Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (36): 5844-5850.doi: 10.12307/2021.353
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of wearable inertial sensor in evaluating the function of human knee joint
Zhou Xiaoxiang, Liao Xinyu, He Lu, Liu Dejian, Wang Guoliang, Jia Di, He Chuan, Li Yanlin
- Department of Sports Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-09Revised:2021-03-10Accepted:2021-05-09Online:2021-12-28Published:2021-09-18 -
Contact:Li Yanlin, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Sports Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Zhou Xiaoxiang, Master candidate, Department of Sports Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760403, 81960409 (to LYL); Chen Shiyi Expert Workstation Project in Yunnan Province, No. 2018IC102 (to LYL); the Yunnan Provincial Medical Leading Talents Project, No. L-201601 (to LYL); the Yunnan Provincial Bone and Joint Disease Clinical Medicine Center Project, No. ZX2019-03-04 (to LYL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Xiaoxiang, Liao Xinyu, He Lu, Liu Dejian, Wang Guoliang, Jia Di, He Chuan, Li Yanlin. Application of wearable inertial sensor in evaluating the function of human knee joint[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5844-5850.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 惯性传感器监测膝关节的重要运动学参数 生理上的关节运动是通过肌肉的等张收缩发生的,收缩力与关节部位肌肉长度的变化密切相关。在收缩过程中,肌肉长度的变化幅度随关节角度、动作和姿势的不同而不同,通过测量关节的运动范围,可以确定肌肉产生的代表关节健康状况的最大力,不同活动水平下的关节角度和姿势也描绘了此时的肌肉力量和耐力[6]。因此,关节监测的主要重点是以有意义的数据(如角度、活动范围、运动和方向)的形式跟踪和记录关节活动,这些数据可以用来估计关节健康状态并提供反馈。为在各种活动中测量和评估人体关节的力学性能,正在使用不同的跟踪技术,这些技术可以根据提取的4个关键参数进行分析:关节角度、关节运动和骨骼追踪与步态分析[7]。 2.1.1 关节角度 人体每个可移动的关节都有一个运动的最佳角度范围,为了达到最佳角度,肌肉应该有合适的长度来承受最大的力量。对于一个健康的成年人,有几个公认的关节角度活动范围的参考值[8],然而,角度范围因性别、年龄、身体结构、日常活动等而异[9]。 无论是男性还是女性,关节的活动范围值都随着年龄的增长而下降,膝关节变化最明显。虽然活动范围值通常会受到年龄的影响,但也可能因如受伤或其他相关问题,导致关节活动范围值减少,因此,研究关节角度对早期发现关节问题或判断关节康复进展具有重要意义。对于关节角度的测量,提出并开发了几种传感系统[10-20],但大多数系统的主要缺点是不够灵活,操作专业门槛高且精度较低。 ARGENT等[21]在一项原始研究中基于单个惯性传感器使用机器学习的方法来评估关节角度,试验招募14名健康参与者进行,使用3D运动捕捉系统(金标准)捕获的运动学数据作为参考标准,利用4种机器学习模型从单个惯性传感器来计算关节角度,并与参考标准进行比较以评估精度,结果表明只使用一个惯性传感器就可以通过多次练习测量关节角度,并且与金标准相比具有很好的准确性。CORDILLET等[22]在一项研究中利用惯性传感器估计骑行过程中的三维膝关节角度,试验招募14名健康的休闲自行车手参与,通过使用基于惯性传感器和基于光电的运动捕获系统来计算身体节段方向和3D膝关节角度的误差,以评估新型传感器的准确性,结果表明使用一对安装在小腿和大腿上的惯性传感器来估计穿过膝盖的三维旋转方法的精度,与传统的标定方法相比,显著提高了三维膝关节角度测量的准确性。OUBRE等[23]在一项研究中将惯性传感器用于膝关节运动学的长时间动态监测,试验招募17名健康者受试者参与,这些人佩戴可伸缩的惯性传感器,固定在膝关节相对节段的2个锚点上,同时以3种不同自选速度行走,在剔除单个离群值受试者后,该系统估计了受试者的膝关节屈伸角度,结果表明该可穿戴惯性传感器可准确估计不同步行速度下运动时的膝关节屈伸角度。STRAATEN等[24]在一项研究中进行基于惯性传感器的运动分析,纳入20名健康对照和19例单侧重度膝关节骨性关节炎患者,使用惯性传感器系统和基于相机的系统(金标准)同时记录了5次单足站立任务,采用一维统计参数图对正常人和重度膝关节骨性关节炎患者的运动学波形进行统计学分析,结果表明其可以区分健康对照组和严重膝关节骨性关节炎患者的侧躯干倾斜度和髋关节屈曲度;与健康对照组相比,有严重膝关节骨性关节炎患者的对侧腿有更多的躯干倾斜,髋部弯曲也更多。与其他技术相比,惯性传感器因其体积小、成本低,并且可以高精度地测量3D膝关节角度,而被越来越多地使用,见图2。"


