Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (35): 5610-5618.doi: 10.12307/2021.289
Previous Articles Next Articles
Visual analysis of literature on transcranial magnetic stimulation for stroke based on Citespace knowledge map
Zhang Jiaming, Tian Yanping, Zhang Yue, Zhong Dongling, Li Yuxi, Zheng Zhong, Li Juan, Jin Rongjiang
- School of Health and Rehabilitation, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2020-10-09Revised:2020-10-12Accepted:2020-11-09Online:2021-12-18Published:2021-08-03 -
Contact:Jin Rongjiang, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Health and Rehabilitation, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jiaming, Master candidate, School of Health and Rehabilitation, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Project of Sichuan Province, No. 2019YFS0019 (to JRJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jiaming, Tian Yanping, Zhang Yue, Zhong Dongling, Li Yuxi, Zheng Zhong, Li Juan, Jin Rongjiang. Visual analysis of literature on transcranial magnetic stimulation for stroke based on Citespace knowledge map[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5610-5618.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
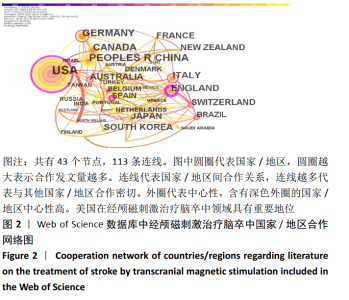
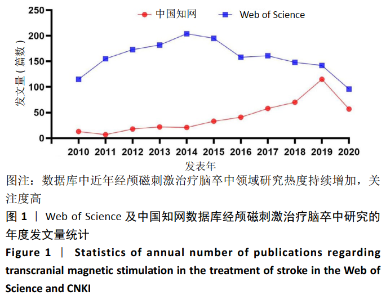
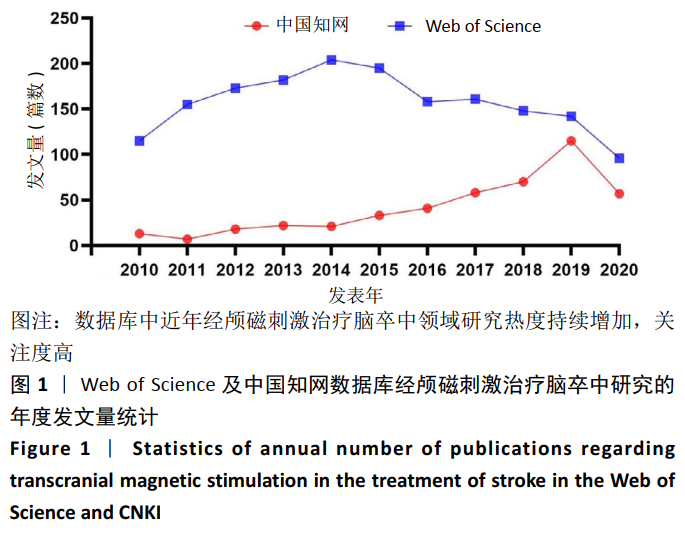
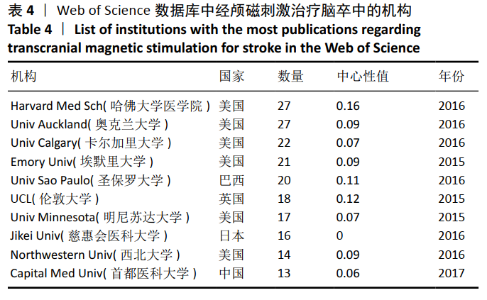
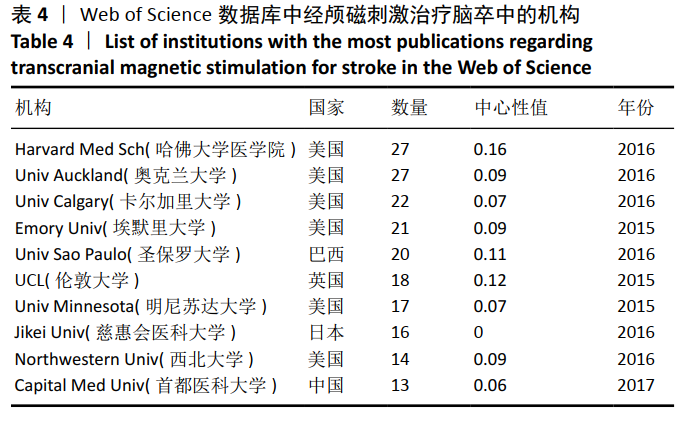
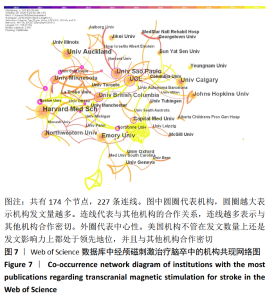
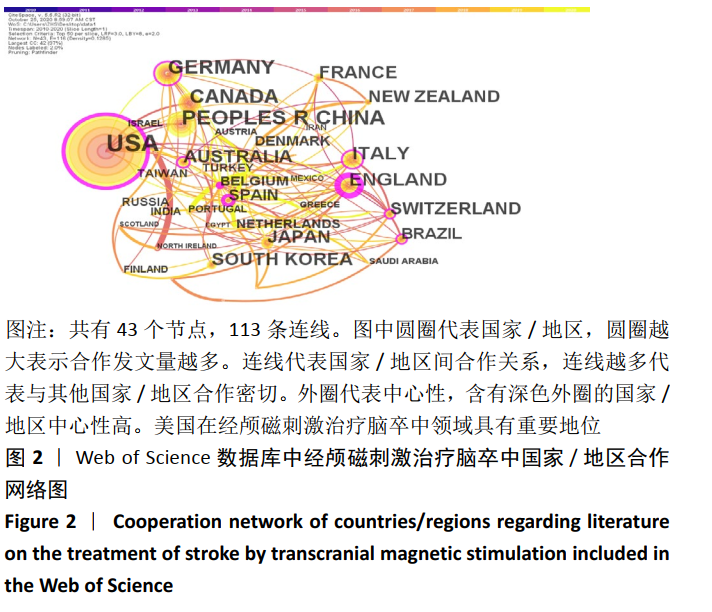
2.2 经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中研究的国家/地区合作可视化分析 针对外文文献,运行Citespace软件,节点选择“Country”,Top N=50时,共有43个节点,113条连线。得到的可视化图谱中共纳入54个国家/地区,其中发文量在50篇以上的共有8个,美国发文量最高,为215篇;中国的发文量位居第2,为90篇,见图2。图谱中圆圈表示国家/地区,圆圈越大表示合作发文量越多。含有深色外圈的国家/地区中心性较高,其中,中心性值可体现不同国家/地区在该领域内的影响力,中心性越高相关研究数量越多,在经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中领域的地位也越重[15-16]。图2可以看出国家/地区间合作较为紧密,其中美国有着举足轻重的地位,中心性为最大的0.49。中国在经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中领域在过去10年间发文量占据一定优势,但相比美国还是有一定差距,且只与美国存在合作关系,基本未与其他国家/地区合作。表1展现了该领域在2010至2020年间发文量前10的国家。"
