Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (16): 2563-2570.doi: 10.12307/2023.137
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress and application prospect of polyethyleneimine in bone tissue engineering
Huang Yixuan1, Du Bin2, Liu Xin2, Yuan Xinwei1, Xi Hongzhong1, Guo Mingbin1, Mai Jianbin1
- 1Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-14Accepted:2022-05-23Online:2023-06-08Published:2022-11-11 -
Contact:Du Bin, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Huang Yixuan, Master candidate, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:General Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82074471 (to DB); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Fund), No. 81804117 (to LX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Yixuan, Du Bin, Liu Xin, Yuan Xinwei, Xi Hongzhong, Guo Mingbin, Mai Jianbin. Research progress and application prospect of polyethyleneimine in bone tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2563-2570.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
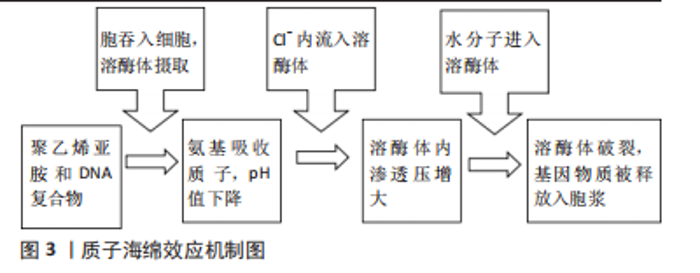
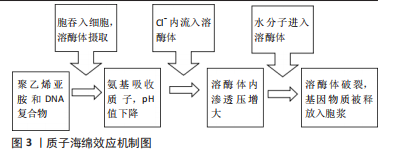
2.1 聚乙烯亚胺的特征 聚乙烯亚胺是由乙烯亚胺在酸性环境下聚合得到一种水溶性阳离子聚合物。根据结构分为线性和支链化两种,线性聚乙烯亚胺胺基团均为伯胺,支链聚乙烯亚胺有比例为1∶2∶1的伯胺及仲胺、叔胺基团[4],以及侧链基团大量的活泼氢,使其具有阳离子活性。 2.2 聚乙烯亚胺的性能 聚乙烯亚胺最突出的特点是丰富的胺基基团及每3个原子就有一个能够质子化的氮原子,因此聚乙烯亚胺具有以下性能:①易修饰性:丰富的胺基基团赋予其较强的可修饰性,利用聚乙烯亚胺对其他物质表面进行改性,使其表面功能化;②易吸附性:阳性表面电荷增强细胞黏附、增殖的能力[5],同时可以通过静电作用吸附核苷酸;③具有质子海绵效应:当聚乙烯亚胺进入细胞内被溶酶体吞噬后,溶酶体内的酸性环境使得聚乙烯亚胺吸收大量质子,导致Cl-离子内流,渗透压失衡后溶酶体破裂,将内吞的载体和携带的药物/基因释放到细胞质内而不被破坏[6];④具有抗菌性:季铵化的聚乙烯亚胺通过与细菌体之间强静电作用,穿透细胞壁,破坏细胞膜。 2.3 聚乙烯亚胺在骨组织工程的应用 因为廉价易制备的特性,聚乙烯亚胺已经被广泛用于污水处理、造纸工业、纤维纺织工业、化妆品、石油开采和生物医药等众多领域。尤其是在医学领域中,聚乙烯亚胺已在生物工程、基因治疗、影像学对比剂和纳米荧光探针等方面得到广泛研究[7-10]。 2.3.1 基因技术修饰骨相关种子细胞 骨组织工程中常见的种子细胞包括成骨细胞、骨髓基质细胞、间充质干细胞及胚胎干细胞。为了让种子细胞更好地黏附于支架并且成骨分化,需要多种生长因子的调控。目前治疗骨缺损领域已经有包括骨形态发生蛋白(bone morphogenetic protein,BMP)、转化生长因子β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)、成纤维细胞生长因子(fibroblast growth factor,FGF)和血小板衍生因子(platelet-derived growth factor,PDFG)等在内的多种生长因子,其中骨形态发生蛋白2已经是有科学界广泛共识的能诱导胚胎骨生长和成人骨修复的重要生长因子[11]。但单纯的生长因子存在提取困难、半衰期短,需大剂量反复使用,且价格较贵的问题。利用基因载体通过将诱导成骨相关基因导入到种子细胞进行调节自身分化并实现持续的骨修复已经是研究热点,借此可以实现长效、高效的成骨因子的释放[12]。聚乙烯亚胺自身自带的大量正电荷和可修饰的胺基基团,与带负电荷的核酸产生带正电荷的复合物,然后复合物与带负电荷的细胞膜相接处,通过胞吞或非胞吞作用的途径进入细胞中。根据目前的“质子海绵效应”假说,不但能够保护遗传物质不被降解而且相比于其他阳离子聚合物载体提高转染效率、降低细胞毒性。质子海绵效应机制图见图3。"
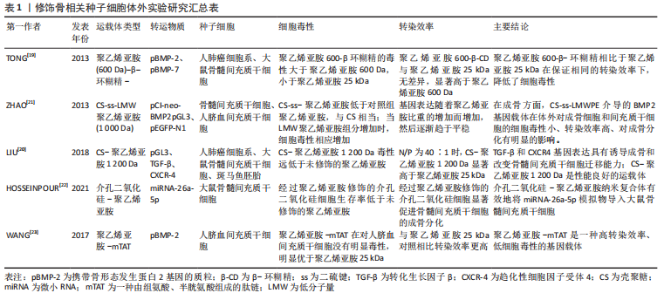
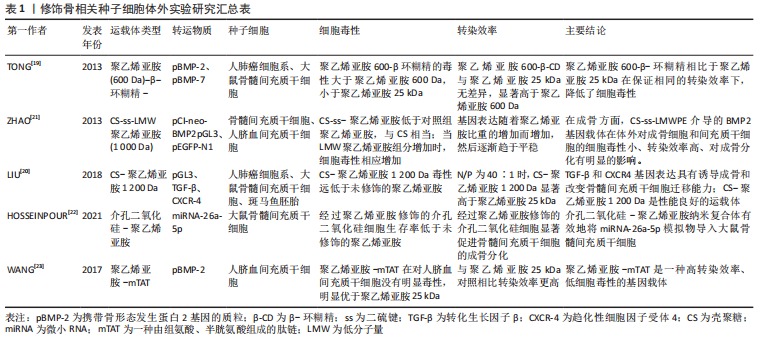
BOUSSIF等[13]最早实现利用聚乙烯亚胺进行基因的转染,在随后的发展中,聚乙烯亚胺衍生物更好地提升其转染的性能。聚乙烯亚胺通过静电作用将DNA或RNA凝聚成稳定的聚合物[14],分子质量越高转染效率越大[15],但细胞毒性也越大,相对分子质量25 000的聚乙烯亚胺是迄今为止最有效的基因传递阳离子聚合物之一。基因的转染效应与毒性之间的矛盾也是聚乙烯亚胺研究中不得不考虑的问题[16],克服此障碍至关重要。 近年来,通过对聚乙烯亚胺的修饰在降低细胞毒性方面取得了许多令人振奋的成果。目前可以通过3种方法实现。一种是通过使用可降解基团将低分子量的聚乙烯亚胺组装为成高分子聚乙烯亚胺,在转染之后降解成低分子量的低毒聚乙烯亚胺;高度支化的聚乙烯亚胺形成更小的复合物,而且能获得更高的转染效率[17]。另一种方法是利用其他分子基团对低分子量的聚乙烯亚胺进行修饰,以提高其转染效率。根据文献报道,聚乙烯亚胺经过与壳聚糖、葡聚糖、环糊精等碳水化合物;或者亮氨酸、组氨酸、精氨酸和络氨酸等氨基酸类的修饰后比未修饰的聚乙烯亚胺更高效和安全[18]。TONG等[19]利用低分子量聚乙烯亚胺与β-环糊精设计了一种新的多链质粒递送剂聚乙烯亚胺600-β-环糊精;相比于未修饰的相对分子质量25 000的聚乙烯亚胺不但降低了细胞毒性,同时明显提高了骨髓间充质干细胞对基因载体的吞噬效率。LIU等[20]则制备了壳聚糖-低分子量聚乙烯亚胺载体来评价该载体的安全性和转染效率。在近几年的发展中,研究者提出了采用将2种方法结合的方式开发新的基因载体复合物。ZHAO等[21]通过对低分子量聚乙烯亚胺与壳聚糖的修饰,并用可逆交联性的二硫键连接,不但进一步降低了毒性,而且在还原性的环境中二硫键的断裂促进DNA的释放,提高了转染效率;成骨分化方法也优于单纯的聚乙烯亚胺和壳聚糖。有团队设计了通过可生物降解的二硫键使低分子量聚乙烯亚胺交联,并用络氨酸修饰;体外实验证实与未修饰或单一修饰相比增强了转染效率并具有良好的生物相容性[15],见表1。"
