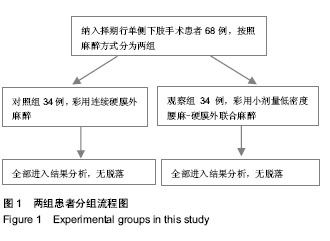
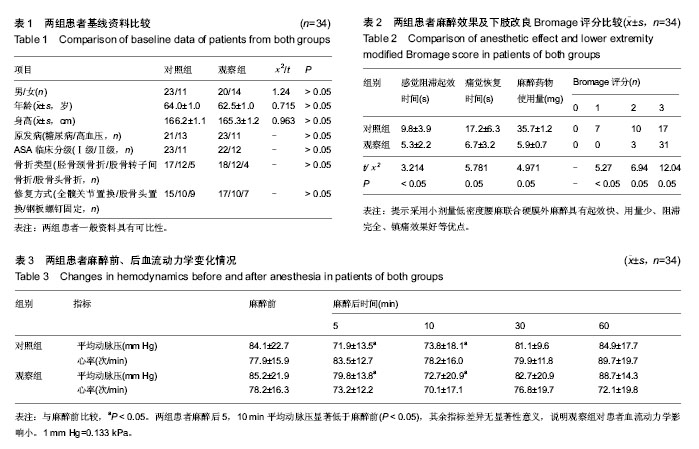
| [1] 张振明,张正迪,蔡铁良.小剂量低浓度罗哌卡因腰-硬联合麻醉用于膝关节镜手术[J].临床军医杂志,2013,41(2):166-169.
[2] 张微,薛昀.小剂量轻比重单侧蛛网膜下腔阻滞联合硬膜外麻醉在高龄患者下肢手术中安全性探讨[J].重庆医学,2013,42(8): 932-934.
[3] 王少华.轻比重罗哌卡因单侧腰麻联合硬膜外麻醉用于高龄髋关节置换术中的镇痛效果[J].浙江创伤外科,2013, 18(2): 269-270.
[4] 赵卫兵,杨小春.小剂量轻比重腰麻-硬膜外联合麻醉在老年下肢骨折手术中的应用[J].重庆医学,2013,42(21):2533-2534.
[5] 李佳清,毛菇,常胜和.不同麻醉方法在高龄患者下肢手术中的应用效果比较[J].山东医药,2013,53(26):70-72.
[6] 邓超,代志刚.腰麻硬膜外联合麻醉在老年股骨头置换术中的应用[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(16):4026-4028.
[7] 唐彦明,杨晓春,吴嘉宾.低比重罗哌卡因复合舒芬太尼腰-硬联合麻醉在高龄髋关节手术中的应用[J].重庆医学,2013,42(30): 3666-3668.
[8] 王玉秀,宗林,倪洋林.小剂量轻比重布比卡因单侧腰麻在老年患者髋关节手术中的应用[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2013,29(9): 919-920.
[9] 张志刚.连续硬膜外麻醉与连续腰麻对老年下肢骨折手术患者循环功能的影响[J].临床合理用药杂志,2013,6(31):116-117.
[10] 杜长黄,贾桂芳.腰-硬联合麻醉用于老年患者下腹部及下肢手术观察[J].中华全科医学,2009,7(3):260-261.
[11] 赵景朝,王振宇,邓海燕.小剂量轻比重布比卡因CSEA麻醉和连续硬膜外麻醉在老年患者下肢手术中效果观察[J].河南外科学杂志,2009,15(2):88-89.
[12] 周小建,李定鲲,黄志超.小剂量轻比重布比卡因蛛网膜下腔-硬膜外联合麻醉在下肢骨折老年患者手术中的应用[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2009,23(8):800-801.
[13] 吴振文,肖华鑫.小剂量轻比重布比卡因腰硬联合麻醉用于老年人下肢骨折手术的分析[J].中国医药导报,2009,6(26):31-32.
[14] 蔡铁良,唐丽,肖兴米.轻比重罗哌卡因在高龄患者腰-硬联合麻醉髋关节手术的应用[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2009,25(5):409-411.
[15] 史艳燕,张雅琴,舒英.0.5%轻比重罗哌卡因腰-硬联合麻醉在高龄患者侧卧位髋关节置换术中的应用[J].武汉大学学报(医学版), 2009,30(6):810-813.
[16] 徐慧.不同比重左旋布比卡因在高龄患者腰麻-硬膜外联合麻醉中的比较研究[J].中国药房,2009,20(17):1326-1328.
