Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (20): 3178-3183.doi: 10.12307/2022.617
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bushen Tiaogan Prescription containing serum in the treatment of osteoarthritis by promoting chondrocyte autophagy in rats
Fan Shuai1, Wu Chunfei1, Liang Zujian1, Xu Zhaohui2, Xie Pingjin2, Zhu Genfu1
- 1Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510240, Guangdong Province, China; 2Luohu District Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2021-09-22Accepted:2021-11-11Online:2022-07-18Published:2022-01-18 -
Contact:Zhu Genfu, MD, Associate chief physician, Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510240 Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Fan Shuai, Master, Attending physician, Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510240 Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Guangdong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, No. 2021A1515011469 (to LZJ); Guangdong Provincial Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Projects, Nos. 20201171 (to FS) and 20211211 (to WCF); Research and Innovation Projects of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Nos. sy201701 and sy2018007 (both to FS); 2020 Basic Research Project of Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee, No. JCYJ20190812170815559 (to XPJ [project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fan Shuai, Wu Chunfei, Liang Zujian, Xu Zhaohui, Xie Pingjin, Zhu Genfu. Bushen Tiaogan Prescription containing serum in the treatment of osteoarthritis by promoting chondrocyte autophagy in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3178-3183.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
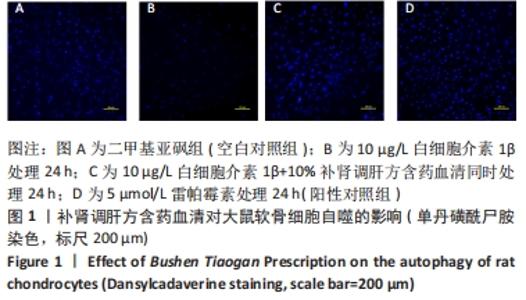
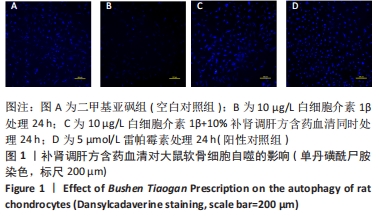
2.1 单丹磺酰尸胺染色法检测补肾调肝方含药血清对软骨细胞自噬的影响 分别用二甲基亚砜、10 μg/L白细胞介素1β、10 μg/L白细胞介素1β+10%补肾调肝方含药血清和5 μmol/L雷帕霉素处理软骨细胞24 h后采用单丹磺酰尸胺检测软骨细胞自噬小体的表达情况。雷帕霉素可抑制AKT/mTOR信号通路的活性,从而诱导细胞发生自噬[17],因而此次研究使用雷帕霉素作为阳性对照组。结果显示与二甲基亚砜组比较,10 μg/L白细胞介素1β组中细胞的自噬小体数量明显减少;自噬诱导剂雷帕霉素处理后的软骨细胞(阳性对照组)与二甲基亚砜组相比,自噬小体的数量明显增多,10 μg/L白细胞介素1β+10%补肾调肝方含药血清组与10 μg/L白细胞介素1β组相比自噬小体明显增多,表明补肾调肝方含药血清能够提高软骨细胞的自噬水平,见图1。"
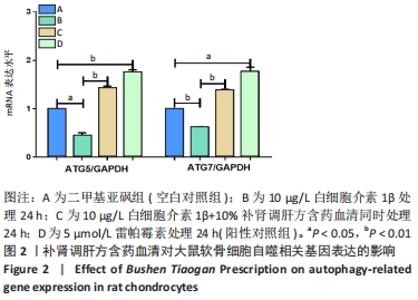
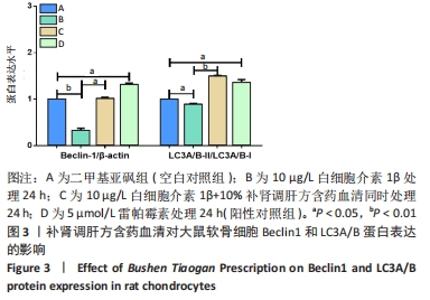
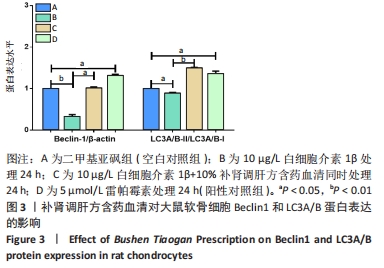
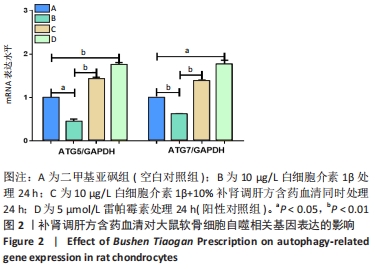
2.2 补肾调肝方含药血清对软骨细胞自噬相关基因和蛋白表达的影响 分别用二甲基亚砜、10 μg/L白细胞介素1β、10 μg/L 白细胞介素1β+10%补肾调肝方含药血清和5 μmol/L 雷帕霉素处理软骨细胞24 h后,采用实时荧光定量PCR检测软骨细胞中自噬相关基因ATG5和ATG7 mRNA表达的情况,Western blot检测软骨细胞中自噬蛋白Beclin1和LC3A/B的表达情况。结果显示,与二甲基亚砜组比较,10 μg/L白细胞介素1β组中细胞的自噬相关基因ATG5、ATG7 mRNA表达水平明显下降(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),Beclin1和LC3A/B-Ⅱ/LC3A/B-Ⅰ蛋白表达水平明显下降(P < 0.01,P < 0.05);自噬诱导剂雷帕霉素处理后的软骨细胞与二甲基亚砜组相比,ATG5、ATG7 mRNA水平明显上升(P < 0.01,P < 0.05),Beclin1和LC3A/B-Ⅱ/LC3A/B-Ⅰ蛋白表达水平明显上升(P < 0.05,P < 0.05);10 μg/L细胞介素1β+10%补肾调肝方含药血清组与白细胞介素1β组相比ATG5、ATG7 mRNA水平明显上升(P < 0.01,P < 0.01),Beclin1和LC3A/B-Ⅱ/LC3A/B-Ⅰ蛋白表达水平明显上升(P < 0.05,P < 0.01)。结果表明,与二甲基亚砜组比较,白细胞介素1β组细胞的自噬能力降低;与10 μg/L白细胞介素1β组相比,白细胞介素1β处理后的细胞经补肾调肝方治疗后细胞自噬水平增强,见图2,3。"
