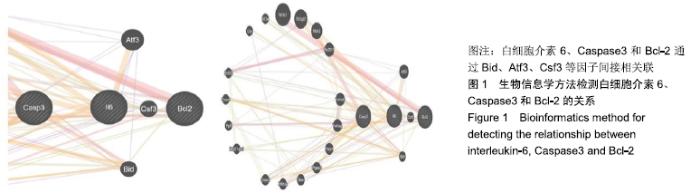
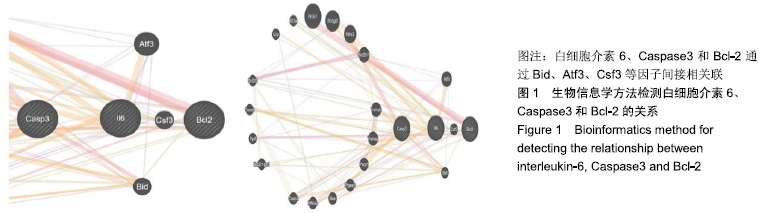
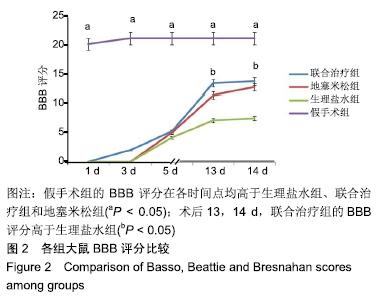
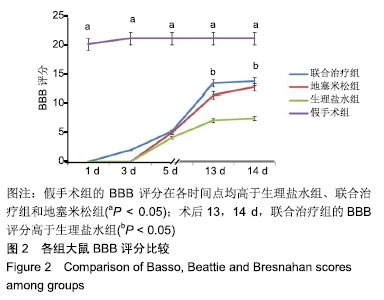
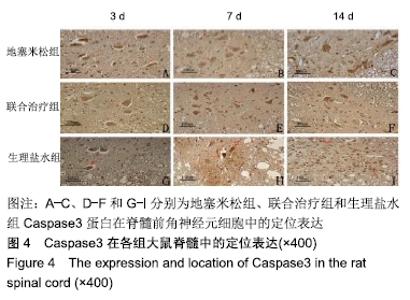
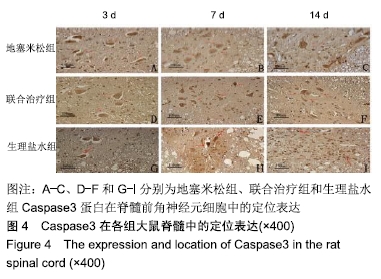
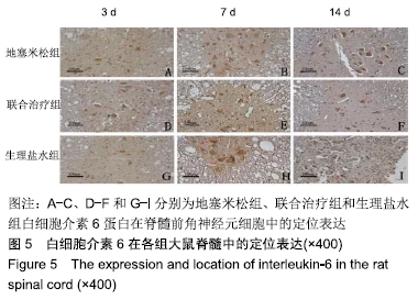
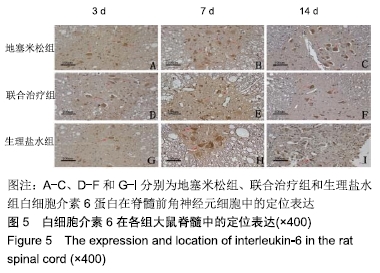
[1] DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Role of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan signaling in regulating neuroinflammation following spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(12):2080-2082.
[2] 李延宏,杨同群,王秉义,等.慢性脊髓损伤后caspase3及凋亡细胞的研究[J].甘肃医药,2013,32(3):161-163.
[3] DE RIVERO VACCARI JP, LOTOCKI G, MARCILLO AE, et al. A molecular platform in neurons regulates inflammation after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 2008;28(13):3404-3414.
[4] STAMMERS AT, LIU J, KWON BK. Expression of inflammatory cytokines following acute spinal cord injury in a rodent model. J Neurosci Res. 2012;90(4):782-990.
[5] SAMANTARAY S, DAS A, MATZELLE DC, et al. Administration of low dose estrogen attenuates gliosis and protects neurons in acute spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurochem. 2016;136(5):1064-1073.
[6] 赵瑞杰,李引乾,王会,等.Caspase家族与细胞凋亡的关系[J].中国畜牧杂志,2010,46(17):73-78.
[7] 曹鹏,石长贵,袁文.甲基强的松龙在急性脊髓损伤中的应用进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(2):174-178.
[8] 邓莉,王特为,李明.地塞米松对脊髓损伤后TNF-α和IL-6表达的影响[J].泸州医学院学报,2011,34(1):1-4.
