Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (19): 3039-3048.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2198
Previous Articles Next Articles
Problems and challenges in regeneration and repair of spinal cord injury
Tian Ting1, Li Xiaoguang1, 2, 3
- 1Beijing Key Laboratory of Biomaterials and Neural Regeneration, School of Biological and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100083, China; 2Beijing International Science and Technology Cooperation Base of Biomaterials and Neural Regeneration, Beijing Biomedical Engineering High-tech Innovation Center, Beihang University, Beijing 100083, China; 3Department of Neurobiology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China
-
Received:2020-05-07Revised:2020-05-13Accepted:2020-06-19Online:2021-07-09Published:2021-01-13 -
Contact:Li Xiaoguang, MD, Professor, Beijing Key Laboratory of Biomaterials and Neural Regeneration, School of Biological and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100083, China; Beijing International Science and Technology Cooperation Base of Biomaterials and Neural Regeneration, Beijing Biomedical Engineering High-tech Innovation Center, Beihang University, Beijing 100083, China; Department of Neurobiology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China -
About author:Tian Ting, Doctoral candidate, Beijing Key Laboratory of Biomaterials and Neural Regeneration, School of Biological and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100083, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31730030 (to LXG); the National Key Research and Development Project, No. 2017YFC1104001 (to LXG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Ting, Li Xiaoguang. Problems and challenges in regeneration and repair of spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3039-3048.
share this article
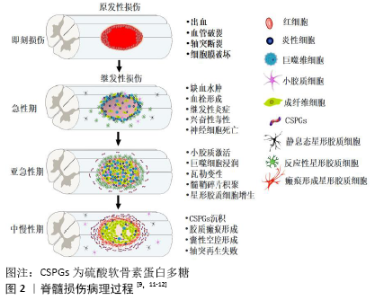
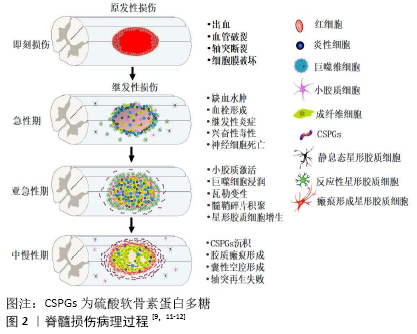
2.1 脊髓损伤病理生理学 脊髓损伤引发一系列复杂的病理生理学变化,病理过程包括2个相互交织的阶段:原发性损伤和继发性损伤,见图2[7-12]。原发性损伤在损伤后即刻发生。骨折脱位、枪弹伤或急性椎间盘断裂等创伤性事件产生的机械力对脊髓造成直接创伤(包括剪切伤、撕裂伤、挫裂伤、急性拉伸伤等)和持续压迫,导致脊髓血管破裂、出血,轴突断裂,细胞膜破坏等[7]。原发性损伤之后,会引发一系列分子级联反应,称为继发性损伤。继发性损伤分为急性期 (48 h内)、亚急性期(2-14 d)、中期(14 d-6个月)和慢性期(大于6个月) [8]。急性期,血管破裂出血以及残存血管痉挛会导致局部组织缺血水肿。受损细胞释放三磷酸腺苷作用于嘌呤能受体,诱导小胶质细胞向损伤区迁移。组织再灌注触发氧化应激、谷氨酸释放及兴奋性毒性,导致周围神经元和胶质细胞死亡。三磷酸腺苷释放、离子稳态失衡以及钙离子超载会激活钙蛋白酶、磷脂酶A2等,产生脂质介质和自由基。此外,内皮细胞损伤导致血小板黏附活化、凝血级联反应以及纤维蛋白原转化为纤维蛋白,促进血栓形成。血小板释放细胞因子、趋化因子和二十烷酸类物质,导致中性粒细胞快速浸润[8]。亚急性期,活化的小胶质细胞释放促炎因子,导致大量炎症细胞(如中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞等)和细胞因子(如肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞介素等)浸润。反应性星形胶质细胞增生、肥大,试图隔离病变区域。瓦勒变性使轴突和髓鞘碎片持续沉积,导致髓鞘相关抑制蛋白积聚,抑制轴突再生[9]。脊髓损伤中期和慢性期,主要特征是动态性血管重构、细胞外基质分子沉积与重塑以及局部和远端神经环路重组。病灶中心大量细胞丢失导致囊性微小空泡形成,微小空泡最终合并成囊性空腔,被纤维结缔组织包裹,成为细胞迁移和轴突再生的重要障碍。反应性星形胶质细胞在损伤区周围形成屏障样结构(胶质瘢痕),隔离病灶中心。星形胶质细胞、周细胞和室管膜细胞产生大量的硫酸软骨素蛋白多糖,沉积于胶质瘢痕周围,限制神经可塑性,阻碍内源性组织修复[10]。 从全身角度看,颈髓和高胸髓损伤会引起呼吸衰竭和严重低血压,这可能进一步加重脊髓缺血性损伤。此外,淋巴器官(如脾脏)交感神经支配缺失会导致继发性免疫缺陷,增加患者的易感性[8]。继发性损伤的严重程度决定了脊髓损伤患者的预后,因此理解继发性损伤的病理生理学过程有助于为脊髓损伤患者开发更为有效的神经保护措施。 "
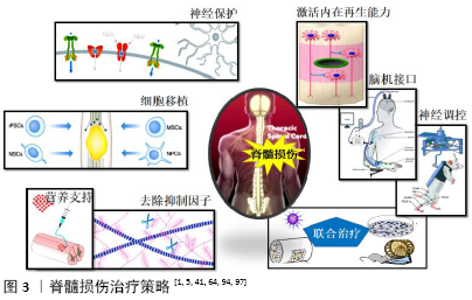
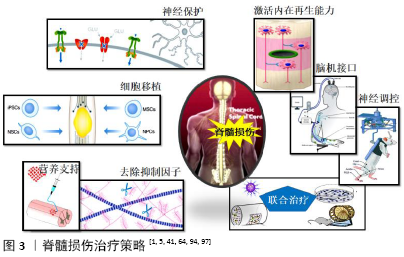
2.2 脊髓损伤治疗策略 脊髓损伤导致脊髓内神经传导束中断以及神经细胞死亡。神经炎症、兴奋性毒性、瘢痕增生等继发性损伤加重了原发性损伤的范围和严重程度,使残存神经组织进一步遭受损害,严重限制了神经可塑性和组织再生。基于脊髓损伤的病理生理过程,研究人员确定了几种潜在治疗策略:①增强神经保护:减少继发性损伤;②促进再生修复:激活神经元内在再生能力,改善微环境,细胞移植,神经调控与康复训练,脑机接口,联合治疗。 2.2.1 增强神经保护,减少继发性损伤 脊髓损伤后,微环境中细胞因子、三磷酸腺苷、一氧化氮等生物分子,会激活mTOR、ERK/MAPK、PI3K/Akt等多条信号通路,触发下游特定的信号级联反应,导致神经炎症、细胞凋亡、神经退行性病变等继发性损伤[6]。为了增强神经保护,减轻继发性损伤,诸多抑制免疫反应、神经炎症的药物被用于脊髓损伤的治疗。这些药物包括非类固醇抗炎药、二甲胺四环素、环孢素A以及皮质类固醇激素等。急性脊髓损伤早期甲基强的松龙冲击疗法存在争议,因为临床试验显示大剂量甲基强的松龙并没有改善感觉、运动功能,而消化道出血、呼吸道感染等并发症的发生率却明显增高[13]。在脊髓损伤动物模型中,二甲胺四环素可以减少神经元和少突胶质细胞凋亡,减少小胶质细胞激活和神经炎症,缓解脊髓损伤后的功能缺陷[14]。但是二甲胺四环素治疗急性脊髓损伤的Ⅱ期临床试验并未显示出明显的功能改善,免疫抑制剂环孢霉素A也有类似矛盾的结 果[15]。总体而言,传统神经保护药物在临床试验中效果并不理想,甚至是停滞不前。 近年来,研究人员开发出一些新型治疗方案,在临床前研究中显示出良好的神经保护作用,为临床脊髓损伤的治疗提供了新视角。敲除小胶质细胞电压门控质子通道Hv1,可以抑制脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞活化,减少促炎细胞因子产生、少突胶质细胞凋亡以及囊性空腔的形成,促进组织修复,Hv1可能是脊髓损伤的潜在治疗靶点[16]。MicroRNAs是参与转录调控的非编码RNA,调控miRNA可以促进脊髓损伤后神经功能恢复。注射miR-340-5p能够改善脊髓损伤引起的神经炎症、氧化应激以及细胞凋亡[17]。啮齿类动物脊髓挫伤后,二十二碳六烯酸通过上调miR-124降低小胶质细胞的吞噬活性,增强了神经保护和运动功能恢复[18]。Nrf2/ARE信号通路在抗炎、抗氧化反应中起着重要作用,2-(-2-苯并呋喃酰)-2-咪唑啉通过激活Nrf2信号通路抑制氧化应激和神经元凋亡,促进大鼠脊髓损伤后运动行为恢复[19]。降糖药物二甲双胍同样可以激活Nrf2信号通路,抑制脊髓损伤后氧化应激反应,改善线粒体功能,增强神经保护作用;二甲双胍还可以稳定微管,促进轴突再生[20]。榄香烯(β-elemene)是从姜科植物莪术中提取的常用抗肿瘤药物。榄香烯能够减轻脊髓损伤后内质网应激,减少细胞凋亡,促进运动神经元存活,改善大鼠运动功能[21]。颗粒蛋白前体是一种分泌性生长因子蛋白,参与胚胎发生、创伤愈合、宿主防御、肿瘤发生、软骨退变等病理生理过程。颗粒蛋白前体衍生物Atsttrin同样可以减轻脊髓损伤导致的神经炎症和细胞凋亡,促进神经功能恢 复[22]。 2.2.2 促进再生修复 (1)激活神经元内在再生能力:中枢神经系统神经元的内在生长能力随着年龄增长而下降,成年神经元损伤后再生能力极其微弱。轴突再生需要多种细胞内机制相互协调,包括生长锥和细胞骨架动力学、轴突mRNA转运和翻译、离子通道、转录以及表观遗传修饰等[23]。通过药物或基因操作调控这些细胞内机制,有望重新激活神经元内在生长程序,诱导轴突再生。 位于轴突顶端的生长锥对于轴突生长和损伤后轴突再生至关重要。生长锥通过微管、微丝的解聚、聚合调控轴突的生长、转向和定位。脊髓损伤后,微管解聚增加,轴突生长锥塌陷,形成回缩球限制轴突再生。大鼠脊髓损伤后,微管稳定剂紫杉醇或埃博霉素全身给药能够抑制微管解聚,诱导轴突再生,改善后肢运动功能[24-25]。但也有研究发现,埃博霉素B会加剧脊髓损伤后的炎症反应,限制功能性恢复[26]。 生长锥中塌陷反应调节蛋白2(collapsin response mediator protein 2,CRMP2)与微管蛋白二聚体相互作用,能够稳定微管聚合,促进轴突生长。