2.1.2 关节运动 关节运动包括屈曲、伸展、内收、外展,旋内、旋外和环转[25]。活动范围值表示关节的全部运动潜力,由于某些健康问题或损伤,关节的活动度可能会减小,因此,关节活动度是评价关节健康状况的重要临床指标。此外,对于关节功能的恢复来说,持续的运动监测是非常重要的。关节运动的测量包括其角度和方向,因此,基于测角仪、光纤传感器或屈伸传感器的关节监视系统不能用于监视关节运 动[26],因为它们只能测量被解释为角度的单轴运动。为了估计关节的角度和方向,最常用的技术是通过应用图像处理技术,捕获几个人体关节动作的视觉数据,以使用人体测量(人体的大小、形状和组成)和参考图像/视频中的已知关节位置来估计关节运动[27]。虽然该系统是一种可靠和成熟的监测技术,但它需要预先配备的环境和设置,不允许进行持续和长期的监测,特别是在日常活动期间。 STETTER等[28]在一项研究中基于可穿戴惯性传感器和机器学习进行运动中膝关节受力的估计,试验招募13名志愿者进行,在他们的右腿上安装2个惯性传感器,参与者测试了各种动作,包括直线运动、改变方向和跳跃,结果表明机器学习方法可以非常准确地估计基于2个惯性传感器获得数据的各种运动的膝关节受力。SIGWARD等[29]在一项研究中应用惯性传感器评价前交叉韧带重建术后膝关节负荷不对称的特征,试验在19例前交叉韧带重建术后(96.7±16.8) d患者中进行,观察小腿角速度与膝关节伸肌力矩的关系,同时使用惯性传感器和基于测力平台标记的运动系统对步态进行评估,结果表明,小腿的运动学特征可以在前交叉韧带重建后恢复步态时提供与膝关节负荷相关的信息,小腿角速度的肢体间差异与未检测到时空不对称性的膝关节伸展力矩的肢体间差异有关。因此,惯性传感器对于膝关节关节运动的测量拥有较好的发展前景,适用于膝关节受力分析、前交叉韧带术后重建的小腿运动学分析,见图3。"

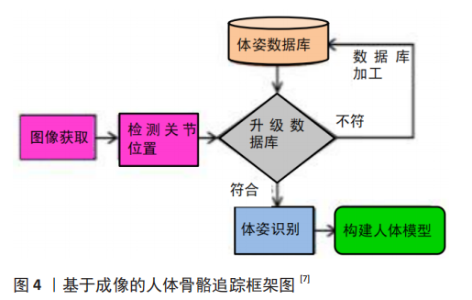
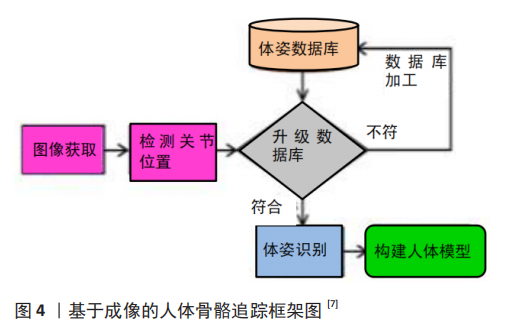
2.1.3 骨骼追踪 骨骼追踪是一种通过检测人体各个关节的位置来建立人体骨骼模型的技术,其有助于通过认识和理解不同功能活动的人类姿势来检测实时人类体态[30]。骨骼追踪的关键应用是通过准确评估人体姿势来检测身体残疾和分析康复过程。大多数骨骼追踪系统基于使用单个摄像机或多个摄像机的网络来捕获图像的图像处理技术,这项技术包括位置和运动的定量测量、分析图像深度的复杂图像处理算法以及跟踪人体关节和创建人体模型的机器学习。已经有一些研究人员不再使用相机或成像传感器和复杂的图像处理技术,而是用放置在人体不同关节位置的多个校准的惯性传感器来取代这种成像系统,以进行骨骼追踪[31-32],这也使该系统更方便和更容易使用。目前,骨骼追踪被广泛应用于多种智能活动监测系统、人机交互、监视、虚拟游戏、模式识别、人体行为检测、运动员成绩分析和康复系统[33-37]。 QIU等[38]计划开发基于惯性传感器的视觉康复训练游戏和可定制的扩展康复项目。作为虚拟现实的输入工具,患者可以在运动感知游戏中进行康复训练,患者不再需要忍受枯燥的康复训练,患者依从性也可以得到相应地提高。欧攀等[39]在研究中使用基于惯性传感器骨骼追踪的快速人体测量方法,结果表明该方法在短时间内获得较为准确的结果,可在狭小环境中完成部分人体特征尺寸的获取。在2018年世界移动通信大会上,来自日本的公司将基于5G通讯的人形机器人通过网络与操作者相连接,借助Xsens公司的动作捕捉系统采集人体运动信息后,让机器人模仿人类操作者的各种复杂动作。AZIZ等[40]在研究中招募12名年轻人通过佩戴在左右膝盖和胸部的3个惯性传感器,对滑倒、绊倒、昏厥等7种造成跌倒的动作进行测试,以便对跌倒者进行有针对的治疗。所以,基于惯性传感器的骨骼追踪技术相比传统的骨骼追踪技术具有更为广泛的使用前景,操作简便且高效,见图4。"

2.1.4 步态分析 步行方式即步态,从长远来看对人们独立生活的能力和健康问题有很大影响,认识到步态分析的重要性只是第一步,还需要了解步态分析的要点。临床步态分析旨在通过生物力学和运动学揭示步态异常的关键联系和影响因素,通过康复训练帮助评估和治疗,并协助临床诊断、疗效评估和病理学研究等[41-42]。 传统的步态分析是基于治疗师的观察和判断,以及足底压力监测,这种方法在很大程度上取决于治疗师的经验,评估结果很可能不准确,部分原因是这些临床评估较为主观[43]。 足底压力监测方法虽然提供了足底压力的详细信息,但是它无法记录摆动阶段的步态参数(例如步速,行走轨迹,关节角度等),这不利于确定和改进下肢治疗计划[44-45]。步态分析通常在特定步态实验室中执行且价格过于昂贵和操作不便,故有必要开发一种无需复杂过程的步态分析方法,这有利于物理治疗师发现异常步态和慢性步态疼痛的原因,以及健身教练发现运动损伤的风险并提供指导[46-47]。 步态分析是一项分析下肢步行运动的技术,旨在研究步行的内在规律,步态分析可以客观和定量地评估与个体的功能限制相关的步态模式,而时空步态参数的评估则提供了最有效的步态和预测跌倒风险的手段[48-49]。此外,步态的时空学和运动学变量也被用来定量评估步态的水平[50]。时空学参数包括步幅时间、步幅长度、步幅频率,运动学参数包括膝关节运动峰峰值[50]。 KAYAALP等[51]在一项研究中使用惯性传感器来进行患者的术后康复监测,试验招募13名健康志愿者进行了5次10 m步行实验,同时收集了传感器和运动捕捉数据,研究表明这种新型的传感器系统可以记录健康受试者行走过程中的矢状膝关节运动学,与运动捕捉系统的记录相当。DE VROEY等[52]在一项研究中使用惯性传感器对膝关节置换人群的步态时间参数进行评估,试验招募16例膝关节置换患者进行了3次步态实验,试验在6 m步道上以自选速度进行,在试验过程中,同时采集小腿的惯性传感器陀螺仪数据和光电摄像机的运动学数据,结果表明,惯性传感器可用于膝关节置换人群中的临时步态参数的实验室外评估。李玳等[53]在一项研究中使用惯性传感器对前交叉韧带断裂三维不对称度进行步态分析,试验招募正常受试者为正常组,在运动医学研究所拟行前交叉韧带重建的术前患者为对照组,结果表明其可作为步态不对称度的分析方法。袁心一等[54]在一项研究中应用惯性传感器来对帕金森病患者的冻结步态进行实时监测,试验招募12名受试者进行,首先采集患者的运动数据,然后经过信号预处理,特征提取和计算机学习算法做出模型,最后通过对数据集采用十折交叉验证来评估模型准确度和精确度,结果表明该系统能够实时监测帕金森病患者日常生活中的冻结步态发作情况,为医生的诊疗提供定量、可靠的参考依据。YEO等[50]在一项研究中将惯性传感器系统用于步态分析的结果,与使用3D运动捕获系统获得的测量结果进行比较,试验招募30名健康参与者进行,步态分析结果表明参与者的时空(步幅时间、步幅长度、节奏、步长)和运动学(膝关节运动峰)参数没有显著差异,两种系统测量的步态时空参数和运动学参数基本一致。