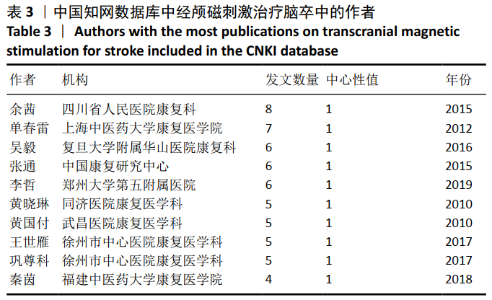
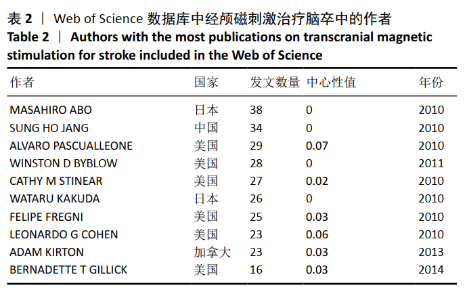
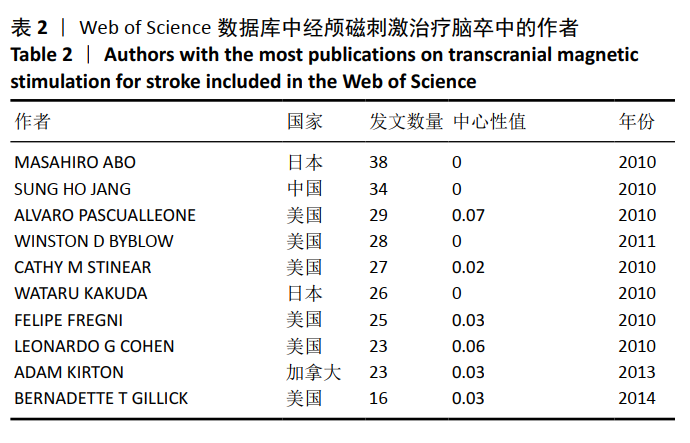
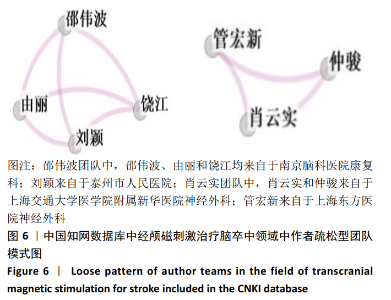
针对中文文献,运行Citespace软件,节点选择Author,Top N=30时,共有119个节点,157条连线。形成后的图谱共纳入328位作者,其中有31位作者的发文量≥3篇,最突出的是余茜团队,发文量为8篇,该作者来自四川省人民医院康复医学科,她在经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中领域的研究方向为应用经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中后认知功能障碍、抑郁症、下肢运动功能障碍和单侧空间忽略等[21-24]。如图4,表3所示,中国作者研究团队分散,彼此间合作较少,联系不紧密,所以作者进行结构相关性计算时,并没有得到有统计学意义的聚类。由图谱可见,形成的团队存在2种形式,第一种形式为紧密型团队模式,见图5,特点是发文量高、团队间成员联系比较紧密;另一种形式是疏松型团队模式,见图6,其特点是发文量低、团队间联系较少。疏松型团队模式的原因在于团队发文量少,有1篇文章将几个作者联系在一起,或者在研究某一方面的时候采用的是多中心的方法,而这样的团队在经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中这个领域中普遍存在。"
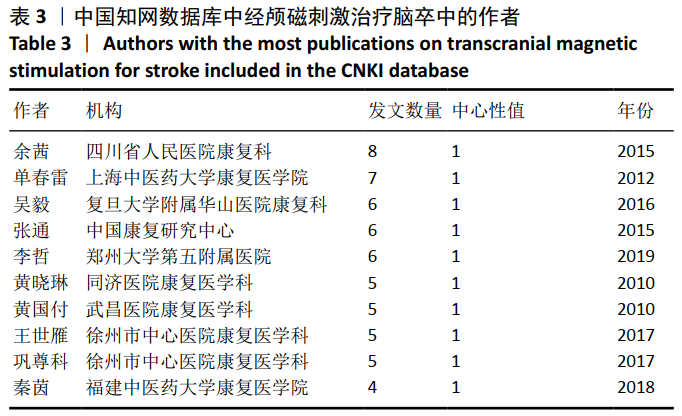
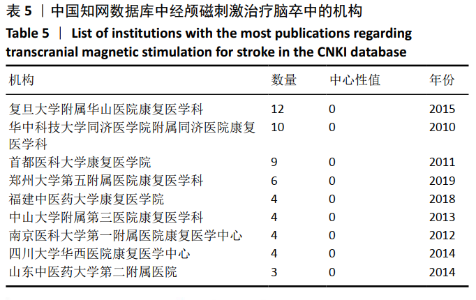
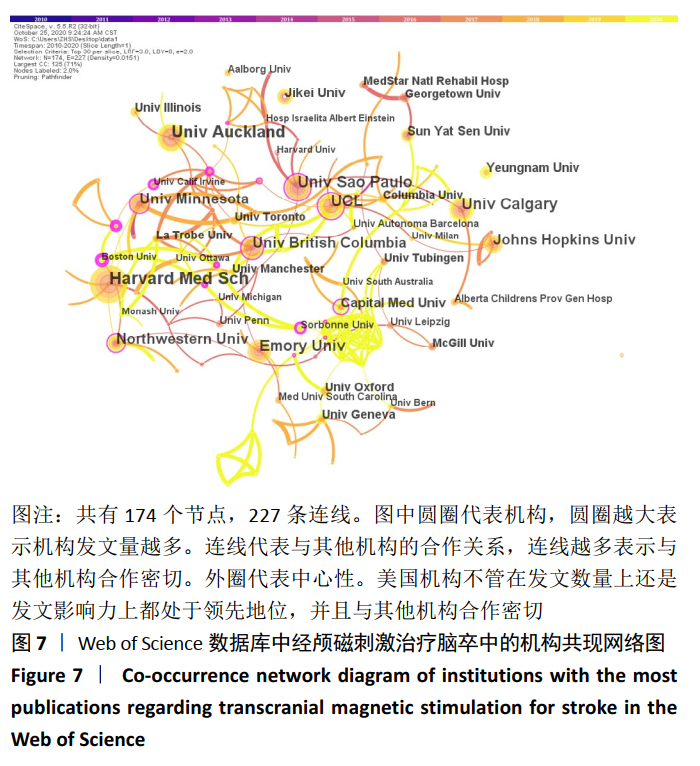
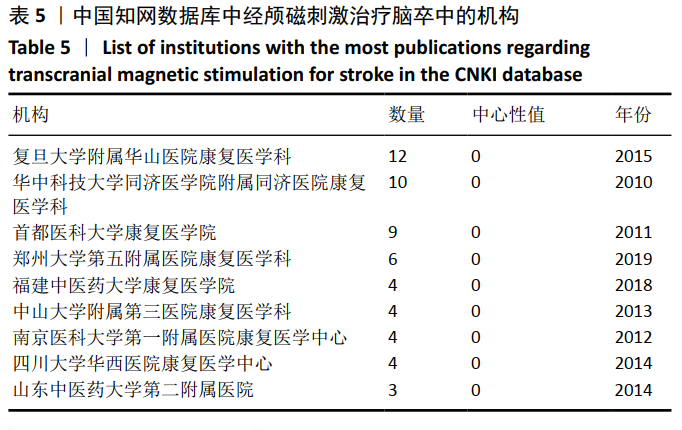
针对中文文献,运行Citespace软件,节点选择“Institution”,Top N=30时,共有39个节点,11条连线。形成后的图谱共纳入298所机构,其中有15所机构发文量≥3篇。由图8及表5可见,每个节点代表一个机构,图中所示的机构发文量均≥2篇,其中发文量最高的是复旦大学附属华山医院康复科,发文量为12篇。各机构中心性低,机构间联系不紧密,有联系的机构多为附属关系。对中国知网数据库中所绘制的图谱进一步分析可知,机构间多为医科大学及其附属医院或学院间存在联系,比较典型的是复旦大学附属华山医院康复科和首都医科大学康复医院,如图9,10。结合图8可看出,不同省份和地域的机构联系较少,有附属关系机构合作机会较多,联系紧密。这样,对此领域发展可能造成地域上的局限性,阻碍此学科的发展。"
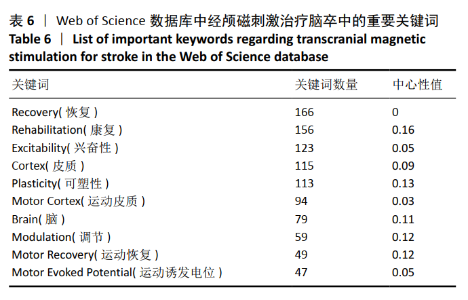
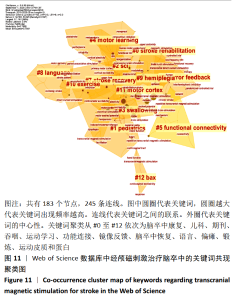
2.5 经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中研究的关键词可视化 2.5.1 关键词共现聚类分析 关键词分析对探索研究前沿及趋势具有重要作用[25-26]。经Web of Science数据库所筛选出的文献,节点类型采用关键词,阈值维持默认值,共有183个节点,245条连线。去除其中与检索策略相关的主题词,共现较高的关键词见图11,表6。根据关键词的共现频次及中心性可知,国外较为热点的关键词为皮质运动区、兴奋性、运动诱发电位和皮质诱发电位等。图11展现了经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中患者关键词共现聚类图,共形成12个聚类,标识了该研究领域的知识结构基础以及其动态演进的过程。每个色块代表1个聚类,色块范围内的节点都属于该聚类。聚类标签通常采用一定算法从标题、关键词和摘要中抽取得到。聚类序号与聚类大小呈反比,最大的聚类以#0标记,其他以此类推。结合图11及表6可知,聚类#11,#3,#7,#9,#2相互交错,联系最为紧密,且聚类#0,#3,#7,#9可归纳为脑卒中及其并发症的情况;聚类#4,#5,#6,#10,#11可归纳为针对脑卒中的治疗方法。 "
