Factors closely related with the stability of pedicle screw are the quality of screw placement and the connection between screw-bone interface and screw. Among these factors, the key is screw-bone interface. It is generally believed that bone mineral density is positively correlated with the stability of screw. With the increasing of screw length and diameter, the contact area in the screw-bone interface increases, the screw stability increases correspondingly. Weinstein et al [5] study showed that 60% of fixation strength of pedicle screw lies in the pedicle, and the cancellous bone of vertebral body increased by 15%-20%, close to but not perforate the front cortex and increased by 16%, perforate the front cortex increased by 20%-25%. Sacrum is the weakest part for pedicle screw in thoracolumbar spine, as in which the channel length is short, only about 30-35 mm; if perforating the front cortex, the fixation strength will increased by 60%. Therefore, perforating the front cortex (especially in sacrum) is an effective way to improve stability of screw, but do not forget to control the perforation of cortical less than 2 mm, so as not to damage the blood vessels and other important tissues. Studies also showed that screw diameter and length synergy with each other. When increase 2 mm in diameter and 10 mm in length, compared with that increase 1 mm in diameter and 5mm in length, there is very significant difference in the increasing of the stability of screw in the former[6-7]. As cortical and cancellous bones are non-homogeneity, stability of screw close to cortex of pedicle is better than that of screw completely located within cancellous bone[8-9]. Yin et al [9-10] showed that when the pedicle screw placed close to the cortex even if very small part of perforation of pedicle cortex, the pullout strength and torque of screw have not been reduced especially in osteoporosis, but more than those of screw completely located within cancellous bone. Using a large size of screw causes pedicle expansion, as long as the insertion direction is accurate, nerve damage caused by pedicle perforation could be avoided. Therefore, application of thicker and longer screws is clinically safe and convenient way to improve stability of screw[5-6].
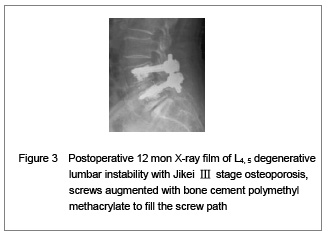
For severe osteoporosis spine, the most reliable method to improve the stability of screw is to use strengthening agent in the screw path, of which polymethyl methacrylate has the best effect. Experimental studies have shown that polymethyl methacrylate can immediately increase the pullout strength of screw by 95%, adding pressure to raise 196%[10-12]. Soshi et al [4] reported that the pullout strength doubled in the osteoporosis spine using bone cement to fill the screw path. However, the application of polymethyl methacrylate has some disadvantages such as: aggregation produces high heat, wrong injection or overflow that will injury the nerve tissue, long-term retention may have some toxic and carcinogenic risks, difficult for further removing, without bone conduction, a layer of connective organization grows between bone and metal screw, which under long-term load can produce relaxation and lead to bone resorption and pedicle fracture[10]. Human artificial chromosome, calcium phosphate cement, composite bio-ceramic bone cement and other new enhancers are blessed with good biocompatibility and bone conductivity, slow degradation in vivo, non-toxication, does not produce high heat. In these areas, they are better than polymethyl methacrylate, but their effect in improving the stability of screw is poor than polymethyl methacrylate. The main complication of new strengthening agent is leakage out of screw path and might cause nerve tissue damage[7, 10, 12]. There was no neurovascular injury or nerve damage in this paper. We understood that probe must be used to verify that there is not rupture of pedicle wall before application of strengthening agent, furthermore, while it is in paste state inject bone cement into vertebral body and screw path, as well as the pressure injected is not too high. In this way to use strengthening agent was yet relatively safe.
Enhancement of bone cement or replacement with thicker and longer screws can increase stability of screw that is the change of absolute value of stability of screw. On the other hand, the role of pedicle screw fixation does not rely solely on a single screw to work, but through connection between screw and rod or plate, that means the whole set of instruments plays a regular role as a whole. Therefore, the upper and the lower screws, the left and the right screws with different connectors, placement of screws in different directions will affect the stability of screws in the device, which named as the change of relative value of stability of screw by Yin et al [13]. Biomechanical tests show that the application of screws with rigid collection between screw and rod with two cross-link devices, screw placement with large angles for the upper and the lower screws in the sagittal plane and the left and the right screws in the horizontal plane, respectively, as well as more fixing segments, will help to improve the relative value of stability of screw in osteoporosis spine [13-14]. As the rod system with rigid connection between screw and rod, and two cross-link devices put the apparatus together into one solid whole, just like screws in a locking plate, which have a good anchor force and pullout strength, meanwhile also have an increase in torque and fatigue resistance stability of apparatus. Screws placed in large angles in the sagittal plane and horizontal plane increase the shear strength of screw, which gives a triangular stability. Krag and Yin et al [13] named them as “toe-nailing effect” in the horizontal and the sagittal planes, respectively. Zhang et al [15] reported that application of thicker and longer screws and a larger horizontal angle of screws placement can improve the stability of screws in less osteoporosis spine and achieve good clinical results.
Polly and other studies[6,8] have shown that the same screw inserted at the first time has the greatest stability, but spin out and then spin in again, the screw torque will drop 34% than the initial. Therefore, in patients with osteoporosis, the screw must be placed in a one-time, do not spin out and replace. Drilling a small hole and placement with a needle to ensure accurate location under C-arm X-ray machine, then placement with screw in the surgery, that is the right way.
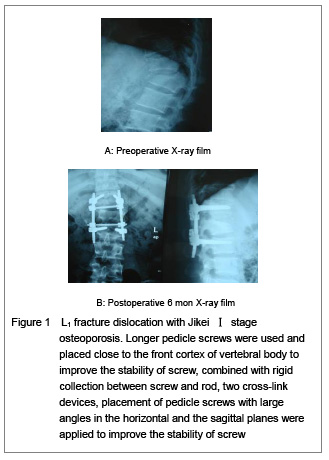
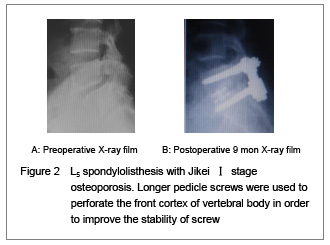
Soshi and other studies[1, 4] showed that for Jikei early and Ⅰ stage osteoporosis spine, an increase of 20% in diameter of screw can double the screw pullout resistance, whereas for Ⅱ and Ⅲ stage osteoporosis spine, the effect of simply increasing the diameter of screw on the increasing of screw pullout resistance is not very obvious, thus other methods must be used in this situation. Instability such as screw loosening and partial loss of correction of reduction in two cases with Jikei Ⅰ stage osteoporosis, in whom non-cement augmented screw was used after 5 to 6 months in this group, that showed the effect of this method was limited and there were still defects, the same method should not be used in patients with Jikei Ⅱ and Ⅲ stage osteoporosis. In general, the authors agreed with views that for Jikei early and Ⅰ stage osteoporosis spine using thicker and longer screws to increase the absolute stability of screw is safe and convenient, combined with rigid collection between screw and rod with two cross-link devices, and placement of pedicle screw with large angles in the horizontal and sagital planes were applied to improve the relative stability of screw. However, for Jikei Ⅱ and Ⅲ stage osteoporosis spine, more reliable method of bone cement must be used to improve the absolute stability of screw[6,16]. According to these principles, we used different methods to improve the stability of screw in 34 cases with osteoporosis, the overall results showed that the methods were safe and effective. Resently, expandable and cannulate fenestrated pedicle screws in osteoporotic patients have achieved good fixation effect, it is a promising research subject[2-3, 16].