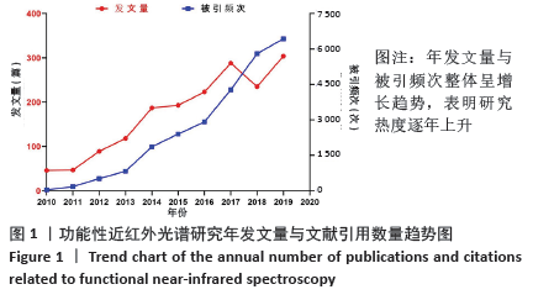
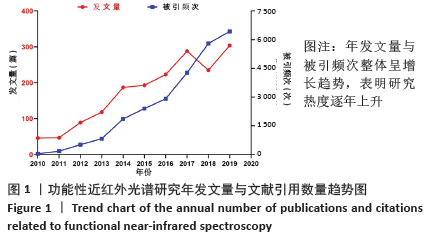
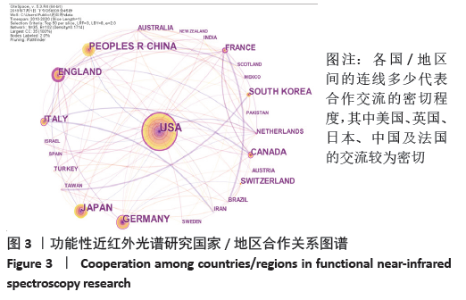
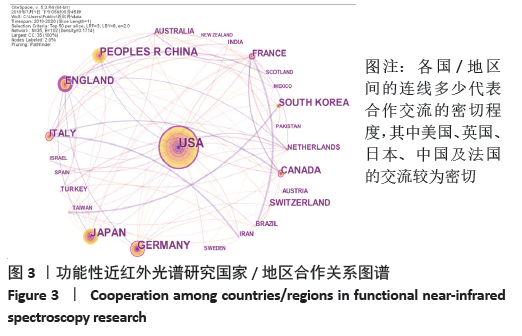
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (23): 3711-3717.doi: 10.12307/2021.044
Previous Articles Next Articles
Development of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in recent 10 years: a visual analysis using CiteSpace
Fan Jin1, Zeng Luyao2, Zhong Dongling1, Li Yuxi1, Tian Yanping1, Huang Yijie1, Jin Rongjiang1
- 1Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China; 2Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350108, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2020-03-23Revised:2020-03-28Accepted:2020-08-15Online:2021-08-18Published:2021-02-24 -
Contact:Jin Rongjiang, MD, Professor, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Fan Jin, Master candidate, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Research Plan of Sichuan Province, No. 2019YFS0019 (to JRJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fan Jin, Zeng Luyao, Zhong Dongling, Li Yuxi, Tian Yanping, Huang Yijie, Jin Rongjiang. Development of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in recent 10 years: a visual analysis using CiteSpace[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3711-3717.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
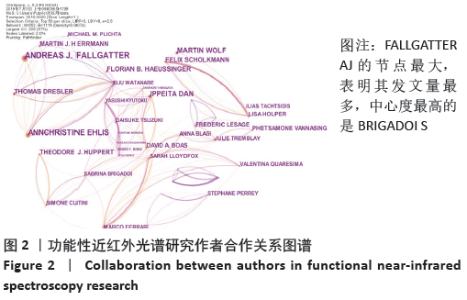
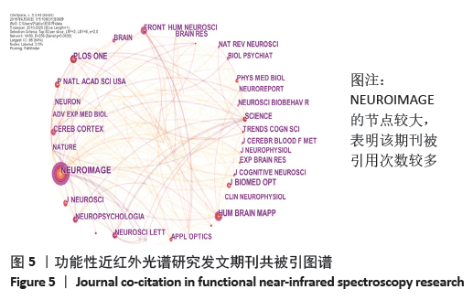
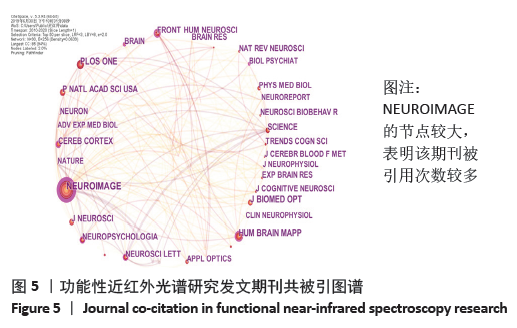
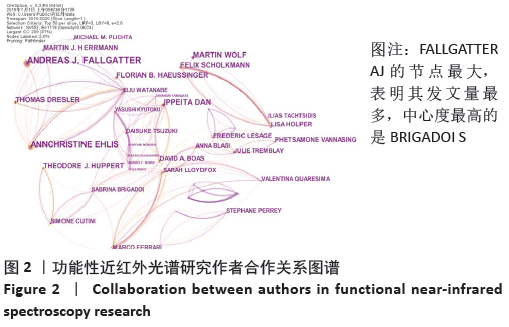
2.2 作者可视化分析 以作者为节点运行CiteSpace,得到节点数为552,连线数为1 119的作者合作关系图谱,见图2。其中每一个节点代表一位作者,节点越大代表该作者发文量越多,节点连线代表作者间的联系或合作关系,作者间的连线多少、颜色、粗细分别表示作者间合作密切程度、发生合作的初始年代以及合作发表论文的频次。结果发现:发文频次前三的作者分别为FALLGATTER AJ 58次、EHLIS AC 45次、IZZETOGLU M 33次。通常情况下研究者用中介中心度来测节点在网络中的重要性,以此来发现和衡量某重要节点。中心度排名第一的为BRIGADOI S,中心度为0.17;第二的为HAEUSSINGER FB、BOAS DA、TSUZUKI D、KATURA T、HAMILTON A、SATO H,中心度都为0.08;第三的为DAN I和TACHTSIDIS I,中心度都为0.06。 "

2.4 机构可视化分析 以机构为节点运行CiteSpace,得到节点数为302,连线数为471的机构合作关系图谱,见图4。节点为年轮状,每一个节点代表一个研究机构,节点的大小代表该机构发文量的多少,标签字号的大小代表中心度的高低[5],节点间的连线代表研究机构间的共现关系,连线粗细代表机构间的关联程度,节点年轮的颜色为蓝色时表示较早的年份,为红色时表示最近的年份。在fNIRS研究领域涉及的机构较多,发文频次排名前三的机构是蒂宾根大学(UnivTubinggen)71次、德雷塞尔大学(Drexel Univ)68次、伦敦大学学院(UCL)60次。中心度前三的机构是伦敦大学学院(UCL)0.38、帕多瓦大学(Padua Univ)0.17、蒙特利尔大学(Montreal Univ)0.16。 "