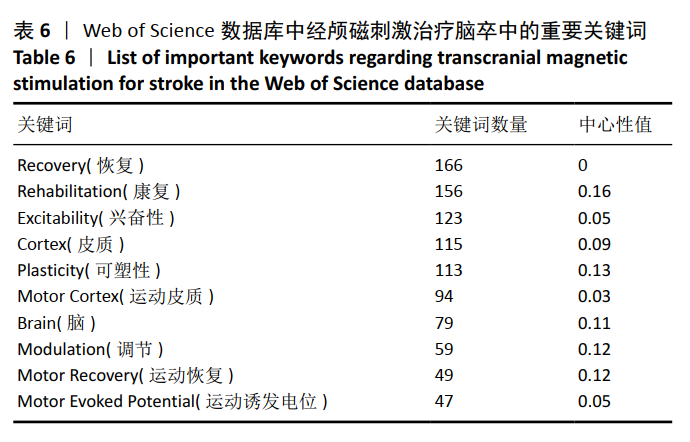
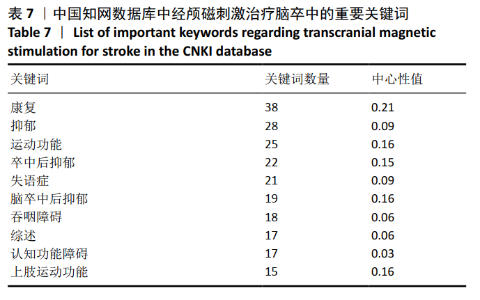
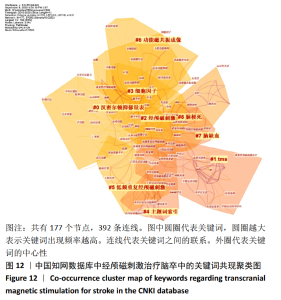
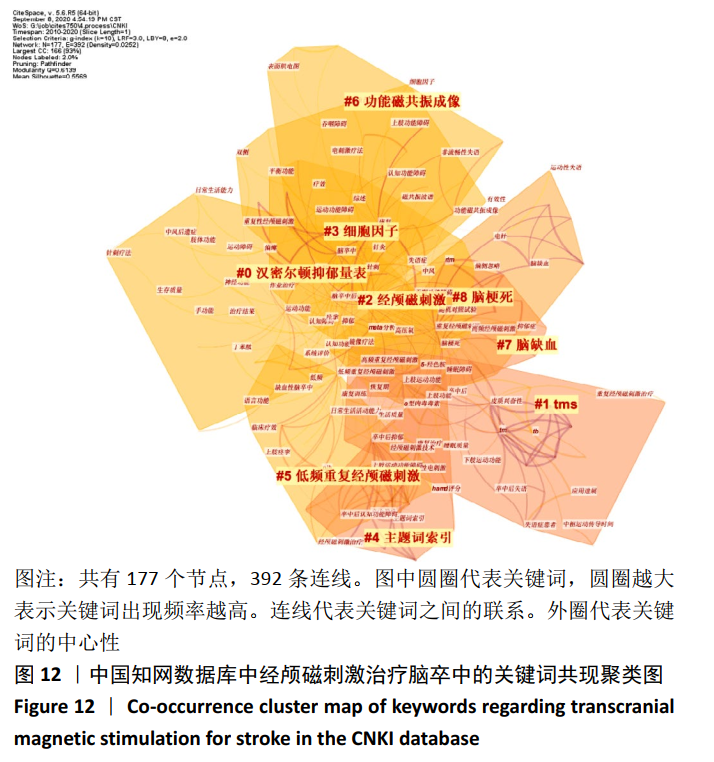
经中国知网数据库所筛选出的文献,在Citespace软件中设置时间分区为1年区分法,采用1年区分,是因为相关文献数量不大。(在关键词运算中3年运算法运用较多,图谱绘制清晰。)节点类型采用关键词,阈值维持默认值,共有177个节点,392条连线。去除其中与检索策略相关的主题词,共现较高的关键词见图12,表7。根据关键词的共现频次及中心性可知,中国较为热点的关键词为康复、运动功能和抑郁等。图12展示了由中国知网数据库数据制作的关键词共现聚类图,共形成8个关键词聚类标签,8个聚类标签均存在一定程度相互交错的情况,相互之间联系较为紧密,且聚类#7,#8可归为脑卒中及其并发症的情况;聚类#0,#1,#2,#5,#6可归为针对脑卒中的治疗方法。 "
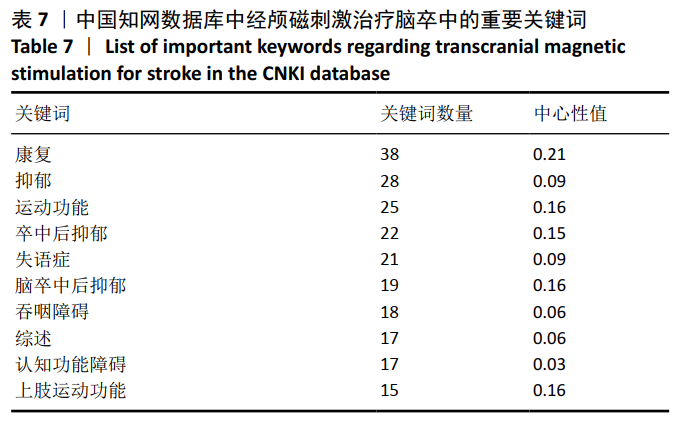
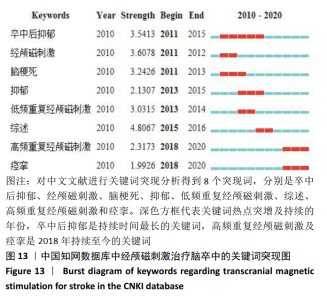
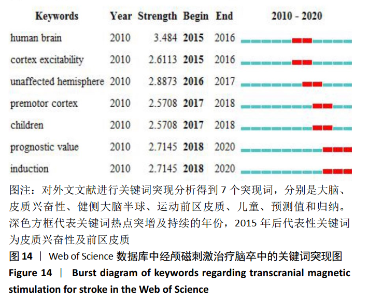
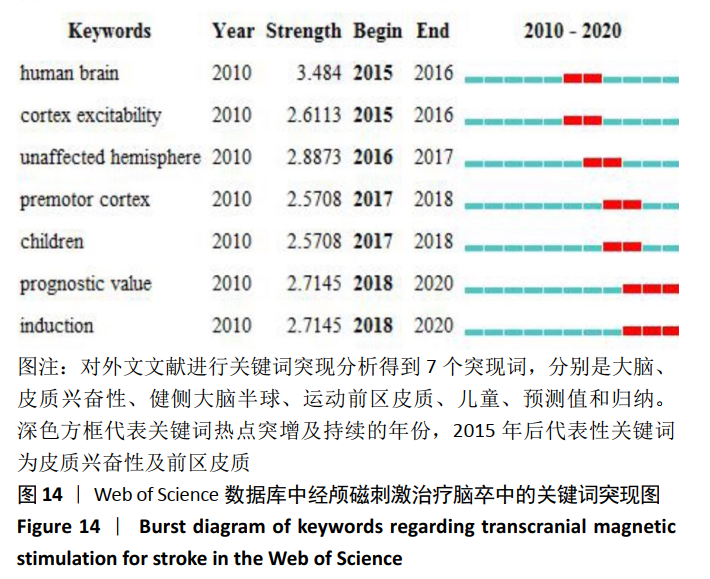
从表7可知中国知网数据库中相关文献关键词的命名存在问题。由于文献作者在关键词书写过程中存在省略或不规范的现象,导致含义相同的词汇时有出现。例如,“抑郁”与“卒中后抑郁”“脑卒中后抑郁”所表示为同一含义,却作为3个独立的关键词出现,在书写过程中,许多作者忽略了这个细节。 2.5.2 关键词突现分析 对关键词进行突现分析,能发现突增的研究热点,并且可以观察到该研究热点持续的年份。对中国知网数据库所筛选出的文献进行突现分析得到8个突现词,其中“经颅磁刺激”为2011至2012年代表性关键词,“低频重复经颅磁刺激”为2013至2014年代表性关键词,“高频重复经颅磁刺激”为2018至2020年代表性关键词,说明以不同频率经颅磁刺激作用于脑卒中是近年中国在该领域的研究热点。此外,卒中后抑郁是持续时间最长的突现词,从2011年持续到2015年,痉挛是2018年持续至今的突现词,见图13。对Web of Science数据库所筛选出的文献进行突现分析得到7个突现词,见图14。2015年后代表性关键词为皮质兴奋性及运动前区皮质,说明国外近年的研究热点是经颅磁刺激针对大脑皮质特定功能区域的研究。"

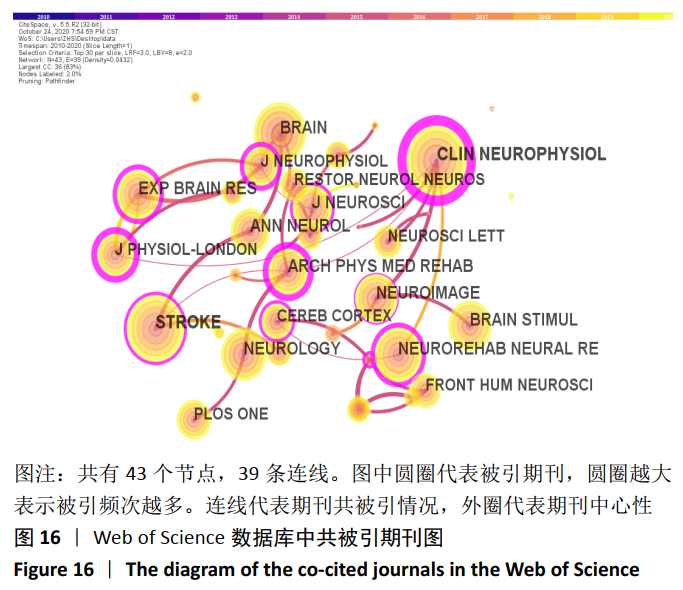
2.5.4 共被引期刊分析 由于Citespace软件无法对中文文献进行共被引期刊分析,所以文章仅分析英文期刊被引情况。经Web of Science数据库所筛选出的文献,运行Citespace软件得到节点为43,连线为39的被引期刊知识图谱,见图16。其中,被引中心性前5的期刊依次为:《CLIN NEUROPHYSIOL》(1.07),《J PHYSIOL-LONDON》(0.64),《Arch PMEDR》(0.6),《EXP BRAIN RES》(0.54)和《J NEUROPHYSIOL》(0.54);被引频次前5的期刊依次为:《CLIN NEUROPHYSIOL》(716),《STROKE》(691),《BRAIN》(641),《NEUROREHAB NEURAL RE》(571)和《NEUROLOGY》(556)。在以上10本期刊中,美国5本,英国2本,爱尔兰2本,德国1本,其中来自于爱尔兰的《CLIN NEUROPHYSIOL》的期刊中心性值及被引频次均为最高。 2.6 基金支持情况分析 由于Citespace软件无法对中文文献进行基金支持情况分析,所以文章仅分析英文文献基金支持情况。经Web of Science数据库所筛选出的文献,运行Citespace软件得到节点为65,连线为38的基金支持情况图谱。国外关于经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中相关研究文献类型中受基金项目支持的为316项,受基金支持项目占比为18.2%。其中,基金支持情况排名前3的依次是国家自然科学基金(49篇),来自于中国;美国国立卫生研究院/美国卫生与公众服务部国立卫生研究院基金(42篇),来自于美国;美国国立卫生研究院卫生与公众服务部基金(28篇),来自于美国。"
