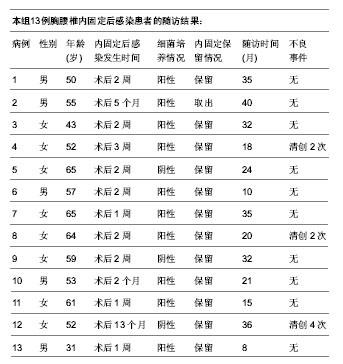
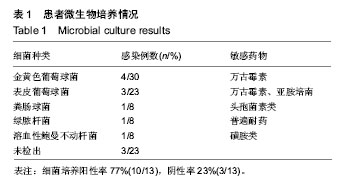
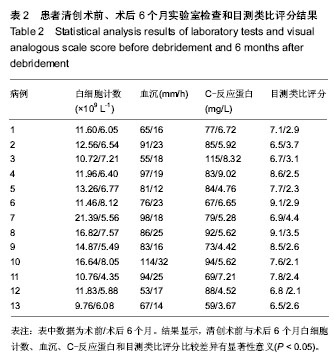
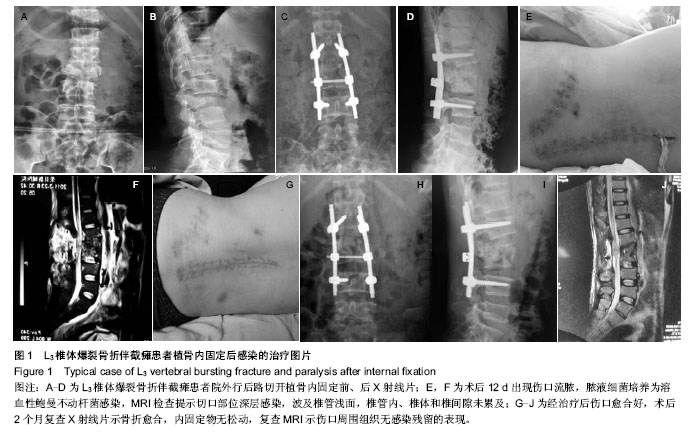
| [1] Pull ter gunne AF, Cohen DB. Incidence, prevalence, and analysis of risk factors for surgical site infection following adult spinal surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(13): 1422-1428.
[2] Rayes M, Colen CB, Bahgat DA, et al. Safety of instrumentation in patients with spinal infection. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010;12(6):647-659.
[3] 林青松,钟招明,陈建庭.脊柱手术后切口感染的危险因素[J]. 实用医学杂志,2014,30(10):587-1590.
[4] 屈伟俊,孙建军,李跃红.脊柱手术后切口感染的危险因素研究[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2013, 23(9):2105-2106.
[5] Hayashi H, Murakami H, Demura S, et al. Surgical site infection after total en bloc spondylectomy: risk factors and the preventive new technology. Spine J. 2014.
[6] Bas T, Bas P, Blasco A, et al. Chronic infections of the spine. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol, 2013, 23 Suppl 1(S35-40.
[7] 李若愚,车武,董健.脊柱术后手术部位感染的治疗进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2012, 22(4):366-369.
[8] 魏军渔.脊柱术后急性感染的治疗策略探讨[J]. 脊柱外科杂志, 2014, 12(4):208-211.
[9] Collins I, Wilson-macdonald J, Chami G, et al. The diagnosis and management of infection following instrumented spinal fusion. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(3):445-450.
[10] Ho C, Skaggs DL, Weiss JM, et al. Management of infection after instrumented posterior spine fusion in pediatric scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(24):2739-2744.
[11] Cahill PJ, Warnick DE, Lee MJ, et al. Infection after spinal fusion for pediatric spinal deformity: thirty years of experience at a single institution. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(12): 1211-1217.
[12] Alpert HW, Farley FA, Caird MS, et al. Outcomes following removal of instrumentation after posterior spinal fusion. J Pediatr Orthop. 2014;34(6):613-617.