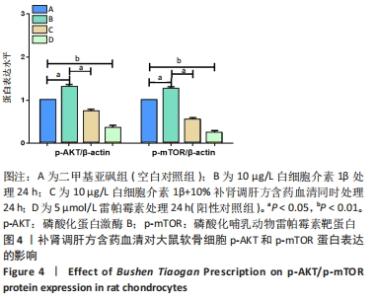
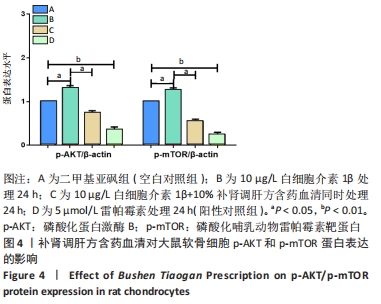
2.3 补肾调肝方含药血清对软骨细胞AKT/mTOR信号通路的影响 分别用二甲基亚砜、10 μg/L白细胞介素1β、10 μg/L白细胞介素1β+10%补肾调肝方含药血清和5 μmol/L 雷帕霉素处理软骨细胞24 h后,采用Western blot法检测p-AKT和p-mTOR蛋白表达的影响。结果显示,与二甲基亚砜组比较,10 μg/L白细胞介素1β组中细胞的p-AKT和p-mTOR蛋白表达水平明显上升(P < 0.05,P < 0.05);雷帕霉素处理后的软骨细胞与二甲基亚砜组相比,p-AKT和p-mTOR蛋白表达水平明显下降(P < 0.01,P < 0.01);10 μg/L白细胞介素1β+10%补肾调肝方含药血清组与10 μg/L白细胞介素1β组相比,p-AKT和p-mTOR蛋白表达水平明显下降(P < 0.05,P < 0.05)。结果表明补肾调肝方含药血清能够抑制软骨细胞的AKT/mTOR信号通路,见图4。"
| [1] ACKERMAN IN, BOHENSKY MA, STEIGER RD, et al. Substantial rise in the lifetime risk of primary total knee replacement surgery for osteoarthritis from 2003 to 2013: an international, population-level analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;25(4):455-461. [2] HARRELL CR, MARKOVIC BS, FELLABAUM C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy of osteoarthritis: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:2318-2326. [3] JEON OH, KIM C, LABERGE RM, et al. Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative environment. Nat Med. 2017;23(6):775-781. [4] VINA ER, KWOH CK. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: literature update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30(2):160-167. [5] LOESER RF. The Role of Aging in the Development of Osteoarthritis. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2017;128:44-54. [6] O’NEILL TW, MCCABE PS, MCBETH J. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors and disease outcomes of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32(2):312-326. [7] CUTOLO M, BERENBAUM F, HOCHBERG M, et al. Commentary on recent therapeutic guidelines for osteoarthritis. Semin Arthrit Rheum. 2015;44:611-617. [8] NAKAMURA S, YOSHIMORI T. New insights into autophagosome-lysosome fusion. J Cell Sci. 2017;130:1209-1216. [9] YU L, CHEN Y, TOOZE SA. Autophagy pathway: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Autophagy. 2018;14(2):207-215. [10] TAKAYAMA K, KAWAKAMI Y, KOBAYASHI M, et al. Local intra-articular injection of rapamycin delays articular cartilage degeneration in a murine model of osteoarthritis. Arthrit Res Ther. 2014;16(6):482-482. [11] CHENG NT, GUO A, CUI YP. Intra-articular injection of Torin 1 reduces degeneration of articular cartilage in a rabbit osteoarthritis model. Bone Joint Res. 2016;5(6):218-224. [12] 梁桂洪,黄和涛,潘建科,等.龙鳖胶囊含药血清对YAP抑制剂诱导人软骨细胞凋亡的保护作用及机制研究[J].中国药房,2021, 32(12):1442-1448. [13] 吴春飞, 易俊, 梁桂洪, 等. 补肾调肝方治疗肝郁肾虚膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J]. 中医临床研究,2017,9(36):74-76. [14] 范帅, 林杰彬, 吴春飞, 等. 补肾调肝方含药血清对白细胞介素1β诱导软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(35): 5594-5598. [15] 策力木格, 张小峰, 苏都娜, 等.血清药物化学在中药领域的应用现状[J].中国药房,2017,28(7):978-981. [16] 李若飞, 于春萍, 兰丁璇, 等.