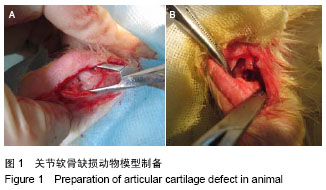
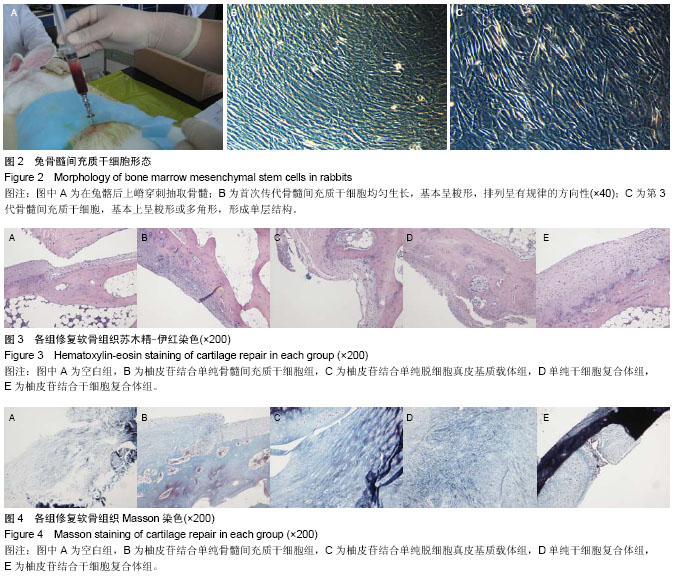
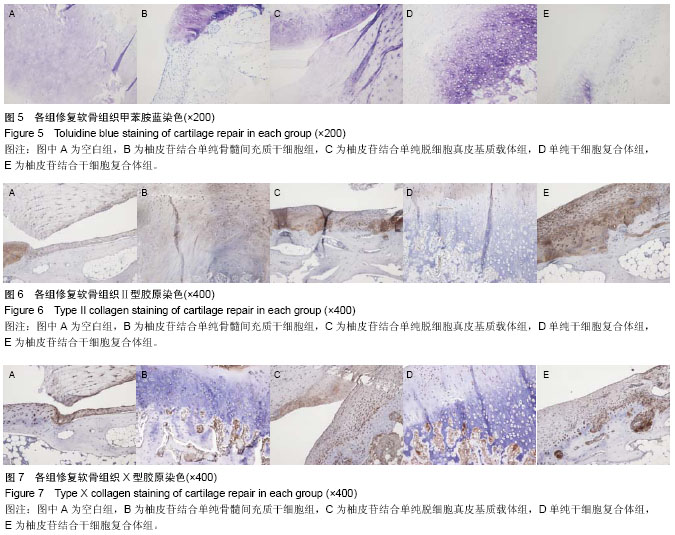
| [1] 杨渊,李小峰,罗道明,等.柚皮甙诱导骨髓间充质干细胞修复兔股骨头坏死[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(49):9232-9235.
[2] 刘伟,赵劲民,苏伟,等.柚皮苷对兔骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞的影响[J].江苏医药,2011,37(14):1632-1636.
[3] Leo AJ, Grande DA.Mesenchymal stem cells in tissue engineering.Cells Tissues Organs. 2006;183(3):112-122.
[4] Meirelles Lda S, Fontes AM, Covas DT,et al.Mechanisms involved in the therapeutic properties of mesenchymal stem cells.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20(5-6):419-427.
[5] de Peppo GM, Sjovall P, Lennerås M,et al.Osteogenic potential of human mesenchymal stem cells and human embryonic stem cell-derived mesodermal progenitors: a tissue engineering perspective.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010; 16(11):3413-3426.
[6] Jaiswal N, Haynesworth SE, Caplan AI,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of purified, culture-expanded human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.J Cell Biochem. 1997;64(2): 295-312.
[7] 俞猛,于方,付胜良.兔骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养定向诱导分化为软骨细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(27): 4951-4954.
[8] 庾佳佳,汪新柱,赵琳,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养及成骨诱导[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(6):974-979.
[9] Harvanová D, Tóthová T, Sarišský M,et al.Isolation and characterization of synovial mesenchymal stem cells.Folia Biol (Praha). 2011;57(3):119-124.
[10] Temenoff JS, Mikos AG.Review: tissue engineering for regeneration of articular cartilage.Biomaterials. 2000;21(5): 431-440.
[11] Mahmoudifar N, Doran PM.Chondrogenesis and cartilage tissue engineering: the longer road to technology development.Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(3):166-176.
[12] 李运涛,程科,胡德志,等.柚皮苷对经TNF-α诱导体外培养兔关节软骨细胞增殖及SOD NOS影响[J].辽宁中医药大学学报, 2008, 10(5):175-177.
[13] 金连峰,韩煜.骨碎补对兔膝骨关节炎关节软骨细胞凋亡相关因子作用实验研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2013,15(11):42-46.
[14] 邓展生,张璇,邹冬青,等.骨碎补有效成分柚皮甙对人骨髓间充质干细胞的影响[J].湘南学院学报:自然科学版,2005,7(4):5-7.
[15] 高晓珺,解骏,肖涟波,等.骨碎补总黄酮对胶原诱导大鼠类风湿关节炎骨破坏治疗作用的实验研究[J].实用临床医药杂志,2013, 17(5):13-17.
[16] 高华利,肖涟波,张子峰,等. 骨碎补总黄酮对胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠关节骨破坏影响的实验研究[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(9): 764-767.
[17] 杨渊,李小峰,罗道明,等.柚皮甙诱导骨髓间充质干细胞修复兔股骨头坏死[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(49):9232-9235.
[18] 郝增涛,冯卫,郝廷,等. BMSCs 来源成骨细胞和内皮细胞复合壳聚糖-羟基磷灰石多孔支架构建血管化组织工程骨研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(4):489-494.
[19] 詹兴旺,韦曙东,姜艳,等. 胶原-壳聚糖支架与软骨细胞的生长[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(38):7090-7094.
[20] 初殿伟,王玮,陈立军,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞/壳聚糖-胶原支架复合体构建软骨组织工程支架[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(42):8248-8252.
[21] 韩爽,卢世璧,刘强,等.自体脂肪间充质干细胞复合人脐带 Wharton胶支架修复兔膝关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(19):3496-3501.
[22] 韦益毅.不同生物材料复合支架对关节软骨缺损的修复评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(25):4723-4725.
[23] 张文林,刘丹平.软骨组织工程载体材料的研究与进展.中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(12):2329-2332.
[24] Qing C, Wei-ding C, Wei-min F.Co-culture of chondrocytes and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro enhances the expression of cartilaginous extracellular matrix components.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2011;44(4):303-310.
[25] Hildner F, Concaro S, Peterbauer A,et al.Human adipose-derived stem cells contribute to chondrogenesis in coculture with human articular chondrocytes.Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(12):3961-3969. |