Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 1270-1276.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3056
Previous Articles Next Articles
Review and prospect of international research on preschool children’s movement development assessment: a CiteSpace-based visual analysis
Luo Lin1, 2, Song Naiqing3, Huang Jin4, Zou Xiaodong1
- 1China Future Postdoctoral Workstation, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China; 2College of Physical Education, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; 3Basic Education Research Center of Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China; 4Department of Education, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
-
Received:2020-02-12Revised:2020-02-22Accepted:2020-05-09Online:2021-03-18Published:2020-12-14 -
Contact:Song Naiqing, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Basic Education Research Center of Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China -
About author:Luo Lin, MD, Associate professor, China Future Postdoctoral Workstation, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China; College of Physical Education, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:East China Normal University-China Future Postdoctoral Workstation Fund, No. 2019A001; Guizhou Philosophy and Social Sciences Fund, No. 19GZYB121
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Lin, Song Naiqing, Huang Jin, Zou Xiaodong. Review and prospect of international research on preschool children’s movement development assessment: a CiteSpace-based visual analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1270-1276.
share this article
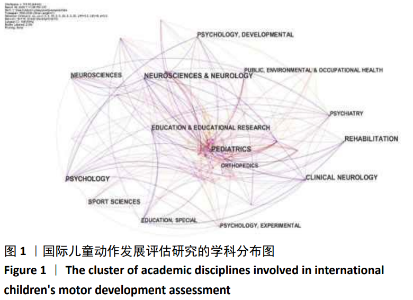
2.1 国际儿童动作发展评估研究的学科领域特征 2.1.1 国际儿童动作发展评估研究的学科计量学特征 对国际儿童动作发展评估研究进行学科计量学分析,得到国际儿童动作发展评估研究学科分布图(见图1)。图谱分析数据显示,在1990至2020年间共有115个学科的专家和学者关注此领域,并且不同学科领域的研究成果产生不同程度的交叉耦合。图1中结点位置代表国际儿童动作发展评估研究的重要学科领域的关键节点,图中线条代表该学科与其他学科的交叉研究,连线越多表示该学科与其他学科交叉越多。按照中心值大小进行排序,排在前5名的学科分别为:环境与职业健康(Public ,Environment and Occupationl Health)、化学(Chemistry)、生物化学与分子生物学(Biochemistry and molecular biology)、神经科学(Neuroscience)、外科学(Surgery),其中心值依次为0.20,0.21,0.15,0.14,0.14。此次研究纳入的研究文献中,体育科学(Sport Science)学科论文共计998篇,其中心值为0.09,提示体育领域学者对儿童动作发展评估相关研究的影响力也较高。从图1中不仅可以看出国际儿童动作发展评估研究的重点学科领域,同时还能体现该领域不同学科交叉融合的知识网络。这些学科对儿童动作发展评估研究的实验设计和研究方法的选取、实验过程的质量监控、结果的呈现以及研究内容扩展与完善都发挥了不同程度的促进作用。"