IBRAHIM等[55]在一项研究中使用惯性传感器得到的步态参数对多发性硬化症患者的疲劳程度进行评估,试验纳入49例患者进行,每个参与者的每只脚上都装有一个小型惯性传感器,通过取测试开始和结束之间的平均步态参数之差对步态参数进行归一化,以消除个体差异,结果表明疲劳水平可以使用基于惯性传感器的系统获得的时空学参数进行预测,以评估其疗效。因此,基于惯性传感器的步态分析技术有利于发现异常步态并可广泛应用于术后行为监测,及时发现运动损伤的风险且对后续康复具有指导意义,见图5。 2.2 讨论 评估运动学特征对于正确理解复杂的功能性运动至关重要,研究运动学有助于评估患者的功能恢复情况[56]。目前主要有4种不同的方法来评估膝关节的运动:①3D运动捕捉;②景深摄像机系统;③来自合格运动专业人员的视觉分析;④自我评估[57],但每种方法都有或多或少的限制。例如,3D运动捕捉系统虽然精确度最好,但需要相当昂贵的红外摄像机来跟踪附着在被摄体上的反射标记,因此,这种类型的运动分析仅适用于专用的实验室环境,很大程度上受到物理空间的限制,而且皮肤安装的标记物也可能会阻碍正常运动;此外,通常需要特定的专业知识来解释处理后的数据并对观察到的结果提出建议[57],因此,该系统很难用于研究室以外的运动评估。 相比之下,景深摄像机系统成本较低、操作简便,如微软的Kinect,近年来这类系统因其低成本和易于设置而越来越多地用于研究和商业目的。然而,这样的系统却有几个较大缺陷:与3D运动捕捉系统相比该系统往往精确度较低,该系统通过跟踪特定的身体位置并基于这些位置重新创建身体节段来操作;身体部位的交叉、不合适的照明(户外)、衣服的移动和其他人的移动经常会造成混乱并由此导致准确性不佳;用户经常必须进行耗时的手动工作来重新标记身体部分,以确保系统准确性。 在基于临床和健身房的环境中,视觉评估通常用于评估下肢运动。对于新手和专家而言,对人体生物力学的视觉评估是主观且不可靠的。由于以上存在的这些问题,人们对使用可穿戴惯性传感器评估膝关节运动的兴趣与日俱增。通过该设备可以在与“真实世界”训练相关的复杂环境中跟踪各种姿势,而不像基于景深摄相机的系统,后者受到位置、遮挡和照明问题的阻碍。学界也已经做出了很多努力来开发可穿戴传感器,以便于在自由生活条件下实时、连续地监测关节健康和运动。因此,惯性传感器最近被用来分析膝关节运动的一系列组成部分,这包括检测和量化给定练习完成的重复次数、计算在这些重复期间关节的运动范围以及对练习时间进行分析等[58]。 惯性传感器已广泛应用于评估关节角度、关节受力以及全膝关节置换术后膝关节活动度,膝关节运动学的长时间动态监测,膝关节的运动学评估,膝关节置换人群步态时间参数评估,术后康复监测,前交叉韧带重建术后膝关节负荷,前交叉韧带断裂三维不对称度的步态分析,帕金森患者的行走能力评估,帕金森病冻结步态的实时监测,多发性硬化症患者的疲劳程度评估。"

| [1] RG A, QLA B. Emotion-relevant activity recognition based on smart cushion using multi-sensor fusion. Information Fusion. 2019;48:1-10. [2] FORTINO G, GALZARANO S, GRAVINA R, et al. A framework for collaborative computing and multi-sensor data fusion in body sensor networks. Information Fusion. 2015;22:50-70. [3] CMA B, WL A, JC A, et al. Adaptive sliding window based activity recognition for assisted livings. Information Fusion. 2020;53:55-65. [4] NCA B, HZ A, SQ A, et al. A sensor-to-segment calibration method for motion capture system based on low cost MIMU - ScienceDirect. Measurement. 2019;131:490-500. [5] TOGNETTI A, LORUSSI F, CARBONARO N, et al. Wearable Goniometer and Accelerometer Sensory Fusion for Knee Joint Angle Measurement in Daily Life. Sensors (Basel). 2015;15(11):28435-28455. [6] HA M, HAN D. The relationship between knee joint angle and knee flexor and extensor muscle strength. J Phys Ther Sci. 2017;29(4): 662-664. [7] FAISAL AI, MAJUMDER S, MONDAL T, et al. Monitoring Methods of Human Body Joints: State-of-the-Art and Research Challenges. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(11):2629. [8] VALEVICIUS AM, JUN PY, HEBERT JS, et al. Use of Optical Motion Capture for the Analysis of Normative Upper Body Kinematics during Functional Upper Limb Tasks: A Systematic Review. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2018:1-15. [9] MOROMIZATO K, KIMURA R, FUKASE H, et al. Whole-body patterns of the range of joint motion in young adults: masculine type and feminine type. J Physiol Anthropol. 