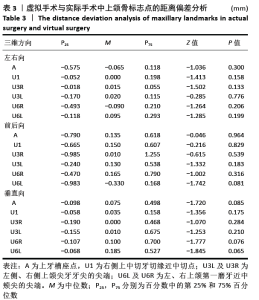
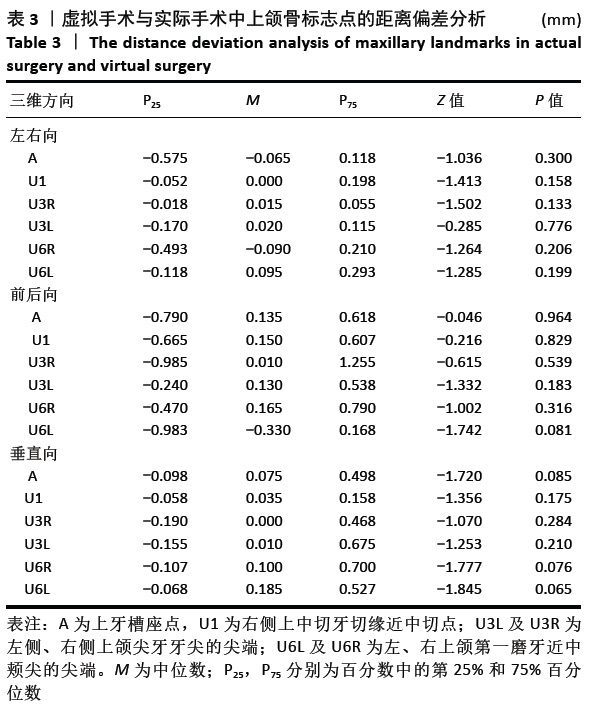
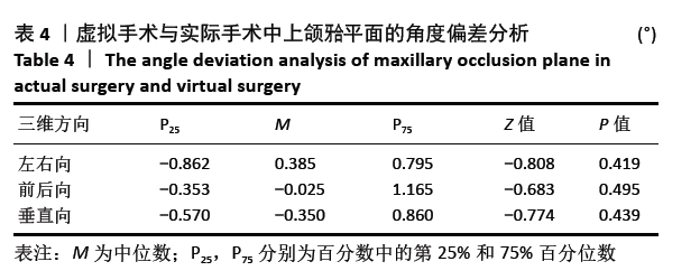
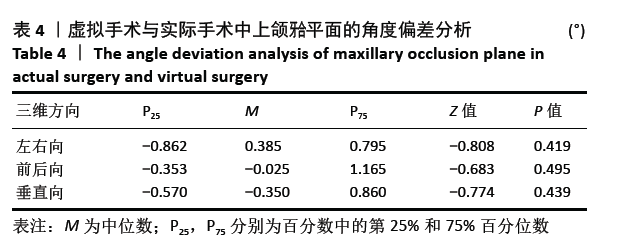
[1] 胡静,沈国芳,刘彦普,等.牙颌面畸形诊断与治疗指南[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2011,9(5):415-419.
[2] LIN HH, LONIC D, LO LJ. 3D printing in orthognathic surgery - A literature review. J Formos Med Assoc. 2018;117(7):547-558.
[3] 蔡鸣, 杨育生, 王旭东, 等. 三维打印精准手术导板与传统咬合导板在偏颌畸形治疗中的对比研究[J]. 中华整形外科杂志,2018,34(6): 417-421.
[4] CHEN H, BI R, HU Z, et al. Comparison of three different types of splints and templates for maxilla repositioning in bimaxillary orthognathic surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020; S0901-5027(20)30375-1.
[5] BARONE M, DE STEFANI A, BACILIERO U, et al. The Accuracy of Jaws Repositioning in Bimaxillary Orthognathic Surgery with Traditional Surgical Planning Compared to Digital Surgical Planning in Skeletal Class III Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):1840.
[6] XU R, YE N, ZHU S, et al. Comparison of the postoperative and follow-up accuracy of articulator model surgery and virtual surgical planning in skeletal class III patients. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;58(8):933-939.
[7] ZINSER MJ, MISCHKOWSKI RA, SAILER HF, et al. Computer-assisted orthognathic surgery: feasibility study using multiple CAD/CAM surgical splints. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012;113(5):673-687.
[8] POLLEY JW, FIGUEROA AA. Orthognathic positioning system: intraoperative system to transfer virtual surgical plan to operating field during orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(5):911-920.
[9] LI B, ZHANG L, SUN H, et al. A novel method of computer aided orthognathic surgery using individual CAD/CAM templates: a combination of osteotomy and repositioning guides. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;51(8):e239-244.
[10] ZHANG N, LIU S, HU Z, et al. Accuracy of virtual surgical planning in two-jaw orthognathic surgery: comparison of planned and actual results. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2016;122(2):143-151.
[11] 沈国芳, 房兵. 正颌外科学[M]. 杭州:浙江科学技术出版社,2013.
