Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (36): 5851-5858.doi: 10.12307/2021.354
Previous Articles Next Articles
Participation and regulatory mechanism of interleukin-1 during bone metabolism
Wang Jing1, Lang Xuemei2, Wang Weiqun1, Zhang Hanxiang1, Zhang Yi3, Wang Xin1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China; 2Pre-hospital First Aid Department of Chongqing First Aid Center, Chongqing 400010, China; 3School of Public Health, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-31Revised:2021-04-08Accepted:2021-04-30Online:2021-12-28Published:2021-09-18 -
Contact:Wang Xin, PhD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China Zhang Yi, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Public Health, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Wang Jing, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China Lang Xuemei, Pre-hospital First Aid Department of Chongqing First Aid Center, Chongqing 400010, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31960209, 31760266 (to WX); Basic Research Program of Guizhou Science and Technology Department, No. Guizhou Science and Technology Foundation [2020]1Y093 (to WX); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82060620 (to ZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jing, Lang Xuemei, Wang Weiqun, Zhang Hanxiang, Zhang Yi, Wang Xin. Participation and regulatory mechanism of interleukin-1 during bone metabolism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5851-5858.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
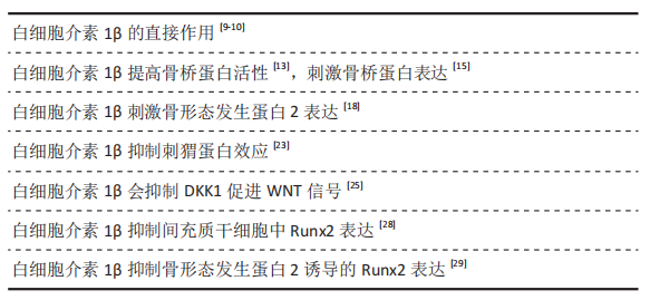
2.1.1 白细胞介素1直接对成骨细胞的影响 成骨细胞起源于多能的间充质干细胞,负责骨基质的合成、分泌和矿化[8]。成骨细胞在骨形成过程中要经历成骨细胞增殖、细胞外基质成熟、细胞外基质矿化和成骨细胞凋亡共4个阶段。炎症是组织修复过程的关键调节剂,炎症因子参与组织修复过程。有研究发现,与小鼠未骨折的四肢相比,四肢骨折后的第2,7天白细胞介素1β的表达均上调并保持较高水平且第2天的白细胞介素1β水平更高,这表明白细胞介素1β参与骨折早期愈合过程[9]。此外,用存在或不存在白细胞介素1β的条件下培养成骨细胞13 d,使用茜素红染色监测矿化骨基质的产生,发现在存在白细胞介素1β的情况下培养的成骨细胞产生的基质能够覆盖每个培养皿的整个表面,而在没有白细胞介素1β的情况下则不行[9],这表明白细胞介素1β可以刺激成骨细胞的增殖和分化。有研究使用雄性Fisher大鼠建立单侧胫骨缺损模型,实验组用微渗透泵向骨缺损处持续泵入人重组白细胞介素1β(0.5 ng/h),记录第1-14天成骨细胞及凋亡小体的浓度,发现白细胞介素1β的添加显著增加了损伤部位的成骨细胞数量,并且凋亡细胞数量明显减少[10],这表明白细胞介素1β可能通过影响分化速率和凋亡率来介导成骨细胞的出现和消失。所以白细胞介素1β可能以其独特的作用机制参与骨愈合的早期阶段,这可能是与白细胞介素1α所不同的。 2.1.2 白细胞介素1对骨桥蛋白的作用 骨桥蛋白不仅参与骨髓间充质干细胞、造血干细胞、破骨细胞和成骨细胞等几种骨相关细胞的增殖、迁移和黏附[11],而且骨桥蛋白还可以刺激成骨细胞增生、钙化并介导由机械应力引起的骨代谢[12]。血管生成在骨愈合过程中十分非常重要,而有研究表明白细胞介素1β提高骨桥蛋白激活的人单核细胞的促血管生成活性[13],这或许会为成骨提供新的策略。此外,有研究在外体条件下向人骨关节炎影响的软骨中添加重组骨桥蛋白抑制了自发的和白细胞介素1β诱导的一氧化氮和前列腺素E2的产生[14],表明在骨关节炎软骨中过表达的关节内骨桥蛋白的功能之一是充当白细胞介素1、一氧化氮和前列腺素E2产生的先天性抑制剂。有研究也发现白细胞介素1β刺激成纤维细胞来源的白细胞介素6通过增加人单核细胞白血病细胞1巨噬细胞的骨桥蛋白而上调了成纤维细胞本身的骨桥蛋白表 达[15]。此外,也有研究表明环境颗粒物诱导的支气管上皮细胞白细胞介素1α和白细胞介素1β的产生效应会被骨桥蛋白通过ERK/JNK途径增强[16]。 2.1.3 白细胞介素1对骨形态发生蛋白的影响 骨形态发生蛋白2是一种生长和分化因子,属于转化生长因子β超家族,它在胚胎发育和骨骼生长中起重要作用[17]。有研究将软骨细胞与转化生长因子β、胰岛素样生长因子1、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α一起培养,通过检测发现白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α分别使骨形态发生蛋白2 mRNA和蛋白水平增加了8倍和15倍,而胰岛素样生长因子1和转化生长因子β没有作用[18],表明正常的骨关节炎软骨细胞中促炎性细胞因子白细胞介素1和肿瘤坏死因子α刺激骨形态发生蛋白2表达。所以白细胞介素1可能会通过影响骨形态发生蛋白进而产生对成骨代谢的影响。 2.1.4 白细胞介素1对刺猬蛋白(Hedgehog,Hh)的影响 刺猬(Hh)家族的蛋白质调节发育的各个方面,该家族成员已被证明可以调节脊椎动物的骨骼形成并控制软骨细胞和成骨细胞的分化[19]。