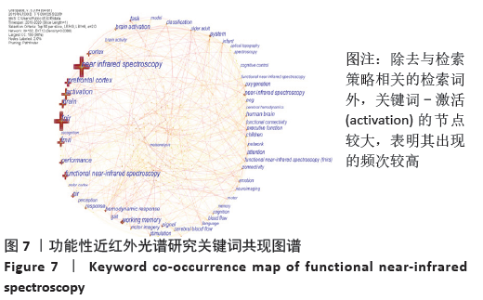
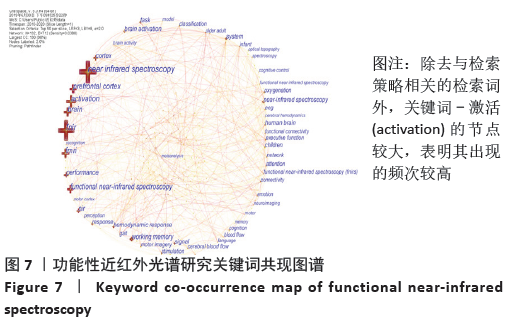
2.7 关键词可视化分析 2.7.1 关键词共现分析 关键词是文章内容的浓缩和提取,能很好地反映出文献的主题和内容[15]。关键词的共现分析是通 过关键词与关键词之间的共现关系来描述某一学术领域内部 组成关系及其结构,以关键词为节点对其进行共现分析,选择Pathfinder进行剪切,运行CiteSpace软件得到图7。图谱中共有192个节点,712条连接线。图中每一个十字节点代表一个关键词,节点大小代表着关键词出现的频次,节点越大说明频次越高。连线代表两个关键词共现在同一篇文献中,连线越粗代表共现越强。中心度和频次高的关键词代表研究热点。从图谱可以看出,除去与检索策略相关的检索词外,频次前五的关键词是激活(activation)330次、功能性磁共振成像263次、前额叶皮质(prefrontal cortex)250次、大脑(brain)246次、皮质(cortex)178次。关键词共现中心度前五依次是前额叶皮质(prefrontal cortex)0.11、婴幼儿(infant)0.11、激活(activation)0.10、大脑激活(brain activation)0.10、血流量(blood flow)0.10、系统(system)0.09、氧化(oxygenation)0.09、认知(perception)0.09、步态(gait)0.08、皮质(cortex)0.07、儿童(children)0.07、注意(attention)0.07、视觉皮质(visual cortex)0.07。通常认为中心度大于0.1的节点在网络结构中的位置比较重要,在知识结构的演变中具有重要意义[16]。根据关键词的引用频次及中心度综合分析可知,此领域研究的热点关键词为大脑激活、磁共振成像技术、系统、前额叶皮质、婴幼儿、血流量、认知、步态等。 "
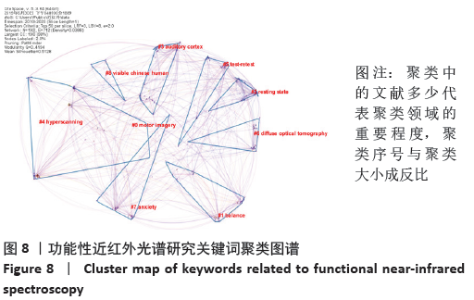
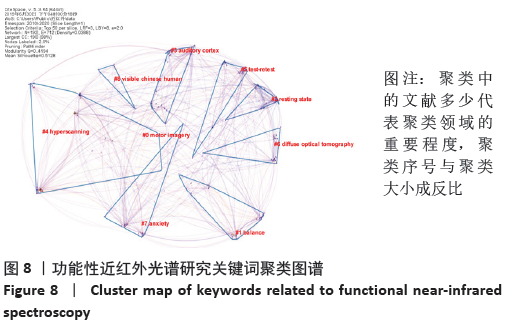
2.7.2 关键词聚类分析 关键词聚类分析有助于发现研究领域的分布情况和科学前沿。关键词共现图谱生成后,通过LLR方法对关键词进行聚类分析,图谱中每个色块代表一个聚类,最大的聚类以#0标记。通过LLR聚类方式命名,共形成了9个关键词聚类标签,见图8。图谱中Modularity表示网络模块度,其值为0.419 4 > 0.3,表明网络模块结构较为显著,聚类效果良好[17],Mean Silhouette表示平均轮廓值,其值为0.512 8 > 0.5,表明聚类间同质性较好,此次聚类为高效的[18],主要聚类中包含的具体关键词见表3。通过关键词的聚类结果发现,聚类的内容多集中在利用fNIRS来测定个体在不同状态下脑区的变化。 "
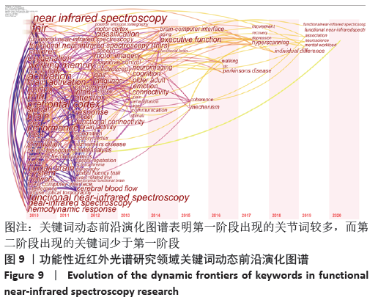
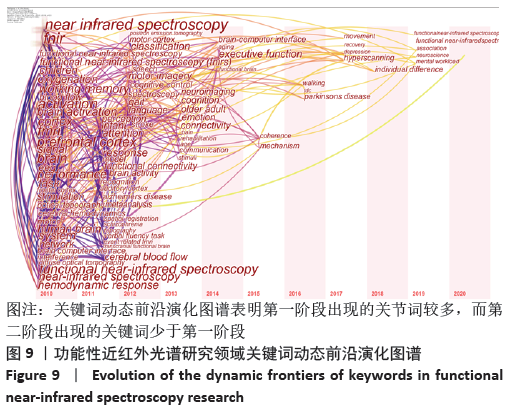
2.7.3 关键词动态前沿演化图谱 Citespace的时区视图(Time Zone)侧重从时间维度上来反映研究前沿的演进轨迹,将关键词共现知识图谱转换为Time Zone时区视图,进一步分析 fNIRS研究领域的热点历史演变情况和前沿,见图9。时区视 图是由一系列表示时区的条形区域组成,时区按时间顺序从 左向右排列,越靠近左下角,表示出现的时间越早,反之,出现于右上角表示出现的时间越近,节点出现的时区为该关键词首次出现的年份,图中关键词字体越大,表示关键词出现频次越多,连线表示两关键词在同一篇文献的共现关系,连线越多,表示关键词之间的相互作用越紧密。根据关键词的时区视图,可以发现fNIRS研究大致可分为两个阶段:第一阶段(2010至2013年)是关键词集中出现的时间段,这一时期主要的关键词有“前额叶皮质,大脑激活,功能性磁共振,脑电,婴儿,干扰,分辨率,可塑性,认知,语言,脑卒中,认知神经科学,刺激,康复”等,表明这个阶段的研究以提高fNIRS分辨率、降低噪声干扰、将fNIRS结合功能性磁共振、脑电等其他脑功能成像技术来检测不同人群在任务刺激下大脑激活为重点。第二阶段(2014至2020年)的主要关键词是“脑机接口,执行功能,一致性,性别差异,机制,经颅磁刺激,恢复,抑郁,个体差异,神经科学,联系”等,表明此阶段的研究热点逐渐演化为对执行功能、脑机接口、与脑相关的各种机制的研究。但研究热点较分散,未形成较为高频的关键词。"
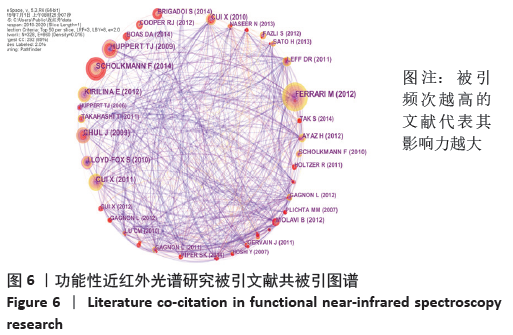
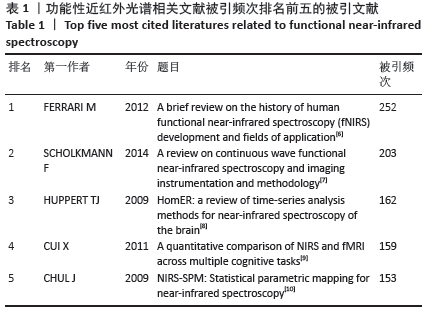
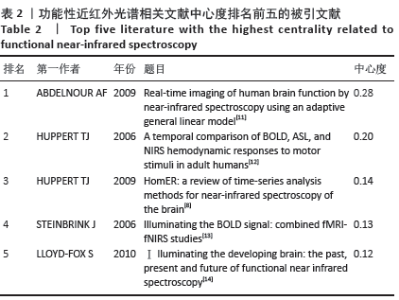