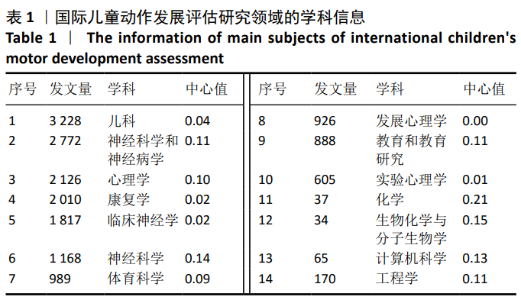
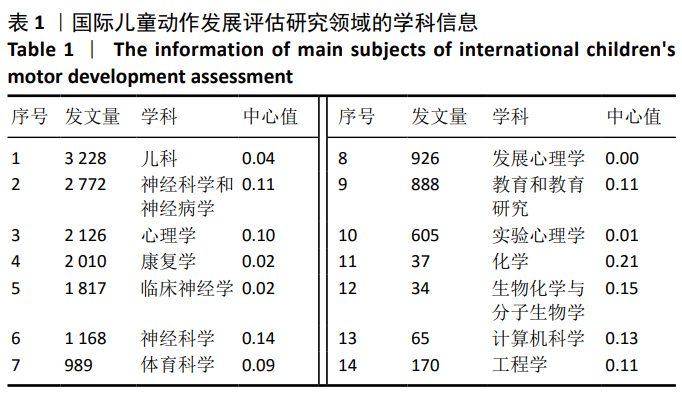
为进一步挖掘不同学科的重要性以及其对该领域的学术贡献,研究者对图1数据进行进一步提炼和转化,得到1990至2020年间国际儿童动作发展评估研究成果的学科发文数量排序信息,表1列出了研究成果发文量居于前10名的学科信息。在发文量前10名的学科中,神经科学与神经病学、心理学、神经科学、教育和教育研究的中心值均高于0.1,说明以上4个学科是儿童动作发展评估研究成果产出最有影响力的学科领域。同时,研究依据不同学科中心值进行排序,发现可视化数据中存在部分低发文量而高中心值的潜优势学科(见表1中11-14)。尤其是化学、生物化学与分子生物学、计算机科学、工程学这些学科,尽管研究成果发文量较少,但相关研究成果具有较高的学术影响力。"

2.1.2 国际儿童动作发展评估研究的多学科耦合特征 为了进一步探究该领域多学科交叉融合研究情况,研究者以“多学科”(interdisciplin* or multidisciplin* or transdisciplin* or crossdisciplin*)和“儿童动作发展评估”(#1“elementary or pupil or primary school or middle school or secondary school or children or preschool or Kindergarten or Pediatrics”与#2 “motor skills or gross motor or fine motor or coordination or motor developmental delay or developmental coordination disorder or motor difficulty or motor development defect or motor development or motor proficiency or motor competencies”与#3“questionnaire or tools or assessment or scale or test”)为检索词在主题中进行检索,共得到249条检索记录。对该次检索文献结果进行分析,得出以下研究结论:①儿童动作发展评估研究领域与多学科交叉融合研究从20世纪90年代开始,呈现逐渐增长趋势,其中1990至1999年发表相关研究成果11篇(占研究成果总数4.41%,下同),2000至2009年为42篇(16.87%),2010至2020年为196篇(78.72%);②儿科发文量共计103篇(41.36%),儿科、临床神经学、康复学、外科学、发展心理学是国际儿童动作发展评估领域多学科交叉和融合研究的前5大学科,占研究成果总数的80.72%;③根据论文第一作者所在国家进行统计,发现该领域进行多学科研究发文量超过10篇,且数量最多的前5名国家依次为美国114篇(45.78%)、英国32篇(12.85%)、澳大利亚25篇(10.04%)、加拿大24篇(9.64%)、意大利17篇(6.83%),而中国在多学科交叉融合研究领域仅发文3篇,提示中国对儿童动作发展评估的交叉学科研究的总体实力较弱。哈佛大学、费城儿童医院、宾夕法尼亚大学、伦敦大学各发表15,14,14,12篇,是1990至2020年期间国际儿童动作发展评估领域多学科交叉研究成果发文量排名前3名的研究机构。 2.2 国际儿童动作发展评估研究的研究领域特征 2.2.1 国际儿童动作发展评估研究的研究主题特征 对所收集到的文献进行主题和关键词统计分析,列出共现词频排列前10名的主题词以及中心值前10名的主题词(见表2)。在1990至2020年这30多年间,关注度最多、影响力最高是脑瘫儿童动作发展评估,而儿童运动表现的测评、儿童粗大动作能力评估、儿童动作发展评估的信效度、动作发展的年龄规律、儿童身体活动和动作发展的关系、儿童协调性的发展以及发育性协调障碍也是过去30年的此领域的重要研究方向。"

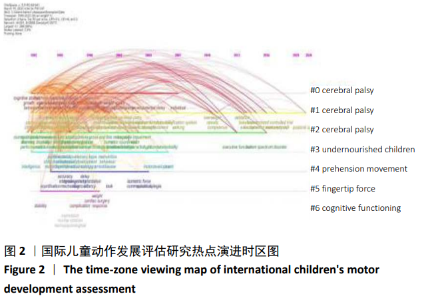
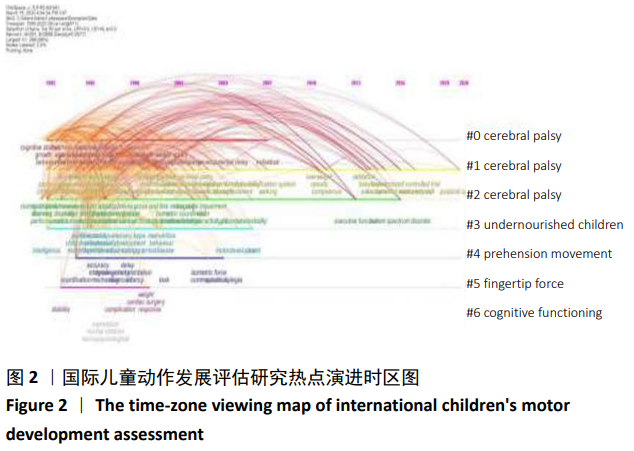