[17] 刘忠祥,张树海,程庆春.小剂量轻比重布比卡因腰硬联合麻醉在剖宫产术中的应用[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2012, 15(1): 49-51.
[18] 职爱丽.等效剂量罗哌卡因、布比卡因腰-硬联合麻醉用于高龄患者股骨颈骨折手术的对比研究[J].重庆医学,2012,41(1): 73-75.
[19] 李圣君,李九会,陈宗仁.硬膜外麻醉与腰-硬联合麻醉用于老年患者下肢骨折的效果[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(7): 1514-1515.
[20] 郭一闽,王忱.轻比重罗哌卡因单侧腰麻用于单侧下肢创伤手术对PCEA的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2012,28(1):46-48.
[21] 刘国泽,王涵.轻密度与重密度布比卡因在下肢手术麻醉中的对比分析[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(9):2361-2363.
[22] 才素分,张立涛,杨东红.两种布比卡因腰麻用于老年人下肢手术的麻醉效果比较[J].河北医药,2012,34(17):2590-2591.
[23] 李永强,肖军.轻比重布比卡因腰麻联合硬膜外麻醉用于剖宫产术50例[J].中国药业,2012,21(19):107-108.
[24] 林华阳,林洁,饶福东.老年人日间肛肠手术中等比重罗哌卡因单次腰麻合理剂量的应用及其安全性评价[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2012,38(6):1196-1200.
[25] 张振明,蔡铁良.小剂量低浓度罗哌卡因在腰-硬联合麻醉中的临床应用研究进展[J].临床军医杂志,2012,40(6):1550-1553.
[26] 黄生剑,黄渊祥,欧曙光.腰麻硬膜外联合麻醉在老年下肢手术中的临床观察[J].现代生物医学进展,2012,12(34):6720-6722.
[27] 邓铭锋,张雪莲.不同比重布比卡因腰麻对老年下肢手术患者的麻醉效果比较[J].广东医学院学报,2011,29(2):157-159.
[28] 王薇,贾东林.轻比重腰麻在临床麻醉中的应用进展[J].山东医药,2011,51(24):113-114.
[29] 王生力,张登文,杨荣国,.腰麻-硬膜外联合麻醉用于下肢皮瓣移植手术的临床观察[J].中国临床研究,2011,24(7):596-597.
[30] 孟秀荣.小剂量轻比重罗哌卡因腰硬联合麻醉用于老年人髋关节手术的观察[J].新乡医学院学报,2011,28(4):462-464.
[31] 陈宗洁,游先红.轻比重罗哌卡因行CSEA用于高龄患者下肢手术的临床观察[J].重庆医学,2011,40(32):3254-3255.
[32] 浦鹏飞,阎位明.轻比重单侧腰麻在下肢手术中的应用研究[J].中国医药导报,2011,8(32):76-78.
[33] 王世斌,刘保江.罗哌卡因复合芬太尼在腰麻-硬膜外联合阻滞的应用[J].中国医院用药评价与分析,2010,10(1):52-54.
[34] 魏小伍,梁亚霞,汤瑞昌.轻比重罗哌卡因单侧腰麻-硬膜外联合麻醉在高龄髋关节置换术中应用[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2010,24(2):173-174.
[35] 王涛,徐贯杰,赵士强.轻比重罗哌卡因腰-硬联合麻醉在腰椎间盘切除术中的应用[J].中国新药与临床杂志,2010,29(2): 139-142.
[36] 裘剑波,赵清振,仲琴.腰麻-硬膜外联合麻醉和硬膜外麻醉在高龄患者经尿道前列腺电切术中的价值比较[J].临床军医杂志, 2010,38(3):377-379.
[37] 曾振平,喻万柏.罗哌卡因连续腰麻在老年患者下肢手术的应用[J].现代医学,2010,38(4):333-336.
[38] 王凤桐.小剂量罗哌卡因腰硬联合麻醉用于高龄老年患者下肢骨折手术的临床观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2010,3(23):11-12.
[39] 张建峰,曹慧敏,唐忠科,等.等比重腰硬联合麻醉用于老年患者下肢手术[J].湖北医药学院学报,2010,29(6):537-538.
[40] 张锋.小剂量轻比重腰麻-硬膜外联合麻醉在老年下肢骨折手术中的应用效果分析[J].中国社区医师,2014,30(20):93-94. |