| [1] JÖBSIS FF. Noninvasive, infrared monitoring of cerebral and myocardial oxygen sufficiency and circulatory parameters. Science. 1977;198(4323):1264-1267. [2] 杨健, 苗硕. 注意缺陷多动障碍患儿认知功能检测方法的进展[J]. 北京医学,2015,37(6):507-508. [3] 刘峤, 李杨, 段宏, 等. 知识图谱构建技术综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2016,53(3):582-600. [4] 侯剑华, 胡志刚. CiteSpace软件应用研究的回顾与展望[J]. 现代情报, 2013,33(4):99-103. [5] 张子石, 吴涛, 金义富. 基于CiteSpace的网络学习知识图谱分析[J]. 中国电化教育,2015(8):77-84. [6] FERRARI M, QUARESIMA V. A brief review on the history of human functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) development and fields of application. Neuroimage. 2012;63(2):921-935. [7] SCHOLKMANN F, KLEISER S, METZ AJ, et al. A review on continuous wave functional near-infrared spectroscopy and imaging instrumentation and methodology. Neuroimage. 2014;85 Pt 1:6-27. [8] HUPPERT TJ, DIAMOND SG, FRANCESCHINI MA, et al. HomER: a review of time-series analysis methods for near-infrared spectroscopy of the brain. Appl Opt. 2009;48(10):D280-D298. [9] CUI X, BRAY S, BRYANT DM, et al. A quantitative comparison of NIRS and fMRI across multiple cognitive tasks. Neuroimage. 2011;54(4): 2808-2821. [10] YE JC, TAK S, JANG KE, et al. NIRS-SPM: statistical parametric mapping for near-infrared spectroscopy. Neuroimage. 2009;44(2):428-447. [11] ABDELNOUR AF, HUPPERT T. Real-time imaging of human brain function by near-infrared spectroscopy using an adaptive general linear model. Neuroimage.2009;46(1):133-143. [12] HUPPERT TJ, HOGE RD, DIAMOND SG, et al. A temporal comparison of BOLD, ASL, and NIRS hemodynamic responses to motor stimuli in adult humans. Neuroimage. 2006;29(2):368-382. [13] STEINBRINK J, VILLRINGER A, KEMPF F, et al. Illuminating the BOLD signal: combined fMRI-fNIRS studies. Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24(4):495-505. [14] LLOYD-FOX S, BLASI A, ELWELL CE. Illuminating the developing brain: the past, present and future of functional near infrared spectroscopy. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2010;34(3):269-284. [15] MA XY. Research progress of career guidance in China since 21 century visual literature analysis based on citespace. Vocat Educ Forum. 2017;16:65-70. [16] CHEN C, CHEN Y, Horowitz M, et al. Towards an explanatory and computational theory of scientific discovery. J Informetr. 