糖原合成酶激酶3β(Glycogen synthetase kinase 3β,GSK3β)介导的磷酸化会阻止CRMP2与细胞骨架蛋白结合,灭活GSK3β能够增强大鼠脊髓损伤后微管聚合及轴突再生[27]。Ras同源基因家族成员A (Ras homolog gene family member A,RhoA)是定位于生长锥的信号分子,脊髓损伤后,活化的RhoA通过Rho激酶(Rho-associated kinase,ROCK)抑制CRMP2以及丝切蛋白Cofilin的功能,导致生长锥塌陷和轴突再生失败[28]。应用细菌毒素C3转移酶灭活RhoA或者β-elemene抑制ROCK活化,能够促进脊髓损伤后轴突再生和运动行为恢复[29-30]。脊髓损伤后,应用siRNA沉默RhoA可以减少损伤部位细胞凋亡、胶质细胞增生以及空腔面积,增强轴突再生[31]。RhoA抑制剂同样可以诱导轴突生长和突触形成,改善大鼠运动功能[32]。Ⅰ/Ⅱa期临床试验结果显示,RhoA抑制剂能够促进颈髓损伤患者运动功能恢复,但是Ⅱb期临床试验因缺乏疗效于2018年底停止[5]。肌动蛋白在轴突再生中的作用机制研究较少。最近Tedeschi等[33]发现肌动蛋白解聚因子/丝切蛋白(ADF/cofilin)是成年背根神经节(dorsal root ganglion,DRG)神经元再生的关键驱动因素。ADF/cofilin通过控制肌动蛋白周转维持脊髓损伤后背根神经节神经元轴突生长,ADF/cofilin可能是未来再生治疗的关键干预靶点。 轴突mRNA转运和翻译在神经元生长、再生以及功能维持等方面发挥重要作用。哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白 (mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)通过激活核糖体激酶启动mRNA翻译及蛋白质合成,参与细胞骨架的动态调控。基因敲除mTOR负性调控因子磷酸酶-张力蛋白基因(gene of phosphate and tension homology deleted on chromsome ten,PTEN),可以促进小鼠脊髓半切术后皮质脊髓束 (corticospinal tract,CST)的强劲再生,该研究为临床慢性脊髓损伤患者提供了潜在治疗方案[34]。阐明神经元发育向成熟切换的触发机制可能为脊髓损伤的治疗提供新思路。电压依赖性钙通道亚基α2δ2是发育开关之一,其能促进突触形成,限制轴突生长和再生[35],应用抗惊厥药物普瑞巴林或加巴喷丁拮抗其表达可以增强成年小鼠脊髓损伤后神经可塑性和轴突再生,促进运动功能恢复[35-36]。钾离子-氯离子共转运体2(K+-Cl-co-transporter 2,KCC2)介导突触抑制、神经保护和神经可塑性,KCC2激动剂能够促进小鼠脊髓损伤后中继神经环路形成以及感觉运动功能恢复[37]。转录因子和表观遗传修饰是决定轴突损伤后再生、出芽及突触形成的重要因素。Krüppel样因子7(Krüppel-like factor 7,KLF7)、信号转导子和转录激活子3 (signal transducers and activators of transcription 3,STAT3)、环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白(cAMP-response element binding protein,CREB)是调控神经发育的重要转录因子,基因调控这些转录因子能够促进脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束出芽、再生及环路重组,改善运动功能[38-40]。表观遗传修饰可以促进转录因子进入基因调控区域,增强转录因子对神经可塑性的调节。应用TTK21激活CREB结合蛋白(CREB binding protein,CBP)依赖性的组蛋白乙酰化,能够促进大鼠脊髓挫伤后感觉、运动轴突出芽、再生,增强突触可塑性[41]。这些发现为临床脊髓损伤的治疗开辟了新途径。 (2)改善微环境:脊髓损伤后,轴突再生除了受神经元自身限制外,损伤局部高度抑制性的微环境以及营养因子缺乏,严重阻碍了轴突再生潜能。因此,去除抑制性因素,增加营养支持,改善损伤局部微环境,有助于增强神经可塑性,促进功能恢复。 去除抑制性分子:脊髓损伤后,反应性星形胶质细胞、少突胶质前体细胞等在病灶周围积聚并持续分泌硫酸软骨素蛋白多糖(chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans,CSPGs),导致细胞外基质中CSPGs大量沉积。CSPGs通过结合蛋白质酪氨酸磷酸酶σ(Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase sigma,PTPσ)或Nogo受体复合物激活RhoA/ROCK信号通路,导致生长锥塌陷和轴突回缩,抑制神经可塑性[9]。硫酸软骨素酶ABC (chondroitin sulfate ABC,ChABC)能够降解CSPGs,大鼠颈髓半切术后,膈肌运动池注射ChABC能够有效促进呼吸功能恢复,并且功能恢复可以维持1.5年以上[42]。犬脊髓损伤后,注射ChABC能明显改善犬前后肢的协调性及早期膀胱顺应性[43]。ChABC还能够促进恒河猴颈髓损伤后皮质脊髓束出芽、突触形成以及手部运动功能恢复[44]。脊髓损伤后CSPGs会持续产生,因此需要长期反复注射ChABC。为了避免重复给药,JAMES等[45] 构建出与哺乳动物兼容的mChABC基因,通过慢病毒载体在损伤部位持续分泌ChABC,可以减轻脊髓病理损伤,改善大鼠上肢运动功能。BURNSIDE等[46]利用免疫逃避双重载体系统精准调控ChABC基因表达,增强了颈髓损伤后神经可塑性和运动功能恢复,大鼠前肢阶梯行走能力和技巧性抓握能力明显改善。应用PTPσ拮抗剂阻断CSPGs介导的抑制,可以增强脊髓损伤后5-羟色胺能轴突再生,促进运动功能、膀胱功能以及呼吸功能恢复[47]。 髓鞘相关抑制蛋白(myelin associated inhibitory protein, MAIP)包括髓鞘相关糖蛋白,少突胶质细胞髓鞘糖蛋白以及Nogo-A。脊髓损伤后,MAIP蛋白聚集在损伤中心周围,与Nogo受体复合物NgR1结合,激活RhoA/ROCK信号通路,抑制轴突再生[23]。脊髓损伤急性期,应用抗体阻断 Nogo-A,能够促进皮质脊髓束、红核脊髓束和中缝脊髓束出芽,以及皮质脊髓束长距离再生[48]。联合给予抗Nogo-A抗体和ChABC能够显著促进大鼠运动功能恢复,表明去除多种抑制因素更有助于轴突再生[49]。抗Nogo-A抗体ATI355的Ⅰ期临床试验已经完成,结果显示ATI355安全性和耐受性良好,患者运动评分增加,部分四肢瘫痪患者转为不完全性脊髓损伤[50]。未来需要更大规模的临床试验进一步验证ATI355的疗效。NgR1是MAIP的高亲和力受体,敲除NgR1可以促进小鼠锥体切断术后皮质脊髓束出芽、再生[51]。应用shRNA抑制NgR1表达,能够降低脊髓损伤后空腔面积和细胞凋亡,增加神经纤维、突触以及髓鞘数量,改善大鼠运动功能[52]。NgR1拮抗剂NgR1(310)-Fc可以有效阻断MAIP与NgR1结合,增强脊髓损伤后中缝脊髓束轴突出芽,改善运动功能[53]。NgR1拮抗剂LOTUS能够促进中缝脊髓束和网状脊髓束轴突再生,减轻皮质脊髓束轴突回缩坏死,增强运动功能恢复和神经传导[54]。 增加营养支持:神经营养因子调控神经元存活、发育,诱导成年神经系统可塑性和轴突再生。脊髓损伤后,损伤局部营养因子缺乏是再生失败的主要原因之一,因此增加营养支持是促进再生修复的潜在治疗策略。常见的神经营养因子包括神经生长因子、脑源性神经营养因子、神经营养因子、睫状神经营养因子等。 神经营养因子可以通过直接注射或者借助生物材料、病毒载体递送等方式作用于损伤脊髓。犬脊髓半切术后,明胶海绵支架/神经营养因子3/丝素复合物能够改善损伤局部微环境,增强神经再生,促进犬后肢运动恢复和神经传导[55]。向腰髓运动神经元靶向递送神经营养因子3,能够减轻脊髓损伤导致的运动神经元树突萎缩,促进运动神经元树突再生、突触形成以及腰骶神经回路重组,增强运动功能恢复[56]。脑源性神经营养因子能够促进神经元存活,增强突触可塑性。脊髓损伤后,应用纳米胶束向损伤区递送脑源性神经营养因子 mRNA,可以有效改善小鼠运动功能[57]。大鼠胸髓损伤后,椎管内注射AAV2-BDNF能够增强5-羟色胺能纤维出芽再生以及与膈肌运动神经元的突触联系,促进膈肌功能恢复[58]。利用纳米胶囊高效递送神经生长因子,可以促进小鼠脊髓损伤后神经再生、组织重塑以及运动功能恢复[59]。胰岛素样生长因子1调控信号传导和蛋白质合成,在控制神经元再生潜能方面起着重要的作用。小鼠脊髓损伤后,向感觉运动皮质递送胰岛素样生长因子和骨桥蛋白,可以促进皮质脊髓束强健再生以及前肢精细运动功能恢复[60]。这些研究为脊髓损伤的临床治疗提供了新思路,未来临床前研究应包括非人灵长类动物以及多种感觉和运动参数,以确定神经营养因子的安全性和疗效。 (3)细胞移植:脊髓损伤后大量神经细胞坏死、丢失,细胞移植是目前最具应用前景的治疗策略之一。研究发现,细胞移植通过多种机制介导脊髓损伤后的功能改善,包括神经保护、免疫调节、轴突再生、中继神经网络形成等[61]。目前广泛应用的细胞包括神经干细胞、神经祖细胞、嗅鞘细胞以及间充质干细胞等。细胞可以通过原位注射或鞘内注射等方式进行移植,但是移植细胞可能会被脑脊液冲散,并且损伤局部抑制性的微环境不利于细胞存活。为此,研究人员将细胞、生物材料和(或)生长因子联合移植,以提高细胞存活效率和治疗效果。生物材料在细胞移植中发挥重要作用,可以为移植细胞和生长因子的长期释放提供临时存储基质,促进移植细胞的黏附存活和分化;同时为移植细胞提供结构支撑,引导细胞生长,促进环路重组[62]。 神经干细胞和神经祖细胞可以分化为神经元、星形胶质细胞、少突胶质细胞,并能分泌营养因子改善微环境,是治疗脊髓损伤最具吸引力的细胞来源[63]。目前人神经祖细胞(NSI-566)移植治疗慢性脊髓损伤的Ⅰ期临床试验已完成,所有受试者对手术耐受性良好,移植后18-27个月内没有发生严重不良事件,2名受试者神经功能得到部分改善,神经祖细胞显示出良好的临床转化前景[64]。细胞重编程技术可以将人类体细胞重编程为神经干细胞/神经祖细胞,有效避免了伦理问题和免疫排斥风险,因此重编程的神经干细胞/神经祖细胞是一种极具吸引力的细胞移植策略。诱导多能干细胞来源的神经干细胞(iPSCs-NSCs)移植能够促进脊髓损伤后功能性神经环路重建和运动功能恢复[65]。但是最近研究发现诱导多能干细胞存在安全问题,特别是致瘤性。应用单纯疱疹病毒1型胸苷激酶选择性消除未成熟的增殖细胞,能够防止诱导多能干细胞来源的神经干细胞/神经祖细胞移植后的肿瘤形成[66]。间充质干细胞因其来源广泛,易于采集,无伦理争议而备受欢迎。间充质干细胞具有抗炎、抗凋亡以及免疫调节作用,间充质干细胞移植可以减轻脊髓损伤导致的组织损伤,增强神经保护和髓鞘保存,促进感觉运动功能恢复[67]。犬脊髓损伤后,移植间充质干细胞衍生神经网络能够改善损伤/移植物周围微环境,促进局部神经环路重塑以及运动功能、电生理传导恢复[68]。