Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (15): 2432-2438.doi: 10.12307/2022.603
Previous Articles Next Articles
Complications of reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: periprosthetic bone resorption and aseptic prosthesis loosening
Li Jianan, Lin Fengsong, Bu Guoyun, Yang Tao, Wei Wanfu
- Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300202, China
-
Received:2021-07-26Revised:2021-09-14Accepted:2021-10-26Online:2022-05-28Published:2022-01-07 -
Contact:Wei Wanfu, MD, Chief physician, Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300202, China -
About author:Li Jianan, MD, Attending physician, Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300202, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jianan, Lin Fengsong, Bu Guoyun, Yang Tao, Wei Wanfu. Complications of reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: periprosthetic bone resorption and aseptic prosthesis loosening[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2432-2438.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
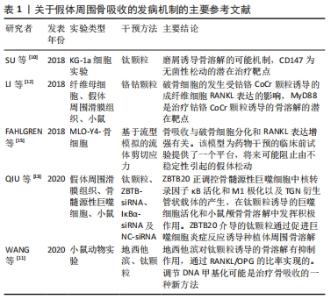
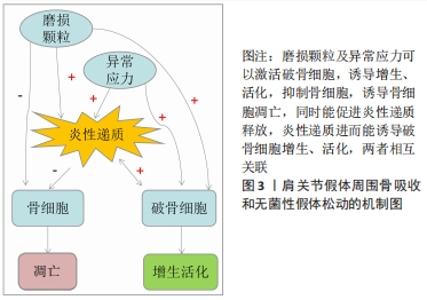
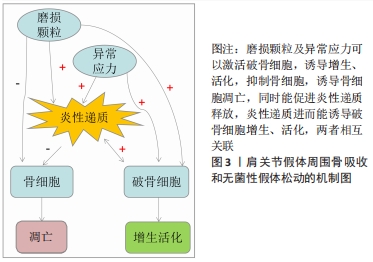
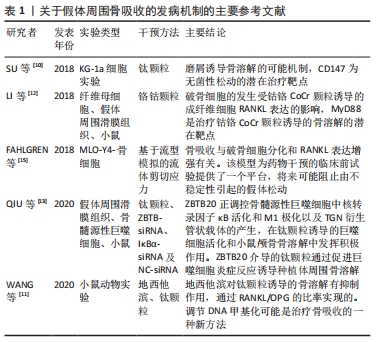
2.1.1 磨损颗粒诱发假体周围骨吸收和无菌性假体松动 磨损颗粒刺激破骨细胞聚集增生,进而出现骨溶解和骨质疏松。磨损颗粒可以诱导假体周围炎性反应、破坏破骨细胞和成骨细胞平衡,主要通过骨保护素(osteoprotegerin,OPG)/核转录因子κB受体激活剂配体 (receptor activator of NF-κB ligand,RANKL)/ 核转录因子κB受体激活剂(receptor activator of NF-κB,RANK)信号通路或者CD147激活破骨细胞[10]。主要的磨损颗粒有聚乙烯、骨、水泥、金属、金属腐蚀产物或羟基磷灰石颗粒,其中以聚乙烯材料最为常见。颗粒的形状、材质、数量和大小明显影响炎性反应的严重程度。有基础实验通过DNA甲基化证实抑制RANKL/OPG比率可以抑制假体周围骨吸收[11]。有研究表明抑制成纤维细胞RANKL表达可以MyD88非依赖性TLR信号通路减轻钴铬颗粒诱导的骨吸收[12]。有研究表明钛合金磨损颗粒通过ZBTB20介导促进巨噬细胞炎症反应进而导致假体周围骨溶解,其实验结果表明假体松动患者滑膜与钛颗粒刺激的骨髓源性巨噬细胞具有明显ZBTB20表达,通过ZBTB20基因敲除可以抑制骨髓源性巨噬细胞促炎因子(如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6及干扰素β)的表达,也可以抑制钛颗粒诱导的核转录κB激活和M1极化,在体内实验通过ZBTB20慢病毒注射,可以减少钛颗粒诱导的小鼠颅骨溶解,抑制钛颗粒诱导的促炎因子和骨体积及骨密度[13]。 2.1.2 假体周围应力不均诱发假体周围骨吸收和无菌性假体松动 假体周围应力分布不均,应力遮挡在中远期较常见,并且因假体不同而不同。非应力区域因能量区域限制导致骨吸收,应力集中区域则出现应力性骨适应[14]。假体与周围骨之间的微小缝隙较之紧密结合能产生更大的剪切应力,对成骨细胞和破骨细胞平衡的破坏更大,假体周围压力性液体流动能激活破骨细胞,促进骨吸收[15]。 2.1.3 假体周围炎性反应诱发假体周围骨吸收和无菌性假体松动 一项针对假体周围骨吸收基因表达的综述分析纳入32项体外实验、16项体内实验和6项临床试验,结果提示主要的差异基因为白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、核转录因子κB、活化T细胞的核因子NFATC1(nuclear factor of activated T cells c1)、半胱氨酸蛋白酶组织蛋白酶 K (Cysteine protease cathepsin K,CATK)及抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶(tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase,TRAP)[16]。