2009;3(3):191-209. [17] 陈悦, 陈超美, 刘则渊, 等. CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J]. 科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. [18] 赵丹群. 基于CiteSpace的科学知识图谱绘制若干问题探讨[J]. 情报理论与实践,2012,35(10):56-58. [19] Di ROSA E, BRIGADOI S, CUTINI S, et al. Reward motivation and neurostimulation interact to improve working memory performance in healthy older adults: A simultaneous tDCS-fNIRS study. Neuroimage. 2019;202:116062. [20] DOWNEY D, BRIGADOI S, TREVITHICK L, et al. Frontal haemodynamic responses in depression and the effect of electroconvulsive therapy. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33(8):1003-1014. [21] CARRIERI M, PETRACCA A, LANCIA S, et al. Prefrontal cortex activation upon a demanding virtual hand-controlled task: a new frontier for neuroergonomics. Front Hum Neurosci. 2016;10:53. [22] HIGHTON D, CHITNIS D, BRIGADOI S, et al. A fibreless multiwavelength nirs system for imaging localised changes in cerebral oxidised cytochrome c oxidase. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1072:339-343. [23] BRIGADOI S, PHAN P, HIGHTON D, et al. Image reconstruction of oxidized cerebral cytochrome C oxidase changes from broadband near-infrared spectroscopy data. Neurophotonics. 2017;4(2):21105. [24] PHAN PHDBS. Spatial distribution of changes in oxidised cytochrome c oxidase during visual stimulation using broadband near infrared spectroscopy imaging. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;(923):195-201. [25] BRIGADOI S, CECCHERINI L, CUTINI S, et al. Motion artifacts in functional near-infrared spectroscopy: a comparison of motion correction techniques applied to real cognitive data. Neuroimage. 2014;85 Pt 1:181-191. [26] CUI X, BRAY S, REISS AL. Functional near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) signal improvement based on negative correlation between oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin dynamics. Neuroimage. 2010;49(4):3039-3046. [27] NASEER N, HONG MJ, HONG KS. Online binary decision decoding using functional near-infrared spectroscopy for the development of brain-computer interface. Exp Brain Res. 2014;232(2):555-564. [28] CHAUDHARY U, XIA B, SILVONI S, et al. Brain-Computer Interface-Based Communication in the Completely Locked-In State. PLoS Biol. 2017;15(1):e1002593. [29] ASLIN R N, SHUKLA M, EMBERSON L L. Hemodynamic correlates of cognition in human infants. Annu Rev Psychol. 