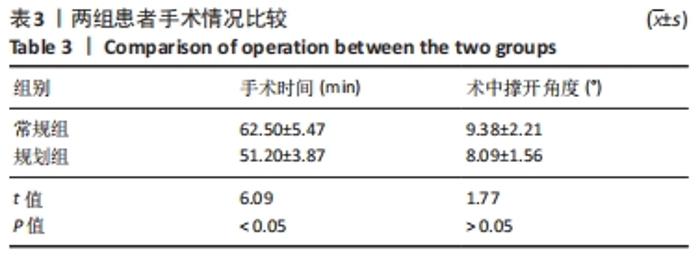
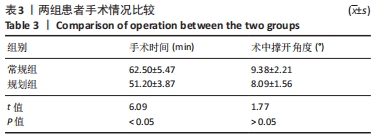
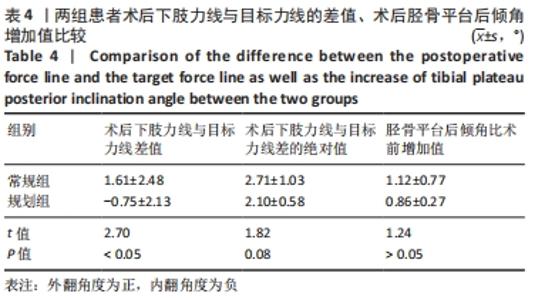
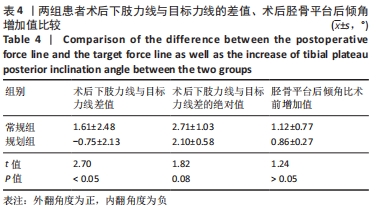
[1] 孙建华,罗本泰,万国生,等.胫骨高位截骨联合关节镜清理术治疗膝内翻型关节炎[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(9):853-855.
[2] HE M, ZHONG X, LI Z, et al. Progress in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with high tibial osteotomy: a systematic review. Syst Rev. 2021;10(1):56.
[3] 金志辉,彭昊,方洪松,等.内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术治疗膝关节内翻畸形的临床应用[J].临床外科杂志,2018,26(7):546-549.
[4] 张子琦,梁佳林,樊立宏,等.开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术治疗膝关节内侧间室骨关节炎疗效观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(8):997-1000.
[5] 王秋实, 刘宁, 郇松玮,等. 开放楔形胫骨高位截骨保膝治疗1例[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(6):458-459.
[6] 谭必知,马骏雄,项良碧.基于影像归档和通信系统的下颈椎椎管旁螺钉相关参数三维测量及可行性研究[J].骨科,2020,11(5):405-410.
[7] 高小康,韩守江,张元华,等.3D打印截骨导板在内侧开放胫骨高位截骨术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(2):137-140.
[8] 高润子,高衡,汪树林,等.3D打印截骨导板在内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术中的应用研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2018,24(4):361-364.
[9] 邓迎杰,肖俞臣,方锐.胫骨高位截骨术治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效评估及对关节软骨再生的影响[J].骨科,2019,10(2):85-89.
[10] VAISHYA R, BIJUKCHHE AR, AGARWAL AK, et al. A critical appraisal of medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy for knee osteoarthritis. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018;9(4):300-306.
[11] 刘冬铖,赵继军,周子红,等.医学影像信息系统辅助全膝置换前计划中的作用与意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(12):1917-1922.
[12] 温立,王胜利,葛站勇.基于医学影像信息系统的精确术前规划实施经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗椎体脆性骨折效果研究[J].中国全科医学,2020, 23(12):1517-1522.
[13] 孙茂淋, 何锐, 郭林,等.开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术的临床应用及研究现状[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(5):640-643.
[14] BENZAKOUR T, HEFTI A, LEMSEFFER M, et al. High tibial osteotomy for medial osteoarthritis of the knee: 15 years follow-up. Int Orthop. 2010;34(2):209-215.
[15] YIN Y, LI S, ZHANG R, et al. What is the relationship between the “Fujisawa point” and postoperative knee valgus angle? A theoretical, computer-based study. Knee. 2020;27(1):183-191.
[16] HERNIGOU P. A 20-year follow-up study of internal gonarthrosis after tibial valgus osteotomy. Single versus repeated osteotomy. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1996;82(3):241-250.
[17] HERNIGOU P, MEDEVIELLE D, DEBEYRE J, et al. Proximal tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis with varus deformity. A ten to thirteen-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(3):332-354.
[18] LEE SS, LEE HI, CHO ST,et al. Comparison of the outcomes between two different target points after open wedge high tibial osteotomy: The Fujisawa point versus the lateral tibial spine. Knee. 2020;27(3):915-922.
[19] 俞颖豪,赵继军,刘冬铖,等.个体化开放楔形胫骨高位截骨治疗内侧间室膝骨关节炎的优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(27):4310-4316.
[20] OGAWA H, MATSUMOTO K, AKIYAMA H. ACL degeneration after an excessive increase in the medial proximal tibial angle with medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(10):3374-3380.
[21] KWON OJ, KIM JM, BIN SI, et al. Morphologic MRI changes of the anterior cruciate ligament are associated with an increase in the medial tibial plateau bony slope after medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy in a non-injured ACL population. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(7):1369-1375.
[22] OGAWA H, MATSUMOTO K, AKIYAMA H. Effect of increased posterior tibial slope on the anterior cruciate ligament status in medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy in an uninjured ACL population. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(6):1085-1091.
[23] SHAW JA, DUNGY DS, ARSHT SS. Recurrent varus angulation after high tibial osteotomy: an anatomic analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(420):205-212.
[24] CHIU KY, ZHANG SD, ZHANG GH. Posterior slope of tibial plateau in Chinese. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(2):224-227.
[25] DRAGOSLOVEANU S, CRISTEA S, DRAGOSLOVEANU C. The effect of high tibial osteotomy on the posterior tibial slope. Maedica (Bucur). 2014;9(2):173-178.
[26] YANG JC, CHEN CF, LUO CA, et al. Clinical Experience Using a 3D-Printed Patient-Specific Instrument for Medial Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:9246529.
[27] HAN SB, KIM HJ, LEE DH. Effect of Computer Navigation on Accuracy and Reliability of Limb Alignment Correction following Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:3803457.
[28] OGAWA H, MATSUMOTO K, AKIYAMA H. New angle measurement device to control the posterior tibial slope angle in medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(3):299-305.
[29] DENG X, CHEN W, ZHAO K, et al. Changes in patellar height and posterior tibial slope angle following uniplanar medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy using a novel wedge-shaped spacer implanation concurrent with proximal partial fibulectomy. Int Orthop. 2021;45(1):109-115.
|