假体周围细胞自噬可能是参与假体周围骨吸收的机制,自噬是一种允许受损物质降解的细胞清洁过程,可在各种应激下上调,除了自噬在降解途径中的经典作用外,自噬还可能参与某些分泌过程。磨损碎片导致自噬的3种主要细胞类型有骨细胞、成骨细胞和巨噬细胞。自噬可介导促炎细胞因子的分泌,如白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8或危险信号蛋白[17]。研究显示通过阻断白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和(或)肿瘤坏死因子α信号通路,可以有效缓解假体周围磨损颗粒导致的炎性反应和骨吸收[18]。 表1简要介绍关于假体周围骨吸收的发病机制的主要参考文献,金属磨损颗粒能诱导骨吸收,诱导假体周围炎性反应、破坏破骨细胞和成骨细胞平衡,主要通过OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路假体周围压力性液体流动能激活破骨细胞,促进骨吸收。"
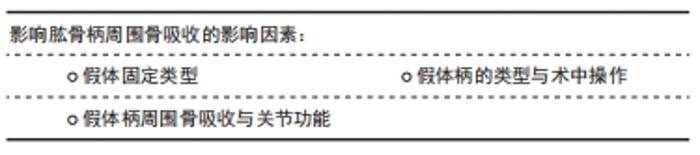
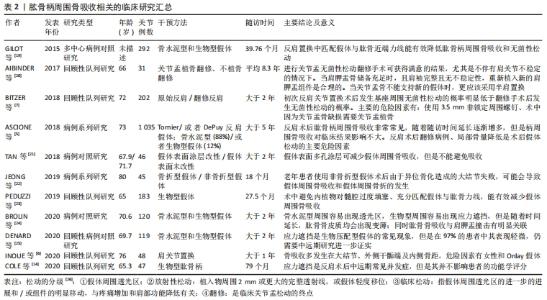
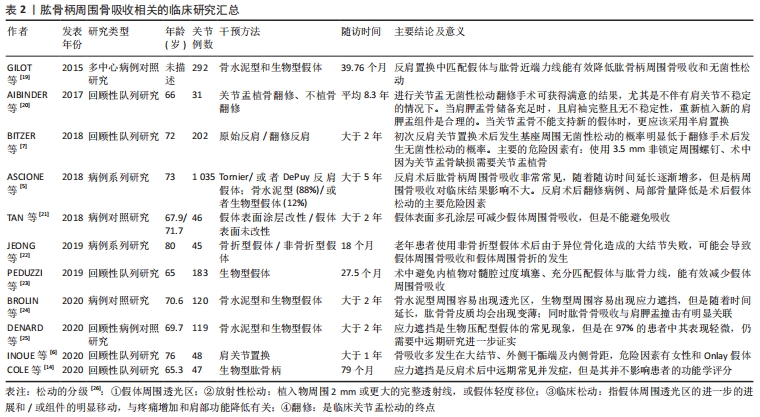
骨吸收的量化指标因假体类型不同而不同:骨水泥型假体周围骨吸收主要通过肩关节前后位片上,上1/3和下1/3处骨皮质的厚度测量来进行测算[27];非骨水泥型假体周围骨吸收采用肩关节前后位片髓腔填充率来评估,即髓腔最狭窄部位假体直径与髓腔内径的比值[6];或者骨皮质的厚度与健侧的比值[28]。肱骨端假体置换后松动的主要影像学表现为:假体下陷、皮质扇形缺损、假体周围透光区形成和远端假体周围的骨性阻挡形成。骨缺损评估有多种,其中经典评分为:①Ⅰ型表现为肱骨干骺端骨丢失,包括关节面、大小结节和内侧骨距;Ⅰ型可以细分为1C型和1G型,1C型表示内侧骨距缺失,1G型表示大结节缺失或畸形愈合,Ⅰ型约占31%的患者。②Ⅱ型表现为骨干骨量丢失,定位于三角肌附着体附近的骨。细分类型ⅡA是指骨干的皮质变薄超过皮质厚度的50%,该厚度根据肱骨健侧相应位置的骨皮质厚度确定。ⅡB型患者三角肌近端骨干和骨骺均出现骨质丢失。③Ⅲ型表现为延伸至三角肌附着体下方的骨干骨丢失。ⅢA型的骨干皮质变薄超过预期皮质厚度的50%,而ⅢB型的骨干大部分受损,同时伴有骨骺和干骺骨骨吸收[29]。该分型也可以用于指导临床,Ⅰ型的骨缺损长度一般在130 mm内,Ⅱ型缺损在150 mm内,Ⅲ型在190 mm内,Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型一般需要肱骨近端植骨、大结节重建,而Ⅲ型则需要更换全肱骨假体。 肱骨柄周围骨吸收主要的危险因素:患者因素如患者性别、骨密度、继发于骨性关节炎及伴有肩袖损伤;基础病如肱骨近端恶性肿瘤;初次手术或者翻修手术;假体因素如假体柄的长短、骨水泥型或者生物型、假体直径及形态;术中操作因素如手术入路(三角肌间隙入路更容易发生骨吸收),假体与肱骨干的匹配程度[30]。 2.2.1 假体固定类型 骨水泥型假体和非骨水泥型假体均会发生周围骨吸收,多数学者认为非骨水泥型假体更容易出现假体松动。INOUE等[6]回顾性研究48例生物型假体周围骨吸收,结果提示假体周围骨吸收率达83.3%,相关性分析认为主要的危险因素为女性骨质疏松患者和生物型假体。BROLIN等[24]研究骨水泥型和非骨水泥型反肩关节置换后肱骨柄周围骨吸收影像学资料,经过平均35.2个月随访,提示骨水泥型更易于出现骨吸收,而非骨水泥型更容易出现应力遮挡,无论哪种方式,肱骨骨皮质随着时间延长均逐渐变薄,肱骨假体周围骨吸收与肩胛颈切割无明显关联。DENARD等[25]对93例生物柄和26例骨水泥柄反肩手术患者行2年随访,结果提示2种假体周围骨吸收率无显著性差异。GREY等[4]通过中远期随访认为,骨水泥型和非骨水泥型假体置换在置换后假体松动和翻修率方面无明显差异,置换后假体松动主要在肿瘤切除后假体置换及半肩关节术失败翻修病例中多见。也有研究认为生物型假体可能具有更低的假体松动率[19]。 2.2.2 假体柄的类型与术中操作 肱骨柄假体的类型及手术操作对假体周围骨吸收产生影响。短柄非骨水泥型假体作为传统假体类型的改良,有广泛应用前景。PEDUZZI等[23]对其假体周围骨适应进行回顾性分析,结果提示假体周围骨适应是一种常见现象,而这种适应与假体在肱骨内填塞比例及假体与肱骨干轴向匹配度有关,在肩关节前后位片上假体与肱骨干轴线平行则可以形成合适的颈干角,内翻成角或者外翻成角则更容易出现骨吸收。尽管增加假体直径能增加假体的力矩及匹配度,多数学者认为增大的直径能增加假体的应力遮挡,进而促进假体周围骨吸收。有学者研究短柄假体近端覆盖多孔钛质涂层对肱骨应力遮挡及骨吸收的影响,结果提示表面多孔涂层能减缓内侧骨距皮质的吸收,但是不能完全抑制其吸收[21]。骨折专用假体比传统假体更有利于大结节的愈合,JEONG等[22]研究发现骨折专用假体与传统型假体在置换后功能及放射学参数方面无明显差异,但是对于老年患者使用传统假体出现大结节不愈合导致的异位骨化可能更容易发生假体松动和假体周围骨折。 2.2.3 假体柄周围骨吸收与关节功能 ASCIONE等[5]通过中长期随访发现肱骨柄周围松动的发生对肩关节功能并无明显影响。肩关节置换再翻修置换后(半肩、全肩及反肩)、肱骨近端肿瘤是发生假体周围骨吸收的重要影响因素。尽管有研究认为假体周围骨吸收对肩关节功能无明显影响,因为反肩关节置换后肩关节功能主要依赖于三角肌产生力矩,如果在较大的结节处有明显的骨吸收,则三角肌包裹的作用将减弱,并且在反肩关节置换后后可能发生不稳定[6]。同时,假体周围骨吸收,也增加了置换后翻修的难度,翻修常需要使用更长的假体[5],见表2。 2.3 肩胛盂基座周围骨吸收 关节盂假体组件无菌性松动是反肩关节置换后翻修的重要指证。翻修的方案有:若关节盂有足够骨量,能为假体基座提供足够把持力,则选用关节盂假体基座重新放置;若关节盂骨量不足以维持基座的稳定,则去除基座,并行关节盂植骨、半肩关节置换[20]。"