2015;66: 349-379. [30] LLOYD-FOX S, RICHARDS JE, BLASI A, et al. Coregistering functional near-infrared spectroscopy with underlying cortical areas in infants. Neurophotonics. 2014;1(2):25006. [31] DUAN L, ZHANG YJ, ZHU CZ. Quantitative comparison of resting-state functional connectivity derived from fNIRS and fMRI: a simultaneous recording study. Neuroimage. 2012;60(4):2008-2018. [32] LU CM, ZHANG YJ, BISWAL BB, et al. Use of fNIRS to assess resting state functional connectivity. J Neurosci Methods. 2010;186(2):242-249. [33] GU Y, MIAO S, HAN J, et al. Complexity analysis of fNIRS signals in ADHD children during working memory task. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):829. [34] GU Y, MIAO S, HAN J, et al. Identifying ADHD children using hemodynamic responses during a working memory task measured by functional near-infrared spectroscopy. J Neural Eng. 2018;15(3):35005. [35] HERFF C, HEGER D, FORTMANN O, et al. Mental workload during n-back task-quantified in the prefrontal cortex using fNIRS. Front Hum Neurosci. 2013;7:935. [36] EGGENBERGER P, WOLF M, SCHUMANN M, et al. Exergame and Balance Training Modulate Prefrontal Brain Activity during Walking and Enhance Executive Function in Older Adults. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016;8:66. [37] FERRARI M, BISCONTI S, SPEZIALETTI M,et al. Prefrontal cortex activated bilaterally by a tilt board balance task: a functional near-infrared spectroscopy study in a semi-immersive virtual reality environment. Brain Topography. 2014;3(27):353-365. [38] ZHANG H, ZHANG YJ, LU CM, et al. Functional connectivity as revealed by independent component analysis of resting-state fNIRS measurements. Neuroimage. 2010;51(3):1150-1161. [39] NIU H, WANG J, ZHAO T, et al. Revealing topological organization of human brain functional networks with resting-state functional near infrared spectroscopy. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45771. [40] WARTENBURGER I, STEINBRINK J, TELKEMEYER S, et al. The processing of prosody: Evidence of interhemispheric specialization at the age of four. Neuroimage. 