2016;35(1):23. [10] ZHANG H, NIU W, ZHANG S. Extremely Stretchable, Stable, and Durable Strain Sensors Based on Double-Network Organogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(38):32640-32648. [11] JEONG SM, KANG Y, LIM T, et al. Hydrophobic Microfiber Strain Sensor Operating Stably in Sweat and Water Environment. Advanced Materials Interfaces. 2018;5(24). doi: 10.1002/admi.201801376 [12] PARK S, AHN S, SUN J, et al. Highly Bendable and Rotational Textile Structure with Prestrained Conductive Sewing Pattern for Human Joint Monitoring. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(10). doi: 10.1002/adfm.201808369 [13] MONTAZERIAN H, DALILI A, MILANI AS, et al. Piezoresistive sensing in chopped carbon fiber embedded PDMS yarns. Composites Part B Engineering . 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.01.090 [14] MILANESE S, GORDON S, BUETTNER P, et al. Reliability and concurrent validity of knee angle measurement: smart phone app versus universal goniometer used by experienced and novice clinicians. Man Ther. 2014; 19(6):569-74. [15] JENNY JY, BUREGGAH A, DIESINGER Y. Measurement of the knee flexion angle with smartphone applications: Which technology is better? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(9):2874-2877. [16] VOHRALIK SL, BOWEN AR, BURNS J, et al. Reliability and validity of a smartphone app to measure joint range. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;94(4):325-330. [17] JOHNSON LB, SUMNER S, DUONG T, et al. Validity and reliability of smartphone magnetometer-based goniometer evaluation of shoulder abduction – A pilot study. Man Ther. 2015;20(6):777-782. [18] CASTAEDA JJ, RUIZ-OLAYA AF, LARA-HERRERA CN, et al. Knee Joint Angle Monitoring System Based on Inertial Measurement Units for Human Gait Analysis. 2017. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-4086-3_173 [19] VARGAS-VALENCIA LS, ELIAS A, ROCON E, et al. An IMU-to-Body Alignment Method Applied to Human Gait Analysis. Sensors (Basel). 2016;16(12):2090. [20] BONNET V, JOUKOV V, KULIC D, et al. Monitoring of Hip and Knee Joint Angles Using a Single Inertial Measurement Unit During Lower Limb Rehabilitation. IEEE Sens J. 2016;16(6):1557-1564. [21] ARGENT R, DRUMMOND S, REMUS A, et al. Evaluating the use of machine learning in the assessment of joint angle using a single inertial sensor. J Rehabil Assist Technol Eng. 2019;6:2055668319868544. [22] CORDILLET S, BIDEAU N, BIDEAU B, et al. Estimation of 3D Knee Joint Angles during Cycling Using Inertial Sensors: Accuracy of a Novel Sensor-to-Segment Calibration Procedure Based on Pedaling Motion. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(11):2474. [23] OUBRE B, DANEAULT JF, BOYER K, et al. A Simple Low-Cost Wearable Sensor for Long-Term Ambulatory Monitoring of Knee Joint Kinematics. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2020;67(12):3483-3490. [24] STRAATEN R, WESSELING M, JONKERS I, et al. Discriminant validity of 3D joint kinematics and centre of mass displacement measured by inertial sensor technology during the unipodal stance task. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(5):e0232513. [25] CHIANG CY, CHEN KH, LIU KC, et al. Data Collection and Analysis Using Wearable Sensors for Monitoring Knee Range of Motion after Total Knee Arthroplasty. Sensors (Basel). 2017;17(2):418. [26] TOTARO M, POLIERO T, MONDINI A, et al. Soft Smart Garments for Lower Limb Joint Position Analysis. Sensors (Basel). 2017;17(10):2314. [27] WANG Z, LIU G, TIAN G. Human skeleton tracking using information weighted consensus filter in distributed camera networks//Chinese Automation Congress (CAC). 2018. [28] STETTER B, RINGHOF S, KRAFFT FC, et al. Estimation of Knee Joint Forces in Sport Movements Using Wearable Sensors and Machine Learning. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(17):3690. [29] SIGWARD SM, CHAN MSM, LIN PE, et al. Characterizing knee loading asymmetry in individuals following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using inertial sensors. Gait Posture. 2016;49:114-119. [30] ISLAM MU, MAHMUD H, ASHRAF FB, et al. Yoga posture recognition by detecting human joint points in real time using microsoft kinect//2017 IEEE Region 10 Humanitarian Technology Conference (R10-HTC). IEEE, 2017. [31] AHMADI A, DESTELLE F, UNZUETA L, et al. 3D Human Gait Reconstruction and Monitoring Using Body-Worn Inertial Sensors and Kinematic Modeling. IEEE Sens J. 2016;16(24):8823-8831. [32] SAUL KR, HU X, GOEHLER CM, et al. Benchmarking of dynamic simulation predictions in two software platforms using an upper limb musculoskeletal model. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2015;18(13):1445-1458. [33] JALAL A, KAMAL S, KIM D. A Depth Video-based Human Detection and Activity Recognition using Multi-features and Embedded Hidden Markov Models for Health Care Monitoring Systems. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence. 2017; 4(4):54. [34] WAN Z, JAILANI R, OMAR AR, et al. Development of MATLAB Kinect Skeletal Tracking System (MKSTS) for gait analysis// 2016 IEEE Symposium on Computer Applications & Industrial Electronics (ISCAIE). IEEE, 2016. [35] STØVE MP, PALSSON TS, HIRATA RP. Smartphone-based accelerometry is a valid tool for measuring dynamic changes in knee extension range of motion. Knee. 2018;25(1):66-72. [36] Bae J, Tomizuka M. A tele-monitoring system for gait rehabilitation with an inertial measurement unit and a shoe-type ground reaction force sensor. Mechatronics. 2013;23( 6):646-651. [37] MAJUMDER S, AGHAYI E, NOFERESTI M, et al. Smart Homes for Elderly Healthcare—Recent Advances and Research Challenges. Sensors (Basel). 