Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (20): 3121-3126.doi: 10.12307/2022.608
Previous Articles Next Articles
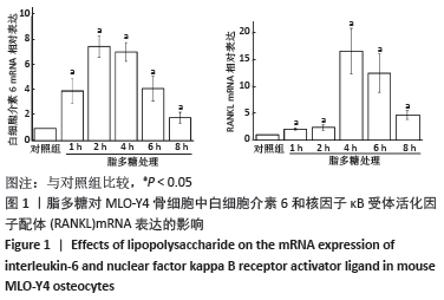
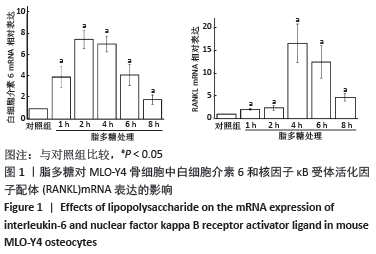
Lipopolysaccharide stimulates the expression of interleukin-6 and nuclear factor kappa B receptor activator ligand in mouse MLO-Y4 osteoblasts
Liu Qiqi1, Liu Min2, Yang Jian1, Yu Ke1
- 1Department of Oral Implantology, 2Department of Prosthodontics, School/Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-07-06Accepted:2021-08-19Online:2022-07-18Published:2022-01-18 -
Contact:Yu Ke, MD, Associate professor, Department of Oral Implantology, School/Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Liu Qiqi, Master candidate, Department of Oral Implantology, School/Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the 2017 Scientific Research Plan of the Educational Department of Sichuan Province, No. 17ZB0481 (to YK); Western Stomatology Clinical Research Fund of Chinese Stomatological Association, No. CSA-W2018-03 (to YK); the Luzhou Municipal People’s Government - Southwest Medical University Strategic Cooperation Project, No. 2020LZXNYDJ31 (to YK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Qiqi, Liu Min, Yang Jian, Yu Ke. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates the expression of interleukin-6 and nuclear factor kappa B receptor activator ligand in mouse MLO-Y4 osteoblasts[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3121-3126.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
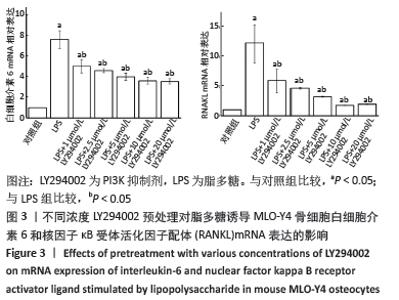
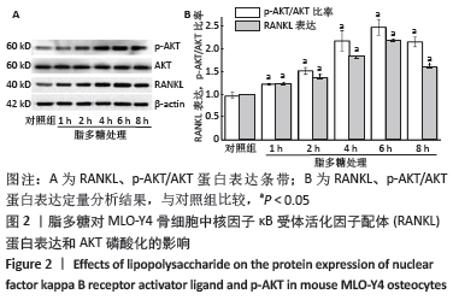
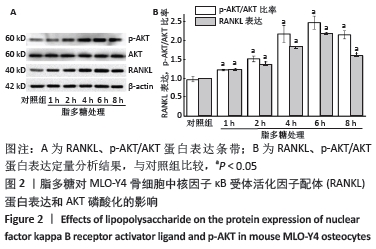
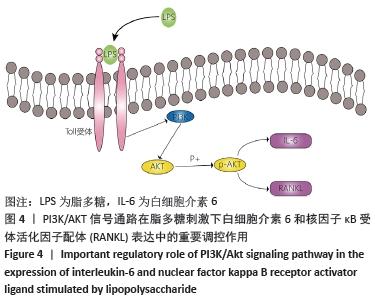
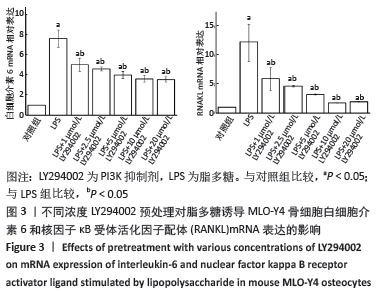
由于AKT磷酸化激活PI3K/AKT信号途径,实验分析p-AKT/AKT蛋白比率以确定PI3K/AKT在脂多糖刺激白细胞介素6和RANKL表达中的作用。与对照组比较,脂多糖处理1 h后的p-AKT/AKT蛋白比率增加(P < 0.05),6 h后的p-AKT/AKT蛋白比率显著高于其他时间点(P < 0.05),然后p-AKT/AKT蛋白比率下降,各时间点间两两比较均差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图2。 2.3 PI3K抑制剂降低脂多糖诱导的骨细胞白细胞介素6和RANKL mRNA表达 与对照组比较,脂多糖处理后骨细胞的白细胞介素6和RANKL mRNA表达显著升高(P < 0.05)。与单独脂多糖处理比较,不同浓度的LY294002预处理+脂多糖处理组骨细胞的白细胞介素6和RANKL mRNA表达显著降低(P < 0.05);其中10 μmol/L LY294002预处理+脂多糖处理组与20 μmol/L LY294002预处理+脂多糖处理组骨细胞的白细胞介素6和RANKL mRNA表达比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但均低于其他浓度LY294002预处理+脂多糖处理组(P < 0.05),见图3。"
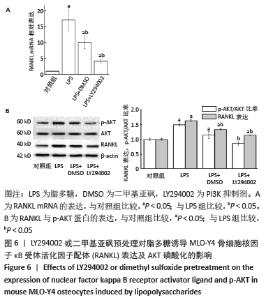
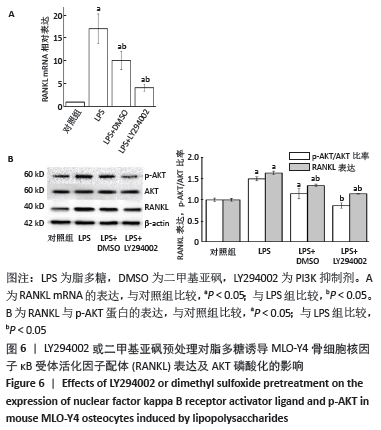
2.5 LY294002或二甲基亚砜对脂多糖诱导骨细胞RANKL表达与AKT磷酸化的影响 与对照组比较,脂多糖组骨细胞的RANKL mRNA和蛋白表达显著升高(P < 0.05),p-AKT蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05)。与脂多糖组比较,二甲基亚砜组骨细胞的RANKL mRNA和蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05),p-AKT蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05),但是并未降到对照组的水平,与对照组比较差异仍有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明二甲基亚砜部分阻断了PI3K/AKT信号通路。与脂多糖组比较,LY294002组骨细胞的RANKL mRNA和蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05),p-AKT蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05),但是RANKL表达并未降到对照组的水平,与对照组比较差异仍有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明10 μmol/L的LY294002可完全抑制AKT的磷酸化,但不能完全阻断脂多糖诱导的RANKL表达,见图6。 "
| [1] BRONZATO JD, DAVIDIAN MES, DE CASTRO M, et al. Bacteria and virulence factors in periapical lesions associated with teeth following primary and secondary root canal treatment. Int Endod J. 2021;54(5):660-671. [2] 刘大勇,王梅蕊,兰玲玲,等.