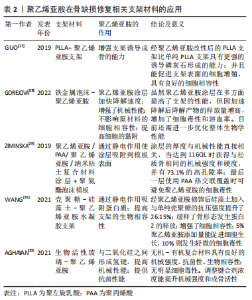
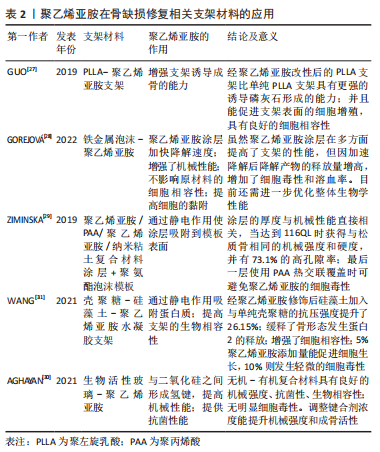
此外,不同于其他组织修复,在骨修复的过程中,环境中的Ca2+发挥了不可或缺的作用,并且直接与骨组织工程的种子细胞相关[24]。ACRI等[25]首次确定了当培养基中Ca2+的浓度在8-12 mmol/L时对用聚乙烯亚胺-pDNA 复合物转染骨髓间充质干细胞产生积极影响。因此,相比于优化转染细胞的方法,探讨细胞外环境如何影响这些转染方式也是另一种值得研究的思路。 综上所述,聚乙烯亚胺的应用提高了种子细胞转染诱导其表达生长因子的效率,避免重复注射相关因子,更有利于干细胞向成骨的分化,加速了新生骨的形成,并且通过进一步的修饰降低了复合物的细胞毒性。虽然聚乙烯亚胺已经在许多的报道中成功使用,但对于遗传物质递送的关键参数仍缺乏共识:DNA和聚乙烯亚胺链的长度、聚乙烯亚胺的电荷密度、结构和化学修饰以及氮/磷酸盐等均会影响聚乙烯亚胺介导的DNA递送。同时像上文合成的较大复合物是如何被细胞摄取并裂解释放质粒DNA的过程尚不明确,因此这类复合物的大小、形态都需要进一步的探索。 2.3.2 骨缺损修复相关支架材料 应用于骨组织工程学的支架材料包括天然支架材料、人工合成的无机和有机高分子材料、复合支架材料。但由于骨组织不同于其他组织的结构,理想的支架材料应有以下特点:①较好的生物相容性;②彻底的生物降解性;③足够的骨细胞攀附孔隙;④降解速率与骨再生速率匹配;⑤足够的支持强度。由于骨组织结构的特殊性[26],没有一种单一材料能完全符合要求,研究者们对其进行一系列修饰改性的研究。凭借聚乙烯亚胺自身特性,目前应用于提高支架结构、性能、抗菌性和促血管化方面。 支架材料的修饰:在生物相容性方面,为了使种子细胞黏附在支架上,目前常用的方法是将细胞悬液直接滴加到支架表面,虽然简便,但存在接种率低、分布不均匀的问题,这严重影响组织工程骨的质量。人工合成有机材料支架聚乳酸(polylactic acid,PLA)及其衍生物目前研究最为广泛,但因为表面活性和亲水性低及细胞黏附性差限制了其在骨组织工程学中的运用。氨解是一种能促进细胞附着和增殖的技术,并且随后可以进行其他化学处理。聚乙烯亚胺通过的氨基与聚左旋乳酸(L-polylactic acid,PLLA)的酯基反应,引入游离的氨基,可以增加亲水性并提高细胞黏附的效率[21]。GUO等[27]首次以聚乙烯亚胺为改性剂,利用氨解结合热诱导相分离技术制备了新的PLLA纳米纤维支架,成骨细胞的增殖性能明显优于单纯PLLA支架。 在支架的降解速率方面,支架的降解速率理想中应与骨组织细胞的生长速率同步,目前金属支架虽然力学性能较好,但降解速率并不理想。针对这一问题,目前已有聚乙二醇、聚乳酸、聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物[poly(L-glutamic acid),PLGA]被用作涂层材料来调整降解速率。GOREJOVá等[28]在铁金属泡沫表面涂层上首次应用聚乙烯亚胺,旨在加快铁金属支架的降解速率,并研究该涂层对支架的机械性能和生物相容性的影响;最后得出聚乙烯亚胺涂层可以加快降解速度,并且能够提高机械性和骨细胞攀附性同时不影响生物稳定性。 在支架孔隙方面,支架的孔隙为骨细胞的生长提供空间,孔隙密集不利于骨细胞的长入,过于稀疏则影响力学性能。因此,ZIMINSKA等[29]开发出的聚乙烯亚胺-聚丙烯酸(polyacrylic acid,PAA)-纳米黏土涂层在开孔的聚氨酯泡沫模板上进行了逐层组装,旨在平衡泡沫板较高的机械性能和较低的孔隙率与涂层厚度之间的关系,该研究结果表明,逐层组装技术的涂层在获得与松质骨相同的力学性能时孔隙率可> 70%。 在支架的机械强度方面,理想的支架材料应具有足够的机械强度以满足骨组织力学性能的要求。生物活性玻璃作为第3代骨修复材料存在力学性能中表现一般的问题,不能适合高负荷应用。AGHAYAN等[30]开发出的70Si30Ca 生物活性玻璃-聚乙烯亚胺的新型多功能无机-有机杂化物,通过观察不同添加不同浓度的三甲氧基硅烷,在聚乙烯亚胺和二氧化硅网络之间建立化学相互作用,从而提高力学性能和控制降解速度,促进骨向植入物内生长,增强骨组织与植入物的结合强度。聚乙烯亚胺在骨缺损修复相关支架材料的应用具体见表2。"
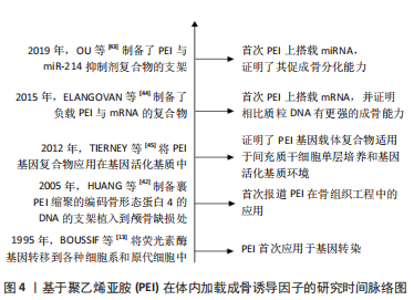
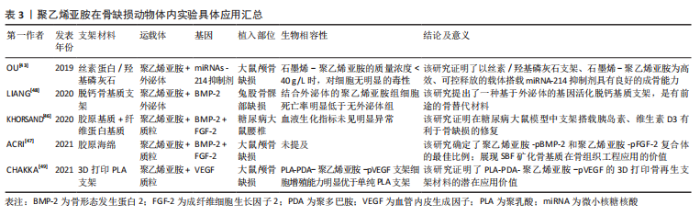
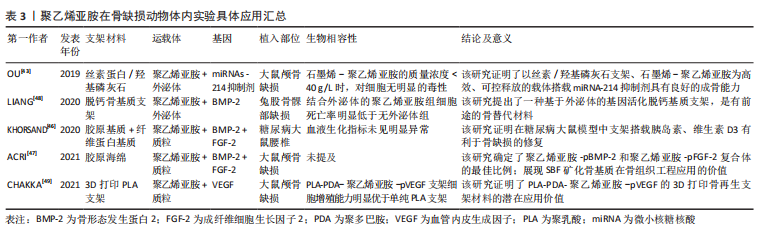
支架材料的抗菌性能:组织工程研究中如何有效抑制局部细菌的滋生是必须面对的问题,如慢性牙周炎因为细菌侵入导致周围组织炎症致使牙周骨组织丧失、吸收和牙齿松动,使用组织工程骨支架成为了修复缺损的可行方案。虽然人工材料的机械性能和耐磨性都有较大提高,但他们的抗菌性能仍然有限,而且还有可能积累更多的细菌[32]。在一些报道中,季胺化的疏水聚乙烯亚胺已经被用作杀菌涂层材料,其原理是能够穿透细菌的细胞膜,从而杀死细菌。BEYTH等[33]研究了季胺化聚乙烯亚胺与复合树脂支架结合后的抗菌活性和机械强度,采用琼脂扩散实验、直接接触实验、淋洗液中细菌生长实验和透射电镜观察等方法检测其对变形链球菌的抗菌活性,发现该材料有至少维持1个月的抗菌活性,并且添加质量分数1%的季胺化聚乙烯亚胺纳米粒子对牙科复合材料的弯曲模量和弯曲强度没有影响,并未改变材料的力学性能。相比于小分子季胺盐类抗菌剂,高分子季胺盐具备更强的抗菌能力,而且季胺化聚乙烯亚胺在静电作用下能与菌体之间形成强烈的吸附作用,抗菌效率进一步提升。然而,单一功能的抗菌材料不能满足理想骨缺损植入物具备的良好生物相容性和生物活性,近几年双功能骨修复材料成为了新的发展方向。朱敏闻等[34]通过静电纺丝技术,在鱼胶原中加入了1 800 Da 聚乙烯亚胺制备了一种引导组织再生膜接种骨髓间充质干细胞上,结果表明这种鱼胶/聚乙烯亚胺电纺膜与单纯鱼胶原电纺膜相比不但具有极强的抗菌能力而且有良好的成骨能力。