2.2.2 国际儿童动作发展评估研究的动态演进 对国际儿童动作发展评估研究领域内不同时间段上的高频词和高中心性关键词进行分析,使用Citespace时间线视图功能,将1990至2020年国际儿童动作评估研究领域的热点主题从时间维度上呈现,并分析该领域的动态演进脉络。国际儿童动作发展评估研究的高频关键词从1992年开始出现,并随着时间的推移在后续的研究中不断的转化和更新,使得该领域的研究热点一直处于动态变化。根据Citespace后台分析数据,以及国际儿童动作发展评估的年度发文量,研究热点时区图(见图2)与该研究领域高突现关键词及其高中心性统计数据(见表2),并结合同时期被引高频次文献,将1990至2020年国际儿童动作发展评估研究的演进历程分为以下几个阶段: (1)阶段一:基础发展阶段(1990至1999年)。在基础发展阶段,儿童动作发展评估研究领域发文量共计716篇,占此次研究研究文献总论的6.1%。学者们从探究儿童表现(perfprmance)、行为(behavior)、智力(intelligence)、生长(growth)的开始,逐渐开始增加对儿童动作发展评估的关注。尤其是对婴儿、脑瘫患儿动作发展的关注较多,在儿童动作发展与儿童认知发展、儿童发展、儿童行为关系等研究领域,产出了一些较高学术影响力的文献。对1990至1999年发表的相关研究成果的共引文献进行聚类分析,发现运动与认知障碍、早产儿动作发展、脑瘫患儿粗大动作评估、儿童精细动作发展、儿童神经状态等主题,是儿童动作发展评估研究领域基础发展阶段的重点研究内容。1990至1995年间儿童动作发展评估的每年发文量都是两位数,并逐年增加。1996至1999年间,儿童动作发展评估的研究成果迅速增加,儿童动作发展评估研究的全球论文产量共有525篇,美国是此阶段研究成果产出最多的国家、其次是加拿大和英国。荷兰虽然论文发文量较少,但其研究成果的影响力较高。法国、澳大利亚、德国、意大利、瑞典、挪威、以色列等国家也相继加入对儿童动作发展评估的研究,并且由不同研究机构联合形成的交叉学科研究成果也开始出现。 (2)阶段二:快速发展阶段(2000至2009年)。该阶段儿童动作发展评估领域发文量共计2 604篇,为上一个阶段的3.64倍,占此次研究文献总量的22.3%。 该阶段学者们在脑瘫患儿运动表现、儿童神经发育结果与动作发展关系、儿童发育性协调障碍、营养不良状态儿童的动作发展,婴儿的动作发展等研究方向进行了大量的研究。2001年世界卫生组织发布了《国际健康、残疾、功能分类》[3]( International classification of functioning, disability and health),随后关于脑瘫患儿的动作评估及干预的研究迅速增加,成为这个阶段关注度和影响力最高的研究重点。该阶段美国、英国依然保持了对该研究领域积极关注,并产出许多对后续研究有影响力的研究成果。新西兰也加大了研究力度,产出一定高质量的研究成果。中国学者从这个时期开始介入儿童动作发展评估研究领域,共发表相关文献共计43篇,从康复学、神经科学、儿科学、心理学、体育科学等多学科领域视角尝试对儿童动作发展评估进行探索。与基础研究阶段相比较,该阶段无论在发文量、研究主题的深度和广度上都较基础研究阶段有较大的拓展,并且交叉学科融合研究逐渐增加,较前一阶段实现了量的突破和质的提升。 (3)阶段三:高速发展阶段(2010至2020年)。该阶段发文量在前两个阶段的基础上实现高速增长,共计发文 8 360篇,占此研究文献总量的71.6%,是前两个阶段发文量合计的2.51倍。其中青少年(adolescents)、身体活动(physical activity)、康复(rehabilitation)、干预(intervention),是这个时期的高频、高中心值关键词,引领着该领域的前行大方向。该阶段的研究重点主要集中在脑瘫儿童的动作发展康复和干预、动作发展与儿童身体活动关系,自闭症儿童的动作发展等方向。美国、澳大利亚、加拿大依然保持了对该领域研究的极大关注,瑞典学者也产出较多具有国际影响力的研究成果。中国学者在这个时期对儿童动作发展评估研究的关注激增,共计发表320篇研究文献,并逐渐开始加大与国外高水平科研机构的多学科交叉研究合作。值得注意的是,尽管1996年世界卫生组织(WTO)发布了《身体活动与健康》[4](Physical Activity and Health),但关于儿童动作发展与身体活动关系的研究确是近10年才逐渐增多,得到体育科学和康复学研究者更多的关注,并且研究对象也从关注疾病患儿到也关注非疾病患儿的动作发展。 结合文章对1990至2020年的国际儿童动作发展评估研究的阶段划分,进一步对各阶段较有代表性的儿童动作发展评估工具进行简要梳理。①基础发展阶段的评估工具。该阶段的研究侧重关注患儿的动作发展,如脑瘫患儿、早产儿、低体质量出生儿的动作发展评估,这个时期美国格塞尔发育量表[5](Gesell Developmental Assessment)、德国儿童身体协调能力测试[6](K?rperkoordinationtest für Kinder)、欧洲体质健康测试[7](Test of Physical Fitness)、瑞典基础运动技能评估[8](Motor skills Development as Basis for Learning)、澳大利亚神经感觉及动作发展评估[9](Neurological Sensory Motor Developmental Assessment)都是此阶段具有代表性评估工具。