[1] EASTELL R, ROSEN CJ, BLACK DM, et al. Pharmacological Management of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women: An Endocrine Society* Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104(5):1595-1622.
[2] WANG C, MAO C, LOU Y, et al. Monotropein promotes angiogenesis and inhibits oxidative stress-induced autophagy in endothelial progenitor cells to accelerate wound healing. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(3):1583-1600.
[3] ROHOWETZ LJ, KRAUS JG, KOULEN P. Reactive oxygen species-mediated damage of retinal neurons: drug development targets for therapies of chronic neurodegen eration of the retina. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19 (11):3362-3372.
[4] WANG S, DENG Z, MA Y, et al.The Role of Autophagy and Mitophagy in Bone Metabolic Disorders. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(14):2675-2691.
[5] SU RJ, JIN XT, ZHANG WF, et al.Particulate matter exposure induces the autophagy of macrophages via oxidative stress-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Chemosphere. 2017;167:444-453.
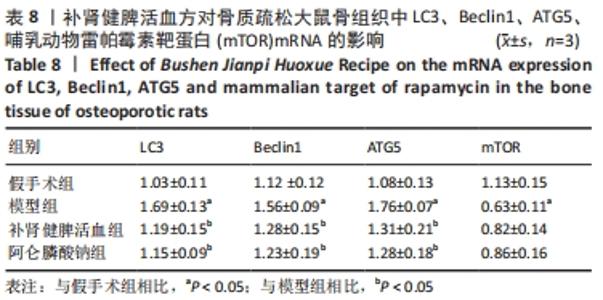
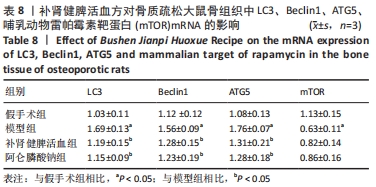
[6] 柴爽,王吉利,黄佳纯,等.补肾健脾活血方对去卵巢大鼠BMP2/Smad 信号通路的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2018,24(20): 129-133.
[7] 刘治军,刘少津,魏合伟,等.补肾健脾活血方干预去势大鼠肌肉骨骼转化生长因子β/ 骨形态发生蛋白2信号通路的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2219-2223.
[8] 刘少津.补肾健脾活血方对去势大鼠股骨TGF-β1/Smads信号通路的影响[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学,2019.
[9] RIZZOLI R. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: Assessment and management.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;32(5):739-757.
[10] WANG NN, XU PC, WANG XP, et al. Integrated pathological cell fifishing and network pharmacology approach to investigate main active components of Er-Xian decotion for treating osteoporosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;241: 111977-111985.
[11] YUAN F, PENG W, YANG C, et al. Teriparatide versus bisphosphonates for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: A meta-analysis. Int J Sur. 2019; 66:1-11.
[12] 曹舒兴,宋永周,李明,等.抗增生胶囊调控去卵巢骨质疏松症大鼠骨代谢及氧化应激指标研究[J].河北中医,2020,42(4):580-585.
[13] 郑红,赵宏斌,袁鑫,等.恒古骨伤愈合剂通过PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β信号通路治疗树鼩绝经后骨质疏松的作用机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2019, 39(3):626-630.