SUN等[35]则利用乙二胺功能化聚甲基丙烯酸缩水甘油酯刷将钛植入物表面进行季胺化聚乙烯亚胺和阿仑膦酸盐功能化,结果表明,新的植入物具备早期抑制细菌感染,后期增强与骨组织整合的能力。这些双功能材料为今后的抗菌骨缺损植入物提供了新的设计与开发的思路。 支架材料的血管化:大面积的骨缺损因为血供不足,而导致移植物难以存活。因此目前骨组织工程学不得不面对的另一个问题就是血管化的问题。目前主要以4种途径来提高血管化的效率:包括了血管内皮细胞和种子细胞的联合培养[36];应用血管内皮生长因子等生长因子促进血管的形成[37];通过显微技术移植筋膜瓣;肌肉瓣和血管束等促进血管的形成[38];将外源性的基因移植入种子细胞中[39]。聚乙烯亚胺在这方面目前文献报道中,依然多以基因治疗的方式来提高血管化水平。除此之外,因聚乙烯亚胺表面丰富的表面阳离子电荷,在HADJIZADEH等[40]制备的聚对苯二甲酸乙二酯纤维支架上,加入乙醛等离子体表面功能化之后,通过细胞黏附性实验证明乙醛和聚乙烯亚胺涂层增强了内皮细胞的黏附性,这也可能和聚乙烯亚胺能够在培养环境中吸附血清中的蛋白质,使得细胞摄取有关。GIGLIOBIANCO等[41]更进一步报道了一种电纺支架,通过聚乙烯亚胺聚阳离子和聚丙烯酸聚阴离子的多层聚合物设计不但有助于细胞的黏附和生长,而且通过ELISA实验证明相比于单纯的聚乙烯亚胺-肝素涂层更有利于结合血管内皮生长因子的能力;植入到鸡绒毛膜尿囊膜中,涂层支架显示出了较强的血管生成活性。但是该设计缺乏对支架表面涂层稳定性的进一步研究。因此,聚乙烯亚胺结合其他材料制备的复合材料支架在促进细胞成骨分化、内皮细胞的黏附生长等方面是未来的发展方向。 2.3.3 体内加载成骨诱导相关因子 在HUANG等[42]首次报道聚乙烯亚胺作为基因载体在修复骨缺损应用以来,随着成骨相关基因片段和支架材料种类的不断丰富,聚乙烯亚胺基因载体复合物在对于诱导种子细胞成骨分化的能力以及骨缺损修复的能力在不断被得到验证[13,42-45]。基因激活基质是基因转染的方式的一种,由基因载体和支架材料构成。不同于上文介绍的体外转染,体内转染法使通过含有生长因子基因的基因激活基质直接植入骨缺损部位,相对较简单,并且减少了污染的风险。聚乙烯亚胺的应用不但增强了对遗传物质的保护,而且提高了成骨相关细胞的转染效率。KHORSAND等[46]设计了由胶原基质(外层)和纤维蛋白基质(内层)组成的双层支架,将封装有胰岛素和维生素D3的PLGA颗粒植入内层;周围包绕含有聚乙烯亚胺-(pBMP-2+pFGF-2)的基因活化基质中,植入到糖尿病大鼠的腰椎区域;实验证明搭载胰岛素和维生素D3药物的成骨能力优于单纯支架植入物。ACRI等[47]进一步确定当pBMP-2∶pFGF-2为5∶3时可获得最佳成骨性能。 除了传统的质粒基因载体外,近几年研究热门外泌体凭借自身阴离子能屏蔽部分聚乙烯亚胺,从而降低细胞毒性[48-49]。LIANG等[48]利用外泌体与搭载pBMP-2的聚乙烯亚胺负载到脱钙骨基质支架上。OU等[43]则未选择促进生长因子表达的质粒DNA,而是选择目前新的热门发展方向microRNA-214抑制剂促进成骨分化;同时将氧化石墨烯纳米片与聚乙烯亚胺的结合实现了miRNA抑制剂的缓释释放。聚乙烯亚胺在骨缺损动物体内实验时间脉络图如图4所示,近3年具体应用进展如表3中所示。"
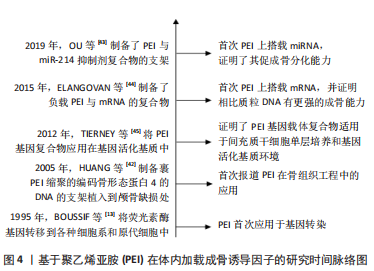

但对于体内转染来说,靶蛋白在其他组织细胞的异位表达和靶细胞内基因的异位插入均阻碍了成骨相关因子基因的正常表达,是目前亟待解决的问题。 2.3.4 药物骨靶向性递送的探索 目前虽然有许多方法实现支架上负载药物的缓控释技术,但是仍受限于载药量以及骨缺损修复周期长等多种因素的影响,植入后不能重新加载药物或生物制剂。例如在股骨头坏死中骨修复及整合的过程较长,研究表明至少3-6个月的免负重期内均为骨修复-整合期;然而支架植入30 d后,药物释放和支架降解速率存在不同步的问题影响了成骨能力,后期骨修复和骨整合的速度明显减缓[50]。因此探索一种体外持续给药系统的方法可以较好解决上述问题。考虑到骨组织血运和结构的特殊性,维持有效的药物浓度而且不会对其他组织细胞产生毒性,药物递送系统的靶向性同样非常重要。 自从“骨靶向”概念被研究者们提出以来,双膦酸盐类得到广泛的研究[51],以双膦酸盐类作为靶头可以去识别和结合羟基磷灰石。FORTE团队[52]用聚乙烯亚胺修饰羟基磷灰石得到了表面带有正电荷的功能化羟基磷灰石晶体,从而促进了带负电的双膦酸盐类以物理方式吸附配合原有的化学吸附的方式固定在其表面,并调控了双膦酸盐类的释放。利用这一成果,可以将聚乙烯亚胺修饰过的羟基磷灰石作为支架材料,并有待开发出一种以双膦酸盐类作为修饰聚合物的药物载体,靶向递送药物的输送系统。最近,PLESSELOVA等[53]报道了一种三元偶联聚合物的设计,即聚乙烯亚胺-BPS-环糊精;环糊精内的疏水空腔可搭载疏水药物阿霉素,非共价键结合的方式不会影响运载药物的药理活性;并且聚乙烯亚胺同时连接了乙烯基砜官能化的靶向配体双膦酸盐和药物载体环糊精。该研究证明了聚乙烯亚胺作为不同材料之间充当“桥梁”的角色,同时连接双膦酸盐作为靶向配体和环糊精作为药物载体。对于羟基磷灰石支架材料,开发一种结合双膦酸盐制备的药物载体,是否具备对支架的靶向药物释放性能,这为研究者提供了新的思路和方向。 除了利用双膦酸盐类递送骨靶向药物外,利用生理病理环境或外部施加环境的智能相应性递送系统也值得研究。DUAN等[54]制备的一种纳米载体聚乙烯亚胺-超顺磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒向关节炎输送治疗性siRNA,在体外实验中诱导特异性基因沉默,外加磁场可以使siRNA在关节局部积累并提高疗效。GONG等[55]同样介绍了聚乙烯亚胺、右旋糖酐及氧化铁纳米颗粒合成的磁性基因载体,在体外磁场环境中将miR302b的质粒转染到骨肉瘤细胞中。在此基础上设想,如果制备出一种磁性支架,通过磁驱动吸引结合在磁性纳米颗粒的基因和药物,则磁性颗粒药物载体从而可以实现靶向递送。通过利用聚乙烯亚胺修饰磁性颗粒表面,使其表面氨基化,可以实现接枝其他载药聚合物。例如AEINEH等[56]利用聚乙烯亚胺和谷胱甘肽开发出一种新型的pH敏感性的表面功能化磁性纳米颗粒,表面聚乙烯亚胺层的氨基与谷胱甘肽的羧基反应形成酰氨键;姜黄素最终通过氢键和/或偶极-偶极相互作用被加载到磁性纳米颗粒中,可用于在酸性环境下姜黄素的靶向传递;体外释放分析中,所制备的磁性纳米颗粒在酸洗介质(pH 5.5)比中性介质(pH 7.4)中药物释放总量高43%;并且流式细胞仪证明了利用聚乙烯亚胺与细胞表面的阴离子蛋白多糖来增加细胞摄取。但目前尚未有利用体内磁性支架吸引磁性纳米颗粒的文献报道,因为药物的释放和药物活性的改变仍然是最大的问题和挑战。 生物素-亲和素体系是一种理想的分子识别模型,之间可以产生非常稳定的非共价键相互作用。在BRICOUT等[57]设计的具有聚多巴胺涂层的铬钴(CoCr)支架,通过聚乙烯亚胺使多巴胺表面胺基化;利用偶联反应将亲和素接枝到CoCr-聚多巴胺-聚乙烯亚胺表面,生物素化的抗凝药EP224283实现了支架表面的固定;在抗凝活性试验中,聚多巴胺-聚乙烯亚胺-亲和素组与单纯裸露的CoCr组比较,前者具有更显著的抗FXA活性,这说明抗凝药EP224283被有效地接枝到CoCr样品上,且不影响药物活性;血小板黏附实验也证实该装置对血小板的活化有抑制作用。该心血管领域的支架设计有一定的启发,是否能利用生物素-亲和素系统将促成骨的药物靶向固定在体内支架表面,同时确保药物活性?这值得进一步的研究。"