这些测评工具主要以结果评价为主,测试项目从几项到几十项不等,多数研究关注了儿童粗大动作发展中身体控制和平衡能力、身体移动能力的评估,少数研究还进行了儿童粗大动作发展中器械操控能力的评估,仅有极少研究在评估儿童粗大动作发展的同时还进行了儿童精细动作发展的评估,其中部分评估工具依然沿用至今。但其中一些评估工具因建模人数较少,跨文化应用信效度低,因而限制这些评估工具的大面积推广和应用。②快速发展阶段的评估工具。该阶段研究更加重视儿童动作发展评估工具信效度,并且开始对各种儿童动作发展问题展开积极探索,如儿童发育性协调障碍和知觉性运动功能障碍的评估,同时开始对评估识别的动作发展问题儿童进行训练干预。该阶段涌现出大量的儿童动作发展评估工具,如德国儿童运动测试[10](Motoriktest für vier-bis sechsj?hrige Kinder4-6)、英国儿童运动能力评估[11](Movement Assessment Battery for Children)、美国皮博迪动作发展量表[12](Peabody Developmental Motor Scales)、粗大动作发展测试[13](Test of Gross Motor Development)和布氏动作精熟度测验[14](Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency)、荷兰的马氏运动技能测试[15](Maastrichtse Motoriek Test)等。部分评估工具已经开始关注非疾病儿童的动作发展障碍和不足,多数评估工具采用了大数据样本构建测评体系,并具有良好的信效度,此阶段许多评估工具得到了广泛推广和应用。此阶段的评估工具观察的维度更加全面,多数评估工具都观察了儿童粗大动作发展的三个维度(身体控制和平衡能力、身体移动能力和器械操控能力),一些同时关注儿童精细动作发展的评估工具,如德国儿童运动测试(MOT 4-6)、英国儿童运动能力评估(MABC2)、美国皮博迪动作发展量表(PDMS-2)均有较高的信效度和跨文化适用性。③高速发展阶段的评估工具。此阶段儿童动作发展评估与儿童其他领域发展关系的研究逐渐增多,如儿童动作发展与儿童体力活动、儿童认知与动作发展、营养因素与儿童动作发展、儿童动作发展与肥胖等研究方向受到了很多学者的关注。大量健康儿童动作发展评估工具涌现出来,如德国基本运动能力测评[16](Basic Motor Competencies)、希腊学前儿童运动筛查工具[17](Democritos Movement Screening Tool for preschool children)、台湾儿童粗大动作量表[18](Preschooler Gross Motor Quality Scale)等。评估的方式由传统的结果评价开始转向过程评价,或与过程评价结合。研究者不仅关注儿童是否能完成该测试条目,同时也开始重视儿童在评估中完成测试动作的质量。并且此阶段社会学、生态学、环境学、工程学等多学科交叉研究逐渐增多,也为该研究领域增加了很多新兴研究方向。 从微观对各阶段儿童动作发展评估工具的梳理可以发现,各阶段的评估工具的发展依然对应宏观视角下的儿童动作发展评估研究的主线,始终围绕儿童动作发展对不同儿童认知、人格和社会适应、身体健康的影响开展。值得注意的是,尽管现有研究报道中已有一些研究开始对儿童动作发展评估中识别出的问题儿童进行训练干预研究,但相关研究方向纵向、横向研究数量仍较少,并且通过评估工具形成标准化测试的较少。"
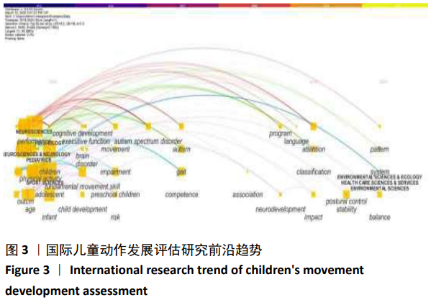
2.2.3 国际儿童动作发展评估研究的前沿趋势 通过对近5年研究文献关键词和特征词的聚类整理、可以可视化近年来儿童动作发展评估研究领域的前沿趋势。对2015至2020年该领域文献进行关键词与特征词共现-聚类的时间线分析(见图3)。图3同时显示了研究学科领域和热点突现关键词和主题词聚类,连线越多,颜色越深代表该关键词或主题词越火热。此次研究将Citespace后台数据进行整理,得到近5年该领域的前沿研究趋势:国际儿童动作发展评估主要集中在儿科学、康复学、临床神经学、神经科学和体育科学这5个学科领域,儿科学中早产儿的动作发展评估和干预、康复学中肌萎缩儿童的动作发展、临床神经学中脑瘫儿童的动作发展、神经科学中孤独症儿童的动作协调问题以及体育科学中儿童动作发展与儿童体质健康的关系、儿童动作发展对儿童体力活动的预测等受到了研究者的积极关注。 (1)早产儿的动作发展评估:早产婴儿的神经行为检查在新生儿学中已经应用了几十年,然而,随着新技术的出现,也许还有更“科学”的评估高危婴儿的方法。