Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (36): 5859-5866.doi: 10.12307/2021.355
Previous Articles Next Articles
Periprosthetic joint infection of hip and knee
Li Shuyuan1, Chen Leilei2, Huang Linfeng1, Zhao Heran1, Wu Suwen1, Jiang Yuankang1
- 1Third School of Clinical Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510378, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2021-02-19Revised:2021-02-22Accepted:2021-04-15Online:2021-12-28Published:2021-09-18 -
Contact:Chen Leilei, MD, Associate chief physician, Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510378, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Li Shuyuan, Doctoral candidate, Third School of Clinical Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81673999 (to CLL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Shuyuan, Chen Leilei, Huang Linfeng, Zhao Heran, Wu Suwen, Jiang Yuankang. Periprosthetic joint infection of hip and knee[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5859-5866.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
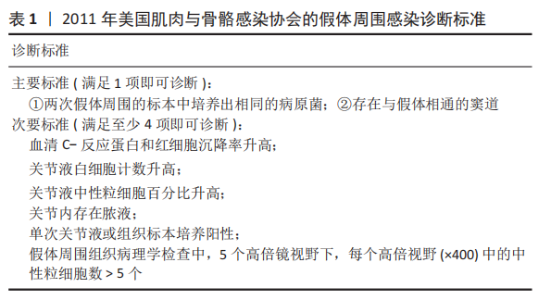
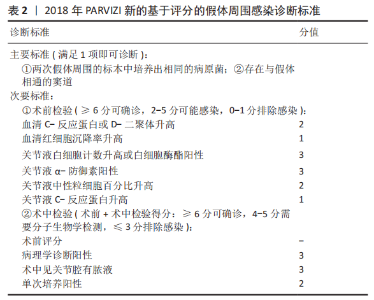
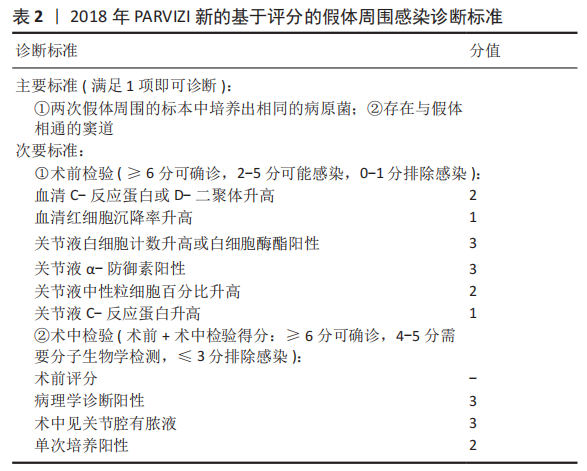
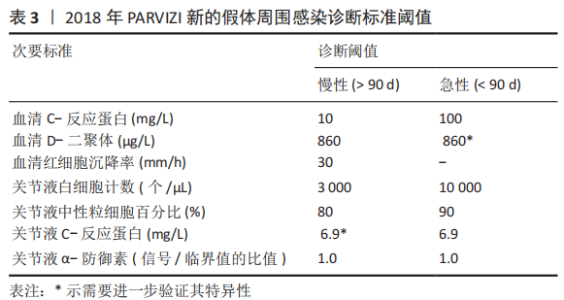
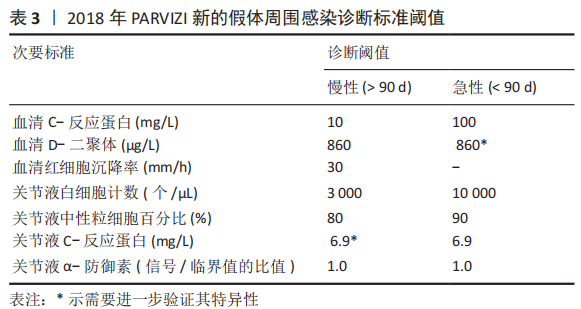
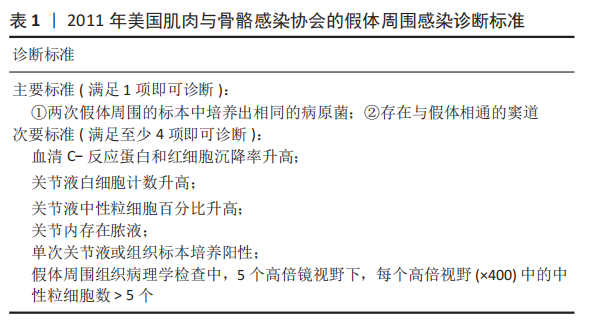
2.1 病因和机制 PJI可以通过多种途径发生[8],多见于以下方面:第一,来自体外细菌的直接传播或连续传播;第二,来自体内其他感染部位的血源性传播;第三,反复感染。在植入物表面和坏死组织上形成生物膜是细菌的基本生存机制。与植入物初次接触后,细菌立即黏附在植入物表面;在黏附后的最初几个小时内,多层细胞的增殖以及细胞与细胞之间的黏附导致菌群形成和生物膜初步生长;成熟的生物膜需要4周才能形成。在生物膜内,细菌受到保护,不受抗生素和宿主免疫反应的影响,随着营养物质的耗尽和代谢废物的积累,细菌进入缓慢生长或不生长的(静止)状态[9]。浮游细菌可以随时分离,激活宿主免疫系统,导致炎症、水肿、疼痛和假体松动。动物实验发现,豚鼠皮下植入聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯和聚四氟乙烯,会导致植入部位感染所需的金黄色葡萄球菌浓度降低100 000多倍[10],这与粒细胞吞噬活性降低(吞噬抑制)导致的局部免疫缺陷有关。生物膜细菌对抗生素的耐药性比浮游菌高1 000倍,体外药敏试验测定的最小抑菌浓度不能反映体内情况。在临床上,抗生素的局部有效浓度不能仅仅通过静脉或口服等全身应用来达到[11]。 2.2 流行病学 PJI的细菌流行病学因国家而异[8]:美国罗斯曼研究所和德国汉堡赫利奥斯医院数据显示,美国最常见的感染菌是耐甲氧西林和甲氧西林敏感的金黄色葡萄球菌,以及耐甲氧西林和甲氧西林敏感的表皮葡萄球菌[12-13];欧洲凝固酶阴性葡萄球菌的感染率最高,其次是金黄色葡萄球菌、链球菌和肠球菌。翻修手术可带来巨大的经济负担,美国住院患者样本数据库最新预测,预计到2030年,美国每年用于治疗髋膝关节PJI的费用估计为18.5亿美元,其中全髋关节置换 PJI为7.5亿美元,全膝关节置换 PJI为11亿美元[14]。一项研究指出,平均每个PJI的治疗费用为95 000欧元,是单纯关节置换手术的5倍[15]。感染的患者对治疗的满意度不高,23%的人感到满意,18%的人表示完全不满意。PJI患者的健康相关生活质量比单纯关节置换术低。此外,感染导致较高的死亡率,Ⅱ期髋关节翻修术后2年内死亡率高达25.8%[16];另有研究报道反复感染患者在二期翻修后4.7年内的死亡率高达50% [17]。 2.3 风险因素 败血症、皮肤或深部组织感染、输血、未得到控制的糖尿病、营养不良、病态肥胖、吸烟、酗酒、免疫损害疾病、药物使用、鼻腔携带金黄色葡萄球菌都是PJI的风险因素[8]。 研究表明,糖尿病患者的术后感染率是非糖尿病患者的7倍[18]。一项研究纳入101例感染患者和1 847例非感染患者,感染患者中的糖尿病患者比例较未感染组多(P < 0.001)[19]。因此,术前应该综合评估血糖的控制情况。 如果血清白蛋白低于34 g/L(正常为34-54 g/L),或淋巴细胞总数低于1.2×109 L-1(正常为3.9×109 L-1-10×109 L-1),则诊断为营养不良。术前营养状况不佳会导致关节置换术后感染增加,适当的营养优化可以减少假体周围关节感染[20]。 肥胖患者(体质量指数> 30.0 kg/m2)关节置换术后高感染率原因在于:肥胖患者的抗生素组织渗透率明显低于正常体质量患者,手术部位的皮下、脂肪组织内药物浓度不足,导致感染风险增加[21]。有数据显示,病态肥胖患者(体质量指数≥40 kg/m2)比非肥胖患者有更高的感染风险[22]。 吸烟和饮酒均会导致术后感染。尼古丁介导的血管收缩、循环不良导致组织缺氧和感染易感性增加[23]。有Meta分析显示术前戒烟可将术后感染减少50%以上[24]。 免疫性疾病和相关的药物使用是感染的危险因素。比如,感染艾滋病毒和丙型肝炎的患者可能面临感染的风险[25]。对术后结果有负面影响的免疫抑制剂包括糖皮质激素、免疫抑制剂、干扰素和肿瘤坏死因子抑制剂。 鼻腔中甲氧西林敏感金黄色葡萄球菌及耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌的定植率分别为29%和1.8%[26];术前鼻腔金黄色葡萄球菌定植者手术部位感染的可能性是非定植者的9 倍[27];术前鼻腔耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌定植可使耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌引起手术部位感染的风险增加11倍[28]。 此外,所有疾病都有遗传基础,假体周围关节感染可能也有遗传因素[29]。 2.4 诊断和分型 因为缺乏绝对准确的诊断标准,髋关节和膝关节PJI的诊断仍然是关节骨科领域一个挑战。美国肌肉骨骼感染学会于2011年制定了PJI的诊断指南[30],即当至少满足主要标准的1项或者次要标准中的4项时便可诊断为PJI,见表1。2013年8月,国际共识协会对美国肌肉骨骼感染学会标准略做修改,增加了白细胞酯酶阳性作为次要标准[31]。 PARVIZI等[32]认为当前指南的次要标准未将近年新的诊断性标志物纳入在内,并且各项诊断指标的权重(敏感度和特异性)也不明确,不利于术前诊断。2018 年PARVIZI等[32]对原有的共识和指南进行归纳总结,制定了一套新的基于评分的PJI 诊断标准,该标准对于PJI的诊断具有较高的敏感性和特异性,见表 2,3。 目前,病原体的培养与鉴定对PJI的诊断至关重要。尽管已经采取许多改进方法(如超声波、延长培养期和强化培养基)[33],病原体的检出率仍然较低[34]。二代测序是一种新兴的实验室诊断技术,可以快速识别给定样本中的所有核酸序列,通过将这些序列与现有的微生物数据库中包含的病原体序列进行匹配,从而明确致病菌[35]。二代测序不但可以检测出与细菌培养结果相一致的病原体,还能发现部分细菌培养无法得到的致病菌,极大地提高了PJI细菌的检出率[36-37]。