中药血清药理学实验方法与相关问题探讨[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2019,6(31):125-136. [17] LI B, YANG J, LU Z, et al. A study on the mechanism of rapamycin mediating the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to cisplatin through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J BUON. 2019;24(2):739-745. [18] WILKINSON DJ, HABGOOD A, LAMB HK, et al. Matriptase induction of metalloproteinase-dependent aggrecanolysis in vitro and in vivo: promotion of osteoarthritic cartilage damage by multiple mechanisms promote cartilage damage in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69(8):1601-1611. [19] HE Y, LI Z, ALEXANDER PG, et al. Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis: Risk Factors, Regulatory Pathways in Chondrocytes, and Experimental Models. Biology. 2020;9(8):194. [20] ZHANG G, CAO J, YANG E, et al. Curcumin improves age-related and surgically induced osteoarthritis by promoting autophagy in mice. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(4):BSR20171691. [21] DUAN R, XIE H, LIU ZZ. The Role of Autophagy in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:1437. [22] LAPLANTE M, SABATINI DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012;149(2):274-293. [23] VASHEGHANI F, ZHANG Y, LI YH, et al. PPARγ deficiency results in severe, accelerated osteoarthritis associated with aberrant mTOR signalling in the articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(3):569-578. [24] DON AS, TSANG CK, KAZDOBA TM, et al. Targeting mTOR as a novel therapeutic strategy for traumatic CNS injuries. Drug Discov Today. 2012;17(15-16):861-868. [25] KIM YC, GUAN KL. mTOR: a pharmacologic target for autophagy regulation. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(1):25-32. [26] ZHANG Y, VASHEGHANI F, LI YH, et al. Cartilage-specific deletion of mTOR upregulates autophagy and protects mice from osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;74(7):1432-1440. [27] NEW J, THOMAS SM. Autophagy-dependent secretion: mechanism, factors secreted, and disease implications. Autophagy. 2019;15(10): 1682-1693. [28] ZHANG Y, VASHEGHANI F, LI Y, et al. Cartilage-specific deletion of mTOR upregulates autophagy and protects mice from osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(7):1432-1440. [29] QIN N, WEI L, LI W, et al. Local intra-articular injection of resveratrol delays cartilage degeneration in C57BL/6 mice by inducing autophagy via AMPK/mTOR pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 2017;134(3):166-174. [30] XUE JF, SHI ZM, ZOU J, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:1252-1261. [31] MUSUMECI G, CASTROGIOVANNI P, TROVATO FM, et al. Biomarkers of Chondrocyte Apoptosis and Autophagy in Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(9):20560-20575. [32] YU Y, ZHAO J. Modulated Autophagy by MicroRNAs in Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:1484152. [33] MATSUZAKI T, ALVAREZ-GARCIA O, MOKUDA S, et al. FoxO transcription factors modulate autophagy and proteoglycan 4 in cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(428): eaan0746. [34] TANG Q, ZHENG G, FENG Z, et al. Trehalose ameliorates oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress via selective autophagy stimulation and autophagic flux restoration in osteoarthritis development. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(10):e3081. [35] LUO P, GAO F, NIU D, et al. The Role of Autophagy in Chondrocyte Metabolism and Osteoarthritis: A Comprehensive Research Review. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5171602. [36] WANG C, YAO Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Metformin Mitigates Cartilage Degradation by Activating AMPK/SIRT1-Mediated Autophagy in a Mouse Osteoarthritis Model. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1114. [37] TIAN F, WANG J, ZHANG Z, et al. LncRNA SNHG7/miR-34a-5p/SYVN1 axis plays a vital role in proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy in osteoarthritis. Biol Res. 2020;53(1):9. [38] ZHONG G, LONG H, MA S, et al. miRNA-335-5p relieves chondrocyte inflammation by activating autophagy in osteoarthritis. Life Sci. 2019; 226:164-172. [39] CAI C, MIN S, YAN B, et al. MiR-27a promotes the autophagy and apoptosis of IL-1beta treated-articular chondrocytes in osteoarthritis through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(16):6371-6384. [40] LIN Z, MIAO J, ZHANG T, et al. JUNB-FBXO21-ERK axis promotes cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by inhibiting autophagy. Aging Cell. 2021;20(2):e13306. |
| [1] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [2] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [3] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [4] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [5] | Cui Xing, Sun Xiaoqi, Zheng Wei, Ma Dexin. Huangqin Decoction regulates autophagy to intervene with intestinal acute graft-versus-host disease in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1057-1062. |
| [6] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [7] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [8] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [9] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [10] | Xu Lei, Han Xiaoqiang, Zhang Jintao, Sun Haibiao. Hyaluronic acid around articular chondrocytes: production, transformation and function characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 768-773. |
| [11] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [12] | Zhang Jian, Lin Jianping, Zhou Gang, Fang Yehan, Wang Benchao, Wu Yongchang. Semi-quantitative MRI evaluation of cartilage degeneration in early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 425-429. |
| [13] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Changes in kinematic parameters after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 390-396. |
| [14] | Wang Chong, Zhang Meiying, Zhou Jian, Lao Kecheng. Early gait changes after total hip arthroplasty through direct anterior approach and posterolateral approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 359-364. |
| [15] | Mi Jianguo, Qiao Rongqin, Liu Shaojin. Bushen Jianpi Huoxue Recipe improves bone metabolism, oxidative stress, and autophagy in osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4147-4152. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||