但神经行为检查、评估仍然是临床实践的重要组成部分,它们有助于提高对婴儿行为的理解,包括他们的长处和弱点,从而能够相应地调整护理策略和家长教育。早产儿的动作发展评估有助于确定具有有发展障碍风险的婴儿,不过需要注意的是尽管现在有很多适用于早产儿的动作发展评估工具,但能够满足多种评估目的的工具还没有,因此临床医生或研究人员需要根据婴儿的妊娠期、评估的目标和培训要求等选择适宜的评估工具。 (2)肌萎缩儿童的动作发展评估:肌营养不良和脊髓性肌萎缩症可导致严重的残疾和进行性功能损害。而动作发展评估工具,可以对疾病的进展和治疗干预的产生积极影响。目前已有专门针对这两种肌萎缩疾病的儿童动作发展评估工具。有的评估工具聚焦肌萎缩儿童上肢运动能力的评估,有的评估工具侧重肌萎缩儿童下肢步态的评估。总体来说,肌萎缩儿童的动作发展评估,可以帮助这些神经系疾病的患儿进行进一步针对行动治疗干预。 (3)脑瘫儿童的动作发展评估:脑瘫儿童身体较健康儿童虚弱,因此与正常儿童相比,他们的体力活动水平较低。研究发现,体育活动可以对脑瘫儿童的整体健康产生良好的影响,减少他们的身体虚弱、肌肉痉挛并改善其身体平衡能力。通过对脑瘫儿童进行动作发展评估,可以帮助临床医生更好的了解脑瘫儿童的身体机能和动作发展水平,可以辅助临床康复医生制定干预方案及评估干预结果。过去30年间国际上用于评估脑瘫儿童动作发展的评估量表超过30种之多。脑瘫儿童的动作发展是过去30年儿科领域一直关注的研究重点,如何帮助脑瘫患儿更好的生活,减少缺乏体力活动带来的损害也是未来研究者们需要继续努力的方向。 (4)孤独症儿童的动作协调问题:孤独症中的运动延迟和损伤是极为常见的,在孤独症的临床描述中已经提及孤独症儿童可能涉及多个运动领域的缺陷。然而,关于孤独症儿童中常用的标准化运动评估、测试特性及其局限性文献尽管不多,但这些评估工具已经开始关注这个特殊的儿童群体,这些评估工具主要识别孤独症儿童早期发育迟缓以及精细和粗大运动功能差异的能力。但由于孤独症儿童自身的特质不同,因此在孤独症儿童中使用这些评估工具仍有很大的局限性。在未来,鉴于孤独症患儿不同的临床特性,有必要对孤独症儿童运动功能的标准化测量进行更多的验证测试,让评估工具成为帮助判别孤独症儿童在生命周期中的不同认知和行为能力的辅助手段。 (5)动作发展对儿童运动表现和身体活动影响:已有研究证明儿童动作能力与儿童身体活动水平存在高度正相关。因此,如果儿童出现动作发展问题不仅会影响儿童认知和知觉的发展,还会影响儿童运动能力和身体活动水平进而影响其体质健康。造成儿童动作发展问题的原因有很多,如疾病、运动缺乏等等。对儿童运动发育缺陷的诊断通常在医疗机构完成,医生通过相应的儿童运动发育评估量表对儿童动作发展情况进行评估。严重的儿童运动发育缺陷一般在其2岁以前就可通过医疗诊断确诊,但轻度的儿童动作发展问题,如动作发展延迟因其表现不明显,平时难以发觉,往往会在儿童进入幼儿园或小学,当儿童需要面对更复杂的任务要求时,才会显现出与同龄典型运动发育儿童之间的差异。并且因为动作发展的延迟,儿童可能会因为难以完成某些对身体基础运动能力(如身体协调性)要求高的活动,进而受挫并丧失对该活动内容或项目的兴趣。3-6岁是儿童基础动作发展的关键时期,如果此时期儿童动作发展问题得不到及时识别和补救,儿童的运动能力就会受到影响,进而影响其健康等多个领域的学习和发展。因此,在儿童生长发育的不同时期,尤其是在儿童进入学前教育环境以后,对儿童进行动作发展情况的评估,识别儿童早期动作发展问题十分重要,并应对检出的问题儿童进行及早的干预改善和针对性训练。"
| [1] GRAY COOK, WITH LEE BURTON, KYLE KIESEL, et al. Movement: functional movement systems: screening,assessment and corrective strategies. On Target Publications Aptos.CA.2010. [2] CHEN M C. CiteSpaceII:Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature.J Am soc Inf Sci Tech. 2006;57(3):359-377. [3] World Health Organization. International classification of functioning, disability and health. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2001. [4] 李文川.身体活动建议演变:范式转换与量的积累[J].体育科学, 2014,34(5):56-65. [5] LORRIE AS. Psychometric Properties of the Gesell Developmental Assessment:A Critique.Early Childhood Research Quarterly. 