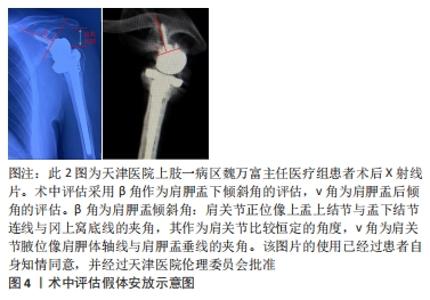
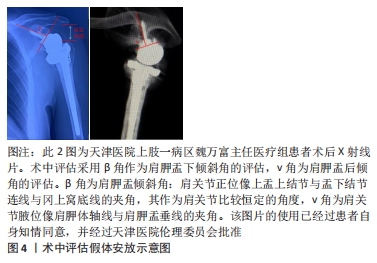
2.3.1 基座松动的影响因素 假体基座松动主要影响因素有:原有肩胛盂缺损、骨质欠佳,需要植骨的病例更容易出现假体松动[7];手术因素:如假体组件安置失误、假体型号不匹配、静息状态下的盂肱关节半脱位及肩袖状态失平衡[26-31]。半肩关节置换后失败行反肩关节置换翻修,更容易出现肩胛盂假体松动及失稳[7]。 2.3.2 基座松动的分级 基座松动可以分为4级[26]:①假体周围透光区:骨水泥界面处的大多数透射线从置换后第1天开始出现,并非植入物的失败,一般不具有临床意义。文献中报告的发病率为30%-96%。②放射性松动:发生率0%-44%,定义为透射线的增加,植入物周围2 mm或更大的完整透射线,或假体轻度移位。③临床松动:指假体周围透光区的进一步的进展和/或组件的明显移动,与疼痛增加和肩部功能降低有关。随着5年或更长时间的随访,临床松动的进展明显增加。④翻修:是临床关节盂松动的终点。在长期随访(10-15年)中,8%-10%的结果是松动植入物的实际修复结果。 2.3.3 基座的倾斜角度与基座松动 肩胛盂的倾斜角度和后倾角度过大,更容易导致假体周围骨质吸收。肩胛盂部件松动的主要原因为盂肱关节周围生物力学偏差,盂肱关节周围肌肉有两个力偶构成肩关节的主要稳定结构:横向力偶(由旋转中心前方的肩胛下肌与后方的冈下肌、小圆肌构成)和冠向力偶(由旋转中心近端的三角肌与远端的肩胛下肌、冈下肌、小圆肌构成),盂肱关节周围力学分布不均将导致假体出现松动[8]。盂肱关节前倾角度每向前或后偏移1°,可以造成旋转中心向前或者向后位移0.5 mm,盂肱关节前倾角度的变化,不仅影响关节的稳定性,也会导致假体周围骨折的发生[32]。前后倾斜角度每增大10°,出现假体周围骨吸收的风险增加6.2倍,因为增大的倾斜角度将增加三角肌张力,进而导致肱骨上移、肩胛盂上缘及假体周围骨应力增加,增加骨吸收风险。因此,在术前设计时应该充分了解肩胛盂的倾斜角度[33],术中操作中应该采用相应的假体去纠正肩胛盂不合理的倾斜角度,术前后倾角度及术中是否矫正对假体松动会产生影响[34]。 然而,有一项分析了健康、矫正骨性关节炎和后倾关节炎关节盂间负荷分配改变的有限元分析,结果提示矫正的关节盂的后倾实际上可能增加应力遮挡和骨水泥失败的风险,并且骨性关节炎患者可以容纳较短的周围钉,因为骨性关节炎患者关节盂骨硬度较高[35]。研究表明,术中维持肩胛盂组件的中型或者轻度下倾可以降低关节盂骨性终板的剪切力,进而减少假体松动的发生概率[36]。随访时使用β角、v角、肱骨外侧偏移、肩肱间隙这4个指标的变化评估假体松动[34]。术中评估采用β角作为肩胛盂下倾斜角的评估,v角为肩胛盂后倾角的评估。β角为肩胛盂倾斜角:肩关节正位像上盂上结节与盂下结节连线与冈上窝底线的夹角,其作为肩关节比较恒定的角度,v角为肩关节腋位像肩胛体轴线与肩胛盂垂线的夹角,见图4 [37]。"

对于B型和C型肩胛盂,在一期手术时,采用矫正角度的基座能纠正肩胛盂的后倾,文献报道8°后部增厚底座,能有效提高肱盂关节匹配程度,减少假体松动的发生[39]。 为评估肩胛盂的缺损程度,也有学者提出采用检测三维CT参数作为标准,结合患侧三维重建CT,计算患侧肩胛盂缺损。PLESSERS等[40]提出基于肩胛骨形态统计学参数拟合构建肩胛骨模型,通过患肩肩胛骨三维CT结果与拟合构建模型进行对比,确认肩胛盂缺损程度(缺损的面积、深度及半脱位的距离及部位),而无需加测健侧三维CT。GUPTA等[41]将关节盂缺损分为中央型(C型)和周围型(E型),其中以周围型多见,治疗的决策因缺损的程度及缺损区域的骨密度而不同。C1型为缺损深度小于关节盂前后直径的50%;C2型为缺损深度大于关节盂前后直径的50%,且两侧弧线壁是稳定的;C3型为空洞型,两侧弧线臂不稳定的C2;C4型为破坏性,关节盂严重破坏。E1型为轻度缺损;E2型为中度缺损,有小于30%骨量缺损;E3型为大块缺损,缺损量在30%-60%之间;E4型为大部分缺损,缺损量大于60%。 关节盂植骨是弥补局部骨缺损、增加局部骨量并减少假体松动的有效方式,一期手术植骨也使后期翻修手术变得更容易。植骨可以采用同种异体松质骨植骨、自体肱骨内松质骨植骨等[42]。 多数的骨缺损可以通过植骨及正常长度基座一期手术而不产生松动,少数需要加长中心基座[41]。对于严重缺损的病例,有文献推荐使用个性化定制假体[43]。 2.3.5 基座类型、固定方式与基座松动 一项骨水泥型假体置换后力学载荷分析结果提示肩关节置换后载荷传递方式发生改变,偏心的固定以及异常的应力分布可导致假体周围骨质变化,从而引发骨吸收的发生[44]。肩胛盂假体在关节盂安置的中心化更能减少假体松动概率,假体的厚度,周围钉的数量、直径及长度均会影响假体的松动[26]。基座中心钉的长度、周围螺钉的长度及肩胛盂骨密度,相对而言,周围螺钉的角度、2枚或者4枚周围螺钉对假体松动影响并不占主要因素[30]。其他因素还有周围螺钉为非锁定螺钉,其中以3.5 mm非锁定螺钉为著[7]。在肩关节外展时,下位的周围螺钉对假体的松动的预防作用更强[30]。