[9] MALVIYA SA, KELLY SD, GREENLEE MM, et al. Estradiol stimulates an anti-translocation expression pattern of glucocorticoid co-regulators in a hippocampal cell model. Physiol Behav. 2013;122:187-192.
[10] SHORT DJ, EL MASRY WS, JONES PW. High dose methylprednisolone in the management of acute spinal cord injury - a systematic review from a clinical perspective. Spinal Cord. 2000;38(5): 273-286.
[11] SENGELAUB DR, XU XM.Protective effects of gonadal hormones on spinal motoneurons following spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(6):971-976.
[12] EL TOUNY LH, HENDERSON F, DJAKIEW D. Biochanin A reduces drug-induced p75NTR expression and enhances cell survival: a new in vitro assay for screening inhibitors of p75NTR expression. Rejuvenation Res. 2010;13(5):527-537.
[13] 娄雪玲.绝经后妇女反复泌尿系感染应用小剂量雌激素预防的效果观察[J].临床医学,2013,33(8):90-91.
[14] GORIO A, MADASCHI L, DI STEFANO B, et al. Methylprednisolone neutralizes the beneficial effects of erythropoietin in experimental spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(45): 16379-16384.
[15] 王一枝,胡析,周秀雅,等.慢病毒干扰TNF-α对脊髓损伤大鼠Caspase-3和Bcl-2表达的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2016,32(17): 2807-2812.
[16] 宋伦,黎燕,孙英勋,等. IL-6抑制地塞米松诱导的人骨髓瘤细胞凋亡[J].中国免疫学杂志,2002,18(11):757-759.
[17] 郑利强,伍亚民,石永江,等.黄芪多糖对大鼠脊髓损伤后运动功能和脊髓病理的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2016,22(11):1269-1275.
[18] 闵友江,程立红,姚海华,等.“三通针法”对脊髓损伤大鼠p75神经营养素受体表达的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2017,23(6):621-627.
[19] WANG LJ, LI J, HAO FR, et al. Dexamethasone suppresses the growth of human non-small cell lung cancer via inducing estrogen sulfotransferase and inactivating estrogen. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016; 37(6):845-856.
[20] 李延宏,杨同群,王秉义,等.慢性脊髓损伤后caspase3及凋亡细胞的研究[J].甘肃医药,2013,32(3):161-163.
[21] 卜志勇,胡良蛟,李晨,等.骨髓间充质干细胞局部移植联合雌二醇肌注治疗脊髓损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(1):53-58.
[22] CHAN MM, LU X, MERCHANT FM, et al. Serial transplantation of NMU-induced rat mammary tumors: a model of human breast cancer progression. Int J Cancer. 2007;121(3):474-485.
[23] OH JS, HA Y, AN SS, et al. Hypoxia-preconditioned adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell increase the survival and gene expression of engineered neural stem cells in a spinal cord injury model. Neurosci Lett. 2010;472(3):215-219.
[24] RAGHAVA N, DAS BC, RAY SK. Neuroprotective effects of estrogen in CNS injuries: insights from animal models. Neurosci Neuroecon. 2017; 6:15-29.
[25] ACOSTA MC, COPLEY PA, HARRELL JR, et al. Estrogen signaling is necessary for exercise-mediated enhancement of motoneuron participation in axon regeneration after peripheral nerve injury in mice. Dev Neurobiol. 2017;77(10):1133-1143.
[26] NGUYEN QD, LAVDAS I, GUBBINS J, et al. Temporal and spatial evolution of therapy-induced tumor apoptosis detected by caspase-3-selective molecular imaging. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(14): 3914-3924.
[27] 朱旻宇,滕红林,王靖,等.雌二醇在大鼠脊髓损伤模型中抗自噬作用的研究[J].中华全科医学,2017,15(2):230-233,337.
[28] SMERAGE JB, BUDD GT, DOYLE GV, et al. Monitoring apoptosis and Bcl-2 on circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2013;7(3):680-692.
[29] MOSQUERA L, COLÓN JM, SANTIAGO JM, et al. Tamoxifen and estradiol improved locomotor function and increased spared tissue in rats after spinal cord injury: their antioxidant effect and role of estrogen receptor alpha. Brain Res. 2014; 1561:11-22.
[30] GUERRERO AR, UCHIDA K, NAKAJIMA H, et al. Blockade of interleukin-6 signaling inhibits the classic pathway and promotes an alternative pathway of macrophage activation after spinal cord injury in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9: 40.
[31] 王涛丽,顾兵,李华南,等.急性脊髓损伤后的炎症反应及其抗炎治疗[J].中国药理学通报,2015,31(4):452-457.
|