2017;17(11):2496. [38] QIU S, WANG H, LI J, et al. Towards Wearable-Inertial-Sensor-Based Gait Posture Evaluation for Subjects with Unbalanced Gaits. Sensors (Basel). 2020;20(4):1193. [39] 欧攀,吴帅,周锴.基于深度传感器骨骼追踪的快速人体测量方法[J].激光与光电子学进展,2017,54(12):229-236. [40] AZIZ O, PARK EJ, MORI G, et al. Distinguishing the causes of falls in humans using an array of wearable tri-axial accelerometers. Gait Posture. 2014;39(1):506-512. [41] VAN SCHOOTEN KS, PIJNAPPELS M, LORD SR, et al. Quality of Daily-Life Gait: Novel Outcome for Trials that Focus on Balance, Mobility, and Falls. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(20):4388. [42] SENSINGER JW, INTAWACHIRARAT N, GARD SA. Contribution of prosthetic knee and ankle mechanisms to swing-phase foot clearance. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2013;21(1):74-80. [43] QIU S, LIU L, ZHAO H, et al. MEMS Inertial Sensors Based Gait Analysis for Rehabilitation Assessment via Multi-Sensor Fusion. Micromachines (Basel). 2018;9(9):442. [44] LEAL-JUNIOR AG, FRIZERA A, AVELLAR LM, et al. Polymer Optical Fiber for In-Shoe Monitoring of Ground Reaction Forces During the Gait. IEEE Sens J. 2018:1-1. [45] VILLENEUVE E, HARWIN W, HOLDERBAUM W, et al. Reconstruction of Angular Kinematics From Wrist-Worn Inertial Sensor Data for Smart Home Healthcare. IEEE Access. 2016;PP(99):1-1. [46] SCHICKETMUELLER A, ROSE G, HOFMANN M. Feasibility of a Sensor-Based Gait Event Detection Algorithm for Triggering Functional Electrical Stimulation during Robot-Assisted Gait Training. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(21):4804. [47] QIU S, LONG L, ZHAO H, et al. MEMS Inertial Sensors Based Gait Analysis for Rehabilitation Assessment via Multi-Sensor Fusion. Micromachines (Basel). 2018;9(9):442. [48] DONATH L, FAUDE O, LICHTENSTEIN E, et al. Validity and reliability of a portable gait analysis system for measuring spatiotemporal gait characteristics: comparison to an instrumented treadmill. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2016;13:6. [49] GOMEZ BERNAL A, BECERRO-DE-BENGOA-VALLEJO R, LOSA-IGLESIAS ME. Reliability of the OptoGait portable photoelectric cell system for the quantification of spatial-temporal parameters of gait in young adults. Gait Posture. 2016;50:196-200. [50] YEO SS, PARK GY. Accuracy Verification of Spatio-Temporal and Kinematic Parameters for Gait Using Inertial Measurement Unit System. Sensors (Basel). 2020;20(5):1343. [51] KAYAALP ME, AGRES AN, REICHMANN J, et al. Validation of a Novel Device for the Knee Monitoring of Orthopaedic Patients. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(23):5193. [52] DE VROEY H, STAES F, WEYGERS I, et al. The implementation of inertial sensors for the assessment of temporal parameters of gait in the knee arthroplasty population. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2018;54:22-27. [53] 李玳,于宏,梁子轩,等.