| [1] MORE N, KAPUSETTI G. Piezoelectric material-a promising approach for bone and cartilage regeneration. Med Hypotheses. 2017;108:10-16. [2] WINKLER T, SASS FA, DUDA GN, et al. A review of biomaterials in bone defect healing, remaining shortcomings and future opportunities for bone tissue engineering: the unsolved challenge. Bone Jt Res. 2018; 7(3):232-243. [3] YANG Y, SONG X, LI X, et al. Recent progress in biomimetic additive manufacturing technology:from materials to functional structures. Adv Mater. 2018;30(36):1706539. [4] Amara M, Kerdjoudj H. Modification of the cation exchange resin properties by impregnation in polyethyleneimine solutions: application to the separation of metallic ions. Talanta. 2003;60(5):991-1001. [5] 吴慎剑,刘源岗,王士斌.PEI用于磁性纳米颗粒载药及联合载药抗肿瘤的研究进展[J].材料导报,2015,29(13):89-92,111. [6] 刘云,潘杰,董伟,等.半乳糖基化壳聚糖-聚乙烯亚胺递送siRNA对肝癌耐药细胞BEL7402/5-Fu中MRE11表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(6):934-939. [7] HUSSAIN Z, PEI R. Necessities, opportunities, and challenges for tympanic membrane perforation scaffolding-based bioengineering. Biomed Mater Bristol Engl. 2020. doi:10.1088/1748-605X/abcf5d. [8] HONG SJ, AHN MH, SANGSHETTI J, et al. Sugar alcohol-based polymeric gene carriers: synthesis, properties and gene therapy applications. Acta Biomater. 2019;97:105-115. [9] ZHU J, LI H, XIONG Z, et al. Polyethyleneimine-coated manganese oxide nanoparticles for targeted tumor PET/MR imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(41):34954-34964. [10] ZHANG B, DUAN Q, LI Y, et al. A “Turn-on” fluorescent probe for glutathione detection based on the polyethylenimine-carbon dots-Cu2+ system. J Photochem. Photobiol B. 2019;197:111532. [11] WANG X, LI Y, HAN R, et al. Demineralized bone matrix combined bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, bone morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth factor-β3 gene promoted pig cartilage defect repair. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e116061. [12] 俞莉敏,马俊轩,李继云,等.稳定表达人骨形态发生蛋白2基因骨组织工程种子细胞的构建[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(17): 2722-2728. [13] BOUSSIF O, LEZOUALC HF, ZANTA MA, et al. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(16):7297-7301. [14] BRONICH T, KABANOV AV, MARKY LA. A thermodynamic characterization of the interaction of a cationic copolymer with DNA. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105(25):6042-6050. [15] KARIMOV M, APPELHANS D, EWE A, et al. The combined disulfide cross-linking and tyrosine-modification of very low molecular weight linear PEI synergistically enhances transfection efficacies and improves biocompatibility. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021;161:56-65. [16] KHORSAND B, ELANGOVAN S, HONG L, et al. A comparative study of the bone regenerative effect of chemically modified RNA encoding BMP-2 or BMP-9. AAPS J. 2017;19(2):438-446. [17] JIANG HL, ISLAM MA, XING L, et al. Degradable polyethylenimine-based gene carriers for cancer therapy. Curr Chem Cham. 2017;375(2):34. [18] KUBCZAK M, MICHLEWSKA S, KARIMOV M, et al. Unmodified and tyrosine-modified polyethylenimines as potential carriers for siRNA: biophysical characterization and toxicity. Int J Pharm. 2022;614:121468. [19] TONG H, WANG C, HUANG Y, et al. Polyethylenimine600-β-cyclodextrin: a promising nanopolymer for nonviral gene delivery of primary mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:1935-1946. [20] LIU M, ZHANG L, ZHAO Q, et al. Lower-molecular-weight chitosan-treated polyethyleneimine: a practical strategy for gene delivery to mesenchymal stem cells. cellular physiology and biochemistry. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(4):1255-1269. [21] ZHAO X, LI Z, PAN H, et al. Enhanced gene delivery by chitosan-disulfide-conjugated LMW-PEI for facilitating osteogenic differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(5):6694-6703. [22] HOSSEINPOUR S, CAO Y, LIU J, et al. Efficient transfection and long-term stability of Rno-miRNA-26a-5p for osteogenic differentiation by large pore sized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J Mater Chem. 2021; 9(9):2275-2284. [23] WANG Y, YOU C, WEI R, et al. Modification of human umbilical cord blood stem cells using polyethylenimine combined with modified TAT peptide to enhance BMP-2 production. BioMed Res Int. 2017; 2017:2971413. [24] ATLURI K, SEABOLD D, HONG L, et al. Nanoplex-mediated codelivery of fibroblast growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein genes promotes osteogenesis in human adipocyte-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Pharm. 2015;12(8):3032-3042. [25] ACRI T M, LAIRD NZ, GEARY SM, et al. Effects of calcium concentration on nonviral gene delivery to bone marrow-derived stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(12):2256-2265. [26] REZNIKOV N, BILTON M, LARI L, et al. Fractal-like hierarchical organization of bone begins at the nanoscale. Science. 2018;360(6388): eaao2189. [27] GUO R, CHEN S, XIAO X. Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylenimine) modified poly (l-Lactic acid) nanofibrous scaffolds. J Biomater Sci Polym. 