| [1] 甘勇,杨婷婷,刘建新,等.国内外脑卒中流行趋势及影响因素研究进展[J].中国预防医学杂志,2019,20(2):139-144. [2] PATEL S, PRAJWAL G, JOSÉ-PEDRO L, et al. Patient-reported experience measures in patients undergoing navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation (nTMS): the introduction of nTMS-PREMs. Acta Neurochir. 2020; 162(7):1673-1681. [3] 赵轩竹,李书宁,崔俊波.非药物疗法治疗卒中后抑郁的临床进展[J].中医研究,2019,32(2):65-70. [4] MENG ZY, SONG WQ. Low frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation improves motor dysfunction after cerebral infarction. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(4):610-613. [5] LIAO X, XING GQ, GUO ZW, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation as an alternative therapy for dysphagia after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2017;31(3):289-298. [6] SHEN X, LIU M, CHENG Y, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for the treatment of post-stroke depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. J Affect Disord. 2017;211:65-74. [7] 董心,郑洁皎,朱婷,等.重复经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中患者上肢运动功能障碍的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(9):1024-1027. [8] GEORGIOU AM, IOANNIS P, CHRYSA G, et al. Can transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) facilitate language recovery in chronic global aphasia post-stroke? Evidence from a case study. J Neurolinguistics. 2020;55:100907. [9] AI HX, SUN YX. Research hotspots and effectiveness of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in stroke rehabilitation. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(11): 2089-2097. [10] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. [11] 石晶晶,薄荣强,胡元会,等.基于Citespace的中医导引术相关研究的可视化分析[J].中国医药导报,2018,15(4):94-98. [12] 李莹,张曙光,刘玉秀.