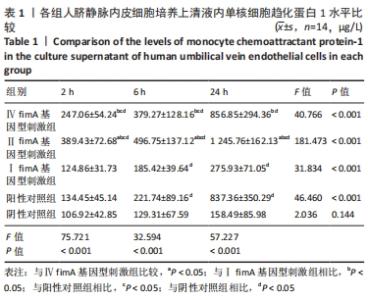
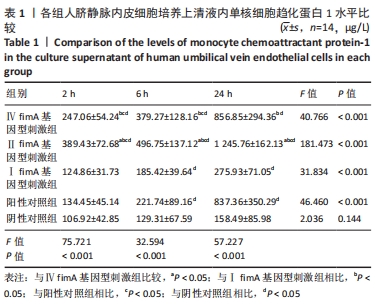
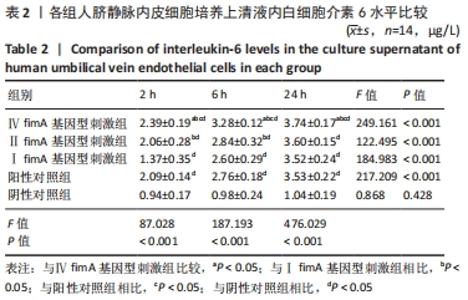
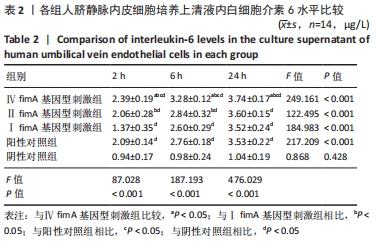
[1] 杜留熠,吕慧欣,王鹞,等.牙龈卟啉单胞菌fimA分型与相关疾病的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2018,34(12):1281-1283.
[2] UDAGAWA S, KATAGIRI S, MAEKAWA S, et al. Effect of Porphyromonas gingivalis infection in the placenta and umbilical cord in pregnant mice with low birth weight. Acta Odontol Scand. 2018;76(6):433-441.
[3] OHNO T, YAMAMOTO G, HAYASHI JI, et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 regulates Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human gingival epithelial cells. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0184825.
[4] BOELS MGS, KOUDIJS A, AVRAMUT MC, et al. Systemic Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 Inhibition Modifies Renal Macrophages and Restores Glomerular Endothelial Glycocalyx and Barrier Function in Diabetic Nephropathy. Am J Pathol. 2017;187(11):2430-2440.
[5] NITKIEWICZ J, BORJABAD A, MORGELLO S, et al. HIV induces expression of complement component C3 in astrocytes by NF-κB-dependent activation of interleukin-6 synthesis. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14(1):23.
[6] DOW CA, STAUFFER BL, BRUNJES DL, et al. Regular aerobic exercise reduces endothelin-1-mediated vasoconstrictor tone in overweight and obese adults. Exp Physiol. 2017;102(9):1133-1142.
[7] BELFIELD LA, BENNETT JH, ABATE W, et al. Exposure to Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS during macrophage polarisation leads to diminished inflammatory cytokine production. Arch Oral Biol. 2017;81:41-47.
[8] XUAN Y, GAO Y, HUANG H, et al. Tanshinone IIA Attenuates Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E Knockout Mice Infected with Porphyromonas gingivalis. Inflammation. 2017;40(5):1631-1642.
[9] GUALTERO DF, LAFAURIE GI, FONTANILLA MR. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional models for studying atherosclerosis pathogenesis induced by periodontopathogenic microorganisms. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2018;33(1):29-37.
[10] LEE K, ROBERTS JS, CHOI CH, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis traffics into endoplasmic reticulum-rich-autophagosomes for successful survival in human gingival epithelial cells. Virulence. 2018;9(1):845-859.
[11] TAKII R, KADOWAKI T, TSUKUBA T, et al. Inhibition of gingipains prevents Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced preterm birth and fetal death in pregnant mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;824:48-56.
[12] ZHENG J, SHI Y, XIONG L, et al. The Expression of IL-6, TNF-α, and MCP-1 in Respiratory Viral Infection in Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:8539294.
[13] DUBAR M, CARRASCO K, GIBOT S, et al. Effects of Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS and LR12 peptide on TREM-1 expression by monocytes. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(7):799-805.
[14] ZHOU L, DÖRFER CE, CHEN L, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharides affect gingival stem/progenitor cells attributes through NF-κB, but not Wnt/β-catenin, pathway. J Clin Periodontol. 2017;44(11):1112-1122.
[15] 白国辉,苗晨琛,陈靖,等.抗牙龈卟啉单胞菌牙周炎基因疫苗的构建及其表达研究[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2018,37(11):5165-5173.
[16] JAYAPRAKASH K, DEMIREL I, GUNALTAY S, et al. PKC, ERK/p38 MAP kinases and NF-κB targeted signalling play a role in the expression and release of IL-1β and CXCL8 in Porphyromonas gingivalis-infected THP1 cells. APMIS. 2017;125(7):623-633.
[17] 杨宇,孙敬涛,王陈保.牙龈卟啉单胞菌感染对人牙周膜细胞的增殖与成骨分化及炎性因子的影响[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2018, 28(12):1871-1875.
[18] 杨芸,陈珊珊,许春梅,等.牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖刺激巨噬细胞表达髓样细胞触发受体-1的研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018, 36(5):475-481.
[19] 宋亮,徐斌,刘阳,等.牙龈卟啉单胞菌刺激树突状细胞激活炎症反应[J].口腔医学,2018,38(6):503-507.
[20] CHEN LL, ZHU J, SCHUMACHER J, et al. SCF-KIT signaling induces endothelin-3 synthesis and secretion: Thereby activates and regulates endothelin-B-receptor for generating temporally- and spatially-precise nitric oxide to modulate SCF- and or KIT-expressing cell functions. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0184154.
[21] 王迪龙,邱宝山,林晶,等.选择性内皮素受体A拮抗剂改善高血压大鼠脑白质病变[J].中国病理生理杂志,2018,34(5):878-883.
[22] 龚志翔,万强,徐驲,等.大蒜素对PM2.5诱导血管平滑肌细胞增殖的抑制作用及机制研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2018,38(3): 345-349.
[23] 田小雨,张清友,黄娅茜,等.内皮素-1对大鼠血管平滑肌细胞一氧化氮及硫化氢体系的影响[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2018, 33(13):1013-1017.
[24] 杨志虹,杨孝芳,张宁,等.体外适宜温热刺激对络脉相关血管内皮细胞血管舒缩物质ET-1、TM、PGI2的影响[J].中华中医药杂志, 2018,33(1):284-286.
[25] 漆正楠,沈妙莲,唐子圣,等.原发性根尖周炎感染根管内牙龈卟啉单胞菌fimA与kgp基因型组合的研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2018,53(1):20-25.
[26] WOO BH, KIM DJ, CHOI JI, et al. Oral cancer cells sustainedly infected with Porphyromonas gingivalis exhibit resistance to Taxol and have higher metastatic potential. Oncotarget. 2017;8(29):46981-46992.
|