2019;30(16):1523-1541. [28] GOREJOVÁ R, ORIŇAKOVÁ R, MACKO J, et al. Electrochemical Behavior, Biocompatibility and Mechanical Performance of Biodegradable Iron with PEI Coating. J Biomed. Mater Res A. 2022;110(3):659-671. [29] ZIMINSKA M, CHALANQUI MJ, CHAMBERS P, et al. Nanocomposite-coated porous templates for engineered bone scaffolds: a parametric study of layer-by-layer assembly conditions. Biomed Mater Bristol Engl. 2019;14(6):065008. [30] AGHAYAN M, ALIZADEH P, KESHAVARZ M. Multifunctional polyethylene imine hybrids decorated by silica bioactive glass with enhanced mechanical properties, antibacterial, and osteogenesis for bone repair. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;131:112534. [31] WANG X, LI Y, REN W, et al. PEI-Modified Diatomite/chitosan composites as bone tissue engineering scaffold for sustained release of BMP-2. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021;32(10):1337-1355. [32] STERZENBACH T, HELBIG R, HANNIG C, et al. Bioadhesion in the oral cavity and approaches for biofilm management by surface modifications. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24(12):4237-4260. [33] BEYTH N, YUDOVIN-FARBER I, BAHIR R, et al. Antibacterial activity of dental composites containing quaternary ammonium polyethylenimine nanoparticles against streptococcus mutans. Biomaterials. 2006;27(21): 3995-4002. [34] 朱敏闻,孙兵,李志耀,等.增强成骨及抗菌性能的鱼胶原/聚乙烯亚胺电纺膜用于牙周组织修复[J].组织工程与重建外科,2021, 17(2):102-107. [35] SUN Y, ZHAO YQ, ZENG Q, et al. Dual-functional implants with antibacterial and osteointegration-promoting performances. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(40):36449-36457. [36] BOULAND C, PHILIPPART P, DEQUANTER D, et al. Cross-talk between mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) in bone regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:674084. [37] LI Y, LIU Y, BAI H, et al. Sustained release of VEGF to promote angiogenesis and osteointegration of three-dimensional printed biomimetic titanium alloy implants. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9: 757767. [38] YANG YP, GADOMSKI BC, BRUYAS A, et al. Investigation of a prevascularized bone graft for large defects in the ovine tibia. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(23–24):1458-1469. [39] WANG XT, LIU PY, TANG JB. PDGF gene therapy enhances expression of VEGF and BFGF genes and activates the NF-κB gene in signal pathways in ischemic flaps. Plast. Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(1):129. [40] HADJIZADEH A. Acetaldehyde plasma polymer-coated PET fibers for endothelial cell patterning: chemical, topographical, and biological analysis. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;94(1):11-21. [41] GIGLIOBIANCO G, CHONG CK, MACNEIL S. Simple surface coating of electrospun Poly-L-Lactic acid scaffolds to induce angiogenesis. J Biomater Appl. 2015;30(1):50-60. [42] HUANG YC, SIMMONS C, KAIGLER D, et al. Bone regeneration in a rat cranial defect with delivery of PEI-condensed plasmid DNA encoding for bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4). Gene Ther. 2005;12(5): 418-426. [43] OU L, LAN Y, FENG Z, et al. Functionalization of SF/HAP scaffold with GO-PEI-MiRNA inhibitor complexes to enhance bone regeneration through activating transcription factor 4. Theranostics. 