研究发现刺猬蛋白信号和骨形态发生蛋白信号之间的串扰通过调节Smad蛋白促进成骨分化[20]。有研究发现骨形态发生蛋白9对间充质干细胞中的Hh信号传导起作用,且骨形态发生蛋白9诱导成骨分化的早期标志物的表达水平。研究发现Hh信号抑制剂环巴胺降低了碱性磷酸酶的活性,而Hh信号激动剂嘌吗啡胺可增加成骨分化的晚期标志物骨桥蛋白和骨钙素的表达水平。此外,骨形态发生蛋白9诱导的Smad1/5/8转录活性和关键成骨转录因子的表达被环巴胺降低却被吗啡胺提高,表明骨形态发生蛋白9对间充质干细胞中的Hh信号传导有作用,并且Hh信号的抑制或增强分别导致骨形态发生蛋白9诱导的间充质干细胞成骨分化的减少和增强[21]。在成骨分化中,Hh通路具有积极作用[22]。MiR-602和miR-608是骨关节炎软骨细胞中Hh表达的重要转录后调节因子,而白细胞介素1β对它们会产生抑制作用[23]。故白细胞介素1可能通过抑制Hh从而影响Hh的成骨代谢继而产生对成骨作用的抑制。 2.1.5 白细胞介素1对Wnt信号途径的影响 Wnt基因最初发现是因为这些基因对于果蝇的胚胎发育和小鼠乳腺癌的恶性转化很重要。在过去的十几年中,一些临床和临床前证据表明Wnt信号对于小梁和皮质骨量至关重要。既往对Wnt信号通路的研究发现,Wnt家族蛋白中Wnt3a,Wnt4,Wnt5a,Wnt7b,Wnt10b,Wnt16以及可能的Wnt1可以通过骨保护素影响成骨细胞的形成[24]。有研究使用T细胞因子报告基因分析法,评估在白细胞介素1β处理的成纤维样滑膜细胞上清液是否存在经典Wnt信号通路的活性,并通过定量PCR和酶联免疫吸附测定法定量Wnt和Wnt通路抑制因子(Dickkopf-1,DKK1)在成纤维样滑膜细胞中的表达。发现培养的成纤维样滑膜细胞的上清液抑制了T细胞因子报告分子的萤光素酶活性,并且通过用抗DKK1抗体对其进行预处理降低了这种作用;此外,由白细胞介素1β处理成纤维样滑膜细胞的上清液对Wnt信号传导的抑制作用降 低[25],表明白细胞介素1β会抑制DKK1的产生,从而促进Wnt信号的激活。故从某一方面来说,白细胞介素1β可能通过Wnt信号的激活产生成骨的积极作用。 2.1.6 白细胞介素1与Runx2的串扰作用 Runx2蛋白是成骨细胞分化和软骨细胞成熟所必需的[26]。在成骨细胞分化过程中,Runx2在未刺激的间充质细胞中弱表达,在未成熟成骨细胞中表达会上调并达到最高水平,而在成熟成骨细胞中表达有所下降。Runx2通过与Hh、FGF和Wnt信号分子以及转录因子(包括Dlx 5和SP7)相互串扰,调节成骨细胞祖细胞的增殖和向成骨细胞的分化[27]。有研究发现白细胞介素1β会抑制人间充质干细胞Runx2和胶原蛋白的表达,但增加碱性磷酸酶的活性和骨矿化作用[28]。HUANG等[29]发现白细胞介素1β不仅可以通过p38的活化和ERK1/2的信号减少骨形态发生蛋白2诱导的Runx2表达,也可单独通过骨形态发生蛋白/Smad途径抑制骨形态发生蛋白2诱导的Runx2表达。白细胞介素1β作为体内强力的炎性因子,可以诱导炎症反应从而破坏软骨和骨组织。LIU等[30]发现Wnt16信号通过经典的WNT/β-catenin和非经典的WNT/JNK-cJUN途径均上调了软骨代谢因子(SOX9和Lubricin)的表达,并通过调节纤维软骨细胞中的Runx2/MMP13级联阻止白细胞介素1β诱导的炎症反应,表明Wnt16可以通过调节软骨合成代谢和分解代谢因子从而为临床上的软骨损伤疾病如骨关节炎提供新的治疗靶点。 2.2 白细胞介素1对破骨细胞及破骨相关蛋白的影响 见图1。"
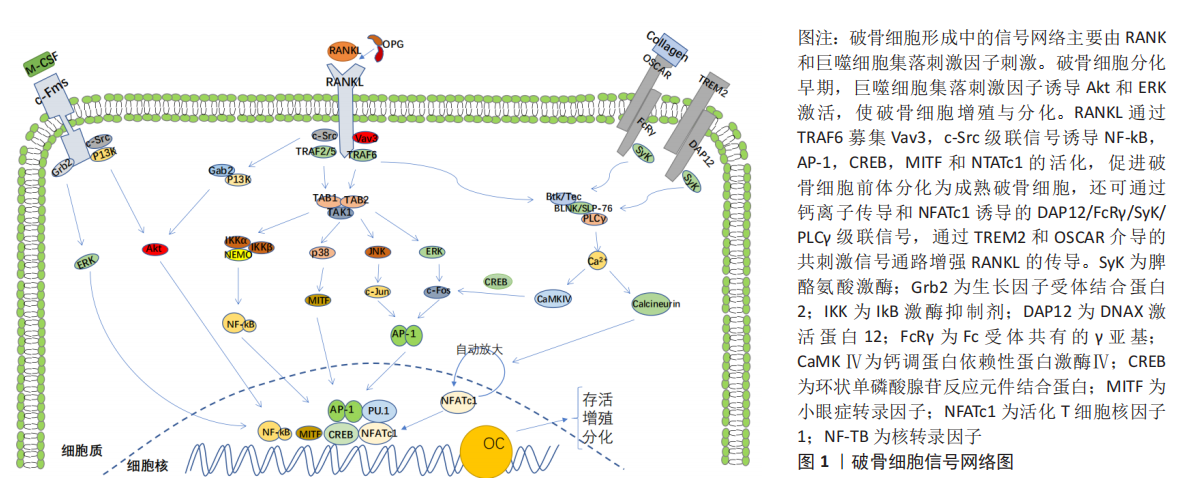
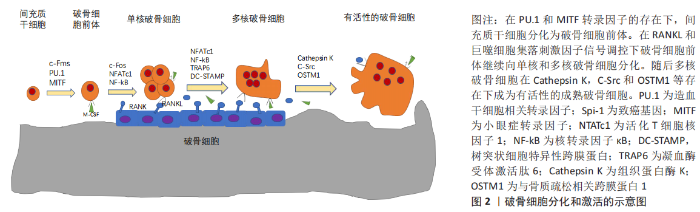
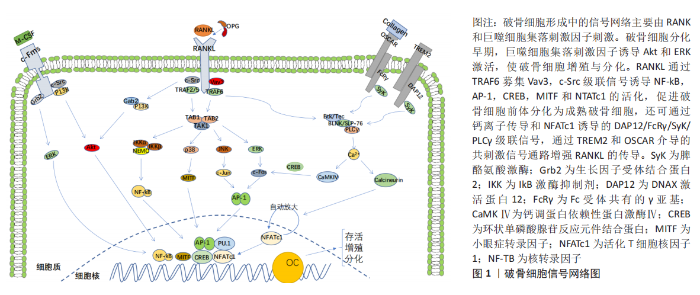
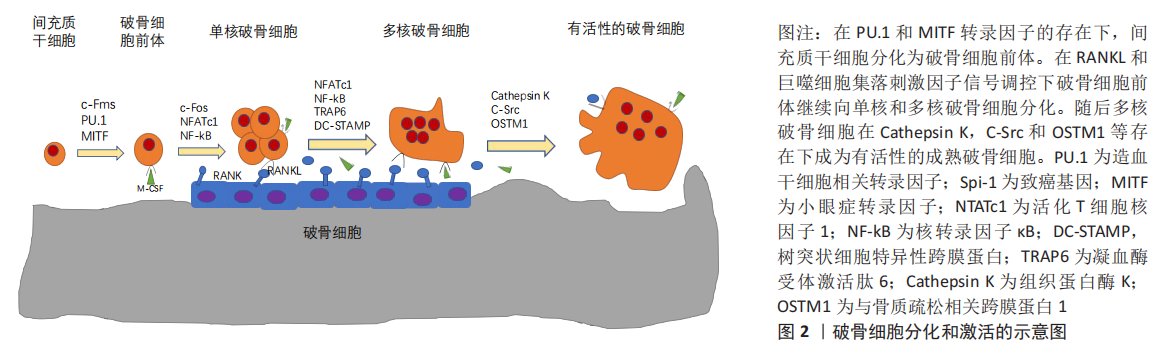
2.2.1 白细胞介素1通过RANKL/RANK的独立机制直接驱动破骨细胞分化 破骨细胞负责骨吸收,是源自单核-巨噬细胞谱系造血祖细胞一种大型的多核细胞,它在暴露于巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和核转录因子κB受体激活剂(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B,RANK)的配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand,RANKL)时会发生分化,而这一过程主要是成骨细胞在起作用。并且破骨细胞通过巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和RANKL与单核细胞/巨噬细胞谱系细胞区分开。RANKL通过信号受体RANK转换其信号。RANKL/RANK信号激活了破骨细胞生成的主要调节剂活化T细胞核因子,从而诱导破骨细胞基因表达。 破骨细胞的分化、存活以及自身活性都离不开两个关键的细胞因子:巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和RANKL。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子由成骨细胞产生,是破骨细胞形成的重要因素[31]。RANKL作为成骨细胞膜关联细胞因子被分泌,破骨细胞前体表达RANK(RANKL的受体),通过细胞间的相互作用识别成骨细胞表达的RANKL,并在存在巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的情况下分化成为破骨细胞。有研究发现RANKL的表达受到骨吸收激素和细胞因子如1α,25-二羟维生素D3、甲状旁腺素、前列腺素E2、白细胞介素1α和白细胞介素11的调节[32]。 而骨保护素是由成骨细胞产生的可溶性RANKL的诱饵受体,通过抑制RANKL-RANKL受体相互作用防止破骨细胞形成并抑制破骨细胞对骨的吸收[33]。此外,集落刺激因子1受体是受体酪氨酸激酶,它介导的信号对于破骨细胞的存活、功能、增殖和分化都至关重要[34]。RANKL中的集落刺激因子1受体介导的信号传导和受体激活是破骨细胞从前体细胞增殖和分化所必需的[35]。在RANK-RANKL结合后,核转录因子κB和MAPK信号通路被激活,来诱导MYC和FOS蛋白表达,从而导致代谢重编程和活化T细胞核因子(破骨细胞生成的主要调控因子)的表达[36]。肿瘤坏死因子受体相关分子TRAF6和c-Fos信号通路均在RANKL下游发挥重要作用,RANKL通过这两个途径选择性诱导活化T细胞核因子表达。Park等[37]发现RANKL还引起钙离子振荡,导致活化T细胞核因子介导的钙调磷酸酶激活,因此触发破骨细胞分化过程中持续地活化T细胞核因子依赖性转录程序。而有研究发现缺少活化T细胞核因子的胚胎干细胞无法响应RANKL刺激而无法分化为破骨细胞,并且活化T细胞核因子的异位表达会导致前体细胞没有RANKL信号传导而无法经历有效的分化[38]。因此,在RANKL下游发挥作用的活化T细胞核因子可能代表调节破骨细胞终末分化的主开关。 