脂多糖干预卵巢切除小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(14):2219-2225. [3] 余科,吴湘楠,刘文佳,等. LPS刺激小鼠骨细胞RANKL/OPG和IL-6表达的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2016(3):220-223. [4] YU K, MA Y, LI X, et al. Lipopolysaccharide increases IL-6 secretion via activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway to up-regulate RANKL gene expression in MLO-Y4 cells. Cell Biol Int. 2017;41(1):84-92. [5] GALARRAGA-VINUEZA ME, DOHLE E, RAMANAUSKAITE A, et al. Anti-inflammatory and macrophage polarization effects of Cranberry Proanthocyanidins (PACs) for periodontal and peri-implant disease therapy. J Periodontal Res. 2020;55(6):821-829. [6] LI G, LIU Y, MENG F, et al. LncRNA MEG3 inhibits rheumatoid arthritis through miR-141 and inactivation of AKT/mTOR signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2019; 23(10):7116-7120. [7] ZHAO X, ALQWBANI M, LUO Y, et al. Glucocorticoids decreased Cx43 expression in osteonecrosis of femoral head: The effect on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat BMSCs. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(1):484-498. [8] KITAURA H, MARAHLEH A, OHORI F, et al. Osteocyte-Related Cytokines Regulate Osteoclast Formation and Bone Resorption. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):5169. [9] FENG W, GUO J, LI M. RANKL-independent modulation of osteoclastogenesis. J Oral Biosci. 2019;61(1):16-21. [10] AMIN N, BOCCARDI V, TAGHIZADEH M, et al. Probiotics and bone disorders: the role of RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32(3):363-371. [11] Martin TJ, Sims NA. RANKL/OPG; Critical role in bone physiology. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2015;16(2):131-139. [12] JIANG J, JIA Y, LU X, et al. Vitexin suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced osteolysis. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(10):17549-17560. [13] FANG L, WANG KK, HUANG Q, et al. Nucleolin Mediates LPS-induced Expression of Inflammatory Mediators and Activation of Signaling Pathways. Curr Med Sci. 2020;40(4):646-653. [14] CHAE BS. Pretreatment of Low-Dose and Super-Low-Dose LPS on the Production of In Vitro LPS-Induced Inflammatory Mediators. Toxicol Res. 2018;34(1):65-73. [15] LEE GL, YEH CC, WU JY, et al. TLR2 Promotes Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Chondrogenic Differentiation and Consequent Calcification via the Concerted Actions of Osteoprotegerin Suppression and IL-6-Mediated RANKL Induction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(3):432-445. [16] KIM HJ, KIM HJ, CHOI Y, et al. Zoledronate Enhances Osteocyte-Mediated Osteoclast Differentiation by IL-6/RANKL Axis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(6):1467. [17] MCGREGOR NE, MURAT M, ELANGO J, et al. IL-6 exhibits both cis- and trans-signaling in osteocytes and osteoblasts, but only trans-signaling promotes bone formation and osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(19):7850-7863. [18] BEZERRA MÉS, BARBERINO RS, MENEZES VG, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) promotes primordial follicle growth and reduces DNA fragmentation through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) signalling pathway. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2018;30(11):1503-1513. [19] DENG S, DAI G, CHEN S, et al. Dexamethasone induces osteoblast apoptosis through ROS-PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:602-608. [20] MA Y, RAN D, ZHAO H, et al. Cadmium exposure triggers osteoporosis in duck via P2X7/PI3K/AKT-mediated osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. Sci Total Environ. 2021;750:141638. [21] DA Y, MOU Y, WANG M, et al. Mechanical stress promotes biological functions of C2C12 myoblasts by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(1):470-477. [22] SONG F, WANG Y, JIANG D, et al. Cyclic Compressive Stress Regulates Apoptosis in Rat Osteoblasts: Involvement of PI3K/Akt and JNK MAPK Signaling Pathways. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0165845. [23] LI ST, DAI Q, ZHANG SX, et al. Ulinastatin attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting the JNK/NF-κB signaling pathway and activating the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018; 39(8):1294-1304. [24] ZHONG Z, CHEN A, FA Z, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells upregulate PI3K/AKT pathway and down-regulate NF-κB pathway by secreting glial cell-derived neurotrophic factors to regulate microglial polarization and alleviate deafferentation pain in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2020;143:104945. [25] PROSSOMARITI A, PIAZZI G, ALQUATI C, et al. Are Wnt/β-Catenin and PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 Distinct Pathways in Colorectal Cancer? Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;10(3):491-506. [26] YAN L, LU L, HU F, et al. Piceatannol attenuates RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by suppressing MAPK, NF-κB and AKT signalling pathways and promotes Caspase3-mediated apoptosis of mature osteoclasts. R Soc Open Sci. 2019;6(6):190360. [27] BONEWALD LF. Establishment and characterization of an osteocyte-like cell line, MLO-Y4. J Bone Miner Metab. 1999;17(1): 61-65. [28] LIN CN, DING SJ, CHEN CC. Synergistic Photoantimicrobial Chemotherapy of Methylene Blue-Encapsulated Chitosan on Biofilm-Contaminated Titanium. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14(4):346. [29] DOUGALL WC, GLACCUM M, CHARRIER K, et al. RANK is essential for osteoclast and lymph node development. Genes Dev. 1999;13(18):2412-2424. [30] MARAHLEH A, KITAURA H, OHORI F, et al. TNF-α Directly Enhances Osteocyte RANKL Expression and Promotes Osteoclast Formation. Front Immunol. 2019;10: 2925. [31] KIM HN, XIONG J, MACLEOD RS, et al. Osteocyte RANKL is required for cortical bone loss with age and is induced by senescence. JCI Insight. 2020;5(19):e138815. [32] UCHIBORI S, SEKIYA T, SATO T, et al. Suppression of tooth movement-induced sclerostin expression using β-adrenergic receptor blockers. Oral Dis. 2020;26(3): 621-629. [33] ALQRANEI MS, CHELLAIAH MA. Osteoclastogenesis in periodontal diseases: Possible mediators and mechanisms. J Oral Biosci. 2020;62(2):123-130. [34] TERAMACHI J, INAGAKI Y, SHINOHARA H, et al. PKR regulates LPS-induced osteoclast formation and bone destruction in vitro and in vivo. Oral Dis. 2017; 23(2):181-188. [35] MENDOZA MC, ER EE, BLENIS J. The Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: cross-talk and compensation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011;36(6):320-328. [36] EVANGELISTI C, CHIARINI F, CAPPELLINI A, et al. Targeting Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(6):5413-5428. [37] DE SANTIS MC, GULLUNI F, CAMPA CC, et al. Targeting PI3K signaling in cancer: Challenges and advances. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019;1871(2):361-366. [38] JOHNSON GE, IVANOV VN, HEI TK. Radiosensitization of melanoma cells through combined inhibition of protein regulators of cell survival. Apoptosis. 2008;13(6):790-802. [39] XIE Y, SHI X, SHENG K, et al. PI3K/Akt signaling transduction pathway, erythropoiesis and glycolysis in hypoxia (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(2):783-791. [40] SUN K, LUO J, GUO J, et al. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(4):400-409. [41] MANNING BD, TOKER A. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network. Cell. 2017; 169(3):381-405. [42] CHEN H, ZHOU L, WU X, et al. The PI3K/AKT pathway in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016;21:1084-1091. [43] BAI L, GAO J, WEI F, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Ginsenosides as an Adjuvant Treatment for Diabetes. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:423. [44] HOARE A, SOTO C, ROJAS-CELIS V, et al. Chronic Inflammation as a Link between Periodontitis and Carcinogenesis. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019:1029857. |