但是目前二代测序应用于PJI诊断尚处于初始阶段,实际应用中还面临样本易污染、宿主正常菌群干扰、抗生素的应用、实验室的条件(设备、专业人员、技术)限制以及检测成本等诸多问题[38],其技术水平、操作流程、敏感性和特异性仍然需要进一步完善和验证。 2004年ZIMMERLI等[39]根据PJI的发生时间首次对其进行系统分类,具体如下:①早期感染,发生于术后3个月内;②延迟感染,发生于术后 3-24个月;③晚期感染,发生于术后24个月后。由于PJI大多数发生在术后4周内,因此,有学者将发生于术后 4周内的感染定义为早期感染[40]。早期感染表现为明显的局部和全身炎症症状,主要由高毒力病原体(如金黄色葡萄球菌、链球菌、肠球菌)引起。延迟或晚期感染症状比较轻微,多由低毒力病原体 (如凝固酶阴性葡萄球菌或痤疮丙酸杆菌)引起[4]。 2.5 治疗 2.5.1 手术治疗 PJI 是骨科领域较为棘手的问题,其治疗一直是骨科医师所面临的难题之一,治疗包括保留假体清创术(debridement antibiotics irrigation and retention,DAIR)、Ⅰ期或Ⅱ期翻修、切除关节成形术、关节融合术、截肢及生物治疗[41]。针对不同患者,需要根据患者自身情况及病情严重程度的评估结果而选择不同的治疗策略。 (1)DAIR:初次置换30 d以内、感染症状持续时间较短(< 3周),假体固定良好,软组织条件较好,应该选择DAIR[40]。在此过程中,先进行物理清创,彻底清理假体周围坏死的组织,包括游离骨水泥和其他异物,还可同时更换假体部件;再进行化学清创,采用大量生理盐水冲洗、聚维酮碘及双氧水浸泡,以上过程重复3遍;冲洗结束后,更换手术衣、手套,重新铺单,更换手术器械。目前尚无证据表明冲洗关节的液体量应为多少,大多数文献报道的量为3- 12 L[42-43]。 保留感染假体的清创手术可以通过关节切开或关节镜来完成。根据报道,与开放手术相比,关节镜下清创和冲洗结果更差[44],其局限性是不能进行充分清创和假体的部分更换。有研究统计,受多种因素影响,DAIR的成功率波动范围较大,为16%-91%[45]。在一项纳入19例链球菌感染、植入物稳定及症状持续时间短的患者的研究中,DAIR的成功率为89%[46]。根据 2013年美国传染病学会指南推荐[40]:敏感性抗生素静脉使用2-6周,联合每日2次口服利福平300- 450 mg,随后利福平加敏感抗生素口服,全髋关节置换感染抗生素的疗程共3个月,全膝关节置换感染共6个月。对于难治性细菌[47],如耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌,可使用万古霉素、达托霉素、利奈唑胺或头孢他林;万古霉素耐药的金黄色葡萄球菌和肠球菌可使用达托霉素;链球菌使用β-内酰胺类抗生素和新一代氟喹诺酮类药物;痤疮丙酸杆菌使用万古霉素、青霉素、头孢曲松、莫西沙星、克林霉素、强力霉素和甲氧苄啶-磺胺甲恶唑;喹诺酮耐药铜绿假单胞菌,应使用第4代头孢菌素、哌拉西林-三唑巴坦、氨曲南、氨基糖苷类或碳青霉烯类药物;肠杆菌科包括大肠杆菌、克雷伯氏菌、变形杆菌等,选择β-内酰胺类抗生素、喹诺酮类、甲氧苄啶磺胺甲恶唑和碳青霉烯类抗生素; 肠球菌单独使用β-内酰胺或万古霉素,或与氨基糖苷类联合治疗。真菌感染建议使用抗真菌药物,如唑类和两性霉素[8]。 (2)Ⅰ期翻修:是指取出所有异物、清创,同时重新植入新假体。这一手术的成功率为86%-100% [48-50],其成功主要取决于清创的程度[51]。一期翻修大多数使用负载抗生素的骨水泥来固定新的假体[51],近年来也有非骨水泥型假体应用于一期翻修并取得良好效果的报道[52-54],但多为回顾性研究,病例数较少,且缺乏对照,仍然需要进一步证实,骨水泥型假体仍然是主要类型。手术适应证包括:感染症状或体征持续时间超过3周;具有充足的骨量;相对较好的软组织条件;没有严重的基础疾病;对抗生素敏感的细菌感染;术口可以一期闭合[51-55]。Ⅰ期翻修的相对禁忌证为:多菌感染;革兰阴性菌,特别是假单胞菌感染;耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌和D组链球菌感染;感染累及神经血管束(股或坐骨神经、髂血管);广泛的软组织受累,并影响术口闭合;细菌培养为阴性结果[51,55]。 根据目前的研究及综述,没有明确的证据表明Ⅱ期翻修比Ⅰ期翻修更有效。有研究表明,Ⅰ期翻修在感染控制方面会产生与Ⅱ期翻修相似的结果[56]。WOLF等[57]回顾分析了92例全髋关节置换术后PJI患者,随访2年,Ⅱ期翻修组有5例再感染,Ⅰ期翻修组有4例再感染;这项研究还发现,只有在全髋关节置换术后发生严重和深度感染的情况下,Ⅱ期翻修才比Ⅰ期翻修效果更好。PANGAUD等[58]的Meta分析发现,膝关节置换术后PJI患者,Ⅰ期翻修感染的平均根除率为87.1%,Ⅱ期翻修感染的平均根除率为84.8%,两组的膝关节功能评分和活动范围相似。SVENSSON等[59]研究表明,对于全髋关节置换术后PJI,Ⅱ期翻修和Ⅰ期翻修术后再次翻修的风险相似。此外,与Ⅱ期翻修相比,Ⅰ期翻修可以减少手术次数、降低死亡率、减轻患者经济负担。 目前的研究还发现,Ⅰ期翻修后再次翻修的最常见原因不是感染复发,而是髋关节不稳/脱位[60]。这些发现强调细致精确的手术技术的重要性,包括植入物定位、软组织完整性以及使用先进的技术,如使用双动关节。此外,该研究还发现,Ⅰ期翻修术后再次翻修和再感染相关的独立因素是伤口引流时间超过1周、术中分离肠球菌以及既往有髋部感染而行手术的病史。 Ⅰ期翻修后,建议敏感抗生素静脉治疗2-6周,每日2次口服利福平300-450 mg,随后利福平加敏感抗生素口服,疗程共3个月。难治性细菌和真菌的治疗与DAIR相似。 (3) Ⅱ期翻修:指去除所有异物,并对可能的感染组织和骨骼进行彻底清创,然后植入抗生素骨水泥占位器,并给予抗生素静脉或口服治疗,待感染控制后,Ⅱ期再行假体置入。二期翻修使用范围较广泛,除一期翻修的适应证外,感染耐药菌、窦道持续存在、软组织覆盖较差的患者也适用[8,40], 此外,糖尿病、自身免疫性疾病、恶性疾病和长期使用抗生素的患者可能会发生真菌或非典型细菌感染,也建议二期翻修[8]。Ⅱ期翻修是北美治疗PJI最常用的方法,通常被视为治疗PJI的金标准,感染的根除率可超过90%[61]。这种方法的不足之处在于分期手术及其较长的间隔期会导致相关并发症,增加住院时间、医疗费用以及死亡风险[62]。CLAASSEN 等[63]回顾分析了50例膝关节PJI采用Ⅱ期翻修的患者,随访1年以上,其中12例患者术后仍存在持续感染,感染控制成功率为76.0%。CHEN等[64]回顾分析了155例(157髋)慢性PJI的两阶段翻修患者,平均随访9.7年,1年后无复发感染的概率为96.8%,3年后为94.3%,5.5年后为91.7%,末次随访Harris平均髋关节评分为85.7分(47-100分)。STEFFEN等[65]回顾分析了59例膝关节PJI采用Ⅱ期翻修的患者,随访1年以上,55例患者(93.2%)实现了感染控制,感染所致的截肢率为6.8%(4/59)。JEPPE等[66]的Meta分析发现,髋关节PJI患者Ⅰ期翻修发生再感染的风险为13.1%,Ⅱ期翻修发生的再感染风险为10.4%。尽管Ⅱ期翻修术在治疗PJI取得了满意的效果,但并不是所有的细菌都能成功地治疗,特别是耐药细菌。SALGADO等[67]报道了12例耐甲氧西林葡萄球菌感染患者,Ⅱ期翻修的失败率为50% 。 负载抗生素的骨水泥占位器通常用于管理死腔和局部抗菌治疗,直到放置永久假体[68]。一些学者不推荐占位器用于耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌、小菌落变异或真菌引起的感染,因为他们认为在这些环境中使用占位器可能不利于根除感 染[26,39];但也有耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌 PJI成功使用占位器治疗的报告[69]。目前,Ⅰ期清创后,假体重新置入的最佳时机尚无金标准,血清血沉和C-反应蛋白已被广泛用于监测和评估假体最佳的再置入时机[40],然而,在感染已经控制的患者中,血沉和C-反应蛋白水平仍然会升高,或者在持续感染的情况下,血沉和C-反应蛋白水平也会正常[70]。有研究认为,D-二聚体在确定再植时机方面要优于血沉和C-反应蛋白[71]。关节液中细胞计数和生物标志物的分析也被广泛用于确定再植时机和预测持续感染,但这些指标敏感性仍然较低[72]。在没有可靠指标可以确定假体重新置入最佳时机的前提下,根据现有的文献结果,重新置入前应该考虑到感染症状是否消退,血清和关节液(如果进行了穿刺)标志物是否有下降趋势[70]。