弧背型假体置换后发生假体松动的概率更低,因为弧背型假体与骨面成弧形接触,应力方向为垂直压缩应力,而非水平剪切,从而避免边缘处的应力集中[26]。研究显示骨水泥型基座在关节盂骨量降低到95%开始出现假体微动,而生物型假体则在关节盂骨量降低到97%时即出现微动[45]。 2.3.6 假体表面改性与假体松动 RIVERA等[46]将地塞米松与羧基官能化TiO2颗粒结合获得洗脱表面,通过地塞米松缓慢释放缓解假体周围骨质吸收,并且地塞米松的释放是周围软组织环境的pH值依赖性的。也有学者使用含有地塞米的纳米钛颗粒涂层采用逐层沉淀的方式进行假体骨界面改良,取得良好的防治假体周围骨吸收的效果[47]。 2.3.7 影响假体周围骨吸收的其他因素 一项有限元分析结果提示骨量较低、受力方向与骨小梁方向差异性高的更容易达到预设值,因此对于骨质疏松患者更容易导致假体周围骨吸收[48]。假体周围骨吸收与肩胛盂骨密度呈明显负相关,尤其是软骨下骨的骨密度值[49]。研究认为骨质疏松症是肩关节置换后假体周围骨折和假体松动的一个重要独立危险因素,并建议对于骨质疏松患者术前应该详细向患者告知这2项并发症的可能[50]。 然而,MARIAUX等[31]对2002-2014年行肩关节CT和反肩关节置换的93例患者进行超过2年的回顾性分析,使用双光子和Q-CT作为骨密度的评价指标,结果提示术前关节盂骨密度降低与置换后假体周围骨质吸收并无明显关联,作者认为假体松动常见时间为5-10年,可能与随访时间、样本量所造成的偏倚有关。一项针对维生素D缺乏的病例对照研究,研究纳入1 674例患者,按1∶3配比纳入5 022例对照者,结果提示维生素D缺乏与肩关节置换后假体松动、假体周围骨折、感染及置换后翻修有明显关联[51]。 WANG等[52]综合唑来膦酸与特立帕肽分别在抑制破骨细胞、激活成骨细胞方面的作用,并在动物实验中证实两种药物的应用能有效降低假体周围骨质吸收,并且二者具有协同作用,当然联合应用的安全性和可行性仍然需要临床试验进一步证实。置换后软组织平衡能维持肱盂关节旋转中心对应,减少不合理应力分布[53]。"

| [1] MCLEAN AS, PRICE N, GRAVES S, et al. Nationwide trends in management of proximal humeral fractures: an analysis of 77,966 cases from 2008 to 2017. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(11):2072-2078. [2] KLUG A A-O, GRAMLICH Y, WINCHERINGER D, et al. Trends in surgical management of proximal humeral fractures in adults: a nationwide study of records in Germany from 2007 to 2016. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019; 139(12):1713-1721. [3] CHALMERS PN, BOILEAU P, ROMEO AA, et al. Revision reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(12):426-436. [4] GREY B, RODSETH RN, ROCHE SJ. Humeral stem loosening following reverse shoulder arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JBJS Rev. 2018;6(5):e5. [5] ASCIONE F, DOMOS P, GUARRELLA V, et al. Long-term humeral complications after Grammont-style reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(6):1065-1071. [6] INOUE K, SUENAGA N, OIZUMI N, et al. Humeral bone resorption after reverse shoulder arthroplasty using uncemented stem. JSES Int. 2020;4(1): 138-143. [7] BITZER A, ROJAS J, PATTEN IS, et al. Incidence and risk factors for aseptic baseplate loosening of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(12):2145-2152. [8] KARELSE A, VAN TONGEL A, VAN ISACKER T, et al. Parameters influencing glenoid loosening. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2016;13(8):773-784. [9] MAGONE K, LUCKENBILL D, GOSWAMI T. Metal ions as inflammatory initiators of osteolysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(5):683-695. [10] SU B, LI D, XU J, et al. Wear particles enhance autophagy through up-regulation of CD147 to promote osteoclastogenesis. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018;21(8):806-812. [11] WANG Y, LIU H, WU J, et al. 5-Aza-2-deoxycytidine inhibits osteolysis induced by titanium particles by regulating RANKL/OPG ratio. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;529(3):629-634. [12] LI D, WANG H, LI Z, et al. The inhibition of RANKL expression in fibroblasts attenuate CoCr particles induced aseptic prosthesis loosening via the MyD88-independent TLR signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(2):1115-1122. [13] QIU J, PENG P, XIN M, et al. ZBTB20-mediated titanium particle-induced peri-implant osteolysis by promoting macrophage inflammatory responses. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(11):3147-3163. [14] COLE EW, MOULTON SG, GOBEZIE R, et al. Five-year radiographic evaluation of stress shielding with a press-fit standard length humeral stem. JSES Int. 2020;4(1):109-113. [15] FAHLGREN A, BRATENGEIER C, SEMEINS C M, et al. Supraphysiological loading induces osteocyte-mediated osteoclastogenesis in a novel in vitro model for bone implant loosening. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(5):1425-1434. [16] VERONESI F, TSCHON M, FINI M. Gene expression in osteolysis:review on the identification of altered molecular pathways in preclinical and clinical studies. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):499. [17] CAMUZARD O, BREUIL V, CARLE GF, et al. Autophagy involvement in aseptic loosening of arthroplasty components. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019; 101(5):466-472. [18] EGER M, HIRAM-BAB S, LIRON T, et al. Mechanism and prevention of titanium particle-induced inflammation and osteolysis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2963. [19] GILOT G, ALVAREZ-PINZON AM, WRIGHT TW, et al. The incidence of radiographic aseptic loosening of the humeral component in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(10):1555-1559. [20] AIBINDER WR, SCHOCH B, SCHLECK C, et al. Revisions for aseptic glenoid component loosening after anatomic shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(3):443-449. [21] TAN MT, READ JW, BOKOR DJ. Does proximal porous coating in short-stem humeral arthroplasty reduce stress shielding? Shoulder Elbow. 2019;11(2 Suppl):56-66. [22] JEONG JJ, KONG CG, PARK SE, et al. Non-fracture stem vs fracture stem of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty in complex proximal humeral fracture of asian elderly. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019;139(12):1649-1657. [23] PEDUZZI L, GOETZMANN T, WEIN F, et al. Proximal humeral bony adaptations with a short uncemented stem for shoulder arthroplasty:a quantitative analysis. JSES Open Access. 2019;3(4):278-286. [24] BROLIN TJ, COX RM, HORNEFF III JG, et al. Humeral-sided radiographic changes following reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2020;8(1):50-57. [25] DENARD PJ, HAIDAMOUS G, GOBEZIE R, et al. Short-term evaluation of humeral stress shielding following reverse shoulder arthroplasty using press-fit fixation compared with cemented fixation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29(5):906-912. [26] GERALDES DM, HANSEN U, AMIS AA. Parametric analysis of glenoid implant design and fixation type. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(4):775-784. [27] SANCHEZ-SOTELO J, O’DRISCOLL SW, TORCHIA ME, et al. Radiographic assessment of cemented humeral components in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2001;10(6):526-531. [28] INOUE K, SUENAGA N, OIZUMI N, et al. Humeral bone resorption after anatomic shoulder arthroplasty using an uncemented stem. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(11):1984-1989. [29] KAHN T, CHALMERS PN. Proximal humeral bone loss in revision shoulder arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(1):87-95. [30] LUNG TS, CRUICKSHANK D, GRANT HJ, et al. Factors contributing to glenoid baseplate micromotion in reverse shoulder arthroplasty:a biomechanical study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(4):648-653. [31] MARIAUX S, OBRIST R, FARRON A, et al. Is preoperative glenoid bone mineral density associated with aseptic glenoid implant loosening in anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):49. [32] NYFFELER RW, SHEIKH R, ATKINSON TS, et al. Effects of glenoid component version on humeral head displacement and joint reaction forces:an experimental study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(5):625-629. [33] WATLING JP, SANCHEZ JE, HEILBRONER SP, et al. Glenoid component loosening associated with increased critical shoulder angle at midterm follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(3):449-454. [34] HO JC, THAKAR O, CHAN WW, et al. Early radiographic failure of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty with structural bone graft for glenoid bone loss. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29(3):550-560. [35] PATEL RJ, GULOTTA L, WRIGHT TM, et al. Effects of osteoarthritis on load transfer after cemented total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(3):407-415. [36] LAVER L, GARRIGUES GE. Avoiding superior tilt in reverse shoulder arthroplasty: a review of the literature and technical recommendations. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(10):1582-1590. [37] MAURER A, FUCENTESE SF, PFIRRMANN CW, et al. Assessment of glenoid inclination on routine clinical radiographs and computed tomography examinations of the shoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(8):1096-1103. [38] WALCH G, BADET R, BOULAHIA A, et al. Morphologic study of the glenoid in primary glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Arthroplasty. 1999;14(6):756-760. [39] VIRK M, YIP M, LIUZZA L, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes with a posteriorly augmented glenoid for Walch B2, B3, and C glenoids in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29(5):e196-e204. [40] PLESSERS K, VERHAEGEN F, VAN DIJCK C, et al. Automated quantification of glenoid bone defects using 3-dimensional measurements. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29(5):1050-1058. [41] GUPTA A, THUSSBAS C, KOCH M, et al. Management of glenoid bone defects with reverse shoulder arthroplasty-surgical technique and clinical outcomes. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(5):853-862. [42] MALAHIAS MA, CHYTAS D, KOSTRETZIS L, et al. Bone grafting in primary and revision reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for the management of glenoid bone loss:A systematic review. J Orthop. 2020;20:78-86. [43] DEBEER P, BERGHS B, POULIART N, et al. Treatment of severe glenoid deficiencies in reverse shoulder arthroplasty: the Glenius Glenoid Reconstruction System experience. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(8): 1601-1608. [44] PATEL RJ, WRIGHT TM, GAO Y. Load transfer after cemented total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(10):1553-1562. [45] VERHAEGEN F, CAMPOPIANO E, DEBEER P, et al. How much bone support does an anatomic glenoid component need? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020; 29(4):743-754. [46] RIVERA MC, PERNI S, SLOAN A, et al. Anti-inflammatory drug-eluting implant model system to prevent wear particle-induced periprosthetic osteolysis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:1069-1084. [47] ALOTAIBI HF, PERNI S, PROKOPOVICH P. Nanoparticle-based model of anti-inflammatory drug releasing LbL coatings for uncemented prosthesis aseptic loosening prevention. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:7309-7322. [48] CHEVALIER Y, SANTOS I, MüLLER PE, et al. Bone density and anisotropy affect periprosthetic cement and bone stresses after anatomical glenoid replacement:A micro finite element analysis. J Biomech. 2016;49(9):1724-1733. [49] TERRIER A, OBRIST R, BECCE F, et al. Cement stress predictions after anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty are correlated with preoperative glenoid bone quality. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(9):1644-1652. [50] CASP AJ, MONTGOMERY SR JR, CANCIENNE JM, et al. Osteoporosis and implant-related complications after anatomic and reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(3):121-127. [51] SMITH JM, CANCIENNE JM, BROCKMEIER SF, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and total shoulder arthroplasty complications. Shoulder Elbow. 2021;13(1):99-105. [52] WANG P, SHANG GQ, XIANG S, et al. Zoledronic acid and teriparatide have a complementary therapeutic effect on aseptic loosening in a rabbit model. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):580. [53] HSU JE, HACKETT DJ JR, VO KV, et al. What can be learned from an analysis of 215 glenoid component failures? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(3):478-486. |
| [1] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [2] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [5] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [6] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [7] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [8] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [9] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [10] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [11] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [12] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [13] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [14] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [15] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||