2019;9(15):4525-4541. [44] ELANGOVAN S, KHORSAND B, DO AV, et al. Chemically modified RNA activated matrices enhance bone regeneration. J Control Release. 2015;218:22-28. [45] TIERNEY EG, DUFFY GP, HIBBITTS AJ, et al. The development of non-viral gene-activated matrices for bone regeneration using polyethyleneimine (PEI) and collagen-based scaffolds. J Control Release Off J Control Release Soc. 2012;158(2):304-311. [46] KHORSAND B, ACRI TM, DO AV, et al. A multi-functional implant induces bone formation in a diabetic model. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020; 9(18):e2000770. [47] ACRI TM, LAIRD NZ, JAIDEV LR, et al. Nonviral gene delivery embedded in biomimetically mineralized matrices for bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(15-16):1074-1083. [48] LIANG Z, LUO Y, LV Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles mediate BMP2 gene delivery and enhance bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(30):6378-6389. [49] CHAKKA JL, ACRI T, LAIRD NZ, et al. Polydopamine functionalized VEGF gene-activated 3D printed scaffolds for bone regeneration. RSC Adv. 2021;11(22):13282-13291. [50] 刘锌,杜斌,孙光权,等.多孔β磷酸三钙-聚吡咯-生物素-淫羊藿素微球复合支架促进骨髓间充质干细胞的募集[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(34):5532-5537. [51] 向海滨,李新霞,梁求真,等.特异性骨靶向纳米递药系统的优势与临床可应用性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(4):612-618. [52] FORTE L, SARDA S, COMBES C, et al. Hydroxyapatite functionalization to trigger adsorption and release of risedronate. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;160:493-499. [53] PLESSELOVA S, GARCIA-CEREZO P, BLANCO V, et al. Polyethylenimine–bisphosphonate–cyclodextrin ternary conjugates: supramolecular systems for the delivery of antineoplastic drugs. J Med Chem. 2021; 64(16):12245-12260. [54] DUAN J, DONG J, ZHANG T, et al. Polyethyleneimine-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for systemic siRNA delivery in experimental arthritis. Nanomed. 2014;9(6):789-801. [55] GONG M, LIU H, SUN N, et al. Polyethylenimine-dextran-coated magnetic nanoparticles loaded with miR-302b suppress osteosarcoma in vitro and in vivo. Nanomed. 2020;15(7):711-723. [56] AEINEH N, SALEHI F, AKRAMI M, et al. Glutathione conjugated polyethylenimine on the surface of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as a theranostic agent for targeted and controlled curcumin delivery. J Biomater Sci Polym. 2018;29(10):1109-1125. [57] BRICOUT N, CHAI F, SOBOCINSKI J, et al. Immobilisation of an anti-platelet adhesion and anti-thrombotic drug (EP224283) on polydopamine coated vascular stent promoting anti-thrombogenic properties. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;113:110967. |
| [1] | Lu Di, Zhang Cheng, Duan Rongquan, Liu Zongxiang. Osteoinductive properties of calcium phosphate ceramic bone repair materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1103-1109. |