Ⅰ期清创到最终置入假体的间隔时间从2周到几个月不等,早期的研究表明,3周内早期再植会导致较高的失败率[73];来自欧洲的研究显示,不是耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌、肠球菌、多重耐药的革兰阴性细菌引起且规律使用抗生素的情况下,2-6周内重新置入假体可以获得良好的结果[39]。应避免较长的间隔时间(> 8周),尤其是在使用占位器的情况下,因为骨水泥中的抗生素浓度会随时间降低,此时已降至最低抑菌浓度以下[4]。有研究认为,间隔时间增加与术后再次感染有较高的相关性[74],而AALIREZAIE 等[75]研究表明间隔时间的延长不能预测术后失败。 2013 年美国传染病学会在PJI 诊疗指南中提出,Ⅰ期旷置后,推荐进行敏感抗生素静脉注射或口服抗菌治疗4-6 周[40]。其中,苯唑西林敏感的葡萄球菌推荐头孢唑林或萘夫西林,其他难治性细菌或真菌感染的治疗方案与DAIR相似。虽然抗生素治疗的持续时间尚有争议,但数据表明,在大多数情况下,6周的疗程可能就足够了[76]。患者通常在重新置入假体前需要一段时间的无抗生素治疗期,以验证感染控制。虽然没有确切时间的要求,但建议在假体再次置入之前有2-4周的空窗期;至少2周很重要,因为如果停止使用抗生素不到2周就采样,组织培养敏感性将低于50%[77]。研究表明,这个间隔时间可能在复发性PJI中没有意义,因为许多病原体可能在假体置入前“休眠”数年,假体置入后重新出现感染[77]。Ⅱ期翻修假体置入时,即使术中细菌培养为阴性,假体置入后仍应继续进行抗生素治疗6周;如果细菌培养阳性,抗生素治疗将从置入假体之日算起延长至12周[78]。PJI不推荐伤口负压治疗,因为海绵会被细菌快速定植,导致感染,这些细菌多为多重耐药的革兰阴性菌和念珠菌[79]。 (4)关节融合术:是将关节周围的骨组织进行骨性融合,一般作为翻修术失败后的补救措施,该手术主要是为了彻底清除感染、缓解临床疼痛症状,保留患肢的负重能力。关节融合术可以用外固定架或髓内钉固定来完成[80],手术的适应证一般为:骨缺损较多、软组织覆盖差的患者,或多重耐药菌引起的感染;身体状况不能进行大手术的患者;或分期翻修后复发感染的患者。关节融合术通常是为了避免患者截肢,术后通常需要4-6周的静脉注射抗生素或口服抗菌药,感染根除率为60%-100%。 (5)关节切除成形术:是指切除感染的假体而不再置入,适应证与关节融合术相似。 (6)截肢:其适应证为坏死性筋膜炎清创效果不明显,严重的骨丢失或血管损害,软组织覆盖差,其他方案无法控制感染或保肢[81]。此外,如果截肢比关节切除成形术或关节融合术更能改善患者的长期功能结果,也可以考虑这种方法。如果所有感染的骨和软组织已经手术切除,并且没有伴随的脓毒血症或菌血症,敏感抗生素治疗应该持续到截肢后24-48 h。如果出现菌血症,治疗持续时间应根据针对这些综合征的治疗方案进行。如果手术后仍有残余的骨和软组织感染,建议接受4-6周的敏感抗生素的静脉注射或口服治疗。 2.5.2 生物治疗 现有的PJI治疗方法都存在各种各样的问题,无法获得较为满意的治疗效果。PJI的生物治疗方法具有抑制或破坏细菌生物膜、降低抗生素最低抑菌浓度、材料生物相容性好、易于降解等优点,愈发受到重视。 (1)水凝胶载药系统:假体表面通过负载抗生素的水凝胶涂层的方式,可以同时实现抗感染和生物相容的目的[82]。DRAGO等[83]发现,水凝胶能使部分抗生素的最小抑菌浓度降低4倍,负载抗生素的水凝胶涂层植入物能更大程度地减少浮游菌和生物膜的数量。CHENG等[84]在仿贻贝水凝胶中加入了抗菌肽和合成硅酸盐纳米颗粒,证明载于水凝胶中的抗菌肽具有良好的抗菌活性,可防止生物膜的形成。此外,水凝胶中的硅酸盐纳米颗粒可以促进人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨。一项多中心前瞻性研究纳入了373例髋膝关节需要初次置换或翻修的患者,采用负载抗生素的水凝胶涂层假体组,术后感染率低于对照组为(1% vs. 6%),这是第一个关于负载抗生素的水凝胶用于关节置换或翻修的临床试验[85]。 (2)抗菌微球载药系统:由于抗生素浸渍的聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯微球球内的抗生素呈非线性释放,长时间植入后由于骨水泥不能生物降解,细菌和生物膜也可以附着在聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯上造成再次感染。因此,需要比聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯更合适的药物输送载体[86]。 目前已经出现多种类型可生物降解的抗生素微球载药系统,包括硫酸钙、乳酸或乙醇酸聚合物、胶原和海藻酸盐等,这些微球载体内的抗生素释放时间较持久,并且可以生物降解,不需要二次手术取出。MARCZAK等[87]回顾了56例全膝关节置换术后PJI二期翻修的患者,Herafill组将负载庆大霉素的Herafill微球(含有硫酸钙和碳酸钙)涂层于假体,对照组未涂层Herafill微球,术后 Herafill组感染复发率明显低于对照组(0% vs. 17.9%)。UENG等[88]发现,冷冻干燥的多聚-L-赖氨酸包被的海藻酸盐微球中万古霉素在第17天释放的浓度仍高于最低抑菌浓度和最低杀菌浓度。AMBROSE等[89]观察到聚DL-乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物、聚乙二醇和妥布霉素组成的微球,在7-28 d时妥布霉素仍呈稳定的线性洗脱,妥布霉素可释放至少4-6周。 (3)生物膜裂解剂:生物膜的形成是细菌发展为多重耐药菌的主要原因之一[90],许多植物的提取物在体外具有抗菌和抗生物膜的功能。研究发现,大蒜提取物能抑制铜绿假单胞菌生物膜形成,降低毒力因子的释放,增强多形核白细胞对铜绿假单胞菌的吞噬和杀灭能力[91-92]。大黄素能抑制铜绿假单胞菌的黏附能力和生物膜的形成,增强氨苄青霉素对铜绿假单胞菌的抑制作用[93]。这些天然植物提取物有望为生物膜相关的感染提供新的治疗策略。 抗菌肽是作用于真菌和细菌生物膜的广谱抗菌剂[94]。YUAN等[95]发现,从福建大头蛙的皮肤分泌物中分离的抗菌肽(Japan icin-2LF),可以同时根除生物膜中的浮游型和定植型耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌,降低耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌感染的幼虫的死亡率。KAZEMZADEH-NARBAT等[96]研究表明,抗菌肽(HHC-36)涂层的钛植入物对金黄色葡萄球菌和铜绿假单胞菌均有良好的抗菌效果。但是,由于天然抗菌肽的抗菌活性低,具有细胞毒性和溶血性,以及不可预知的副反应(例如肾损伤、中枢神经损伤等)[97],未来需要开发与天然抗菌肽相比具有更高稳定性和活性的新型抗菌肽。 此外,其他基础研究表明,噬菌体、生物表面活性剂同样具有抑制细菌生物膜形成或生长的作用[97]。 "
| [1] KURTZ TM, LAU E, WATSON H, et al. Economic burden of periprosthetic joint infection in the United State. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(8 Suppl):61-65. [2] WHITEHOUSE MR, PARRY MC, KONAN S, et al. Deep infection after hip arthroplasty staying current with change. Bone Joint J. 2016;98(1):27-30. [3] HUBERT J, BEIL FT, ROLVIEN T, et al. Restoration of the hip geometry after two-stage exchange with intermediate resection arthroplasty for periprosthetic joint infection. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1-10. [4] IZAKOVICOVA P, BORENS O, TRAMPUZ A. Periprosthetic joint infection: current concepts and outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019;4(7):482-494. [5] KOH CK, ZENG I, RAVI S, et al. Periprosthetic joint infection is the main cause of failure for modern knee arthroplasty: an analysis of 11134 knees. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(9):2194-2201. [6] BUCHALTER DB, KIRBY DJ, TEO GM, et al. Topical Vancomycin Powder and Dilute Povidone-Iodine Lavage Reduce the Rate of Early Periprosthetic Joint Infection Following Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(1):1-21. [7] 朱崇尊, 杨闯, 沈灏. 关节假体感染的预防研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2019,13(2):206-212. [8] KAPADIA BH, BERG RA, DALEY JA, et al. Periprosthetic joint infection. Lancet. 2016;387(10016):386-394. [9] ANDERL JN, ZAHLLER J, ROE F, et al. Role of nutrient limitation and stationary-phase existence in Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm resistance to ampicillin and ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003; 47:1251-1256. [10] ZIMMERLI W, WALDVOGEL FA, VAUDAUX P, et al. Pathogenesis of foreign body infection: description and characteristics of an animal model. J Infect Dis.1982;146:487-497. [11] Stewart PS, Costerton JW. Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet. 2001;358:135-138. [12] PULIDO L, GHANEM E, JOSHI A, et al. Periprosthetic joint infection: the incidence, timing, and predisposing factors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:1710-1715. [13] AGGARWAL VK, BAKHSHI H, ECKER NU, et al. Organism profi le in periprosthetic joint infection: pathogens diff er at two arthroplasty infection referral centers in Europe and in the United States. J Knee Surg. 2014;27:399-406. [14] PREMKUMAR A, KOLIN DA, FARLEY KX, et al. Projected Economic Burden of Periprosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip and Knee in the United States. J Arthroplasty. 2020;9:1-10. [15] KAPADIA BH, MCELROY MJ, ISSA K, et al. The economic impact of periprosthetic infections following total knee arthroplasty at a specialized tertiary-care center. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29: 929-932. [16] TOULSON C, WALCOTT-SAPP S, HUR J, et al. Treatment of infected total hip arthroplasty with a 2-stage reimplantation protocol: update on “our institution’s” experience from 1989 to 2003. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24: 1051-1060. [17] BEREND KR, LOMBARDI AV JR, MORRIS MJ, et al. Two-stage treatment of hip periprosthetic joint infection is associated with a high rate of infection control but high mortality. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471: 510-518. [18] DOWSEY MM, CHOONG PF. Obese diabetic patients are at substantial risk for deep infection after primary TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:1577-1581. [19] MRAOVIC B, SUH D, JACOVIDES C, et al. Perioperative hyperglycemia and postope rative infection after lower limb arthroplasty. J Diabetes Sci Tech. 2011;5:412-418. [20] Mainous MR, Deitch EA. Nutrition and infection.Surg Clin North Am. 1994;74:659-676. [21] TOMA O, SUNTRUP P, STEFANESCU A, et al. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of cefoxitin in obesity: implications for risk of surgical site infection. Anesth Analg. 2011;113:730-737. [22] D’APUZZO MR, NOVICOFF WM, BROWNE JA. The John Insall award: morbid obesity independently impacts complications, mortality, and resource use after TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;473:57-63. [23] SILVERSTEIN P. Smoking and wound healing. Am J Med. 1992;93: 22S-24S. [24] SØRENSEN LT. Wound healing and infection in surgery. The clinical impact of smoking and smoking cessation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Surg. 2012;147:373-383. [25] POUR AE, MATAR WY, JAFARI SM, et al. Total joint arthroplasty in patients with hepatitis C. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:1448-1454. [26] PRICE CS, WILLIAMS A, PHILIP G, et al. Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization in preoperative orthopaedic outpatients.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(11):2842-2847. [27] KALMEIJER MD, VAN NIEUWLAND-BOLLEN E, BOGAERS-HOFMAN D, et al. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus is a major risk factor for surgical-site infections in orthopedic surgery. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2000;21:319-323. [28] YANO K, MINODA Y, SAKAWA A, et al. Positive nasal culture of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a risk factor for surgical site infection in orthopedics. Acta Orthop. 2009;80(4):486-490. [29] LEE JP, HOPF HW, CANNON-ALBRIGHT LA. Empiric evidence for a genetic contribution to predisposition to surgical site infection. Wound Repair Regen. 2013;21:211-215. [30] PARVIZI J, ZMISTOWSKI B, BERBARI EF, et al.New definition for periprosthetic joint infection: from the Workgroup of the musculoskeletal infection society. Clin Orthop. 2011;469:2992e4. [31] PARVIZI J, GEHRKE T. International Consensus Group on Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Definition of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:1331. [32] PARVIZI J, TAN TL, GOSWAMI K, et al. The 2018 definition of periprosthetic hip and knee infection: An evidence-based and validated criteria. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(5):1309-1314. [33] HUANG Z, LI W, LEE GC, et al. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of synovial fluid demonstrates high accuracy in prosthetic joint infection diagnostics: mNGS for diagnosing PJI. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(7):440-449. [34] AHMED SS, HADDAD FS. Prosthetic joint infection. Bone Joint Res. 2019;8(11):570-572. [35] GOLDBERG B, SICHTIG H, GEYER C, et al. Making the leap from research laboratory to clinic: challenges and opportunities for next-generation sequencing in infectious disease diagnostics. MBio. 2015;6: e01888-01815. [36] TARABICHI M, SHOHAT N, GOSWAMI K, et al. Can next generation sequencing play a role in detecting pathogens in synovial fluid? Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B:127-133. [37] THOENDEL MJ, JERALDO PR, GREENWOOD-QUAINTANCE KE, et al. Identification of prosthetic joint infection pathogens using a shotgun metagenomics approach. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;67:1333-1338. [38] KARAN G, JAVAD P. Culture-negative periprosthetic joint infection: is there a diagnostic role for next-generation sequencing? Exp Rev Mol Diagn. 2020;20:269-272. [39] ZIMMERLI W, TRAMPUZ A, OCHSNER PE. Prosthetic-joint infections. N Eng J Med. 2004;351(16):1645-1654. [40] OSMON DR, BERBARI EF, BERENDT AR, et al. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(1):e1-e25. [41] GEORGE J, NEWMAN JM, CARAVELLA JW, et al. Predicting functional outcomes after above knee amputation for infected total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(2):532-536. [42] ZHANG CF, HE L, FANG XY, et al. Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention for Acute Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Orthop Surg. 2020; 12(2):463-470. [43] BEDAIR HS, KATAKAM A, BEDEIR YH, et al. A decision analysis of treatment strategies for acute periprosthetic joint infection: Early irrigation and debridement versus delayed treatment based on organism. J Orthop. 2020;22:1-15. [44] LIU CW, KUO CL, CHUANG SY, et al. Results of infected total knee arthroplasty treated with arthroscopic debridement and continuous antibiotic irrigation system. Indian J Orthop. 