2007;1(34):416-425. [41] ELWELL CE, KOLYVA C. Making light work: illuminating the future of biomedical optics. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2011;369(1955): 4355-4357. [42] Di LORENZO R, PIRAZZOLI L, BLASI A, et al. Recommendations for motion correction of infant fNIRS data applicable to multiple data sets and acquisition systems. Neuroimage. 2019;200:511-527. [43] BULGARELLI C, BLASI A, ARRIDGE S, et al. Dynamic causal modelling on infant fNIRS data: A validation study on a simultaneously recorded fNIRS-fMRI dataset. Neuroimage. 2018;175:413-424. [44] LUDYGA S, MUCKE M, COLLEDGE F, et al. A Combined EEG-fNIRS Study Investigating Mechanisms Underlying the Association between Aerobic Fitness and Inhibitory Control in Young Adults. Neuroscience. 2019;419:23-33. [45] NIU R, YU Y, LI Y, et al. Use of fNIRS to Characterize the Neural Mechanism of Inter-Individual Rhythmic Movement Coordination. Front Physiol, 2019;10:781. [46] LI H, ZHU N, KLOMPARENS EA, et al. Application of functional near-infrared spectroscopy to explore the neural mechanism of transcranial direct current stimulation for post-stroke depression. Neurol Res. 2019; 41(8):714-721. |
| [1] | Wang Mengting, Gu Yanping, Ren Wenbo, Qin Qian, Bai Bingyi, Liao Yuanpeng. Research hotspots of blood flow restriction training for dyskinesia based on visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1264-1269. |
| [2] | Luo Lin, Song Naiqing, Huang Jin, Zou Xiaodong. Review and prospect of international research on preschool children’s movement development assessment: a CiteSpace-based visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1270-1276. |
| [3] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Yang Qin, Zhou Honghai, Chen Longhao, Zhong Zhong, Xu Yigao, Huang Zhaozhi. Research status and development trend of pelvic reconstruction techniques: a bibliometric and visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3718-3724. |
| [6] | Huang Maomao, Hu Yue, Wang Binchuan, Zhang Chi, Xie Yujie, Wang Jianxiong, Wang Li, Xu Fangyuan. Bibliometric and visual analysis of international literature addressing ischemic stroke rehabilitation in recent 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3725-3733. |
| [7] | Ren Wenbo, Liao Yuanpeng. Visualization analysis of traumatic osteoarthritis research hotspots and content based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3374-3381. |
| [8] | Li Wenhui, Liu Guobin. Knowledge mapping analysis on the international research of diabetic foot: a visual analysis based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3178-3184. |
| [9] | Wei Jinqiang, Huang Dengcheng, Cao Xuewei, Zhou Jianwei, Sun He, Li Zehui. Analysis of researches on TCM treatments for cartilage diseases in recent 20 years by mapping knowledge domains [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3202-3209. |
| [10] | Zhang Kai, Zhang Xiaobo, Shi Jintao, Wang Keping, Zhou Haiyu. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: a bibliometric and visualization analysis based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3031-3038. |
| [11] | Wen Shuaibo, Han Jie, Wu Yukun. Bibliometric and visual analysis of literature on cartilage repair in the Web of Science in recent 15 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2657-2663. |
| [12] | Huang Na, Liu Jiayue, Huang Yingjie, Wen Junmao, Wang Haibin, Zhang Qingwen, Zhou Chi . Bibliometric and visualized analysis of research on osteonecrosis of the femoral head from the Web of Science in the last 5 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2711-2718. |
| [13] | Song Yahan, Wu Yunxia, Fan Daoyang. Knowledge mapping of three-dimensional printing in biomedical field based on VOSviewer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2385-2393. |
| [14] | Tian Yanping, Li Juan, Liu Xiaobo, Zhang Huiling, Shi Lihong, Jin Rongjiang. Knowledge network mapping of literature regarding platelet-rich plasma in recent 5 years: a visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1745-1752. |
| [15] | Wang Liqun, Li Yuxi, Jin Rongjiang, Wang Wenchun, Pang Richao, Zhang Anren. Application of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in the study of depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1799-1804. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||