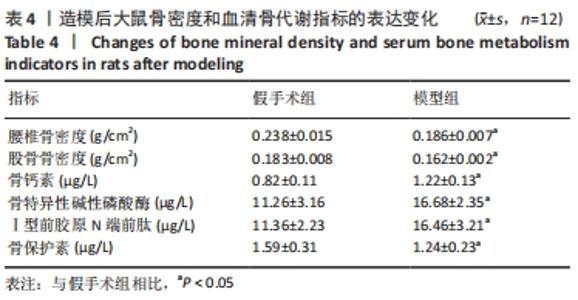
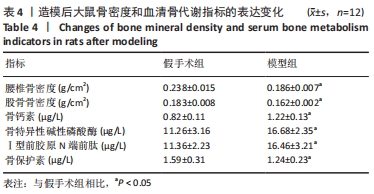
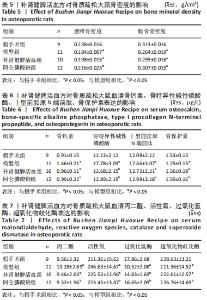
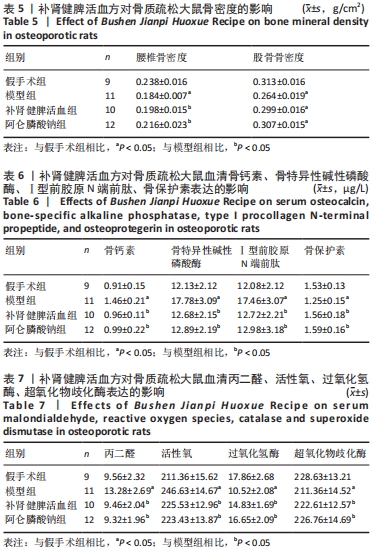
[14] 柴爽,黄佳纯,王吉利,等.补肾健脾活血方对大鼠绝经后骨质疏松症的防治作用[J].中成药,2019,41(9):2213-2216.
[15] 万雷,黄宏兴,蔡桦,等.补肾健脾活血方对老年女性骨质疏松患者疼痛和血清β-CTx、N-MID、T-PINP的影响[J].辽宁中医杂志,2015,42(9): 1690-1692.
[16] WANG W, YAO GD, SHANG XY, et al.Eclalbasaponin I from Aralia elata (Miq.) Seem. Reduces oxidative stress-induced neural cell death by autophagy activation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;97:152-161.
[17] LI M, HAO L, LIU L, et al. Cinnamtannin B-1 Prevents Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis via Attenuating Osteoclastogenesis and ROS Generation. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1023.
[18] YU L, CHEN Y, TOOZE SA. Autophagy pathway: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Autophagy. 2018;14(2):207-215.
[19] DESELM CJ, MILLER BC, ZOU W, et al. Autophagy proteins regulate the secretory component of osteoclastic bone resorption. Dev Cell. 2011;21(5): 966-974.
[20] CHUNG YH, YOON SY, CHOI BK, et al. Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 regulates Cdc42-dependent actin ring formation in osteoclast. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44(6):989-997.
[21] ARAI A, KIM S, GOIDSHTEYN V, et al. Beclin1 modulates bone homeostasis by regulating osteoclast and chondrocyte differentiation. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(9):1753-1766.
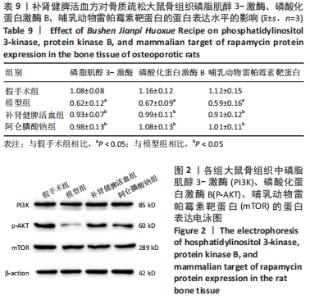
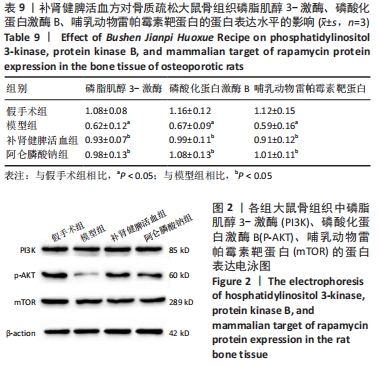
[22] 强胜林,刘涛,贾永龙,等.补肾固本方对大鼠骨质疏松模型中PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路表达的调控研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(7): 983-987.
[23] 朱伟,李智斌,杨利学,等.抗疏强骨合剂对去势骨质疏松模型大鼠骨组织中自噬相关蛋白表达的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2020,29(25): 2752-2756.
[24] GARG AD, DUDEK AM, FERREIRA GB, et al.ROS-induced autophagy in cancer cells assists in evasion from determinants of immunogenic cell death. Autophagy. 2013;9(9):1292-1307.
[25] ZHOU H, JIAO G, DONG M, et al. Orthosilicic Acid Accelerates Bone Formation in Human Osteoblast-Like Cells Through the PI3K-Akt–mTOR Pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019;190(2):327-335.
[26] LI DY, YU JC, MIAO W, et al. Autophagy attenuates the oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of Mc3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(24):5548-5556.
|