白细胞介素1不仅能够激活破骨细胞,还参与破骨细胞的分化、多核化和存活。有研究发现白细胞介素1具有通过RANKL/RANK独立机制的受体激活剂来驱动破骨细胞分 化[39]。尽管白细胞介素1对RANKL诱导破骨细胞形成具有协同作用,但是由于某些细胞(如骨髓来源的巨噬细胞)缺乏白细胞介素1的信号转导,故白细胞介素1不能诱导该类细胞破骨细胞前体向破骨细胞的分化。有研究还发现在骨髓来源的巨噬细胞中白细胞介素1RⅠ通过c-Fos蛋白的过度表达可使得白细胞介素1通过RANKL/RANK轴诱导破骨细胞生成。RANKL可通过c-Fos蛋白和活化T细胞核因子来上调白细胞介素1RⅠ的表达。此外,向白细胞介素1RⅠ过度表达的骨髓来源的巨噬细胞中添加白细胞介素1会很大程度上激活破骨细胞生成的标志性基因(如核转录因子kB、JNK激酶、p38蛋白激酶和ERK等)[39]。此外,还有研究发现白细胞介素1/白细胞介素1RⅠ不会在基础水平上诱导c-Fos和活化T细胞核因子,但却会在很大程度上激活转录因子MITF,随后诱导破骨细胞特异性基因,如破骨细胞相关受体和抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶[40]。所以,白细胞介素1有在特定的微环境下通过转录因子MITF诱导破骨细胞分化的能力。 2.2.2 白细胞介素1通过增加巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和前列腺素E2产生减少骨保护素产生刺激破骨细胞生成 有3个关键因素参与破骨细胞的分化和功能:骨保护素、RANK和RANKL[33]。RANKL作为肿瘤坏死因子大家族的成员,作为膜相关蛋白被成骨细胞/基质细胞表达,而RANK则通过与sRANKL(成骨/基质细胞间分泌的可溶性RANKL)的相互作用的来识别RANKL[41]。此外,巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和sRANKL可以协同诱导破骨祖细胞分化为破骨细胞[42]。而骨保护素/RANKL/RANK系统轴作为近几年研究热点,其在骨代谢中的作用也越发的凸显出来。 白细胞介素1作为与破骨细胞紧密关联的细胞因子,其2种同工型白细胞介素1α和白细胞介素1β均可激活破骨细胞,产生对骨的吸收。有研究将RAW 264.7细胞分化为大小型破骨细胞,并用白细胞介素1α或白细胞介素1β处理后,发现白细胞介素1α刺激了大型破骨细胞的形成并增加了吸收凹坑的数量,而白细胞介素1β改变了大型破骨细胞的形态和整联蛋白β3磷酸化[43],表明白细胞介素1α和白细胞介素1β可激活2个破骨细胞群体内的不同信号通路。此外,白细胞介素1α水平升高会引起破骨细胞重塑[44],这对骨的萌发塑型有着重要意义。研究表明,白细胞介素1主要增强“病理活化的破骨细胞”,从而导致骨的丢失[45]。而白细胞介素1α则通过增加成骨细胞中的巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和前列腺素E2并且减少骨保护素的产生来刺激破骨细胞样细胞的形 成[46]。 2.2.3 白细胞介素1对核转录因子κB家族影响 核转录因子κB和核转录因子激活蛋白1是破骨细胞谱系中细胞进行破骨细胞分化的两个关键信号通路。研究发现降低RANKL或骨保护素的产生,可以激活或抑制核转录因子κB和核转录因子激活蛋白1途径[47]。在破骨细胞活化中,核转录因子κB在白细胞介素1信号的下游,故白细胞介素1通过核转录因子κB调节破骨细胞的生成。核转录因子κB家族中P50有5个成员(P50,P52,P65,RelB基因和CREL),其中核转录因子κBp50和p52的表达对于体内破骨细胞形成至关重要[48]。有研究对核转录因子κBp50或p52敲除的小鼠和白细胞介素1处理的野生型小鼠进行实验,发现白细胞介素1对WT小鼠破骨细胞前体的形成和存活有促进作用而基因敲除的小鼠没有此作用,并且核转录因子κB基因敲除小鼠对白细胞介素1处理的破骨细胞反应受损[49],故白细胞介素1诱导的骨吸收需要破骨细胞前体表达核转录因子κBp50或p52,表明它们参与体内白细胞介素1诱导破骨细胞形成。白细胞介素1促进了体外形成的鼠破骨细胞样细胞的存活并激活了破骨细胞样细胞的转录因子核转录因子κB,而核转录因子κB的激活与白细胞介素1促进的破骨细胞样细胞的存活有关,破骨细胞样细胞表达白细胞介素1RⅠ,而白细胞介素1通过与白细胞介素1RⅠ结合直接激活破骨细胞样细胞的核转录因子κB[50]。此外,白细胞介素1也可通过涉及前列腺素E2合成的机制刺激了小鼠骨髓培养物中破骨细胞样细胞的形成[51]。但前列腺素E2诱导的内源性白细胞介素1β的表达被H-89(蛋白激酶A的有效抑制剂)显著抑制,同时H-89还会抑制前列腺素E2刺激的破骨细胞形成[52],故前列腺素E2会通过蛋白激酶A表达的内源性白细胞介素1β刺激破骨细胞的形成。 2.2.4 白细胞介素1诱导单核破骨细胞融合导致多核化 破骨细胞分化和激活的示意图见图2。在破骨细胞分化过程中,破骨细胞先分化为酸性磷酸酶同工酶第5型(TRAP)阳性的单核细胞,然后通过细胞与细胞间融合和不完全的胞质分裂变成巨大的多核细胞。有研究发现树突状细胞特异性跨膜结构蛋白是破骨细胞相互融合的必要分子,并且正常小鼠多核破骨细胞比树突状细胞特异性跨膜结构蛋白缺陷小鼠中看到的单核破骨细胞具有更高的骨吸收活性[53]。成熟破骨细胞是巨型、极化和多核的,其中生成一个由肌动蛋白环包裹的皱褶缘降解和吸收骨质基质[54],而作为破骨细胞成熟的标志,多核化常发生在破骨细胞分化的后期。多项研究表明,没有进行多核化的破骨细胞常表达破骨细胞独有的表现型,例如TRAP和组织蛋白酶K,而这种没有进行多核化的破骨细胞常对骨的吸收能力不强[55],这意味着靶向抑制破骨细胞多核化会减少而不消除破骨细胞的骨吸收活性,很大程度上减少成骨细胞的抑制作用而形成的负面效应。 有研究发现白细胞介素1通过预防自发性凋亡,延长了在鼠成骨细胞/基质细胞和骨髓细胞共培养物中形成的多核破骨细胞样细胞的存活[56]。此外,巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和白细胞介素1均可延长多核破骨细胞样细胞的存活,但是只在白细胞介素1处理的融合前的破骨细胞中观察到了多核细胞形成的肌动蛋白环(破骨细胞功能性标志物)[56]。 2.2.5 白细胞介素1受体相关激酶M(Interleukin Receptor Associated Kinase,IRAK)为破骨细胞分化激活的主要调节剂 破骨细胞从单核吞噬细胞分化为多核巨细胞除了巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和RANKL的参与,白细胞介素1R的激动剂(Toll样受体)在破骨细胞的分化和激活中也起着关键作用[57]。而与Toll样受体4结合的配体脂多糖参与炎症介导的骨丢失,脂多糖不会影响成骨细胞中SDF-1/CXCR4(Stromal衍生因子1及其独特的趋化因子受体)轴的表达,但会通过Toll样受体4上调破骨细胞中CXCR4的表达,从而增强破骨细胞的迁移[58]。 