[12] QUAST A, SANTANDER P, WITT D, et al. Traditional face-bow transfer versus three-dimensional virtual reconstruction in orthognathic surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019;48(3):347-354.
[13] LEGAL S, MORALIS A, WAISS W, et al. Accuracy in orthognathic surgery─comparison of preoperative plan and postoperative outcome using computer-assisted two-dimensional cephalometry by the Onyx Ceph(®) system. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;46(10):1793-1799.
[14] 何锦泉, 黄珞, 欧阳可雄, 等. 3D打印技术在上颌Le Fort Ⅰ型截骨术中的应用[J]. 口腔医学研究,2018,34(8):881-884.
[15] MONTEIRO CARNEIRO NC, OLIVEIRA DV, REAL FH, et al. A new model of customized maxillary guide for orthognathic surgery: Precision analysis. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2020;48(12):1119-1125.
[16] HEUFELDER M, WILDE F, PIETZKA S, et al. Clinical accuracy of waferless maxillary positioning using customized surgical guides and patient specific osteosynthesis in bimaxillary orthognathic surgery. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017;45(9):1578-1585.
[17] 李彪, 姜腾飞, 沈舜尧, 等. 3D打印个体化钛板在正颌手术中的应用及其准确性评价[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2016,14(5):419-424.
[18] HANAFY M, AKOUSH Y, ABOU-ELFETOUH A, et al. Precision of orthognathic digital plan transfer using patient-specific cutting guides and osteosynthesis versus mixed analogue-digitally planned surgery: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020; 49(1):62-68.
[19] BADIALI G, RONCARI A, BIANCHI A, et al. Navigation in Orthognathic Surgery: 3D Accuracy. Facial Plast Surg. 2015;31(5):463-473.
[20] SHIROTA T, SHIOGAMA S, ASAMA Y, et al. CAD/CAM splint and surgical navigation allows accurate maxillary segment positioning in Le Fort I osteotomy. Heliyon. 2019;5(7):e02123.
[21] LARTIZIEN R, ZACCARIA I, NOYELLES L, et al. Quantification of the inaccuracy of conventional articulator model surgery in Le Fort 1 osteotomy: evaluation of 30 patients controlled by the Orthopilot((R)) navigation system. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019;57(7):672-677.
[22] 郑海英, 王亚男, 孙健, 等. 两种数字化咬合导板颌骨定位精度比较研究[J]. 精准医学杂志,2020,35(5):415-419.
[23] VAN DEN BEMPT M, LIEBREGTS J, MAAL T, et al. Toward a higher accuracy in orthognathic surgery by using intraoperative computer navigation, 3D surgical guides, and/or customized osteosynthesis plates: A systematic review. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;46(12): 2108-2119.
[24] COUSLEY RRJ, BAINBRIDGE M, ROSSOUW PE. The accuracy of maxillary positioning using digital model planning and 3D printed wafers in bimaxillary orthognathic surgery. J Orthod. 2017;44(4):256-267.
[25] HAMMOUDEH JA, HOWELL LK, BOUTROS S, et al. Current Status of Surgical Planning for Orthognathic Surgery: Traditional Methods versus 3D Surgical Planning. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3(2):e307.
[26] HSU SS, GATENO J, BELL RB, et al. Accuracy of a computer-aided surgical simulation protocol for orthognathic surgery: a prospective multicenter study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(1):128-142.
[27] ALKHAYER A, PIFFKÓ J, LIPPOLD C. Accuracy of virtual planning in orthognathic surgery: a systematic review. Head Face Med. 2020; 16(1):34.
[28] SUN Y, LUEBBERS HT, AGBAJE JO, et al. Accuracy of upper jaw positioning with intermediate splint fabrication after virtual planning in bimaxillary orthognathic surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2013;24(6): 1871-1876.
[29] BUI AA, HSU W, ARNOLD C, et al. Imaging-based observational databases for clinical problem solving: the role of informatics. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2013;20(6):1053-1058.
[30] 于晓青, 曹慧, 魏德健. 数据融合技术及其在医学领域的应用[J]. 中国医疗设备,2017,32(3):99-102.
[31] MARLIÈRE DA, DEMÉTRIO MS, SCHMITT AR, et al. Accuracy between virtual surgical planning and actual outcomes in orthognathic surgery by iterative closest point algorithm and color maps: A retrospective cohort study. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2019;24(2):e243-e253.
[32] ENDER A, ATTIN T, MEHL A. In vivo precision of conventional and digital methods of obtaining complete-arch dental impressions. J Prosthet Dent. 2016;115(3):313-320.
[33] PETERS MC, DELONG R, PINTADO MR, et al. Comparison of two measurement techniques for clinical wear. J Dent. 1999;27(7):479-485.
[34] SHAHEEN E, COOPMAN R, JACOBS R, et al. Optimized 3D virtually planned intermediate splints for bimaxillary orthognathic surgery: A clinical validation study in 20 patients. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018; 46(9):1441-1447.
|