中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (51): 8330-8336.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.51.025
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
关节镜下外侧支持带松解后的髌骨轨迹分析
张建兵,郝建桥,申云龙,王合围,薛永安,刘 斌
- 河北省文安县医院骨科,河北省文安县 065800
-
出版日期:2014-12-10发布日期:2014-12-10 -
通讯作者:张建兵,河北省文安县医院骨科,河北省文安县医院 065800 -
作者简介:张建兵,男,1971年生,河北省廊坊市人,汉族,2009年河北医科大学毕业,博士,主任医师。
Analysis of patellar maltracking after arthroscopic lateral retinacular release
Zhang Jian-bing, Hao Jian-qiao, Shen Yun-long, Wang He-wei, Xue Yong-an, Liu Bin
- Department of Orthopaedics, Wenan Hospital, Wenan 065800, Hebei Province, China
-
Online:2014-12-10Published:2014-12-10 -
Contact:Zhang Jian-bing, Department of Orthopaedics, Wenan Hospital, Wenan 065800, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jian-bing, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopaedics, Wenan Hospital, Wenan 065800, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
背景:外侧支持带松解是治疗髌股关节紊乱症首选的治疗方法,然而有些文献报道部分病例的长期随访结果并不满意。
目的:分析关节镜下外侧支持带松解后的髌骨轨迹,以探讨外侧支持带松解后部分病例随访优良率下降的原因。
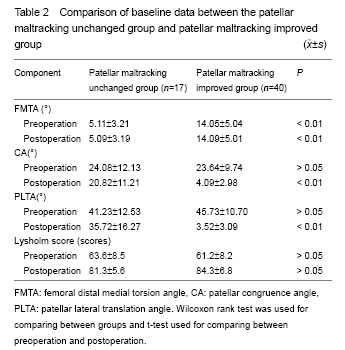
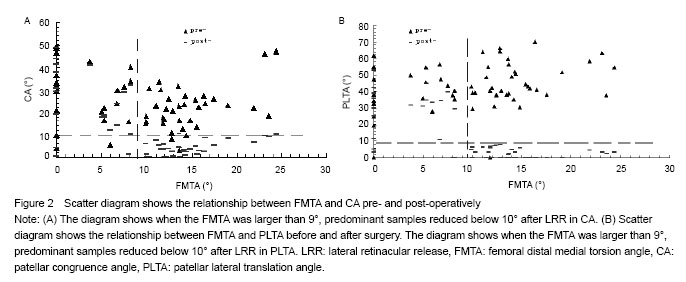
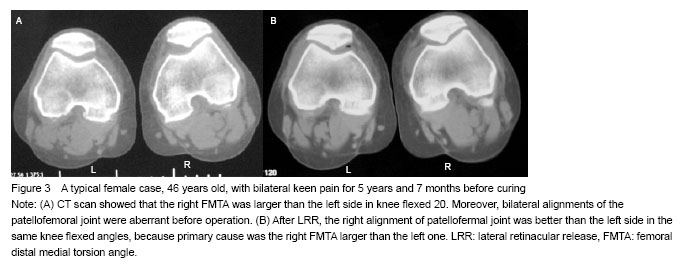
方法:临床采集符合纳入标准的57膝(34例)样本,松解前后分别行10°,20°,30°,40°屈膝位髌股关节CT扫描,测量髌股适合角、髌骨外移角和股骨远端内侧扭转角,比较松解前后髌骨轨迹的变化。
结果与结论:通过测量髌股适合角,髌骨外移角发现髌骨轨迹17膝松解后无改善,40膝明显改善。40膝的股骨远端内侧扭转角均大于9°,17膝的股骨远端内侧扭转角均小于9°。说明股骨远端内侧扭转角可能是影响外侧支持带松解后髌骨轨迹的一个重要因素。
中图分类号:
引用本文
张建兵,郝建桥,申云龙,王合围,薛永安,刘 斌. 关节镜下外侧支持带松解后的髌骨轨迹分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(51): 8330-8336.
Zhang Jian-bing, Hao Jian-qiao, Shen Yun-long, Wang He-wei, Xue Yong-an, Liu Bin. Analysis of patellar maltracking after arthroscopic lateral retinacular release[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(51): 8330-8336.