白细胞介素1受体相关激酶M在由白细胞介素1R/Toll样受体家族成员启动的信号传导途径中起着至关重要的作用[59]。该家族的成员具有保守的“Toll样受体和白细胞介素1R相关”胞质内结构域,因此该家族不同成员的激活诱导了类似的信号级联反应,最终达到IκB激酶复合体和有丝分裂原激活的蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)激活的目的。这种激活导致核转录因子κB、c-Jun NH 2末端激酶(JNK)、p38和细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)1/2以及核转录因子激活蛋白1依赖性转录反应的激活[60-61]。所有白细胞介素受体相关激酶IRAK均具有功能性ATP结合位点并具有高度的序列同一性[62]。IRAK家族由2个活性激酶IRAK和IRAK-4以及2个非活性激酶IRAK-2和IRAK-M组成。IRAK-M通过阻止IRAK与髓样分化因子88,并维持IRAK-TRAF6和ILAK之间的复合物完整性,从而充当白细胞介素1R/Toll样受体信号的负调节剂[63]。有研究通过将不同类型的IRAK捕获在受体复合物中,发现IRAK-M阻止了核转录因子κB和MAPK信号通路的下游激活[63],因此IRAK-M可能是巨噬细胞中白细胞介素1R/Toll样受体下游的主要负性调节剂。此外,有研究发现IRAK-M缺乏型的小鼠破骨细胞生长速度和数量增加并且破骨细胞半衰期会延长,而缺乏IRAK-M的破骨细胞在白细胞介素1R/Toll样受体链接反应中会产生核转录因子κB的超表达和MAPK信号通路过度激活[64]。所以IRAK-M是由于破骨细胞吸收而引起骨流失的关键调节剂。 2.2.6 白细胞介素1不同受体亚型表达对破骨细胞的影响 白细胞介素1对骨骼的影响取决于许多因素之间复杂的相互作用,包括白细胞介素1α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素1Rα、白细胞介素1R和白细胞介素1受体辅助蛋白等。研究发现有两种不同的白细胞介素1受体:Ⅰ型信号受体(白细胞介素1RⅠ)介导对白细胞介素1的细胞反应并同等地结合白细胞介素1激动剂和拮抗剂;Ⅱ型诱饵受体(白细胞介素1RⅡ)优先与白细胞介素1的激动剂结合,但不引起细胞内信号传导,并且通常在质膜上被蛋白水解切割,以可溶性的形式释放到细胞外环境中[65]。有研究发现雌激素可以通过减少白细胞介素1的生物学反应并增加其凋亡率的方式特异性调节人破骨细胞样细胞中白细胞介素1受体亚型的表达[66],因此白细胞介素1调节破骨细胞骨吸收的直接作用可能不仅取决于成骨细胞或骨髓或循环细胞分泌的白细胞介素1α、白细胞介素1β或白细胞介素1Rα的水平,还取决于破骨细胞表达的白细胞介素1受体的类型。此外,有研究还检测到源自人骨的人类破骨样细胞和多核人破骨样细胞细胞表达白细胞介素1RⅠ和白细胞介素1RⅡ受体的mRNA,并且在多核人破骨样细胞中白细胞介素1RⅠ介导白细胞介素1的反应[66]。因此,人类破骨样细胞或许是在体内情况下白细胞介素1作用的直接靶标。 2.3 药物调控白细胞介素1与骨代谢的关系 近年已经发现对白细胞介素1产生抑制作用的药物,抗骨质疏松症的治疗药物双膦酸盐是焦磷酸盐的细胞毒性类似物,与骨牢固结合,在骨吸收期间被吸收到破骨细胞中,并表现出长效的抗骨吸收作用[67];狄诺塞麦是一种单克隆抗体,主要调控破骨细胞分化中最重要的骨保护素/RANKL/RANK信号通路进而抑制破骨细胞活性[68]。另一方面,重组人甲状旁腺激素在多方面与白细胞介素1产生串扰激活成骨代谢:甲状旁腺激素在骨骼干细胞中增加了Runx2的表达;甲状旁腺激素减少成骨细胞凋亡,增强成骨细胞中Wnt信号传导等。Silva等[69]发现采用间歇性(每日1次)注射甲状旁腺激素(iPTH)治疗骨质疏松患者1个月后,活检发现松质、皮质内膜和骨膜表面的骨形成率提高了四五倍。故iPTH治疗可增加骨量,增加骨形成并减少高危人群的骨折。另外有研究使用甲状旁腺素相关肽(PTHrP)治疗骨质疏松症患者18个月后(每天1次皮下注射),发现治疗组患者骨质明显增加且再发骨折概率显著降低[70]。目前,iPTH/PTHrP是美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)批准的惟一可刺激新骨形成的抗骨质疏松症药物[71]。 白细胞介素1表达增加和异常激活的白细胞介素1信号都与炎性反应进展显著相关。骨折早期血肿炎症阶段白细胞介素1大量产生,而大量的炎性因子不利于骨的愈合。使用天然存在的白细胞介素1R拮抗剂(白细胞介素1Rα)阿那白滞素阻断白细胞介素1信号传导或用抗白细胞介素1单克隆抗体中和会使得炎性因子对骨的破坏作用明显减 低[72]。虽然许多抗炎药物已经开发,研究者仍需继续研究白细胞介素1的深层次信号通路,为接下来的药物治疗提供更多的有效靶点。 "
| [1] CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107. [2] BORASCHI D, ITALIANI P, WEIL S, et al. The family of the interleukin-1 receptors. Immunol Rev. 2018;281(1):197-232. [3] WESCHE H, KORHERR C, KRACHT M, et al. The interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) is essential for IL-1-induced activation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) and stress-activated protein kinases (SAP kinases). J Biol Chem. 1997;272(12):7727-7731. [4] WANG Q, DELCORDE J, TANG T, et al. Regulation of IL-1 signaling through control of focal adhesion assembly. FASEB J. 2018;32(6):3119-3132. [5] AKATSU T, TAKAHASHI N, UDAGAWA N, et al. Role of prostaglandins in interleukin-1-induced bone resorption in mice in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 1991;6(2):183-189. [6] CAO Y, JANSEN ID, SPRANGERS S, et al. IL-1β differently stimulates proliferation and multinucleation of distinct mouse bone marrow osteoclast precursor subsets. J Leukoc Biol. 2016;100(3):513-523. [7] AMARASEKARA DS, YUN H, KIM S, et al. Regulation of Osteoclast Differentiation by Cytokine Networks. Immune Netw. 2018;18(1):e8. [8] LEE WC, GUNTUR AR, LONG F, et al. Energy Metabolism of the Osteoblast: Implications for Osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2017;38(3):255-266. [9] LANGE J, SAPOZHNIKOVA A, LU C, et al. Action of IL-1beta during fracture healing. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(6):778-784. [10] OLMEDO ML, LANDRY PS, SADASIVAN KK, et al. Regulation of osteoblast levels during bone healing. J Orthop Trauma. 1999;13(5):356-362. [11] SI J, WANG C, ZHANG D, et al. Osteopontin in Bone Metabolism and Bone Diseases. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e919159. [12] FORSPRECHER J, WANG Z, GOLDBERG HA, et al. Transglutaminase-mediated oligomerization promotes osteoblast adhesive properties of osteopontin and bone sialoprotein. Cell Adh Migr. 2011;5(1):65-72. [13] NALDINI A, LEALI D, PUCCI A, et al. Cutting edge: IL-1beta mediates the proangiogenic activity of osteopontin-activated human monocytes. J Immunol. 2006;177(7):4267-4270. [14] ATTUR MG, DAVE MN, STUCHIN S, et al. Osteopontin: an intrinsic inhibitor of inflammation in cartilage. Arthritis Rheum, 2001;44(3):578-584. [15] SHIMODAIRA T, MATSUDA K, UCHIBORI T, et al. Upregulation of osteopontin expression via the interaction of macrophages and fibroblasts under IL-1b stimulation. Cytokine. 2018;110:63-69. [16] WANG J, HUANG J, ZHU M, et al. Osteopontin potentiates PM-induced IL-1α and IL-1β production via the ERK/JNK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019;171:467-474. [17] REDDI AH. Bone and cartilage differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994;4(5):737-744. [18] FUKUI N, ZHU Y, MALONEY WJ, et al. Stimulation of BMP-2 expression by pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1 and TNF-alpha in normal and osteoarthritic chondrocytes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A Suppl 3: 59-66. [19] SKODA AM, SIMOVIC D, KARIN V, et al. The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: a comprehensive review. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2018;18(1):8-20. [20] SILVESTRI L, NAI A, DULJA A, et al. Hepcidin and the BMP-SMAD pathway: an unexpected liaison. Vitam Horm. 2019;110:71-99. [21] LI L, DONG Q, WANG Y, et al. Hedgehog signaling is involved in the BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 2015;35(6):1641-1650. [22] HU Z, CHEN B, ZHAO Q. Hedgehog signaling regulates osteoblast differentiation in zebrafish larvae through modulation of autophagy. Biol Open. 2019;8(5):bio040840. [23] AKHTAR N, MAKKI MS, HAQQI TM. MicroRNA-602 and microRNA-608 regulate sonic hedgehog expression via target sites in the coding region in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(2):423-434. [24] LERNER UH, OHLSSON C. The WNT system: background and its role in bone. J Intern Med. 2015;277(6):630-649. [25] YOSHIDA Y, YAMASAKI S, OI K, et al. IL-1β Enhances Wnt Signal by Inhibiting DKK1. Inflammation. 