[1] LI Y, GU J, ZHOU J, et al. The epidemiology of traumatic brain injury in civilian inpatients of Chinese Military Hospitals, 2001-2007. Brain Inj. 2015;29(7-8):981-988.
[2] RAGHUPATHI R. Cell death mechanisms following traumatic brain injury. Brain Pathol. 2004;14(2):215-222.
[3] MCGRAW J, HIEBERT GW, STEEVES JD. Modulating astrogliosis after neurotrauma. J Neurosci Res. 2001;63(2):109-115.
[4] ZHAO Z, MA Y, CHEN Z, et al. Effects of Feeder Cells on Dopaminergic Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;10:291.
[5] PIXLEY FJ, STANLEY ER. CSF-1 regulation of the wandering macrophage: complexity in action. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14(11):628-638.
[6] YOSHIDA H, HAYASHI S, KUNISADA T, et al. The murine mutation osteopetrosis is in the coding region of the macrophage colony stimulating factor gene. Nature. 1990;345(6274):442-444.
[7] MORANDI A, BARBETTI V, RIVERSO M, et al. The colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) receptor sustains ERK1/2 activation and proliferation in breast cancer cell lines. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27450.
[8] CHITU V, GOKHAN Ş, NANDI S, et al. Emerging Roles for CSF-1 Receptor and its Ligands in the Nervous System. Trends Neurosci. 2016;39(6): 378-393.
[9] FADEN AI, DEMEDIUK P, PANTER SS, et al. The role of excitatory amino acids and NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury. Science. 1989; 244(4906):798-800.
[10] ANTHONYMUTHU TS, KENNY EM, BAYIR H. Therapies targeting lipid peroxidation in traumatic brain injury. Brain Res. 2016;1640(Pt A):57-76.
[11] SIMON DW, MCGEACHY MJ, BAYIR H, et al. The far-reaching scope of neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13(9):572.
[12] VILLAPOL S, BALAREZO MG, AFFRAM K, et al. Neurorestoration after traumatic brain injury through angiotensin II receptor blockage. Brain. 2015;138(Pt 11):3299-3315.
[13] FAIZ M, SACHEWSKY N, GASCÓN S, et al. Adult Neural Stem Cells from the Subventricular Zone Give Rise to Reactive Astrocytes in the Cortex after Stroke. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17(5):624-634.
[14] MURADASHVILI N, LOMINADZE D. Role of fibrinogen in cerebrovascular dysfunction after traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2013;27(13-14): 1508-1515.
[15] RAMLACKHANSINGH AF, BROOKS DJ, GREENWOOD RJ, et al. Inflammation after trauma: microglial activation and traumatic brain injury. Ann Neurol. 2011;70(3):374-383.
[16] BÉLANGER M, ALLAMAN I, MAGISTRETTI PJ. Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab. 2011; 14(6):724-738.
[17] GӦBEL J, ENGELHARDT E, PELZER P, et al. Mitochondria-Endoplasmic Reticulum Contacts in Reactive Astrocytes Promote Vascular Remodeling. Cell Metab. 2020;31(4):791-808.
[18] NG SY, LEE AYW. Traumatic Brain Injuries: Pathophysiology and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:528.
[19] ZHOU Y, SHAO A, YAO Y, et al. Dual roles of astrocytes in plasticity and reconstruction after traumatic brain injury. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18(1):62.
[20] XIANG Z, XU L, LIU M, et al. Lineage tracing of direct astrocyte-to-neuron conversion in the mouse cortex. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(4): 750-756.
[21] GORDON S, MARTINEZ FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. 2010;32(5):593-604.
[22] POLLARD JW. Trophic macrophages in development and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9(4):259-270.
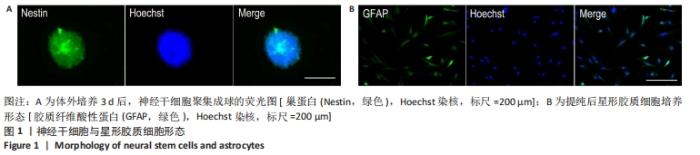
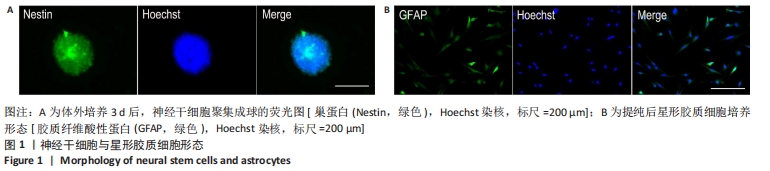
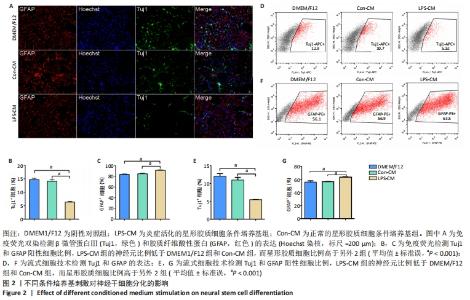
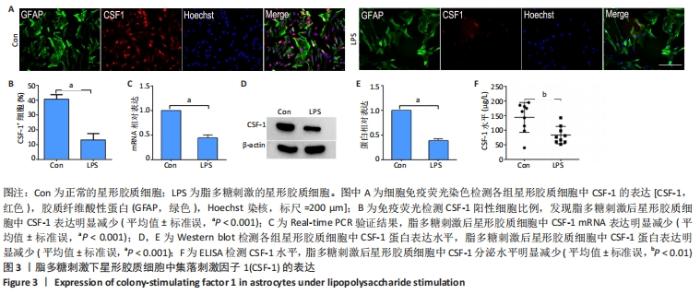
|