| [2] | Tang Haotian, Liao Rongdong, Tian Jing. Application and design of piezoelectric materials for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [3] | Xu Yan, Li Ping, Lai Chunhua, Zhu Peijun, Yang Shuo, Xu Shulan. Piezoelectric materials for vascularized bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [4] | Qin Yuxing, Ren Qiangui, Li Zilong, Quan Jiaxing, Shen Peifeng, Sun Tao, Wang Haoyu. Action mechanism and prospect of bone microvascular endothelial cells for treating femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 955-961. |
| [5] | Zhang Min, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin. Application potential of naringin in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 787-792. |
| [6] | Liu Huan, Li Han, Ma Yunhao, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu. Osteogenic capacity of partially demineralized dentin particles in the maxillary sinus lift [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 354-359. |
| [7] | Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440. |
| [8] | Zong Mingrui, Liu Haiyan, Li Bing, Wu Xiuping. Application of carboxymethyl chitosan in tissue engineering of stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 447-452. |
| [9] | Li Zhen, Liu Hongbao. Influencing factors and mechanism of nanoparticle renal targeting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 453-460. |
| [10] | Wei Tengfei, He Xiaoming, Wei Yurou, Zhan Zhiwei, He Mincong, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Differential expression of Piezo1 in osseous tissue of steroid- and alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 270-275. |
| [11] | Chen Feng, Ren Guowu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Shi Rusheng. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand signal transduction mechanism and osteoclast activation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 293-299. |
| [12] | Zhang Jie, Tian Ai. Advances in the signaling pathway of M2 macrophages involved in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 314-321. |
| [13] | Liang Hanying, Ma Yunhao, Li Han, Li Dongyang, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu. Osteogenic effects of partially demineralized autogenous dentin particles in implant site preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2488-2492. |
| [14] | Jia Yuanyuan, Duan Mianmian, Tang Zhenglong. Research and application of local drug delivery system in promoting fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2587-2594. |
| [15] | Lu Di, Wan Xinyu, Yang Jinxin, Ding Kexin, Zhang Cheng, Duan Rongquan, Liu Zongxiang. Preparation and osteoinductive properties of tricalcium phosphate ceramics with submicron topology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2473-2479. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||