自体间充质干细胞移植治疗慢性脊髓损伤的Ⅱ期临床试验显示出良好的安全性和耐受性,患者在运动能力、痉挛、敏感性、神经性疼痛、性功能以及括约肌功能障碍等方面得到不同程度改善[69]。嗅鞘细胞是一种神经胶质细胞,嗅鞘细胞移植可以限制脊髓损伤后免疫细胞活化和炎性细胞浸润,减轻组织损伤,促进血管生成,通过神经保护和免疫调节机制,为神经元存活和轴突再生创造支持环境[70]。嗅鞘细胞移植能够促进大鼠颈髓损伤后攀爬能力和呼吸功能恢复,缓解自主神经反射障碍,同时可以提高犬脊髓损伤后前后肢的协调能力[71-72]。许旺细胞是另一种很有前途的脊髓修复治疗策略。许旺细胞移植可以减少组织损伤,维持轴突可塑性,促进轴突再生和再髓鞘化,从而改善脊髓损伤后的感觉运动功能障碍[73]。亚急性脊髓损伤患者自体许旺细胞移植的Ⅰ期临床试验显示,自体许旺细胞移植安全可行,无不良事件及神经并发症发生[74]。 (4)神经调控与康复训练:脊髓损伤后下行神经传导通路被中断,损伤平面以下未受损的神经网络因无法接收高位中枢(皮质和脑干)的兴奋性输入而导致运动功能丧失。以活动为基础的康复训练可以增强脊髓损伤后残余纤维的神经可塑性和轴突再髓鞘化,促进神经环路重建,从而改善运动功能[75]。近年来,研究人员应用神经调控技术增强机体的活动能力,并与康复训练相结合,旨在进一步增强神经可塑性,促进神经功能恢复。神经调控是利用各种形式的电刺激增强或修改神经元功能活动的技术,目前已经在多种神经系统疾病中应用[76]。脊髓损伤后神经调控方式包括脊髓刺激和脑刺激。 脊髓刺激:脊髓硬膜外电刺激最初被用来治疗慢性疼 痛,但是越来越多的研究显示硬膜外电刺激可以促进脊髓损伤后神经功能恢复。腰骶脊髓硬膜外电刺激结合康复训练,能够促进下肢完全瘫痪患者独立站立、辅助行走以及腿部自主运动恢复[77]。硬膜外电刺激联合负重跑步机训练,使2名慢性完全性脊髓损伤患者恢复了独立站立和地面独立行走的能力[78]。慢性胸髓损伤患者接受硬膜外电刺激治疗和多模式康复训练43周后可以不依赖减重支持系统在跑步机上进行双侧跨步行走,同时可以使用助行器在地面独立行走[79]。持续硬膜外电刺激可能会阻断本体感觉输入,COURTINE团队开发出时空硬膜外电刺激以避免持续硬膜外电刺激对本体感觉信息的干扰。时空硬膜外电刺激增强了对运动神经元的活动控制,同时保留了拮抗肌之间的相互作用,确保下肢运动的协调性和稳定性[80]。时空硬膜外电刺激结合运动康复训练,使3例慢性脊髓损伤患者运动能力明显改善,患者在时空硬膜外电刺激作用下可以在室外环境中站立、行走甚至是骑车,并且能够在没有硬膜外电刺激作用下自主控制瘫痪肢体,表明大脑和脊髓重新建立了功能性连接[81]。此外,硬膜外电刺激能够促进慢性脊髓损伤患者心血管功能恢复,有效改善低血压状态,提高了患者生活质量[82]。患者的排便和膀胱控制能力以及性功能也得到了改善,而这些能力往往是患者更为看重的。在某些情况下,即使关闭刺激器,这些功能改善依然存在[83]。这些研究为脊髓损伤后促进功能恢复和提高生活质量建立了技术框架。 脑刺激:即使是被诊断为完全性脊髓损伤的患者,脊髓内仍然保留一些来自高位中枢的下行传导通路。应用电刺激可以激活这些残存通路,促进对瘫痪肢体的自主控制[84]。深部脑刺激是将电极植入大脑特定核团,用以激活或纠正大脑的神经电活动,目前已经用于治疗多种运动障碍疾病[85]。运动皮质电刺激可以促进大鼠脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束轴突出芽及运动功能恢复[86]。运动皮质电刺激结合脊髓神经调控,能够显著改善大鼠颈髓损伤后前肢精细运动功能[87]。无创脑部刺激技术是非常具有应用前景的干预措施。经颅直流电刺激是一种无创皮质刺激方法,现已广泛应用于治疗多种疾病,如抑郁症、强迫症、慢性疼痛等。当与重复任务训练相结合时,经颅直流电刺激可以促进慢性颈髓损伤患者上肢精细运动功能的恢复[88],未来还需要更多的研究以确定经颅直流电刺激是否可以转化为脊髓损伤患者的长期康复策略。经颅磁刺激是另一种无创皮质刺激技术。早期经颅磁刺激干预治疗能够增强脊髓损伤后皮质神经元可塑性,促进大鼠感觉运动功能恢复[89]。高频经颅磁刺激能够缓解脊髓损伤患者肢体痉挛,改善脊髓神经传导功能[90]。慢性颈髓损伤患者接受经颅磁刺激和外周神经刺激联合治疗后,手部精细运动功能和室内活动能力均得到改善,并且功能改善能够维持几个月,说明经颅磁刺激能够稳定诱导神经可塑性[91]。这些无创干预措施成本低、风险低,是临床治疗脊髓损伤极具吸引力的选择。 (5)脑机接口:脑机接口是结合神经生理学、计算机科学和工程学的一种新型治疗技术,旨在恢复严重瘫痪患者的感觉运动功能。脑机接口的核心思想是记录和解码来自大脑的运动信号,并利用这些信号产生功能性运动输出[76]。脑机接口可以直接控制仿生假肢如机械臂,也可以绕过损伤部位,直接控制损伤部位以下的肌肉。当与康复训练相结合时,长期持续使用脑机接口能够改善患者自主运动能力,表明脑机接口增强了大脑和(或)脊髓的神经可塑性。 脑机接口首先在猕猴中成功应用,通过脑控制的功能性电刺激恢复了猕猴瘫痪上肢的自主控制,目前脑机接口已经用于临床研究。脑机接口使四肢瘫痪患者能够通过意念控制机械臂的三维伸展和抓握运动[92],为患者生活提供了诸多方便,但是机械臂并不能促进患者运动功能恢复。将脑机接口与虚拟现实和机械外骨骼相结合,能够使慢性完全性截瘫患者实现对瘫痪肢体的自主控制,结合步态康复训练,患者躯体感觉和自主运动控制均得到改善,50%的患者升级为不完全性截瘫。该研究表明,脑机接口结合康复训练,可以触发脑和脊髓的神经可塑性,促进神经功能恢复[93]。外骨骼介导的肢体活动实质上是肌肉的被动运动,并没有解决修复神经连接的根本问题,也不能有效防止瘫痪肢体的肌肉萎缩。为此,脑机接口将皮质信号转化为功能性电刺激直接控制肌肉收缩,使高颈髓损伤患者能够进行手指屈伸,拇指内收、外展,甚至还能完成倾倒和搅拌动作[94]。理论上讲,脑机接口也可以恢复大脑对腿部肌肉活动的控制,但是下肢运动过程中每块肌肉复杂的激活模式对该技术构成了巨大挑战。COURTINE团队开发出时空硬膜外电刺激以提高脊髓损伤大鼠的步态质量和熟练运动能力[95]。该团队将时空硬膜外电刺激与腿部运动皮质活动相结合,构建出脑-脊髓接口实时控制系统,有效缓解了恒河猴脊髓损伤后的步态缺陷,恢复了恒河猴在跑步机以及地面的负重运动能力[96]。当与运动康复训练结合时,脑-脊髓接口能够使脊髓损伤大鼠进行地面行走及楼梯攀爬,促进运动功能的持久恢复[97]。脑-脊髓接口为改善脊髓损伤患者的运动控制提供了新思路。 (6)联合治疗:尽管单一治疗措施在临床前脊髓损伤动物模型中显示出治疗希望,但是再生效果有限,不足以促进人类脊髓损伤后的功能恢复。针对脊髓损伤多病理过程及再生相关机制,联合多种治疗策略,有望逆转脊髓损伤后的再生失败,协同促进神经再生。 神经再生策略联合神经保护或营养支持治疗,可以促进脊髓损伤后神经元存活和轴突再生。SOFRONIEW团队应用骨桥蛋白、胰岛素样生长因子1以及睫状神经营养因子激活脊髓固有神经元的再生能力;应用成纤维细胞生长因子2和表皮生长因子提供营养支持;应用胶质源性神经营养因子提供化学吸引;同时应用生物材料时空控释上述生物因子。3种机制共同作用,能够刺激啮齿类动物脊髓损伤后脊髓固有轴突的强健再生;再生轴突跨越损伤区与残存神经元形成突触联系,电生理传导功能得以恢复[98]。作者所在团队应用可降解的生物活性材料壳聚糖长效缓释神经营养因子3,能够改善脊髓损伤后局部微环境(抗炎和神经保护),激活内源性神经发生,壳聚糖-神经营养因子3诱导内源性神经干细胞向损伤区迁移并且高比例分化为神经元,促进突触形成及功能性神经网络重建,有效改善了大鼠感觉运动功能[99]。此外,壳聚糖-神经营养因子3能够促进恒河猴脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束长距离再生以及感觉运动功能恢复[100],该研究为壳聚糖-神经营养因子3的临床转化提供了坚实的研究基础。大鼠慢性脊髓挫伤后,联合应用外周神经支架、成纤维细胞生长因子以及ChABC,可以为神经元提供良好的再生微环境,维持神经元生长潜力,有效改善了大鼠运动功能和膀胱功 能[101]。将神经再生药物多西他赛和组合生长因子联合靶向递送至脊髓损伤部位,可以减轻炎症反应、巨噬细胞活化、细胞凋亡以及瘢痕形成,促进轴突再生及运动功能恢复[102]。 应用海藻酸盐凝胶长效缓释神经保护药物盐酸米诺环素和神经再生药物紫杉醇,可以减轻脊髓损伤后炎症反应,减少瘢痕形成,增强轴突再生,大鼠运动功能得到快速持久的改 善[103]。联合应用多聚唾液酸和盐酸米诺环素,能够减轻大鼠脊髓损伤后神经元及髓鞘损伤,减少胶质瘢痕形成,促进轴突长距离再生及运动功能恢复[104]。 细胞移植联合生物材料和(或)生长因子可以协同促进运动功能恢复。作者之前的研究显示,大鼠完全性脊髓损伤后,联合移植脱细胞神经支架和胎盘间充质干细胞能够提高细胞的定植存活,促进胎盘间充质干细胞向神经元分化以及宿主轴突再髓鞘化,大鼠后肢运动功能明显改善[105]。TUSZYNSKI团队将神经干细胞植入含有10种生长因子混合物的纤维蛋白基质中,移植到大鼠脊髓横断缺损处,移植神经干细胞分化为神经元并跨越损伤区长距离生长,与宿主脊髓形成中继神经环路,有效改善了运动功能和电生理传导[106]。利用该联合方案移植神经祖细胞,促进了脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束的强健再生和功能性突触形成,大鼠前肢精细运动功能显著改善[107]。应用3D仿生脊髓支架移植神经祖细胞,进一步促进了神经祖细胞黏附生长、宿主轴突再生以及功能性神经网络的重建[108]。该团队将人脊髓来源的人神经祖细胞移植到恒河猴颈髓损伤缺损处,促进了功能性中继神经网络形成以及前肢运动功能恢复[109],为神经祖细胞治疗人类脊髓损伤提供了转化数据。康复训练在促进轴突再生和神经可塑性中起重要作用。嗅鞘细胞移植结合长期步态训练,能够促进严重脊髓损伤后轴突再生以及腰骶运动神经回路的重建,改善大鼠后肢运动功能和电生理传导[110]。抗Nogo-A抗体结合强化运动训练,可以有效促进脊髓损伤后下行神经纤维出芽以及与局部神经网络的相互作用,显著改善大鼠运动功能[111]。 大鼠胸髓挫伤后,星形胶质细胞选择性表达基质金属蛋白酶ADAMTS4降解CSPGs,联合后肢康复训练,能够增强皮质脊髓束出芽以及尾端5-羟色胺能纤维密度,促进大鼠后肢运动功能恢复[112]。神经调控结合康复训练同样可以增强神经可塑性和神经环路重建,促进脊髓损伤患者运动功能恢复。硬膜外电刺激结合步态训练使截瘫患者能够重新站立,自主控制瘫痪肢体,甚至能在辅助支撑下长距离行走[79-81]。脑机接口结合特定任务训练,可以促进颈髓损伤患者上肢精细运动功能恢复[94]。综上所述,联合治疗比单一治疗更具临床应用前景,有望解决成年脊髓损伤后轴突再生失败的难题。 脊髓损伤治疗策略模式图见图3。 2.3 临床转化现状与挑战 脊髓损伤后,研究人员采用多种治疗策略修复或重新激活受损神经环路。许多治疗策略在临床前研究中取得了显著疗效,但只有小部分完成临床试验。目前针对神经保护的临床试验大都以失败告终[5]。再生修复策略中少数已经进入临床试验阶段,包括抗Nogo-A抗体、赛生灵以及细胞移植等,目前已完成Ⅰ/Ⅱa期临床试验,患者有不同程度的功能改善,无明显不良反应[50,64,113]。ChABC具有较大临床应用潜力,虽然尚未进行临床试验,但最近在犬和恒河猴进行的临床前研究取得了非常满意的结果[43-44]。 