知识图谱在学科发展分析中的应用[J].医学研究生学报,2013,26(8):875-877. [13] 田艳萍,李涓,刘小菠,等.富血小板血浆5年国内外研究成果文章可视化的知识网络图谱分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(11):1745-1752. [14] 张千,吴青,凌武娟,等. 2008-2017中医翻译对比研究现状及展望[J].世界中医药,2019,14(3):633-637. [15] 宋英.数据挖掘技术中聚类算法的研究[J].科学咨询,2010(15):69-70. [16] 李倩,于娱,施琴芬.基于知识图谱的国内外颠覆式创新研究对比分析[J].科技管理研究,2020,40(15):9-19. [17] TAKEKAWA T, KAKUDA W, UCHIYAMA M, et al. Brain perfusion and upper limb motor function: a pilot study on the correlation between evolution of asymmetry in cerebral blood flow and improvement in Fugl-Meyer Assessment score after rTMS in chronic post-stroke patients. J Neuroradiol. 2014;41(3):177-183. [18] HARA T, ABO M, KAKITA K, et al. Does a combined intervention program of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and intensive occupational therapy affect cognitive function in patients with post-stroke upper limb hemiparesis? Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(12):1932-1939. [19] ABO M, KAKUDA W, MOMOSAKI R, et al. Randomized, multicenter, comparative study of NEURO versus CIMT in poststroke patients with upper limb hemiparesis: the NEURO-VERIFY Study. Int J Stroke. 2014;9(5):607-612. [20] HARA T, ABO M, KOBAYASHI K, et al. Effects of low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with intensive speech therapy on cerebral blood flow in post-stroke aphasia. Transl Stroke Res. 2015;6(5): 365-374. [21] 何成松,余茜,杨大鉴,等.低频重复经颅磁刺激对脑损伤后抑郁症患者的干预效应[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(28):6044-6045. [22] 徐丽,余茜.认知障碍的康复治疗方法研究进展[J].实用医院临床杂志, 2015,12(3):189-192. [23] 李静,徐丽,黄林,等.重复经颅磁刺激联合视觉扫描训练对脑卒中后单侧空间忽略的临床疗效研究[J].实用医院临床杂志,2020,17(4):24-27. [24] 李亚梅,黄林,张晶,等.重复经颅磁刺激对脑梗死患者下肢运动功能的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2016,38(11):839-842. [25] 余思奕,胡幼平.国际艾灸研究时空分布特征、热点及前沿知识图谱分析[J].中医杂志,2017,58(19):1686-1690. [26] 刘丹阳,叶静,钟冬灵,等.