中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (51): 8337-8345.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.51.026
• 组织构建基础实验 basic experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
差异蛋白基因生物信息学在冠心病血瘀证遗传相关验证中的应用
郑景辉1,袁肇凯2,张敏州1,李 杰2,王丽萍3,宁桂兰4,孙贵香2,简维雄2,黄献平2,刘吉勇2
- 1广州中医药大学第二附属医院重症医学科,广东省广州市 510120;2湖南中医药大学中医诊断研究所,湖南省长沙市 410007;3湖南怀化医学高等专科学校,湖南省怀化市 418000;4广西中医药大学附属瑞康医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530011
Bioinformatics analysis of differential genes correlated with blood stasis syndrome of coronary heart disease
Zheng Jing-hui1, Yuan Zhao-kai2, Zhang Min-zhou1, Li Jie2, Wang Li-ping3, Ning Gui-lan4, Sun Gui-xiang2, Jian Wei-xiong2, Huang Xian-ping2, Liu Ji-yong2
- 1ICU of Second Hospital Affiliated to Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China; 2Institute of TCM Diagnosis, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410007, Hunan Province, China; 3Hunan University of Medicine, Huaihua 418000, Hunan Province, China; 4Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
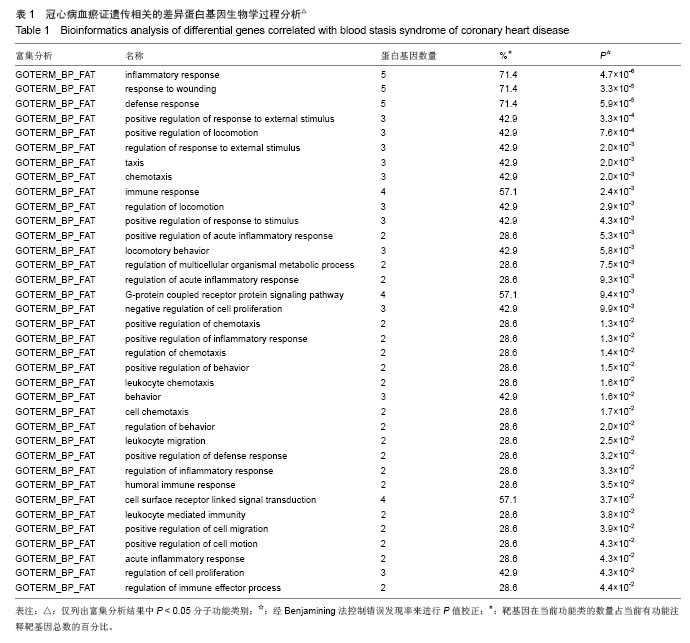
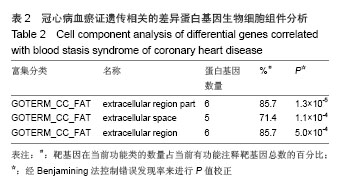
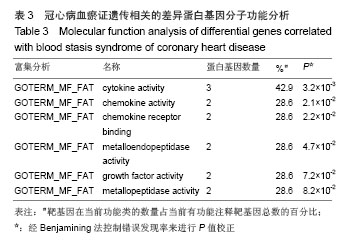
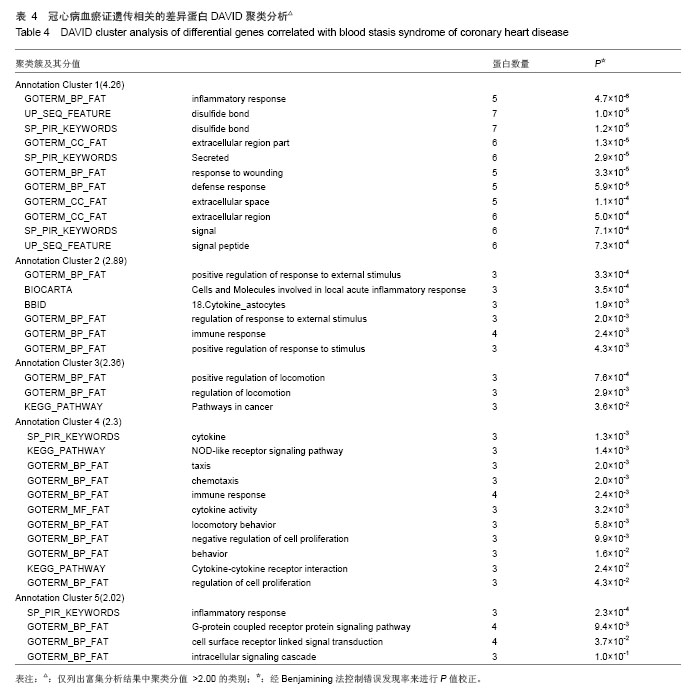
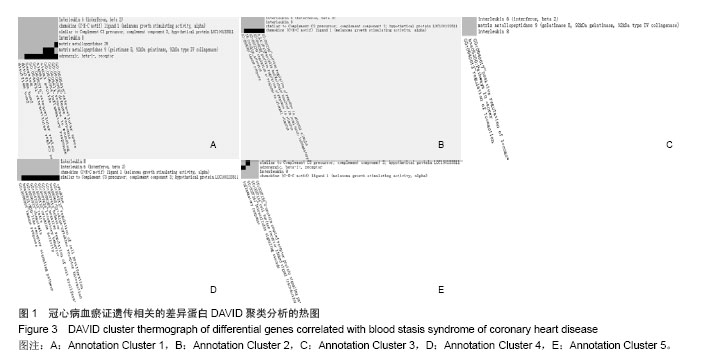
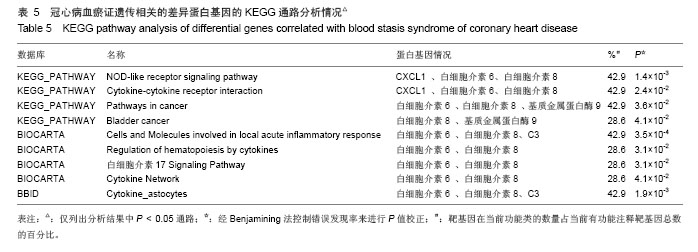
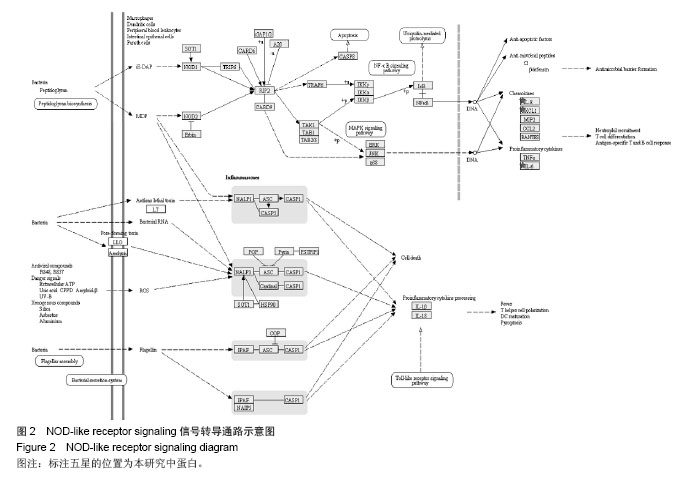
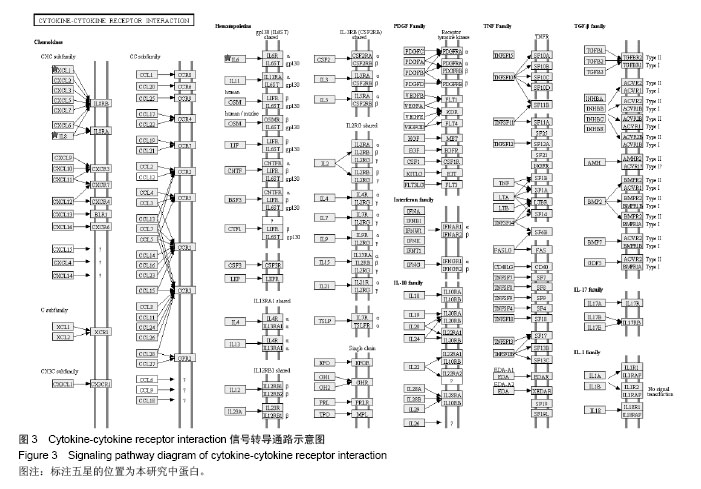
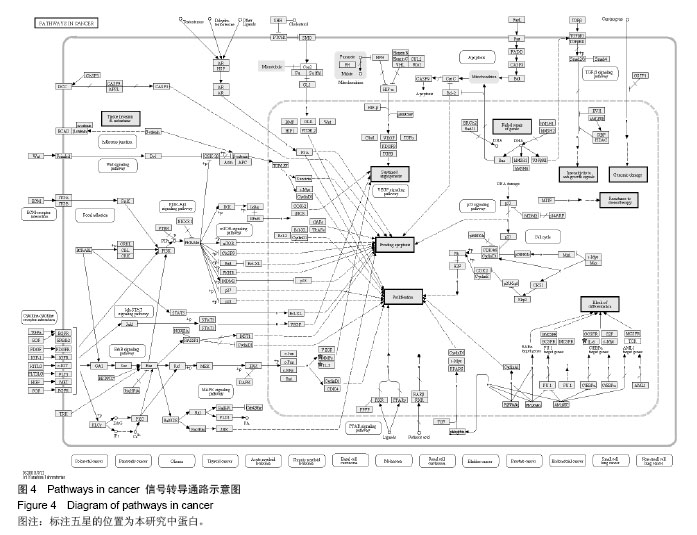
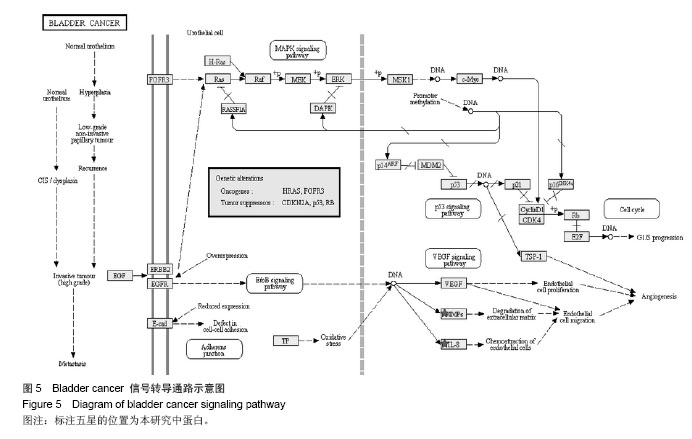
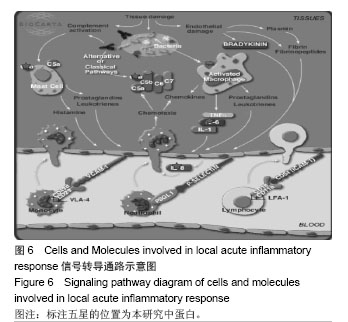