2013;47:93-97. [45] VOLPIN A, SUKEIK M, ALAZZAWI S, et al. Aggressive early debridement in treatment of acute periprosthetic joint infections after hip and knee replacements. Open Orthop J. 2016;10(Suppl 2):669-678. [46] MEEHAN AM, OSMON DR, DUFFY MC, et al. Outcome of penicillin-susceptible streptococcal prosthetic joint infection treated with debridement and retention of the prosthesis. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36: 845-849. [47] MILLER R, HIGUERA CA, WU J, et al. Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Review of Antibiotic Treatment. JBJS Rev. 2020;8(7):1-9. [48] URE KJ, AMSTUTZ HC, NASSER S, et al. Direct-exchange arthroplasty for the treatment of infection after total hip replacement: an average ten-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80:961-968. [49] RAUT VV, SINEY PD, WROBLEWSKI BM. One stage revision of infected total hip replacements with discharging sinuses. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994;76:721-724. [50] CALLAGHAN JJ, KATZ RP, JOHNSTON RC. Onestage revision surgery of the infected hip:a minimum 10-year followup study. Clin Orthop. 1999;369:139-143. [51] SENTHI S, MUNRO JT, PITTO RP. Infection in total hip replacement:meta-analysis. Int Orthop.2011;35:253-260. [52] YOO JJ, KWON YS, KOO KH, et al. One-stage cementless revision arthroplasty for infected hip replacements. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5): 1195-1201. [53] BORI G, MUÑOZ-MAHAMUD E, CUÑÉ J, et al. One-Stage Revision Arthroplasty Using Cementless Stem for Infected Hip Arthroplasties. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(5):1076-1081. [54] LI P, HOU M, ZHU ZQ, et al. Cementless revision for infected hip arthroplasty: an 8.6 years follow-up. Orthop Surg. 2015;7(1):37-42. [55] ZAHAR A, GEHRKE TA. One-stage revision for infected total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016;47:11-18. [56] SETOR K, KUNUTSOR, MICHAEL R, et al. One-and two-stage surgical revision of peri-prosthetic joint infection of the hip: a pooled individual participant data analysis of 44 cohort studies. Eur J Epidemiol. 2018; 33(10):933-946. [57] WOLF M, CLAR H, FRIESENBICHLER J, et al. Prosthetic joint infection following total hip replacement: results of one-stage versus two-stage exchange. Int Orthop. 2014;38(7):1363-1368. [58] PANGAUD C, OLLIVIER M, ARGENSON JN. Outcome of single-stage versus two-stage exchange for revision knee arthroplasty for chronic periprosthetic infection. EFORT Open Rev. 2019;4(8):495-502. [59] SVENSSON K, ROLFSON O, KÄRRHOLM J, et al. Similar Risk of Re-Revision in Patients after One- or Two-Stage Surgical Revision of Infected Total Hip Arthroplasty: An Analysis of Revisions in the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register 1979–2015. J Clin Med. 2019;8(4):485. [60] ABDELAZIZ H, GRÜBER H, GEHRKE T, et al. What are the Factors Associated with Re-revision After One-stage Revision for Periprosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip? A Case-control Study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019;477(10):2258-2263. [61] MASRI BA, PANAGIOTOPOULOS KP, GREIDANUS NV, et al. Cementless two-stage exchange arthroplasty for infection after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22:72-78. [62] BEDAIR H. CORR Insights®: What are the Factors Associated With Re-revisionAfter One-stage Revision for Periprosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip? A Case-control Study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019;477(10): 2264-226. [63] CLAASSEN L, PLAASS C, DANIILIDIS K, et al. Two-Stage Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty in Cases of Periprosthetic Joint Infection: An Analysis of 50 Cases. Open Orthop J. 2015;9:49-56. [64] CHEN SY, HU CC, CHEN CC, et al. Two-Stage Revision Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Hip Infection: Mean Follow-Up of Ten Years. Biomed Res Int. 2015:1-7. [65] STEFFEN H, ANNA S, GEORG G, et al. Eradication rates, risk factors, and implant selection in two-stage revision knee arthroplasty: a mid-term follow-up study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):93. [66] JEPPE L, ANDERS T, REIMAR W, et al. Chronic infections in hip arthroplasties: comparing risk of reinfection following one-stage and two-stage revision: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Epidemiol. 