近5年经颅磁刺激相关研究的可视化分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(9):1107-1111. [27] NAKASE T, YOSHIOKA S, SASAKI M, et al. Clinical evaluation of lacunar infarction and branch atheromatous disease. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;22(4):406-412. [28] BOYD LA, VIDONI ED, WESSEL BD. Motor learning after stroke: is skill acquisition a prerequisite for contralesional neuroplastic change? Neurosci Lett. 2010;482(1):21-25. [29] KHEDR EM, ETRABY AE, HEMEDA M, et al. Long-term effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor function recovery after acute ischemic stroke. Acta Neurol Scand. 2010;121:30-37. [30] KHEDR EM, ABDEL-FADEIL MR, FARGHALI A, et al. Role of 1 and 3 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor function recovery after acute ischaemic stroke. Eur J Neurol. 2009;16(12):1323-1330. [31] LUFT AR, MACKO RF, FORRESTER LW, et al. Treadmill exercise activates subcortical neural networks and improves walking after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke. 2008;39(12):3341-3350. [32] DI PINO G, PELLEGRINO G, ASSENZA G, et al. Modulation of brain plasticity in stroke: a novel model for neurorehabilitation. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014; 10(10):597-608. [33] VECCHIO F, MIRAGLIA F, CURCIO G, et al. Cortical connectivity in fronto-temporal focal epilepsy from EEG analysis: a study via graph theory. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;26(6):1108-1116. [34] LEFAUCHEUR JP, ALEMAN A, BAEKEN C, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): an update (2014-2018). Clin Neurophysiol. 2020;131(2):474-528. [35] ROSSI S, HALLETT M, ROSSINI PM, et al. Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clin Neurophysiol. 2009;120(12):2008-2039. [36] HSU WY, CHENG CH, LIAO KK, et al. Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor functions in patients. Stroke. 