前交叉韧带断裂三维不对称度步态分析初探[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(8): 956-962. [54] 袁心一,王家莉,仇一青,等.帕金森病冻结步态的实时监测系统[J].北京生物医学工程,2019,38(2):182-189. [55] IBRAHIM AA, KÜDERLE A, GAßNER H, et al. Inertial sensor-based gait parameters reflect patient-reported fatigue in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2020;17(1):165. [56] WEYGERS I, KOK M, KONINGS M, et al. Inertial Sensor-Based Lower Limb Joint Kinematics: A Methodological Systematic Review. Sensors (Basel). 2020;20(3):673. [57] O’REILLY M, CAULFIELD B, WARD T, et al. Wearable Inertial Sensor Systems for Lower Limb Exercise Detection and Evaluation: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2018;48(5):1221-1246. [58] GIGGINS O, SWEENEY KT, CAULFIELD B. The use of inertial sensors for the classification of rehabilitation exercises. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;2014:2965-2968. |
| [1] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [4] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [5] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [6] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [7] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [8] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [9] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [10] | Peng Kun, Lin Yimin, Gan Xiaoling, Wu Zhiyong. Development prospect of orthopedic rehabilitation medicine based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 632-637. |
| [11] | Wei Haoxin, Wang Caiping, Deng Qian, Song Yan, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Design and clinical application of personalized cervical spine correction pillow with three-dimensional printing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5741-5746. |
| [12] | Ma Chenghao, Huang Hai, Lü Ruonan, Qin Zuohai, Wang Hao, Nie Zhixing, Han Dapeng, Ouyang Guilin. Effect of crossing acupoints of the same name of hands and feet on pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5798-5803. |
| [13] | Wan Dadi, Duan Xiangrui, Fan Xinchao, Yuan Ye, Huang Teng, Pan Dikang, Liu Jingyan, Li Xicheng. Efficacy of posterior cruciate ligament retaining versus posterior stabilized prostheses in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5897-5904. |
| [14] | Zhang Jiaming, Tian Yanping, Zhang Yue, Zhong Dongling, Li Yuxi, Zheng Zhong, Li Juan, Jin Rongjiang. Visual analysis of literature on transcranial magnetic stimulation for stroke based on Citespace knowledge map [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5610-5618. |
| [15] | Gu Mingxi, Zhu Yunong, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Medial pivot versus posterior stabilized prostheses for total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5395-5403. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||