2012;4:57-73. [67] SALGADO CD, DASH S, CANTEY JR, et al. Higher risk of failure of methicillin -resistant Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;461:48-53. [68] MABRY TM, HANSSEN AD. Articulating antibiotic spacers: a matter of personal preference. Orthopedics. 2007;30:783-785. [69] LEUNG F, RICHARDS CJ, GARBUZ DS, et al. Two-stage total hip arthroplasty: how often does it control methicillin-resistant infection? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469:1009-1015. [70] TÖZÜN IR, OZDEN VE, DIKMEN G,et al. Trends in the treatment of infected knee arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev. 2020;5(10):672-683. [71] SHAHI A, KHEIR MM, TARABICHI M, et al Serum D-dimer test is promising for the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection and timing of reimplantation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99:1419-1427. [72] MÜHLHOFER HML, KNEBEL C, POHLIG F, et al. Synovial aspiration and serological testing in two-stage revision arthroplasty for prosthetic joint infection: evaluation before reconstruction with a mean follow-up of twenty seven months. Int Orthop. 2018;42:265-271. [73] RAND JA, BRYAN RS. Reimplantation for the salvage of an infected total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983;65:1081-1086. [74] SABRY FY, BULLER L, AHMED S, et al. Preoperative prediction of failure following two-stage revision for knee prosthetic joint infections. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:115-121. [75] AALI REZAIE A, GOSWAMI K, SHOHAT N, et al. Time to Reimplantation: Waiting Longer Confers No Added Benefit. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(6): 1-15. [76] BEJON P, BERENDT A, ATKINS BL, et al. Two-stage revision for prosthetic joint infection: predictors of outcome and the role of reimplantation microbiology. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010;65:569-575. [77] SCHINDLER M, CHRISTOFILOPOULOS P, WYSSA B, et al. Poor performance of microbiological sampling in the prediction of recurrent arthroplasty infection. Int Orthop. 2011;35:647-654. [78] PETRA I, OLIVIER B, ANDREJ T. Periprosthetic joint infection: current concepts and outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019;4(7):482-494. [79] YUSUF E, JORDAN X, CLAUSS M, et al. High bacterial load in negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) foams used in the treatment of chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2013;21:677-681. [80] MABRY TM, JACOFSKY DJ, HAIDUKEWYCH GJ, et al. Comparison of intramedullary nailing and external fixation knee arthrodesis for the infected knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;464:11-15. [81] SIA IG, BERBARI EF, KARCHMER AW. Prosthetic joint infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2005;19:885-914. [82] OVERSTREET D, MCLAREN A, CALARA F, et al. Local gentamicin delivery from resorbable viscous hydrogels is therapeutically effective. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(1):337-347. [83] DRAGO L, BOOT W, DIMAS K, et al. Does implant coating with antibacterial-loaded hydrogel reduce bacterial colonization and biofilm formation in vitro?. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(11): 3311-3323. [84] CHENG H, YUE K, KAZEMZADEH-NARBAT M, et al. Mussel-inspired multifunctional hydrogel coating for prevention of infections and enhanced osteogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(13): 11428-11439. [85] ROMANÒ CL, MALIZOS K, CAPUANO N, et al. Does an antibioticloaded hydrogel coating reduce early post-surgical infectionafter joint arthroplasty? J Bone Jt Infect. 2016;1:34-41 [86] BAYSTON R, RODGERS J. Production of extra-cellular slime by staphylococcus epidermidis during stationary phase of growth: Its association with adherence to implantable devices. J Clin Pathol. 1990;43:866-870. [87] MARCZAK D, SYNDER M, SIBIŃSKI M, et al. The use of calcium carbonate beads containing gentamicin in the second stage septic revision of total knee arthroplasty reduces reinfection rate. Knee. 2016;23(2):322-326. [88] UENG SW, LEE SS, LIN SS, et al. Biodegradable alginate antibiotic beads. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;380:250-259. [89] AMBROSE CG, GOGOLA GR, CLYBURN TA, et al. Antibiotic microspheres: preliminary testing for potential treatment of osteomyelitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;415:279-285. [90] CH’NG JH, CHONG KK, LAM LN, et al. Biofilm-associated infection by Enterococci. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2019;17(2):82-94. [91] BJARNSHOLT T, JENSEN PO, RASMUSSEN TB, et al. Garlic blocks quorum sensing and promotes rapid clearing of pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Microbiology. 2005;151:3873-3880. [92] HARJAI K, KUMAR R, SINGH S. Garlic blocks quorum sensing and attenuates the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010;58:161-168. [93] DING X, YIN B, QIAN L, et al. Screening for novel quorum-sensing inhibitors to interfere with the formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. J Med Microbiol. 2011;60:1827-1834. [94] PLETZER D, COLEMAN SR., HANCOCK RE. Anti-biofilm peptides as a new weapon in antimicrobial warfare. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016; 33:35-40. [95] YUAN Y, ZAI Y, XI X, et al. A novel membrane-disruptive antimicrobial peptide from frog skin secretion against cystic fibrosis isolates and evaluation of anti-MRSA effect using Galleria mellonella model. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen. Subj. 2019;1863:849-856. [96] KAZEMZADEH-NARBAT M, LAI BF, DING C, et al. Multilayered coating on titanium for controlled release of antimicrobial peptides for the prevention of implant-associated infections. Biomaterials. 2013;34(24):5969-5977. [97] MISHRA R, PANDA AK, DE MANDAL S, et al. Natural Anti-biofilm Agents: Strategies to Control Biofilm-Forming Pathogens. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:566325. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [3] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [4] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [5] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [6] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [7] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [8] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [9] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [10] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [11] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [12] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [13] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [14] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [15] | Liu Yafei, Wang Yalin, Zuo Yanping, Sun Qi, Wei Jing, Zhao Lixia. Structural changes of the temporomandibular joint in adolescents with skeletal Class III malocclusions after maxillary protraction: an X-ray measurement analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1154-1159. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||