1992;7: 47-52. [6] SIMONS J. Introductie tot de psychomotoriek AntwerpenApeldoorn Garant.2004. [7] SIGMUNDSSON H, HAGA M. Motor competence is associated with physical fitness in four- to six-year-old preschool children.European Early Childhood Education Research Journal.2016;24(3):477-488. [8] DAYAN E, COHEN LG. Neuroplasticity Subserving Motor Skill Learning.Neuron.2011;72(3): 204-209. [9] OLSEN JE, ALLINSON LG, DOYLE LW, et al. Preterm and term-equivalent age general movements and 1-year neurodevelopmental outcomes for infants born before 30 weeks’ gestation.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2018;60(1):47-53. [10] ZIMMER R. Diagnostik der Bewegungsentwicklung von Kindern:Beobachten Einschätzen Dokumentieren.2nd international conference Learning processes in early childhood and assessment issues. 2006;15(6):22-24. [11] VALENTINI NC, RAMALHO MH, OLOVEIRA MA. Movement assessment battery for children-2: translation, reliability, and validity for Brazilian children. Res Dev Disabil.2014;35(3):733-740. [12] FOLIO M, FEWELL R. Peabody Developmental Motor Scales. Examiner’s Manual. 2nd Edn. Austin.Texas: Pro-Ed. 2000. [13] HANDS B, LARKIN D, ROSE E. The psychometric properties of the McCarron assessment of neuromuscular development as a longitudinal measure with Australian youth.Hum Mov Sci.2013;32:485-497. [14] WUANG YP, SU CY. Reliability and responsiveness of the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency-Second Edition in children with intellectual disability. Res Dev Disabil.2009;30:847-855. [15] JULIE M, LBPhty MA, YVONNE B. Performance on the nsmdaduring the first and second year of life to predict functional ability at the age of 4 in children with cerebral palsy.Hong Kong Physiotherapy Journal.2005;23(1):40-44. [16] HERRMANN C, SEELIG H. Structure and Profiles of Basic Motor Competencies in the Third Grade-Validation of the Test Instrument MOBAK-3.Percept Mot Skills. 2017;124(1):5-20. [17] KAMBAS A, VENETSANOU F. The Democritos Movement Screening Tool for preschool children (DEMOST-PRE©):Development and factorial validity.Res Dev Disabil. 2014;35(7):1528-1533. [18] HARRIET G, WILLIAMS KA, PFEIFFER MD, et al. A Field-Based Testing Protocol for Assessing Gross Motor Skills in Preschool Children: The Children’s Activity and Movement in Preschool Study Motor Skills Protocol.Meas Phys Educ Exerc Sci. 2009;13(3):151-165. |