神经调控技术与康复策略相结合,目前在临床研究中也取得了一定进展。硬膜外电刺激提高了患者独立站立和地面行走的能力[78,81],脑机接口实现了截瘫患者上肢的自主运动[94],这些研究使瘫痪患者重新行走的希望更接近现实,也是目前最有希望的治疗方案之一。但是神经调节是一种复杂、昂贵的医疗手段,短期内可能不会对所有人开放。要在临床中广泛、长期应用,还必须克服大量的挑战,包括设备的可负担性、可获得性、电极的生物相容性和耐用性以及操作设备所需的专业知识等。耐用性是关键问题之一,因为植入电极会导致植入部位周围组织损伤和神经胶质增生,导致记录和刺激效率下降。具有更大灵活性、更小尺寸的纳米电极阵列可能有助于最小化组织损伤,同时提高设备的效率和寿命[114]。随着材料科学、纳米技术和生物制品的进步,以及可穿戴技术和无线设备的不断发展,电极在刺激和记录能力、特异性及寿命等方面也会有重大改进。 尽管许多治疗措施在脊髓损伤动物模型中显示出良好的治疗效果,使瘫痪动物恢复了行走或抓握能力,但是当进行临床试验时,这些措施却无法转化为有效的临床治疗。临床转化的主要问题是临床前研究缺乏稳定性和重复性,因此在治疗措施进入临床阶段之前,有必要由独立的第三方实验室对临床前研究结果进行验证性复制[115]。当多种策略组合时,这将变得更加复杂,联合治疗方案可能需要定制的实验设计和分析框架。当面对诸多可能有效的治疗和组合方法时,需要积累更多研究数据之后再开始临床转化试验。临床转化的道路艰辛而漫长,需要考虑诸多因素,例如哪些治疗措施联合效果最好,实验模型是否与治疗目的有关,治疗措施是否安全、可耐受等。实验模型应该尽可能接近人类情况,挫伤和压迫损伤模型与临床脊髓损伤更相关。与啮齿动物相比,人类脊髓要厚得多,解剖结构不同,治疗效果也相差甚远[116],因此干预措施应该在多种动物模型中进行测试,包括大动物(如灵长类动物或猪),以拓宽对治疗局限性的理解。此外,非运动系统直接影响生活质量,并且往往是患者更为关注和看重的,但是临床前实验较少报道该方面的相关研究,无法确定这些潜在治疗措施是否会在人体中产生不良反应,因此在进行临床试验之前,不仅要仔细分析运动系统的变化,还要评估相关动物模型的感觉、自主和认知功能的变化。"
| [1] ASHAMMAKHI N, KIM HJ, EHSANIPOUR A, et al. Regenerative Therapies for Spinal Cord Injury. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019; 25(6):471-491. [2] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282. [3] SOFRONIEW MV. Dissecting spinal cord regeneration. Nature. 2018;557(7705): 343-350. [4] KARSY M, HAWRYLUK G. Modern Medical Management of Spinal Cord Injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19(9):65. [5] GRIFFIN JM, BRADKE F. Therapeutic repair for spinal cord injury: combinatory approaches to address a multifaceted problem. EMBO Mol Med. 2020;12(3): e11505. [6] PASCHON V, CORREIA FF, MORENA BC, et al. CRISPR, Prime Editing, Optogenetics, and DREADDs: New Therapeutic Approaches Provided by Emerging Technologies in the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(4):2085-2100. [7] ROWLAND JW, HAWRYLUK GW, KWON B, et al. Current status of acute spinal cord injury pathophysiology and emerging therapies: promise on the horizon. Neurosurg Focus. 2008;25(5):E2. [8] BADHIWALA JH, AHUJA CS, FEHLINGS MG. Time is spine: a review of translational advances in spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018;30(1):1-18. [9] BRADBURY EJ, BURNSIDE ER. Moving beyond the glial scar for spinal cord repair. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3879. [10] LINDSAY SL, MCCANNEY GA, WILLISON AG, et al. Multi-target approaches to CNS repair: olfactory mucosa-derived cells and heparan sulfates. Nat Rev Neurol. 2020;16(4):229-240. [11] BARNABÉ-HEIDER F, GÖRITZ C, SABELSTRÖM H, et al. Origin of new glial cells in intact and injured adult spinal cord. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(4):470-482. [12] GÖRITZ C, DIAS DO, TOMILIN N, et al. A pericyte origin of spinal cord scar tissue. Science. 2011;333(6039):238-242. [13] LIU Z, YANG Y, HE L, et al. High-dose methylprednisolone for acute traumatic spinal cord injury: A meta-analysis. Neurology. 2019;93(9):e841-e850. [14] TENG YD, CHOI H, ONARIO RC, et al. Minocycline inhibits contusion-triggered mitochondrial cytochrome c release and mitigates functional deficits after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(9):3071-3076. [15] CASHA S, ZYGUN D, MCGOWAN MD, et al. Results of a phase II placebo-controlled randomized trial of minocycline in acute spinal cord injury. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 4): 1224-1236. [16] LI X, LIU R, YU Z, et al. Microglial Hv1 exacerbates secondary damage after spinal cord injury in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Feb 19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.012. Online ahead of print. [17] QIAN Z, CHANG J, JIANG F, et al. Excess administration of miR-340-5p ameliorates spinal cord injury-induced neuroinflammation and apoptosis by modulating the P38-MAPK signaling pathway. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;87:531-542. [18] YIP PK, BOWES AL, HALL JCE, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid reduces microglia phagocytic activity via miR-124 and induces neuroprotection in rodent models of spinal cord contusion injury. Hum Mol Genet. 2019;28(14):2427-2448. [19] LIN X, ZHU J, NI H, et al. Treatment With 2-BFI Attenuated Spinal Cord Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:567. [20] WANG H, ZHENG Z, HAN W, et al. Metformin Promotes Axon Regeneration after Spinal Cord Injury through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Stabilizing Microtubule. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:9741369. [21] WANG J, LI H, REN Y, et al. Local Delivery of β-Elemene Improves Locomotor Functional Recovery by Alleviating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Reducing Neuronal Apoptosis in Rats with Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018; 49(2):595-609. [22] WANG C, ZHANG L, NDONG JC, et al. Progranulin deficiency exacerbates spinal cord injury by promoting neuroinflammation and cell apoptosis in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):238. [23] HUTSON TH, DI GIOVANNI S. The translational landscape in spinal cord injury: focus on neuroplasticity and regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(12):732-745. [24] SANDNER B, PUTTAGUNTA R, MOTSCH M, et al. Systemic epothilone D improves hindlimb function after spinal cord contusion injury in rats. Exp Neurol. 