2018;41(5):1945-1954. [26] KOMORI T. Molecular Mechanism of Runx2-Dependent Bone Development. Mol Cells. 2020;43(2):168-175. [27] KOMORI T. Regulation of Proliferation, Differentiation and Functions of Osteoblasts by Runx2. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(7):1694. [28] DING J, GHALI O, LENCEL P, et al. TNF-alpha and IL-1beta inhibit RUNX2 and collagen expression but increase alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralization in human mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2009; 84(15-16):499-504. [29] HUANG RL, YUAN Y, TU J, et al. Opposing TNF-α/IL-1β- and BMP-2-activated MAPK signaling pathways converge on Runx2 to regulate BMP-2-induced osteoblastic differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(4): e1187. [30] LIU X, LI X, HUA B, et al. WNT16 is upregulated early in mouse TMJ osteoarthritis and protects fibrochondrocytes against IL-1β induced inflammatory response by regulation of RUNX2/MMP13 cascade. Bone. 2021;143:115793. [31] ONO T, NAKASHIMA T. Recent advances in osteoclast biology. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):325-341. [32] SUDA T, TAKAHASHI N, UDAGAWA N, et al. Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev. 1999;20(3):345-357. [33] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021; 39(1):19-26. [34] MUN SH, PARK PSU, PARK-MIN KH. The M-CSF receptor in osteoclasts and beyond. Exp Mol Med. 2020;52(8):1239-1254. [35] GYŐRI DS, MÓCSAI A. Osteoclast signal transduction during bone metastasis formation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:507. [36] PARK-MIN KH. Metabolic reprogramming in osteoclasts. Semin Immunopathol. 2019;41(5):565-572. [37] PARK JH, LEE NK, LEE SY. Current understanding of RANK signaling in osteoclast differentiation and maturation. Mol Cells. 2017;40(10):706-713. [38] TAKAYANAGI H, KIM S, KOGA T, et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002;3(6):889-901. [39] KIM J.H, JIN HM, KIM K, et al. The mechanism of osteoclast differentiation induced by IL-1. J Immunol. 2009;183(3):1862-1870. [40] ZHOU, J, SONG J, PING F, et al. Enhancement of the p38 MAPK and PKA signaling pathways is associated with the pro-melanogenic activity of Interleukin 33 in primary melanocytes. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;73(2):110-116. [41] NAKAGAWA N, KINOSAKI M, YAMAGUCHI K, et al. RANK is the essential signaling receptor for osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;253(2):395-400. [42] MA QL, FANG L, JIANG N, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell secretion of sRANKL/OPG/M-CSF in response to macrophage-mediated inflammatory response influences osteogenesis on nanostructured Ti surfaces. Biomaterials. 2018;154:234-247. [43] TREBEC-REYNOLDS DP, VORONOV I, HEERSCHE JN, et al. IL-1alpha and IL-1beta have different effects on formation and activity of large osteoclasts. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109(5):975-982. [44] MENG M, CHEN Y, CHEN X, et al. IL-1α Regulates Osteogenesis and Osteoclastic Activity of Dental Follicle Cells Through JNK and p38 MAPK Pathways. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(24):1552-1566. [45] PUTNAM NE, FULBRIGHT LE, CURRY JM, et al. MyD88 and IL-1R signaling drive antibacterial immunity and osteoclast-driven bone loss during Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. PLoS Pathog. 2019; 15(4):e1007744. [46] TANABE N, MAENO M, SUZUKI N, et al. IL-1 alpha stimulates the formation of osteoclast-like cells by increasing M-CSF and PGE2 production and decreasing OPG production by osteoblasts. Life Sci. 2005;77(6):615-626. [47] INFANTE M, FABI A, COGNETTI F, et al. RANKL/RANK/OPG system beyond bone remodeling: involvement in breast cancer and clinical perspectives. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):12. [48] WILLIAMS LM, GILMORE TD. Looking Down on NF-κB. Mol Cell Biol. 2020;40(15):e00104-e00120. [49] XING L, CARLSON L, STORY B, et al. Expression of either NF-kappaB p50 or p52 in osteoclast precursors is required for IL-1-induced bone resorption. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18(2):260-269. [50] JIMI E, NAKAMURA I, IKEBE T, et al. Activation of NF-kappaB is involved in the survival of osteoclasts promoted by interleukin-1. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(15):8799-8805. [51] HWANG YH, KIM T, KIM R, et al. The Natural product 6-gingerol inhibits inflammation-associated osteoclast differentiation via reduction of prostaglandin E₂ levels. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):2068. [52] MALTY RH, HUDMON A, FEHRENBACHER JC, et al. Long-term exposure to PGE2 causes homologous desensitization of receptor-mediated activation of protein kinase A. J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13(1):181. [53] MIYAMOTO T. The dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein DC-STAMP is essential for osteoclast fusion and osteoclast bone-resorbing activity. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16(6):341-342. [54] KODAMA J, KAITO T. Osteoclast multinucleation: review of current literature. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5685. [55] DOU C, DING N, LUO F, et al. Graphene-based microRNA transfection blocks preosteoclast fusion to increase bone formation and vascularization. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(2):1700578. [56] JIMI E, NAKAMURA I, DUONG LT, et al. Interleukin 1 induces multinucleation and bone-resorbing activity of osteoclasts in the absence of osteoblasts/stromal cells. Exp Cell Res. 1999;247(1):84-93. [57] HEGEWALD AB, BREITWIESER K, OTTINGER SM, et al. Extracellular miR-574-5p induces osteoclast differentiation via TLR 7/8 in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:585282. [58] XING Q, DE VOS P, FAAS MM, et al. LPS promotes pre-osteoclast activity by up-regulating CXCR4 via TLR-4. J Dent Res. 2011;90(2):157-62. [59] KESSELRING R, GLAESNER J, HIERGEIST A, et al. IRAK-M expression in tumor cells supports colorectal cancer progression through reduction of antimicrobial defense and stabilization of STAT3. Cancer Cell. 2016; 29(5):684-696. [60] GHOSH S, KARIN M. Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell. 2002; 109 Suppl:S81-S96. [61] KYRIAKIS JM, AVRUCH J. Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev. 2001;81(2):807-869. [62] SCARNEO SA, HUGHES PF, YANG KW, et al. A highly selective inhibitor of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases 1/4 (IRAK-1/4) delineates the distinct signaling roles of IRAK-1/4 and the TAK1 kinase. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(6):1565-1574. [63] KOBAYASHI K, HERNANDEZ LD, GALÁN JE, et al. IRAK-M is a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell. 2002;110(2):191-202. [64] LI H, CUARTAS E, CUI W, et al. IL-1 receptor-associated kinase M is a central regulator of osteoclast differentiation and activation. J Exp Med. 2005;201(7):1169-1177. [65] SCHLÜTER T, SCHELMBAUER C, KARRAM K, et al. Regulation of IL-1 signaling by the decoy receptor IL-1R2. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018;96(10): 983-992. [66] SUNYER T, LEWIS J, COLLIN-OSDOBY P, et al. Estrogen’s bone-protective effects may involve differential IL-1 receptor regulation in human osteoclast-like cells. J Clin Invest. 1999;103(10):1409-1418. [67] ENDO Y, KUMAMOTO H, NAKAMURA M, et al. Underlying mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ). Biol Pharm Bull. 2017;40(6):739-750. [68] DEEKS ED. Denosumab: a review in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Drugs Aging. 2018;35(2):163-173. [69] SILVA BC, COSTA AG, CUSANO NE, et al. Catabolic and anabolic actions of parathyroid hormone on the skeleton. J Endocrinol Invest. 2011;34(10):801-810. [70] MILLER PD, HATTERSLEY G, RIIS BJ, et al. Effect of abaloparatide vs placebo on new vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;316(7):722-733. [71] WEIN MN, KRONENBERG HM. Regulation of bone remodeling by parathyroid hormone. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(8):031237. [72] SKARIA T, BACHLI E, SCHOEDON G. Gene ontology analysis for drug targets of the whole genome transcriptome of human vascular endothelial cells in response to proinflammatory IL-1. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:414. [73] WANG X, LUO Y, MASCI PP, et al. Influence of interleukin-1 Beta on platelet-poor plasma clot formation: a potential impact on early bone healing. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0149775. [74] KOGA T, NIIKURA T, LEE SY, et al. In vitro hypertrophy and calcification of human fracture haematoma-derived cells in chondrogenic differentiation. Int Orthop. 2013;37(5):961-967. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [5] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [6] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [7] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [8] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [9] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [10] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [11] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [12] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [13] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [14] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||