| [1] | Li Weiming, Xu Qingwen, Li Yijun, Sun Yanbo, Cui Jin, Xu Pengyuan . Deep seawater promotes wound healing in diabetic mice by activating PI3K/Akt pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 724-729. |
| [2] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [3] | Wei Zhoudan, Li Wenjin, Zhu Li, Wang Yu, Zhao Jiaoyang, Chen Yanan, Guo Dong, Hao Min. Platelet-rich fibrin as a material for alveolar ridge preservation significantly reduces the resorption of alveolar bone height and width after tooth extraction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 643-648. |
| [4] | Mi Jianguo, Qiao Rongqin, Liu Shaojin. Bushen Jianpi Huoxue Recipe improves bone metabolism, oxidative stress, and autophagy in osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4147-4152. |
| [5] | Yan Nan, Wu Yanlong, Tang Xiaohui, Zhang Xiaoyan, Wang Hui, Yang Tianze, Zhou Maochun, Wang Zhengdong, Yang Xiaoxia. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells may alleviate brain damage caused by the microglial overactivation in the cortex around ischemic site of stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3790-3795. |
| [6] | Yang Ruijuan, Li Yangyang, Cai Ruiyan, Liu Huibin, Guo Chun. Interleukin-1 alpha induces osteoclast activation and bone loss [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3691-3699. |
| [7] | Cai Zhiguo, Du Shasha, Yang Kun, Zhao Na, Liu Qi. Lipopolysaccharides mediate autophagy of mouse insulinoma βtc6 cells in high glucose state [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3127-3132. |
| [8] | Sun Youqiang, Ma Chao, Liang Mengmeng, Xin Pengfei, Zhang Hua, Xiang Xiaobing. The pivotal role of autophagy in bone cells: bone-related cell activity and bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 276-282. |
| [9] | Li Kun, An Jie, Dong Suge, Cui Lili, Liu Lei, Li Tingting. Effects of different fimA genotypes of Porphyromonas gingivalis on the secretion related proteins and cytokines in human umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3043-3047. |
| [10] | Yang Qin, Wang Min. Constructing a mouse model of periodontitis with occlusal trauma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2667-2672. |
| [11] | Zhang Shuling, Li Junhan, Wang Jiaqian, Li Yalong, Wang Chun. Effects of aerobic exercises on JAK2/STAT5 signal pathway in the liver of mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2690-2695. |
| [12] | Li Jianan, Lin Fengsong, Bu Guoyun, Yang Tao, Wei Wanfu. Complications of reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: periprosthetic bone resorption and aseptic prosthesis loosening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2432-2438. |
| [13] | Sun Haitao, Huang Yonghui, Gong Aihua, Cao Xingbing, Li Zhen. Protective effect of lipopolysaccharide-preconditioned astrocyte extracellular vesicles on neurons [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 1985-1992. |
| [14] | Li Min, Yu Yang, Cheng Jiyan. Mechanism of paeoniflorin on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells intervened by lipopolysaccharide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 2000-2005. |
| [15] | Shan Wen, Shi Wei. Expression and function of colony-stimulating factor 1 in differentiation of neural stem cells induced by activated astrocyte conditioned medium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 2069-2074. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||