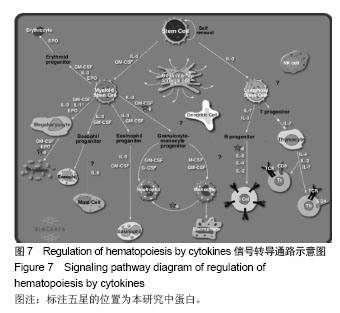
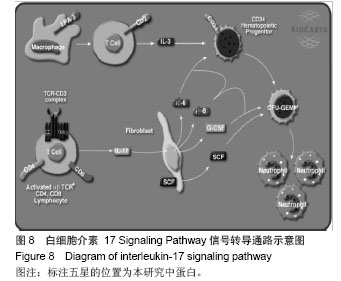
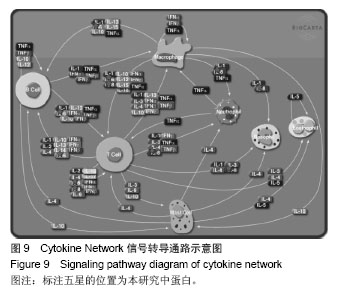
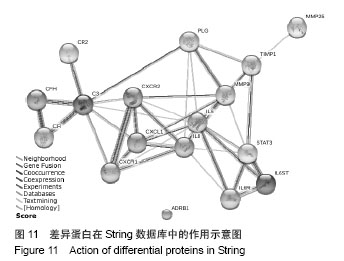
背景:课题组前期通过临床流行病学和分子流行病学显示冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病血瘀证具有一定的家族聚集倾向,发现其相关的差异基因与炎症、斑块形成及血管内皮损伤密切相关。 目的:对冠心病血瘀证遗传相关的差异蛋白基因进行生物信息学分析。 方法:根据流行病学调查基础上基因芯片技术确定的冠心病血瘀证遗传相关的差异蛋白基因,通过DAVID数据库搜索软件结合GO数据库搜索进行注释和富集度分析;KEGG、BIOCARTA、BBIOD数据库进行信号转导通路分析;VISANT、DIP数据库检索蛋白质相互作用。 结果与结论:差异蛋白基因主要参与43种生物学过程、3种细胞组分、6种分子途径,差异蛋白主要参与10条信号转导通路,这些蛋白在多条信号转导通路上相互发生作用,发现节点189个,路径映射5个,节点的功能种类包括29类。冠心病血瘀证患者遗传差异基因的功能、通路以及相互作用主要体现在炎症反应、免疫调节、细胞因子趋化、细胞增殖等方面;冠心病血瘀证在多位点、多环节、多种生物学进程中共同发挥作用的复杂病理反应,基因组学生物信息学技术可以站在“整体观”的角度对中医证候的机制作出预测,结合进一步分子生物学验证是一条很好的中医药现代化途径。
中图分类号: