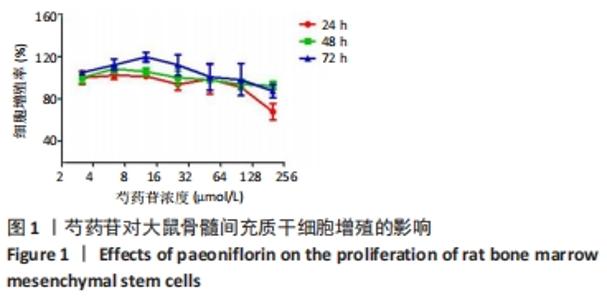
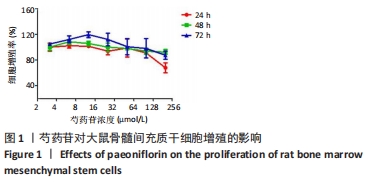
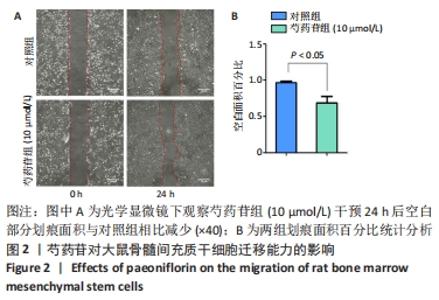
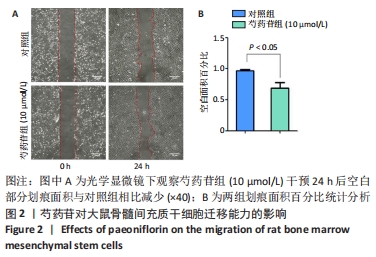
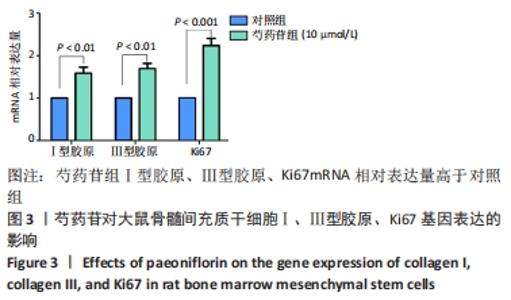
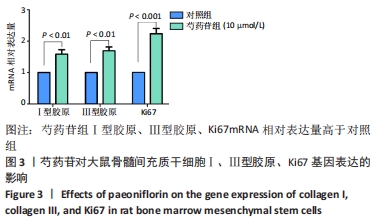
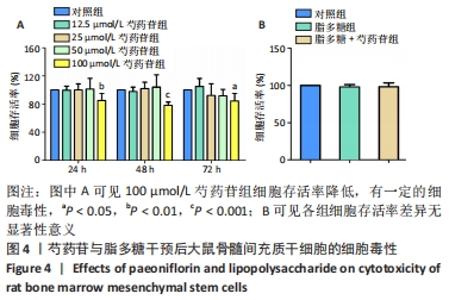
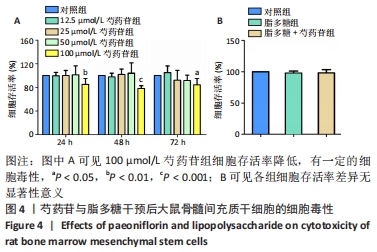
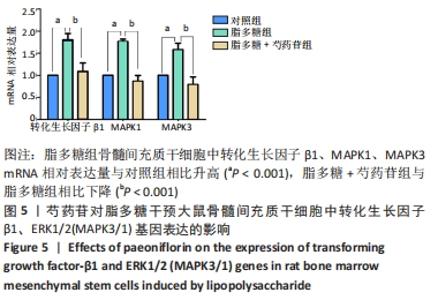
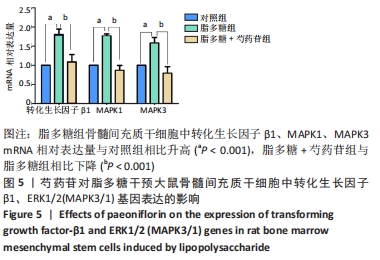
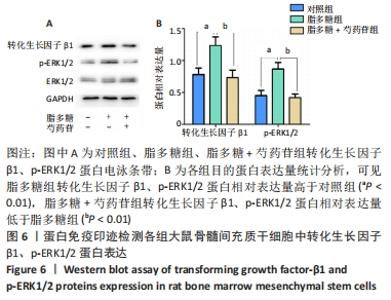
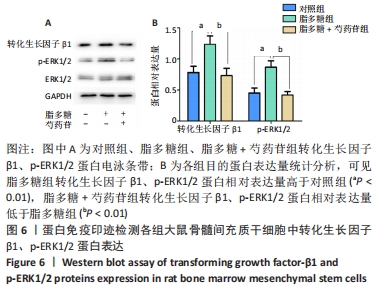
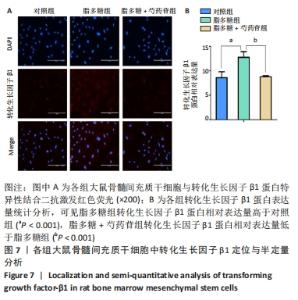
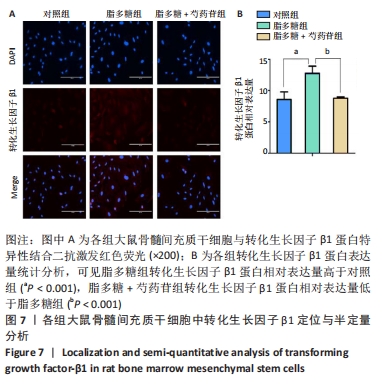
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (13): 2000-2005.doi: 10.12307/2022.324
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of paeoniflorin on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells intervened by lipopolysaccharide
Li Min, Yu Yang, Cheng Jiyan
- Department of Histology and Embryology, Basic Medical College, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2020-12-02Revised:2020-12-05Accepted:2020-12-25Online:2022-05-08Published:2021-12-18 -
Contact:Cheng Jiyan, Professor, Master, Department of Histology and Embryology, Basic Medical College, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Li Min, Master candidate, Department of Histology and Embryology, Basic Medical College, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province, No. 2014,LY-05 (to CJY); the Education Department of Sichuan Province, No. 13ZB0258 (to CJY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Min, Yu Yang, Cheng Jiyan. Mechanism of paeoniflorin on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells intervened by lipopolysaccharide[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 2000-2005.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] 荣为为,韩明子,金世柱,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在组织工程研究中的应用新进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2017,17(5):982-984. [2] 雷蓉,罗勇.骨髓间充质干细胞移植入心脏后存活率的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,7(14):182-183. [3] LAKE D, CORRÊA SA, MÜLLER J. Negative feedback regulation of the ERK1/2 MAPK pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(23):4397-4413. [4] 贾骏麒,赵路,陈媛丽,等.TGF-β1 在放射性颌骨骨髓炎发病过程中对骨髓间充质干细胞的影响及其分子机制的体外研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2020,36(3):428-432. [5] 郑世存,李晓宇,欧阳兵,等.芍药苷药理作用研究新进展[J].中国药物警戒,2012,9(2):100-103. [6] XIU GH, ZHOU X, LI XL, et al. Role of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Attenuating Inflammatory Reaction in Lipopolysaccaride-induced Acute Kidney Injury of Rats Associated with TLR4-NF-κB Signaling Pathway Inhibition. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2018;48(6): 743-750. [7] 李晓峰,赵劲民,苏伟,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(10):1721-1725. [8] 张婉,符伟国,史振宇.过表达 FOSL1 改善骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和迁移能力[J].老年医学与保健,2020,26(2):187-190. [9] ZHOU Y, HU X, ZHENG X, et al. Differentiation Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Adipose Tissue vs Bone Marrow Toward Annulus Fibrosus Cells In vitro. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(5): 432-439. [10] ZHANG Y, NAGURO I, HERR AE. In Situ Single-Cell Western Blot on Adherent Cell Culture. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019;58(39): 13929-13934. [11] PARRA ER, URAOKA N, JIANG M, et al. Validation of multiplex immunofluorescence panels using multispectral microscopy for immune-profiling of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded human tumor tissues. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):13380. [12] LUO Z, WU F, XUE E, et al. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival by inducing HIF-1α in injured neuronal cells derived exosomes culture system. Cell Death Dis. 2019; 10(2):134. [13] DENG YB, YE WB, HU ZZ, et al. Intravenously administered BMSCs reduce neuronal apoptosis and promote neuronal proliferation through the release of VEGF after stroke in rats. Neurol Res. 2010;32(2):148-156. [14] HAN S, WANG B, LI X, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional culture promote neuronal regeneration by neurotrophic protection and immunomodulation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(7):1759-1769. [15] JU S, TENG GJ, LU H, et al. In vivo MR tracking of mesenchymal stem cells in rat liver after intrasplenic transplantation. Radiology. 2007; 245(1):206-215. [16] CHEN S, SHI J, ZHANG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-laden anti-inflammatory hydrogel enhances diabetic wound healing. Sci Rep. 2015;5:18104. [17] GONG DJ, WANG L, YANG YY, et al. Diabetes aggravates renal ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats by exacerbating oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Ren Fail. 2019;41(1):750-761. [18] LIU X, ZHENG L, ZHOU Y, et al. BMSC Transplantation Aggravates Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Fibrosis and Impairs Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Front Physiol. 2019;10:87. [19] 陈谱,阮安民,周俊,等.基于NF-kB信号通路探讨芍药苷对LPS诱导的人软骨细胞炎症及退变的作用机制[J].北京中医药大学学报,2020,43(11):903-909. [20] ZHANG YC, CHEN BX, XIE XY, et al. Role of Tenascin-X in regulating TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in pathogenesis of slow transit constipation. World J Gastroenterol. 2020;26(7):717-724. [21] MULDER KM. Role of Ras and Mapks in TGFbeta signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000;11(1-2):23-35. [22] FEZZA M, MOUSSA M, AOUN R, et al. DKK1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma inflammation, migration and invasion: Implication of TGF-β1. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):e0223252. [23] JI Y, DOU YN, ZHAO QW, et al. Paeoniflorin suppresses TGF-β mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary fibrosis through a Smad-dependent pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016;37(6):794-804. [24] BLOBE GC, SCHIEMANN WP, LODISH HF. Role of transforming growth factor beta in human disease. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(18):1350-1358. [25] 陈彩云,许秋霞,张吟,等.水飞蓟素对急性胰腺炎大鼠急性肺损伤及MAPK/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2019,35(2): 192-197. [26] BEI Y, TIANQIAN H, FANYUAN Y, et al. ASH1L Suppresses Matrix Metalloproteinase through Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway in Pulpitis. J Endod. 2017;43(2):306-314.e2. [27] PIRELLI L, YU PJ, GULKAROV I, et al. Inhibition of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs) as a Strategy to Prevent Intimal Hyperplasia Following Cardiovascular Interventions. Vascular Disease Prevention. 2008;3(1):173-183. [28] SEGER R, KREBS EG. The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J. 1995;9(9): 726-735. [29] QIANG Y, MA F, WANG Z, et al. LukS-PV induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through p38/ERK MAPK signaling pathway in NSCLC cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;521(4):846-852. [30] HAWKE LG, MITCHELL BZ, ORMISTON ML. TGF-β and IL-15 Synergize through MAPK Pathways to Drive the Conversion of Human NK Cells to an Innate Lymphoid Cell 1-like Phenotype. J Immunol. 2020;204(12): 3171-3181. |
| [1] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [2] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [3] | Wang Qin, Shen Cheng, Liao Jing, Yang Ye. Dapagliflozin improves renal injury in diabetic nephropathy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1216-1222. |
| [4] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [5] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [6] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [7] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [8] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [9] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [10] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [11] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [12] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [13] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [14] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [15] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||