Variation of patellar tracking after arthroscopic lateral retinacular release
| [1]Di Giulio M, Donaldson WR. Complications of patello-femoral joint surgery. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2004;12:172-184. [2]Fulkerson JP. Operative management of patellofemoral pain. Ann Chir Gynaecol 1991;80:224-229. [3]Fulkerson JP. Diagnosis and treatment of patients with patellofemoral pain. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30:447-456. [4]Myers P, Williams A, Dodds R, et al. The three in one proximal and distal softt issue patella realignment procedure. Results and its place in the management of patellafemoral instability. Am J Sports Med. 1999;27:575-579. [5]Clifton R, Ng CY, Nutton RW. What is the role of lateral retinacular release? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(1):1-6. [6]Scuderi G, Cuomo F, Scott WN. Lateral release and proximal realignment for patellar subluxation and dislocation. A long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988;70:856-861. [7]Vahasarja V, Kinnunen P, Serlo W. Lateral release and proximal realignment for patellofemoral malalignment. A prospective study of 40 knees in 36 adolescents followed for 1-8 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 1998;69:159-162. [8]Kolowich P, Paulos L, Rosenberg T, et al. Lateral release of the patella: indications and contraindications. Am J Sports Med. 1990;18:359-365. [9]Ford D, Post W. Open or arthroscopic lateral release. Indications, techniques, and rehabilitation. Clin Sports Med. 1997;16:29-49. [10]Fulkerson JP, Schcutzer SF, Ramsby GR, et al. Computerized tomography of the patellofemoral joint before and after lateral release or realignment. Arthroscopy. 1987; 3: 19-24. [11]Handy M, Miller M. Surgical treatment of acute patellar dislocation. Oper Tech Sports Med. 2001;9:164-168. [12]Farr J. Distal realignment for recurrent patellar instability. Oper Tech Sports Med. 2001;9:176-182. [13]Ahmad C, Stein B, Matuz D, et al. Immediate surgical repair of the medial patellar stabilizers for acute patellar dislocation. A review of eight cases. Am J Sports Med. 2000; 28:804-810. [14]Bigos S, McBride G. The isolated lateral retinacular release in the treatment of patellofemoral disorders. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;186:75-80. [15]Dzioba R. Diagnostic arthroscopy and longitudinal open lateral release. A four year follow-up study to determine predictors of surgical outcome. Am J Sports Med. 1990;18: 343-348. [16]Gerbino PG, Zurakowski D, Soto R, et al. Long-term functional outcome after lateral patellar retinacular release in adolescents: an observational cohort study with minimum 5-year follow-up. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008;28(1):118-123. [17]Harrison RK, Magnussen RA, Flanigan DC. Avoiding complications in patellofemoral surgery. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2013;21(2):121-128. [18]Dandy D, Desai S. The results of arthroscopic lateral release of the extensor mechanism for recurrent dislocation of the patella after 8 years. Arthroscopy. 1994;10:540-545. [19]Christoforakis J, Bull AM, Strachan RK, et al. Effects of lateral retinacular release on the lateral stability of the patella. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14: 273-277. [20]Lee CH, Wu CC, Pan RY, et al. Medial retinacular flap advancement and arthroscopic lateral release for symptomatic chronic patellar lateral subluxation with tilting. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(10):2499-2504. [21]Zaffagnini S, Colle F, Lopomo N, et al. The influence of medial patellofemoral ligament on patellofemoral joint kinematics and patellar stability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(9):2164-2171. [22]Duchman KR, DeVries NA, McCarthy MA, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction. Iowa Orthop J. 2013;33:64-69. [23]Fulkerson JP. Diagnosis and treatment of patients with patellofemoral pain. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30(3):447-456. [24]McCarthy MM, Strickland SM. Patellofemoral pain: an update on diagnostic and treatment options.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2013;6(2):188-194. [25]Schepsis AA, Watson FJ. Patellofemoral Arthritis with Malalignment. Common Patellofemoral Problems. Rosemont, IL: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2005. [26]Sheehan FT, Derasari A, Brindle TJ, et al. Understanding patellofemoral pain with maltracking in the presence of joint laxity: complete 3D in vivo patellofemoral and tibiofemoral kinematics. J Orthop Res. 2009;27:561-570. [27]Wilson NA, Press JM, Koh JL, et al. In vivo noninvasive evaluation of abnormal patellar tracking during squatting in patients with patellofemoral pain. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:558-566. [28]State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution. 1994-09-01. [29]Nomura E, Inoue M. Cartilage lesions of the patella in recurrent patellar dislocation. Am J Sports Med. 2004; 32:498-502. [30]Simpson LA, Barrett JP Jr. Factors associated with poor results following arthroscopic subcutaneous lateral retinacular release. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;186: 165-171. [31]Dzioba RB. Diagnostic arthroscopy and longitudinal open lateral release. A four year follow-up study to determine predictors of surgical outcome. Am J Sports Med. 1990;18: 343-348. [32]Panni AS, Tartarone M, Patricola A, et al. Long-term results of lateral retinacular release. Arthroscopy. 2005;21: 526-531. [33]Marx RG, Jones EC, Allen AA, et al. Reliability, validity, and responsiveness off our knee outcome scales fo rathletic patients. J Bone Joint Surg. 2001;83A:1459-1469. [34]Pal S, Besier TF, Draper CE, Patellar tilt correlates with vastus lateralis:vastus medialis activation ratio in maltracking patellofemoral pain patients. J Orthop Res. 2012; 30(6):927-933. [35]Lin F, Wilson NA, Makhsous M, et al. In vivo patellar tracking induced by individual quadriceps components in individuals with patellofemoral pain. J Biomech. 2010; 43(2): 235-243. [36]McNally EG. Imaging assessment of anterior knee pain and patellar maltracking. Skeletal Radiol. 2001;30:484-495. [37]Lee TQ, Anzel SH, Bennett KA, et al. The influence of fixed rotational deformities of the femur on the patellofemoral contact pressures in human cadaver knees. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;302:69-74. [38]Besier TF, Gold GE, Delp SL, et al. The influence of femoral internal and external rotation on cartilage stresses within the patellofemoral joint. J Orthop Res. 2008;26:1627-1635. [39]Katchburian MV, Bull AM, Shih YF, et al. Measurement of patellar tracking: assessment and analysis of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;412:241-259. [40]Elkousy H. Complications in brief: Arthroscopic lateral release. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(10):2949-2953. [41]Koh JL, Stewart C. Patellar instability. Clin Sports Med. 2014;33(3):461-76. |
| [1] | 黄登承, 王志科, 曹学伟. 体外冲击波疗法治疗中老年膝骨关节炎短期疗效对比的荟萃分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [2] | 李大地, 朱 梁, 郑 力, 赵凤朝. 全膝关节置换疗效及患者满意度与人格特征的关联性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [3] | 韦 玮, 李 剑, 黄林海, 兰敏东, 卢显威, 黄绍东. 全膝或全髋关节置换后老年人首次活动时跌倒恐惧的影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [4] | 王金军, 邓增发, 刘 康, 何智勇, 余新平, 梁建基, 李 晨, 郭洲洋. 全膝关节置换静脉滴注氨甲环酸联合含氨甲环酸鸡尾酒局部应用的止血效果及安全性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [5] | 肖国庆, 刘选泽, 严钰皓, 钟喜红. 后交叉韧带替代型假体全膝关节置换术后屈曲受限的影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [6] | 彭智浩, 冯宗权, 邹勇根, 牛国庆, 吴 峰. 活动平台单髁置换后下肢力线与外侧间室骨关节炎进展的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [7] | 黄泽晓, 杨 妹, 林诗炜, 何和与. 血清n-3多不饱和脂肪酸水平与全膝关节置换早期股四头肌肌力变化的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [8] | 张 冲, 刘志昂, 姚帅辉, 高军胜, 姜 岩, 张 陆. 局部应用氨甲环酸减少老年股骨颈骨折全髋关节置换后引流的安全和有效性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [9] | 陈心敏, 李文标, 熊凯凯, 熊晓燕, 郑利钦, 李木生, 郑永泽, 林梓凌. 钉道强化股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年A3.3型股骨转子间骨折:最佳骨水泥量有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [10] | 杜秀鹏, 杨朝晖. 65岁以下嵌插型股骨颈骨折初始畸形程度对颈缩短的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [11] | 周继辉, 李新志, 周 游, 黄 卫, 陈文瑶. 髌骨骨折修复内植物选择的多重问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [12] | 陈俊名, 岳 辰, 何沛霖, 张俊涛, 孙墨渊, 刘又文. 髋关节置换与股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定修复高龄股骨转子间骨折效果的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [13] | 李中峰, 陈明海, 凡一诺, 魏秋实, 何 伟, 陈镇秋. 右归饮治疗激素性股骨头坏死作用机制的网络药理学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [14] | 仲鹤鹤, 孙鹏鹏, 桑 鹏, 吴术红, 刘 毅. 模拟重建膝关节后外侧复合体核心韧带后膝关节稳定性评估[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [15] | 蔡群斌, 邹 霞, 胡剑涛, 陈心敏, 郑利钦, 黄培镇, 林梓凌, 姜自伟. 有限元法分析尖顶距与股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定股骨转子间骨折稳定性的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
Design
Patients who had undergone isolated LRR at Wenan Hospital from May 2006 to December 2012 were eligible for inclusion in this study. Attempts were made to contact all of the patients by messaging and phone. When a patient could not be contacted after three attempts, the patient was considered to be lost to follow-up. Patients were free to discontinue the study at any point. Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1.
.jpg)
.jpg)
FMTA, CA, and PLTA were measured.
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||