[13] Fang XT, Wood KB. Management of postoperative instrumented spinal wound infection. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(20):3817-3821.
[14] Ishii M, Iwasaki M, Ohwada T, et al. Postoperative deep surgical-site infection after instrumented spinal surgery: a multicenter study. Global Spine J. 2013;3(2):95-102.
[15] Kim JI, Suh KT, Kim SJ, et al. Implant removal for the management of infection after instrumented spinal fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(4):258-265.
[16] Dubee V, Lenoir T, Leflon-guibout V, et al. Three-month antibiotic therapy for early-onset postoperative spinal implant infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55(11):1481-1487.
[17] 曹海云.脊柱手术后并发感染的原因及处理[J].中国实用医药, 2011, 6(25):119-120.
[18] Glotzbecker MP, Riedel MD, Vitale MG, et al. What's the evidence? Systematic literature review of risk factors and preventive strategies for surgical site infection following pediatric spine surgery. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013;33(5): 479-487.
[19] Goni V, Bahl A, Gopinathan NR, et al. Iatrogenic aortic pseudoaneurysm following anterior thoracic spine surgery masquerading as chronic infection. Chin J Traumatol. 2013;16(6):368-370.
[20] Chen SH, Lee CH, Huang KC, et al. Postoperative wound infection after posterior spinal instrumentation: analysis of long-term treatment outcomes. Eur Spine J. 2014.
[21] Mok JM, Guillaume TJ, Talu U, et al. Clinical outcome of deep wound infection after instrumented posterior spinal fusion: a matched cohort analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2009;34(6): 578-583.
[22] 庄泽民,李强.胸椎骨折术后感染经皮固定器治疗一例[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011, 26(8):713.
[23] Nunez-pereira S, Pellise F, Rodriguez-pardo D, et al. Implant survival after deep infection of an instrumented spinal fusion. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(8):1121-1126.
[24] Takahashi J, Shono Y, Hirabayashi H, et al. Usefulness of white blood cell differential for early diagnosis of surgical wound infection following spinal instrumentation surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(9):1020-1025.
[25] Cyteval C, Bourdon A. Imaging orthopedic implant infections. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2012;93(6):547-557.
[26] 何鱼,权正学.脊柱手术术后感染防治中抗菌药物的应用[J].重庆医学, 2012, 41(35):3772-3774.
[27] Kasliwal MK, Tan LA, Traynelis VC. Infection with spinal instrumentation: Review of pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention, and management. Surg Neurol Int. 2013; 4(Suppl 5):S392-403.
[28] Miksic NG. Spinal infections with and without hardware: the viewpoint of an infectious disease specialist. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23 Suppl 1:S21-28.
[29] Yano MH, Klautau GB, Da silva CB, et al. Improved Diagnosis of Infection Associated to Osteosynthesis by Use of Sonication of Fracture-Fixation Implants. J Clin Microbiol. 2014.
[30] Bemer P, Corvec S, Tariel S, et al. Significance of Propionibacterium acnes-positive samples in spinal instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(26): E971-976.
[31] Barrey C, Launay O, Freitas E, et al. The follow-up of patients with postoperative infection of the spine. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23 Suppl 1:S29-34.
[32] Messina AF, Berman DM, Ghazarian SR, et al. The management and outcome of spinal implant-related infections in pediatric patients: a retrospective review. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014;33(7):720-723.
[33] Li H, Hamza T, Tidwell JE, et al. Unique antimicrobial effects of platelet-rich plasma and its efficacy as a prophylaxis to prevent implant-associated spinal infection. Adv Healthc Mater. 2013;2(9):1277-1284.
[34] Kato S, Hozumi T, Yamakawa K, et al. Antibiotic-impregnated cement embedding technique for spinal instrumentation infections. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2014;75(6): 479-484.
[35] Ferry T, Valour F, Lustig S, et al. The challenge of infection prevention in spine surgery: an update. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23 Suppl 1:S15-19. |