| [1] | Shu Wenbo, Chen Mengchi, Li Hua, Huang Liqian, Huang Binbin, Zhang Wenhai, Wu Yachen, Wang Zefeng, Li Qiaoli, Liu Peng. Correlation between body fat distribution and characteristics of daily physical activity in college students [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1277-1283. |
| [2] | Pan Qile, Zhang Hong, Zhou Huikang, Cai Guang. Comparison of the Greulich-Pyle method, the CHN method and the China 05 method for assessing bone age in children and adolescents [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 662-667. |
| [3] | Tan Jiachang, Yuan Zhenchao, Wu Zhenjie, Liu Bin, Zhao Jinmin. Biomechanical analysis of elastic nail combined with end caps and wire fixation for long oblique femoral shaft fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 334-338. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Feng Shuo, Yang Zhi, Zhang Ye, Sun Jianning, An Lun, Chen Xiangyang. Three-dimensional gait of patients with developmental dysplasia of hip undergoing total hip arthroplasty with high hip center [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 350-355. |
| [5] | Li Kun, Li Zhijun, Zhang Shaojie, Gao Shang, Sun Hao, Yang Xi, Wang Xing, Dai Lina . A 4-year-old child model of occipito-atlanto-axial joints established by finite element dynamic simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3773-3778. |
| [6] | Fan Jin, Zeng Luyao, Zhong Dongling, Li Yuxi, Tian Yanping, Huang Yijie, Jin Rongjiang. Development of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in recent 10 years: a visual analysis using CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3711-3717. |
| [7] | Yang Qin, Zhou Honghai, Chen Longhao, Zhong Zhong, Xu Yigao, Huang Zhaozhi. Research status and development trend of pelvic reconstruction techniques: a bibliometric and visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3718-3724. |