2018;306: 250-259. [25] HELLAL F, HURTADO A, RUSCHEL J, et al. Microtubule stabilization reduces scarring and causes axon regeneration after spinal cord injury. Science. 2011; 331(6019):928-931. [26] MAO L, GAO W, CHEN S, et al. Epothilone B impairs functional recovery after spinal cord injury by increasing secretion of macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(11):e3162. [27] LIZ MA, MAR FM, SANTOS TE, et al. Neuronal deletion of GSK3β increases microtubule speed in the growth cone and enhances axon regeneration via CRMP-2 and independently of MAP1B and CLASP2. BMC Biol. 2014;12:47. [28] CURCIO M, BRADKE F. Axon Regeneration in the Central Nervous System: Facing the Challenges from the Inside. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2018;34:495-521. [29] FOURNIER AE, TAKIZAWA BT, STRITTMATTER SM. Rho kinase inhibition enhances axonal regeneration in the injured CNS. J Neurosci. 2003;23(4):1416-1423. [30] WANG J, LI H, YAO Y, et al. β-Elemene Enhances GAP-43 Expression and Neurite Outgrowth by Inhibiting RhoA Kinase Activation in Rats with Spinal Cord Injury. Neuroscience. 2018;383:12-21. [31] GWAK SJ, MACKS C, JEONG DU, et al. RhoA knockdown by cationic amphiphilic copolymer/siRhoA polyplexes enhances axonal regeneration in rat spinal cord injury model. Biomaterials. 2017;121:155-166. [32] DEVAUX S, CIZKOVA D, MALLAH K, et al. RhoA Inhibitor Treatment At Acute Phase of Spinal Cord Injury May Induce Neurite Outgrowth and Synaptogenesis. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017;16(8):1394-1415. [33] TEDESCHI A, DUPRAZ S, CURCIO M, et al. ADF/Cofilin-Mediated Actin Turnover Promotes Axon Regeneration in the Adult CNS. Neuron. 2019;103(6):1073-1085. [34] DU K, ZHENG S, ZHANG Q, et al. Pten Deletion Promotes Regrowth of Corticospinal Tract Axons 1 Year after Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurosci. 2015;35(26): 9754-9763. [35] TEDESCHI A, DUPRAZ S, LASKOWSKI CJ, et al. The Calcium Channel Subunit Alpha2delta2 Suppresses Axon Regeneration in the Adult CNS. Neuron. 2016; 92(2):419-434. [36] SUN W, LARSON MJ, KIYOSHI CM, et al. Gabapentinoid treatment promotes corticospinal plasticity and regeneration following murine spinal cord injury. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(1):345-358. [37] CHEN B, LI Y, YU B, et al. Reactivation of Dormant Relay Pathways in Injured Spinal Cord by KCC2 Manipulations. Cell. 2018;174(3):521-535. [38] LI WY, WANG Y, ZHAI FG, et al. AAV-KLF7 Promotes Descending Propriospinal Neuron Axonal Plasticity after Spinal Cord Injury. Neural Plast. 2017;2017: 1621629. [39] LANG C, BRADLEY PM, JACOBI A, et al. STAT3 promotes corticospinal remodelling and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. EMBO Rep. 2013;14(10):931-937. [40] BRADLEY PM, DENECKE CK, ALJOVIC A, et al. Corticospinal circuit remodeling after central nervous system injury is dependent on neuronal activity. J Exp Med. 2019;216(11):2503-2514. [41] HUTSON TH, KATHE C, PALMISANO I, et al. Cbp-dependent histone acetylation mediates axon regeneration induced by environmental enrichment in rodent spinal cord injury models. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(487):eaaw2064. [42] WARREN PM, STEIGER SC, DICK TE, et al. Rapid and robust restoration of breathing long after spinal cord injury. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4843. [43] HU HZ, GRANGER N, PAI SB, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of microtube-embedded chondroitinase ABC in a canine clinical model of spinal cord injury. Brain. 2018; 141(4):1017-1027. [44] ROSENZWEIG ES, SALEGIO EA, LIANG JJ, et al. Chondroitinase improves anatomical and functional outcomes after primate spinal cord injury. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22(8):1269-1275. [45] JAMES ND, SHEA J, MUIR EM, et al. Chondroitinase gene therapy improves upper limb function following cervical contusion injury. Exp Neurol. 2015;271:131-135. [46] BURNSIDE ER, DE WINTER F, DIDANGELOS A, et al. Immune-evasive gene switch enables regulated delivery of chondroitinase after spinal cord injury. Brain. 2018; 141(8):2362-2381. [47] LANG BT, CREGG JM, DEPAUL MA, et al. Modulation of the proteoglycan receptor PTPσ promotes recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature. 2015;518(7539): 404-408. [48] ZÖRNER B, SCHWAB ME. Anti-Nogo on the go: from animal models to a clinical trial. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1198 Suppl 1:E22-34. [49] ZHAO RR, ANDREWS MR, WANG D, et al. Combination treatment with anti-Nogo-A and chondroitinase ABC is more effective than single treatments at enhancing functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Eur J Neurosci. 2013; 38(6):2946-2961. [50] KUCHER K, JOHNS D, MAIER D, et al. First-in-Man Intrathecal Application of Neurite Growth-Promoting Anti-Nogo-A Antibodies in Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2018;32(6-7):578-589. [51] FINK KL, STRITTMATTER SM, CAFFERTY WB. Comprehensive Corticospinal Labeling with mu-crystallin Transgene Reveals Axon Regeneration after Spinal Cord Trauma in ngr1-/- Mice. J Neurosci. 2015;35(46):15403-15418. [52] ZHAO X, PENG Z, LONG L, et al. Lentiviral vector delivery of short hairpin RNA to NgR1 promotes nerve regeneration and locomotor recovery in injured rat spinal cord. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):5447. [53] WANG X, YIGITKANLI K, KIM CY, et al. Human NgR-Fc decoy protein via lumbar intrathecal bolus administration enhances recovery from rat spinal cord contusion. J Neurotrauma. 2014;31(24):1955-1966. [54] ITO S, NAGOSHI N, TSUJI O, et al. LOTUS Inhibits Neuronal Apoptosis and Promotes Tract Regeneration in Contusive Spinal Cord Injury Model Mice. eNeuro. 2018;5(5):e0303-0318. [55] LI G, CHE MT, ZENG X, et al. Neurotrophin-3 released from implant of tissue-engineered fibroin scaffolds inhibits inflammation, enhances nerve fiber regeneration, and improves motor function in canine spinal cord injury. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(8):2158-2170. [56] HAN Q, ORDAZ JD, LIU NK, et al. Descending motor circuitry required for NT-3 mediated locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury in mice. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):5815. [57] CROWLEY ST, FUKUSHIMA Y, UCHIDA S, et al. Enhancement of Motor Function Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice by Delivery of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor mRNA. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;17:465-476. [58] CHARSAR BA, BRINTON MA, LOCKE K, et al. AAV2-BDNF promotes respiratory axon plasticity and recovery of diaphragm function following spinal cord injury. FASEB J. 2019;33(12):13775-13793. [59] XU D, WU D, QIN M, et al. Efficient Delivery of Nerve Growth Factors to the Central Nervous System for Neural Regeneration. Adv Mater. 2019;31(33): e1900727. [60] LIU Y, WANG X, LI W, et al. A Sensitized IGF1 Treatment Restores Corticospinal Axon-Dependent Functions. Neuron. 2017;95(4):817-833. [61] ASSINCK P, DUNCAN GJ, HILTON BJ, et al. Cell transplantation therapy for spinal cord injury. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20(5):637-647. [62] COURTINE G, SOFRONIEW MV. Spinal cord repair: advances in biology and technology. Nat Med. 2019;25(6):898-908. [63] LADRAN I, TRAN N, TOPOL A, et al. Neural stem and progenitor cells in health and disease. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2013;5(6):701-715. [64] CURTIS E, MARTIN JR, GABEL B, et al. A First-in-Human, Phase I Study of Neural Stem Cell Transplantation for Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Stem Cell. 2018; 22(6):941-950. [65] LU P, WOODRUFF G, WANG Y, et al. Long-distance axonal growth from human induced pluripotent stem cells after spinal cord injury. Neuron. 2014;83(4): 789-796. [66] KOJIMA K, MIYOSHI H, NAGOSHI N, et al. Selective Ablation of Tumorigenic Cells Following Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Stem/Progenitor Cell Transplantation in Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(3): 260-270. [67] ROPPER AE, THAKOR DK, HAN I, et al. Defining recovery neurobiology of injured spinal cord by synthetic matrix-assisted hMSC implantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(5):E820-E829. [68] WU GH, SHI HJ, CHE MT, et al. Recovery of paralyzed limb motor function in canine with complete spinal cord injury following implantation of MSC-derived neural network tissue. Biomaterials. 2018;181:15-34. [69] VAQUERO J, ZURITA M, RICO MA, et al. Intrathecal administration of autologous mesenchymal stromal cells for spinal cord injury: Safety and efficacy of the 100/3 guideline. Cytotherapy. 2018;20(6):806-819. [70] KHANKAN RR, GRIFFIS KG, HAGGERTY-SKEANS JR, et al. Olfactory Ensheathing Cell Transplantation after a Complete Spinal Cord Transection Mediates Neuroprotective and Immunomodulatory Mechanisms to Facilitate Regeneration. J Neurosci. 2016;36(23):6269-6286. [71] GILMOUR AD, RESHAMWALA R, WRIGHT AA, et al. Optimizing Olfactory Ensheathing Cell Transplantation for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. J Neurotrauma. 2020;37(5):817-829. [72] GRANGER N, BLAMIRES H, FRANKLIN RJ, et al. Autologous olfactory mucosal cell transplants in clinical spinal cord injury: a randomized double-blinded trial in a canine translational model. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 11):3227-3237. [73] KANNO H, PEARSE DD, OZAWA H, et al. Schwann cell transplantation for spinal cord injury repair: its significant therapeutic potential and prospectus. Rev Neurosci. 2015;26(2):121-128. [74] ANDERSON KD, GUEST JD, DIETRICH WD, et al. Safety of Autologous Human Schwann Cell Transplantation in Subacute Thoracic Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2017;34(21):2950-2963. [75] TORRES-ESPÍN A, BEAUDRY E, FENRICH K, et al. Rehabilitative Training in Animal Models of Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(16):1970-1985. [76] JAMES ND, MCMAHON SB, FIELD-FOTE EC, et al. Neuromodulation in the restoration of function after spinal cord injury. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(10): 905-917. [77] ANGELI CA, EDGERTON VR, GERASIMENKO YP, et al. Altering spinal cord excitability enables voluntary movements after chronic complete paralysis in humans. Brain. 2014;137(Pt 5):1394-1409. [78] ANGELI CA, BOAKYE M, MORTON RA, et al. Recovery of Over-Ground Walking after Chronic Motor Complete Spinal Cord Injury. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(13): 1244-1250. [79] GILL ML, GRAHN PJ, CALVERT JS, et al. Neuromodulation of lumbosacral spinal networks enables independent stepping after complete paraplegia. Nat Med. 2018;24(11):1677-1682. [80] FORMENTO E, MINASSIAN K, WAGNER F, et al. Electrical spinal cord stimulation must preserve proprioception to enable locomotion in humans with spinal cord injury. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21(12):1728-1741. [81] WAGNER FB, MIGNARDOT JB, LE GOFF-MIGNARDOT CG, et al. Targeted neurotechnology restores walking in humans with spinal cord injury. Nature. 2018;563(7729):65-71. [82] HARKEMA SJ, WANG S, ANGELI CA, et al. Normalization of Blood Pressure With Spinal Cord Epidural Stimulation After Severe Spinal Cord Injury. Front Hum Neurosci. 2018;12:83. [83] WILLYARD C. How a revolutionary technique got people with spinal-cord injuries back on their feet. Nature. 2019;572(7767):20-25. [84] SQUAIR JW, BJERKEFORS A, INGLIS JT, et al. Cortical and vestibular stimulation reveal preserved descending motor pathways in individuals with motor-complete spinal cord injury. J Rehabil Med. 2016;48(7):589-596. [85] MAHLKNECHT P, LIMOUSIN P, FOLTYNIE T. Deep brain stimulation for movement disorders: update on recent discoveries and outlook on future developments. J Neurol. 2015;262(11):2583-2595. [86] ZAREEN N, DODSON S, ARMADA K, et al. Stimulation-dependent remodeling of the corticospinal tract requires reactivation of growth-promoting developmental signaling pathways. Exp Neurol. 2018;307:133-144. [87] YANG Q, RAMAMURTHY A, LALL S, et al. Independent replication of motor cortex and cervical spinal cord electrical stimulation to promote forelimb motor function after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol. 2019;320:112962. [88] CORTES M, MEDEIROS AH, GANDHI A, et al. Improved grasp function with transcranial direct current stimulation in chronic spinal cord injury. NeuroRehabilitation. 2017;41(1):51-59. [89] KRISHNAN VS, SHIN SS, BELEGU V, et al. Multimodal Evaluation of TMS - Induced Somatosensory Plasticity and Behavioral Recovery in Rats With Contusion Spinal Cord Injury. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:387. [90] LESZCZYŃSKA K, WINCEK A, FORTUNA W, et al. Treatment of patients with cervical and upper thoracic incomplete spinal cord injury using repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Int J Artif Organs. 2020;43(5):323-331. [91] RODIONOV A, SAVOLAINEN S, KIRVESKARI E, et al. Restoration of hand function with long-term paired associative stimulation after chronic incomplete tetraplegia: a case study. Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2019;5:81. [92] HOCHBERG LR, BACHER D, JAROSIEWICZ B, et al. Reach and grasp by people with tetraplegia using a neurally controlled robotic arm. Nature. 2012;485(7398): 372-375. [93] DONATI AR, SHOKUR S, MORYA E, et al. Long-Term Training with a Brain-Machine Interface-Based Gait Protocol Induces Partial Neurological Recovery in Paraplegic Patients. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30383. [94] AJIBOYE AB, WILLETT FR, YOUNG DR, et al. Restoration of reaching and grasping movements through brain-controlled muscle stimulation in a person with tetraplegia: a proof-of-concept demonstration. Lancet. 2017;389(10081): 1821-1830. [95] WENGER N, MORAUD EM, GANDAR J, et al. Spatiotemporal neuromodulation therapies engaging muscle synergies improve motor control after spinal cord injury. Nat Med. 2016;22(2):138-145. [96] CAPOGROSSO M, MILEKOVIC T, BORTON D, et al. A brain-spine interface alleviating gait deficits after spinal cord injury in primates. Nature. 2016;539 (7628):284-288. [97] BONIZZATO M, PIDPRUZHNYKOVA G, DIGIOVANNA J, et al. Brain-controlled modulation of spinal circuits improves recovery from spinal cord injury. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):3015. [98] ANDERSON MA, O’SHEA TM, BURDA JE, et al. Required growth facilitators propel axon regeneration across complete spinal cord injury. Nature. 2018;561 (7723):396-400. [99] YANG Z, ZHANG A, DUAN H, et al. NT3-chitosan elicits robust endogenous neurogenesis to enable functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(43):13354-13359. [100] RAO JS, ZHAO C, ZHANG A, et al. NT3-chitosan enables de novo regeneration and functional recovery in monkeys after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(24):E5595-E5604. [101] DEPAUL MA, LIN CY, SILVER J, et al. Combinatory repair strategy to promote axon regeneration and functional recovery after chronic spinal cord injury. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):9018. [102] WANG Q, ZHANG H, XU H, et al. Novel multi-drug delivery hydrogel using scar-homing liposomes improves spinal cord injury repair. Theranostics. 2018;8(16): 4429-4446. [103] NAZEMI Z, NOURBAKHSH MS, KIANI S, et al. Co-delivery of minocycline and paclitaxel from injectable hydrogel for treatment of spinal cord injury. J Control Release. 2020;321:145-158. [104] WANG XJ, PENG CH, ZHANG S, et al. Polysialic-Acid-Based Micelles Promote Neural Regeneration in Spinal Cord Injury Therapy. Nano Lett. 2019;19(2): 829-838. [105] TIAN T, YU Z, ZHANG N, et al. Modified acellular nerve-delivering PMSCs improve functional recovery in rats after complete spinal cord transection. Biomater Sci. 2017;5(12):2480-2492. [106] LU P, WANG Y, GRAHAM L, et al. Long-distance growth and connectivity of neural stem cells after severe spinal cord injury. Cell. 2012;150(6):1264-1273. [107] KADOYA K, LU P, NGUYEN K, et al. Spinal cord reconstitution with homologous neural grafts enables robust corticospinal regeneration. Nat Med. 2016;22(5): 479-487. [108] KOFFLER J, ZHU W, QU X, et al. Biomimetic 3D-printed scaffolds for spinal cord injury repair. Nat Med. 2019;25(2):263-269. [109] ROSENZWEIG ES, BROCK JH, LU P, et al. Restorative effects of human neural stem cell grafts on the primate spinal cord. Nat Med. 2018;24(4):484-490. [110] TAKEOKA A, JINDRICH DL, MUÑOZ-QUILES C, et al. Axon regeneration can facilitate or suppress hindlimb function after olfactory ensheathing glia transplantation. Version 2. J Neurosci. 2011;31(11):4298-4310. [111] CHEN K, MARSH BC, COWAN M, et al. Sequential therapy of anti-Nogo-A antibody treatment and treadmill training leads to cumulative improvements after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol. 2017;292:135-144. [112] GRIFFIN JM, FACKELMEIER B, CLEMETT CA, et al. Astrocyte-selective AAV-ADAMTS4 gene therapy combined with hindlimb rehabilitation promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2020;327:113232. [113] FEHLINGS MG, KIM KD, AARABI B, et al. Rho Inhibitor VX-210 in Acute Traumatic Subaxial Cervical Spinal Cord Injury: Design of the SPinal Cord Injury Rho INhibition InvestiGation (SPRING) Clinical Trial. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(9): 1049-1056. [114] MINEV IR, MUSIENKO P, HIRSCH A, et al. Biomaterials. Electronic dura mater for long-term multimodal neural interfaces. Science. 2015;347(6218):159-163. [115] SCHAFFRAN B, BRADKE F. Reproducibility - The key towards clinical implementation of spinal cord injury treatments? Exp Neurol. 2019;313:135-136. [116] FRIEDLI L, ROSENZWEIG ES, BARRAUD Q, et al. Pronounced species divergence in corticospinal tract reorganization and functional recovery after lateralized spinal cord injury favors primates. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(302):302ra134. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [3] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [4] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [5] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [6] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [7] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [8] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [9] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [10] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [11] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [12] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [13] | Zeng Zhen, Hu Jingwei, Li Xuan, Tang Linmei, Huang Zhiqiang, Li Mingxing. Quantitative analysis of renal blood flow perfusion using contrast-enhanced ultrasound in rats with hemorrhagic shock during resuscitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1201-1206. |
| [14] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [15] | Wang Mengting, Gu Yanping, Ren Wenbo, Qin Qian, Bai Bingyi, Liao Yuanpeng. Research hotspots of blood flow restriction training for dyskinesia based on visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1264-1269. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||