功能减退,有导致痴呆的风险,五禽戏练习对血管危险因素产生积极影响以提高老年人认知功能,以此增强患者自信心和自我管理能力,提高患者生活质量。此外,张丽等[53]提出振动训练对于老年患者具有更好的依从性,往往老年患者难以达到有效运动强度,全身振动训练能增加瘦体质量及肌肉水平并抑制脂肪组织的形成,在不会造成过重心肺负担的同时有效改善代谢综合征。还有学者指出交叉点的运动训练模式对绝经后中老年女性代谢综合征能产生更积极作用[54]。 "

| [1] REAVEN GM.Diet and syndrome X. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2000; 2(6):503-507. [2] REAVEN GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988;37(12):1595-1607. [3] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会代谢综合征研究协作组.中华医学会糖尿病学分会关于代谢综合征的建议[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2004,12(3): 5-10. [4] LU J, WANG L, LI M, et al. Metabolic Syndrome Among Adults in China: The 2010 China Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(2): 507-515. [5] 尹士男,江华.代谢综合征的诊治进展[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2018(11):1121-1123. [6] 李文敏,高凯. 2014—2017年我国居民代谢综合征患病率的meta分析[J].慢性病学杂志,2018,19(11):1476-1480. [7] 王晓东,谢友红,孙兴国,等.心肺运动试验精准制定个体化强度运动处方对代谢综合征患者心肺功能的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2019,38(01):3-9. [8] 张蓉.代谢综合征的流行病学研究进展[J].江西医药,2011,46(1): 78-81. [9] 张春燕,童人杰,李海华,等.综合干预在儿童代谢综合征中的疗效及对患儿生存质量的影响观察[J]. 实用预防医学,2018,25(5): 597-600. [10] 张晨.12-15岁青少年体力活动水平现状与代谢综合征指标的关联性研究[D].天津:天津体育学院,2013. [11] OKOSUN IS, BOLTRI JM, LYN R, et al.Continuous Metabolic Syndrome Risk Score, Body Mass Index Percentile, and Leisure Time Physical Activity in American Children. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2010;12(8):636-644. [12] KAMATH CC,VICKERS KS,EHRLICH A,et al.Behavioral Interventions to Prevent Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review and Metaanalyses of Randomized Trials. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(12):4606-4615. [13] 叶萍. PPARγ基因Pro12Ala和C1431T、ADIPOQ基因-11377C>G多态性及身体活动与儿童代谢综合征的关系[D]. 广州:南方医科大学, 2013. [14] 王凯风,叶萍,王丹,等. ADIPOQ基因11377C/G位点多态性与身体活动对儿童代谢综合征的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2015,31(23): 3853-3856. [15] 牛林艳,黄金. 儿童及青少年代谢综合征的干预进展[J]. 医学综述. 2013,19(3):525-527. [16] MCMURRAY RG, BANGDIWALA SI, HARRELL JS, et al. Adolescents with metabolic syndrome have a history of low aerobic fitness and physical activity levels. Dyn Med. 2008;7:5. [17] 陈联辉,朱伟芬,梁黎,等.非高密度脂蛋白胆固醇对肥胖儿童非脂性心血管疾病危险因素的预测作用[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2013, 15(5):356-360. [18] 阳玉晶. 有氧运动对肥胖青少年心外膜脂肪厚度的影响[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2016. [19] 斯坦博格,庄稼英. 关注儿童青少年中的代谢综合征[J]. 糖尿病天地(临床),2010,4(7):296-305. [20] 吴海英,沈才杰. 饮食及运动干预对代谢综合征儿童左室结构及功能改善的作用[J].浙江中西医结合杂志, 2018,28(8): 667-670. [21] NETO AS, DE CAMPOS W, SANTOS GD, et al. Metabolic syndrome risk score and time expended in moderate to vigorous physical activity in adolescents. BMC Pediatrics. 2014:42. [22] 关尚一,朱为模.身体活动与青少年代谢综合征风险的“剂量-效应”关系[J].西安体育学院学报,2013,30(02):211-216. [23] 李晓南.关注儿童青少年肥胖相关并发症的监测和指导[J].中国儿童保健杂志,2018,26(12):1277-1279. [24] 张磊,李智慧.运动干预对肥胖代谢综合征青少年脑功能的影响[J]. 河北体育学院学报,2019,33(1):79-86. [25] RÄIKKÖNEN K, MATTHEWS KA, SALOMON K.Hostility predicts metabolic syndrome risk factors in children and adolescents. Health Psychology. Health Psychol. 2003;22(3):279-86. [26] GERMAIN CM, VASQUEZ E, BATSIS J A. Physical Activity, Central Adiposity, and Functional Limitations in Community- Dwelling Older Adults. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2016;39(2):71-6. [27] 麻新远,衣雪洁.论身体活动和运动干预对2型糖尿病的作用[J]. 沈阳体育学院学报,2010,29(3):69-72. [28] KI-WOL S. Relationship of daily activity and biochemical variables in the elderly with diabetes mellitus. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011; 41(2):182-190. [29] 巫丽丽,李必迅,邱晔,等.生活方式干预对代谢综合征患者影响10年随访研究[J].内科, 2018,13(6):823-826. [30] 谢文娟,卞晓嘉,何志敏,等.身体行为活动与血脂异常、高血压、糖尿病关系的研究[J]. 实用预防医学,2017, 24(3): 319-323. [31] 马丽.