| [8] | Lin Dongxin, Huang Xuecheng, Qin Qingguang, Yang Yang, Deng Yuping, Tan Jinchuan, Wang Mian, Su Weiwei, Huang Tao, Huang Wenhua. Comparison of motion range of cervical spine after two cervical manipulations based on motion capture technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3281-3285. |
| [9] | Lin Tianye, Yang Peng, Xiong Binglang, He Xiaoming, Yan Xinhao, Zhang Jin, He Wei, Wei Qiushi . Comparison of preoperative three-dimensional reconstruction simulation and intraoperative drawing of femoral osteotomy to measure rotation angle in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3349-3353. |
| [10] | Pan Xuan, Zhao Meng, Zhang Xiumei, Zhao Jie, Zhai Yunkai. Research and application of biological three-dimensional printing technology in the field of precision medicine: analysis of Chinese and English literature [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3382-3389. |
| [11] | Wei Jinqiang, Huang Dengcheng, Cao Xuewei, Zhou Jianwei, Sun He, Li Zehui. Analysis of researches on TCM treatments for cartilage diseases in recent 20 years by mapping knowledge domains [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3202-3209. |
| [12] | Lin Haiqi, Chen Liang, Tang Lu, Weng Xiquan, Lin Wentao. Significance of urinary proteomics assessing pathological changes in the body [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3259-3266. |
| [13] | Qu Xingyue, Zhou Jianqiang, Xu Xuebin, Zhang Shaojie, Li Zhijun, Wang Xing. Finite element analysis of screw-bone anti-pullout in four models of anterior lower cervical fixation in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2816-2821. |
| [14] | Liu Jiahui, Zhang Zhongjiu, Jia Dianxiang, Zhai Aoqing, Niu Guangyun, Jiang Haibo. Research status and clinical application of artificial knee joint testing machine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2895-2901. |
| [15] | Zhang Shuang, Tan Rui, Wang Chunxiao, Wu Fengyu, Guo Hongyu. MicroRNAs for assessing the motion control of human skeletal muscles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2755-2760. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||