骨质疏松症是一种与年龄增长相关的退行性疾病,表现为骨骼的骨量丢失和微结构的破坏。这些骨的退行性改变不但增加了骨骼发生骨折的风险,而且也严重影响骨折后手术固定的稳定性。当骨折处受到外力时,内固定-骨界面间的负荷传递产生的应变往往超过了内固定周围骨的最大容忍程度,易导致微骨折和内固定松动的发生
[5],常不能提供满意的瞬时固定效果,因此临床上在术后早期由于内固定置入界面破坏导致治疗失败的病例很多。从材料学角度分析,骨骼是一个由磷灰石和胶原组成的两相材料,磷灰石维持着骨的压缩强度而胶原则提供其抗拉伸能力。但骨骼并不是一个单纯的生物材料,而是有着活跃的骨重建活动的人体器官。正常人体的骨骼依靠骨形成和骨吸收的动态平衡来维持自身结构和功能的完整性,这些组成的结构和强度是其力学强度维持的必要条件。在年龄增长和雌激素缺乏等多因素的作用下,骨吸收超过骨形成,骨重建的动态平衡被打破,形成了骨质疏松症。疏松的骨骼表现为皮质骨内膜的再吸收和髓腔扩大,以及松质骨网状连接的断裂和骨小梁变细;最终影响了整个骨骼的弯曲、扭转等力学强度并易发生低能量的骨折。因此,骨质疏松骨折是由轻微外力所致的病理性骨折,和一般暴力性骨折的力学、生物学特点有着本质区别。这种类型的骨折常见于椎体、髋部、腕部、胫骨和肱骨近段。由于四肢骨干骺端的主要组成为松质骨,骨质疏松发生后所受的影响最大,因此骨折时多为粉碎性,而且常累及关节,给临床治疗带来困难。如果骨折固定不恰当或保守治疗的制动过长可造成血栓发生、肺部炎症、压疮等并发症;并且容易造成骨骼和肌肉退化。所以,牢固的内固定和早期的康复锻炼对于这种类型的骨折患者而言显得非常重要。
对传统的内固定技术改进使其适应骨质疏松性骨折治疗的需要,是提高骨质疏松性骨折疗效的方法之一。这些改进的原则是使用相对稳定的技术使内固定与骨共同承担负荷,从而减少骨-内固定界面的应力应变等。具体表现在骨质疏松骨折内固定的优化设计、内固定材料的改进以及手术技术完善等方面。但是由于内固定所固定部位骨的力学特性较差,因此单纯进行这些改进往往还是不能满足固定维持的需要。骨质疏松骨骼处于的特殊病理状态,对骨折的愈合过程也有较大影响
[6]。虽然,骨质疏松骨折的愈合方式与一般骨折愈合方式基本相似,最终也能获得骨折愈合;但是大多研究者认为骨质疏松骨折的愈合时间与正
常骨折愈合时间相比有明显的延长。通过比较老年大鼠骨折与正常大鼠骨折愈合过程发现,老年大鼠组的骨折愈合时间延长,且其愈合后骨的刚度和强度要显著低于正常组[7]。这可能是由于骨质疏松机体内的间充质干细胞较少,骨形态发生蛋白含量下降所引起
[8-9]。研究表明,被固定部位的骨矿物质密度降低、多孔性的增加会导致螺钉把持力的下降
[10],并有研究者发现固定部位骨矿物质密度与螺钉的把持能力成线性相关
[11]。虽然可以通过增加螺钉螺纹的直径来提高螺钉的把持能力,可当固定部位的骨矿物质密度低于0.4 g/cm
2,这种螺纹直径变化的影响将消失
[12]。因此,比较理想的措施是利用自体骨、异体骨或其他骨替代物来直接增强固定部位“骨的质和量”。因此,针对骨质疏松特殊病理状态和局部骨生物力学特点,开展骨质疏松骨折内固定的力学及生物学研究,增加骨折固定的瞬时稳定性、长期稳定性来提供良好的骨愈合环境具有重要的临床意义。
临床上对骨质疏松骨折内固定增强的最初尝试是使用无生物活性的聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯。由于聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯的高压缩强度、高刚度的力学特性能显著增加内固定的瞬时稳定性
[13]。但是,从生物力学角度看,这种聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯高压缩强度、高刚度又导致了增强部位和周围骨骼力学性能的不匹配,增加了临界部位的骨折风险。从生物学角度看,聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯不能降解,不具有被新骨替代的生物学活性
[14],同时,聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯不能与骨组织直接结合,两者间会形成一层结缔组织薄膜,长期负荷下可发生螺钉的松动和移位,所以使用聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯增强只是一种权宜之计。近年来受到普遍重视的可注射型生物型骨水泥的强度和刚度与松质骨相当,并具有较好的力学相容性,更为重要的是其具有聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯所没有的骨生物活性,能随着新骨长入逐渐被吸收替代
[15]。这种生物型骨水泥包括磷酸钙骨水泥、硫酸钙水泥和生物玻璃等
[16-18],其中以磷酸钙骨水泥和硫酸钙水泥的应用更为普遍,如用于四肢骨质疏松骨折内固定增强和椎体压缩性骨折增强的治疗
[19]。硫酸钙作为人工合成的骨植入材料应用已有超过百年的历史,自然存在的硫酸钙为二水化合物,通过对其加热使二水化合物脱水生成半水化合物,临床上将这些半水化合物与水混合时即可生成固态的二水化合物来修复骨缺损。直到最近十年,临床上才出现手术级的MIIG
TM115及MIIG
TMX3。尤其MIIG
TMX3硫酸钙骨水泥的出现改写了硫酸钙力学特性差、低压缩强度及较脆的历史,它不但具有传统硫酸钙的促骨再生能力,而且具有较大抗拉、抗压的力学特征
[20]。因此,这种美国FDA认证的第2代高强度可注射型硫酸钙骨水泥(MIIG
TMX3)具有骨质疏松骨折内固定增强的应用可能。目前,椎弓根螺钉内固定已经成为脊柱外科领域的重要技术之一,椎弓根螺钉钉棒系统可提供即时、坚强内固定效果,为脊柱矫形、植骨融合建立基础。但术后椎弓根螺钉松动、拔出等并发症在临床上不少见,尤其多见于骨质疏松的患者。所以在手术过程中通过硫酸钙骨水泥增强椎弓根螺钉可以获得良好的临床效果。
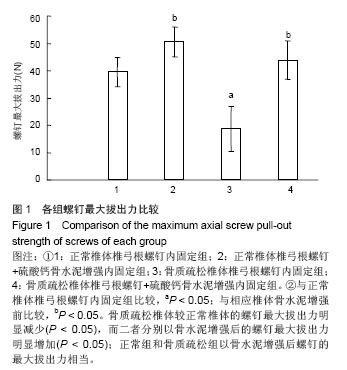
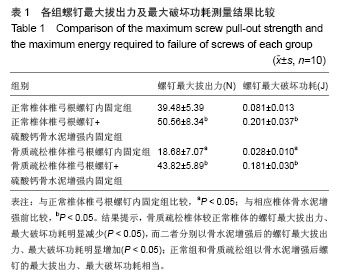
在本实验发现在脱钙处理的骨质疏松椎体内置入椎弓根螺钉,其螺钉的最大拔出力和最大破坏功耗较正常椎体明显下降,给予硫酸钙骨水泥增强后,其最大拔出力和最大破坏功耗与正常相仿,能够获得良好的生物力学稳定性。但是,本部分生物力学测试中施加于螺钉的外力为单轴拉力。而骨折内固定器械受力种类往往很多,内固定中的螺钉所受到的外力多为剪切力;且这些作用力常为一定频率的循环外力,所以单纯使用拉力来评估螺钉的稳定性有一定的局限性。此外,本实验中螺钉增强所应用的硫酸钙骨水泥虽然有较高的强度,但是有一定的脆性,断裂强度相对也较低,因此动态的疲劳性加载或许更能深入了解该骨水泥材料增强螺钉的不足之处。并且,由于实验动物的解剖特性导致其在受力上与人类有着很大差异,因此这种增强不能完全模拟出实际的骨折增强情况。因此,有必要进行人体生物力学测试来进一步验证硫酸钙骨水泥的力学增强效果,这些均是今后所要研究的。

.jpg)