2012;43: 1849-1857. [37] SASAKI N, MIZUTANI S, KAKUDA W, et al. Comparison of the effects of high- and low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on upper limb hemiparesis in the early phase of stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;22(4):413-418. [38] 庄志成.经颅磁刺激治疗产后抑郁的效果及预后分析[J].中国实用医药, 2020,15(20):94-96. [39] 胡雪艳,江晓峰,张通.重复经颅磁刺激治疗在脑卒中后失语症中的应用进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2015,21(2):138-141. [40] KIM WS, KWON BS, SEO HG, et al. Low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over contralesional motor cortex for motor recovery in subacute ischemic stroke: a randomized sham-controlled trial. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2020;34(9):856-867. [41] ZHANG Q. The effect of transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with melodic intonation therapy treatment in stroke patients with non-fluent aphasia. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2018;61:e172. [42] 胡佳卉,孟庆刚.基于CiteSpace的中药治疗2型糖尿病知识图谱分析[J].中华中医药杂志,2017,32(9):4102-4106. |
| [1] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Wang Mengting, Gu Yanping, Ren Wenbo, Qin Qian, Bai Bingyi, Liao Yuanpeng. Research hotspots of blood flow restriction training for dyskinesia based on visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1264-1269. |
| [4] | Luo Lin, Song Naiqing, Huang Jin, Zou Xiaodong. Review and prospect of international research on preschool children’s movement development assessment: a CiteSpace-based visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1270-1276. |
| [5] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [6] | Peng Kun, Lin Yimin, Gan Xiaoling, Wu Zhiyong. Development prospect of orthopedic rehabilitation medicine based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 632-637. |
| [7] | Guo Wen, Leng Jun, Liu Huimin, Zhang Chen, Fang Xiaolei, Wei Fangyue. Visual analysis of literature regarding post-stroke urinary incontinence in the past 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5676-5681. |