身体活动对城市老年人代谢性疾病患病风险的影响——基于PASE的流行病学调查[J].上海体育学院学报,2018,42(4):100-104. [32] 安德里亚,谭婷婷. 即便进行运动,久坐行为仍与代谢综合征强相关[J].糖尿病天地(临床),2012,6(7):318-323. [33] ROZINA A, BIN YB, JUNAID M, et al. Pattern of physical activity among persons with type 2 diabetes with special consideration to daily routine. Pak J Med Sci. 2016;32(1): 234-238. [34] 于洪军,仇军.身体活动负荷对我国老年人患慢性疾病风险率的影响研究——基于对清华大学老年人群PASE问卷的流行病学调查[J]. 中国体育科技,2013,49(02):139-145. [35] 王菂.不同运动方式对2型糖尿病康复的影响[J].中国民族民间医药, 2014,23(17):82-83. [36] YANG Z, SCOTT C A, MAO C, et al. Resistance Exercise Versus Aerobic Exercise for Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2014;44(4):487-499. [37] 张崇林,王卉,刘绍生,等.有氧运动对代谢综合征大鼠炎症反应的影响及其机制研究[C].无锡:第四届(2016)全国运动生理与生物化学学术会议,2016. [38] 金萌萌,潘长玉,田慧,等.老年人群代谢综合征与十年心脑血管疾病死亡率关系的研究[J].中华心血管病杂志,2008,36(2): 118-122. [39] 刘萍,孙静.治疗型生活方式对中老年人代谢综合征的影响[J].中国临床保健杂志,2009,12(4):408-409. [40] 陈巍,李娟,陈庆合.运动促进骨骼肌功能康复改善代谢综合征的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2012,27(6):577-582. [41] 董聪敏.力量训练对老年代谢综合征患者空腹和摄糖后自主神经功能调节的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2017,37(20): 5020-5022. [42] ROBERTS CK, HEVENER AL, BARNARD RJ. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance:underlying causes and modification by exercise training. Compr Physiol. 2013;3(1):1-58. [43] 罗曦娟.有氧和抗阻运动对糖尿病前期人群糖调节的影响及其机制探讨[D].北京:北京体育大学, 2015. [44] 金晓飞. 抗阻力训练对老年人机体健康影响的研究[J]. 运动, 2015(17):155-156. [45] KIM TN, PARK MS, LIM KI, et al. Skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio is associated with metabolic syndrome and arterial stiffness: The Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS). Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;93(2):285-91. [46] 陈巍,李娟,陈庆合,等.抗阻训练中运动肌血流限制对肥胖者体成分及胰岛素敏感度的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2010,29(6): 646-649. [47] HUH JY, SIOPI A, MOUGIOS V, et al. Irisin in Response to Exercise in Humans With and Without Metabolic Syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(3):E453-457. [48] 陈宝宜,李婷,徐鑫亚.抗阻-有氧联合训练对中老年2型糖尿病患者运动干预的影响分析[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2017, 17(54): 46-49. [49] 石劢.老年2型糖尿病患者运动干预效果的系统评价与实证研究[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学, 2016. [50] 何江山. 老年人代谢综合征及其组分与抑郁状态的相关性研究[D]. 遵义:遵义医学院, 2018. [51] 宁秋芬,张晓莉,周刚柱.抗抑郁药联合有氧运动对抑郁症的早期治疗阶段的临床疗效观察[J]. 山西医药杂志12018,47(6): 675-677. [52] 刘海明.五禽戏对代谢综合征老年人认知功能的影响[J]. 武汉体育学院学报,2012,46(10):56-61. [53] 张丽,瓮长水.全身振动训练在老年康复领域应用的研究进展[J]. 中国康复理论与实践12015,21(2):163-167. [54] 张晓涵,张培珍.交叉点的运动训练对女性代谢综合征影响的研究进展[J]. 中国预防医学杂志,2018,19(10):783-786. |
| [1] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [2] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [3] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [4] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [5] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [6] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [7] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [8] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [9] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [10] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [11] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [12] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [13] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [14] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [15] | Shui Xiaoping, Li Chunying, Li Shunchang, Sun Junzhi, Su Quansheng . Effects of aerobic and resistance exercises on brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nuclear factor-kappa B and inflammatory cytokines in skeletal muscle of type II diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 669-675. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||