| [8] | Hui Xiaoshan, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Wang Shiqi, Yang Shuai, Zhang Hui, Wang Jie. Cardiomyocyte direct reprogramming: a scientometric and visualization analysis based on the Web of Science [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5123-5131. |
| [9] | Yuan Chunhua, Cui Zhenzhen, Wu De. Meta-analysis of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 5018-5024. |
| [10] | Xiong Binglang, Lin Tianye, Yang Peng, Xu Jingli, Zou Qizhao, Lai Qizhong, Zhang Qingwen. Visualization of global status and trends in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4656-4663. |
| [11] | Fan Jin, Zeng Luyao, Zhong Dongling, Li Yuxi, Tian Yanping, Huang Yijie, Jin Rongjiang. Development of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in recent 10 years: a visual analysis using CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3711-3717. |
| [12] | Yang Qin, Zhou Honghai, Chen Longhao, Zhong Zhong, Xu Yigao, Huang Zhaozhi. Research status and development trend of pelvic reconstruction techniques: a bibliometric and visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3718-3724. |
| [13] | Huang Maomao, Hu Yue, Wang Binchuan, Zhang Chi, Xie Yujie, Wang Jianxiong, Wang Li, Xu Fangyuan. Bibliometric and visual analysis of international literature addressing ischemic stroke rehabilitation in recent 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3725-3733. |
| [14] | Zhu Rui, Zeng Qing, Huang Guozhi. Ferroptosis and stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3734-3739. |
| [15] | Bao Sairong, Lin Lihua, Shan Sharui, Yang Xingping, Liu Chunlong. Effect of electrical deep muscle stimulate on muscle tone, elasticity, and stiffness of biceps brachii in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3138-3143. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||