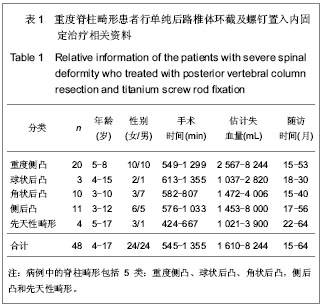
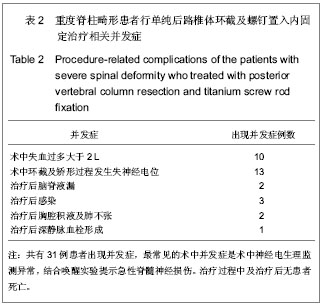
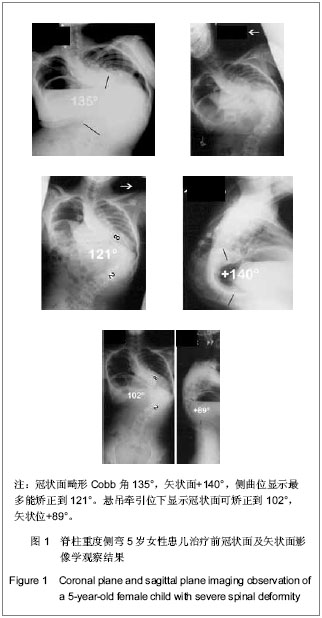
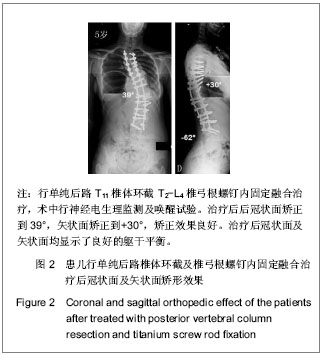
| [1] Dick J, Boachie-Adjei O, Wilson M. One-stage versus two-stage anterior and posterior spinal reconstruction in adults. Comparison of outcomes including nutritional status, complication rates, hospital costs, and other factors . Spine. 1992; 17: 310-316 .
[2] Johnson JR, Holt RT. Combined use of anterior and posterior surgery for adult scoliosis. Orthop Clin North Am. 1988;19: 361-370.
[3] Leatherman KD , Dickson RA . Two-stage corrective surgery for congenital deformities of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979;61:324-328 .
[4] Leatherman KD. The management of rigid spinal curves. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973;93:215-224.
[5] Bradford DS. Vertebral column resection. Printed abstract from the Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons Annual Meeting. Orthop Trans. 1987;11:502.
[6] Boachie-Adjei O, Bradford DS. Vertebral column resection and arthrodesis for complex spinal deformities. J Spinal Disord. 1991;4:193-202 .
[7] Suk SI, Chung ER, Lee SM, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection in fi xed lumbosacral deformity. Spine. 2005; 30: E703-E710.
[8] Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim WJ, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe spinal deformity. Spine. 2002;27:2374- 2382 .
[9] Suk SI, Chung ER, Kim JH, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe rigid scoliosis. Spine. 2005;30:1682-1687 .
[10] Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine. Is it safe? Spine. 2004; 29:333-342.
[11] Bradford DS, Tribus CB. Vertebral column resection for the treatment of rigid coronal decompensation. Spine. 1997;22: 1590-1599.
[12] Lenke LG, O’Leary PT, Bridwell KH, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection (VCR) for severe pediatric deformity: Minimum 2-year follow-up of 35 consecutive patients. Spine . 2009; 34:2213-2221.
[13] Lenke LG, Sides BA, Koester LA, et al. Vertebral column resection for the treatment of severe spinal deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:687- 699.
[14] Powers A , O’Shaughnessy BA , Lenke LG . Posterior thoracic vertebral column resection. In: Wang JC, ed. Advanced Reconstruction: Spine . Instructional Course Lecture 58: North American Spine Society, Rosemont, IL: AAOS; 2011;58: 265-275.
[15] Dorward I, Lenke LG. Osteotomies in the posterior-only treatment of complex adult spinal deformity: a comparative review. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;28:E4.
[16] Giampietro PF, Blank RD, Raggio CL, et al. Congenital and idiopathic scoliosis: clinical and genetic aspects. Clin Med Res. 2003;1(2):125-136.
[17] Winter RB, Moe JH, Lonstein JE. Posterior spinal arthrodesis for congenital scoliosis. An analysis of the cases of two hundred and ninety patients, five to nineteen years old. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(8):1188-1197.
[18] Lazar RD, Hall JE. Simultaneous anterior and posterior hemivertebra excision. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(364):76-84.
[19] Mcmaster MJ, David CV. Hemivertebra as a cause of scoliosis. A study of 104 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986; 68(4):588-595.
[20] Kesling KL, Lonstein JE, Denis F, et al. The crankshaft phenomenon after posterior spinal arthrodesis for congenital scoliosis: a review of 54 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003; 28(3):267-271.
[21] Uzumcugil A, Cil A, Yazici M, et al. Convex growth arrest in the treatment of congenital spinal deformities, revisited. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24(6):658-666.
[22] Hosseinpour-Feizi H, Soleimanpour J, Sales JG, et al. Lenke and King classification systems for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: interobserver agreement and postoperative results. Int J Gen Med. 2011;4:821-825.
[23] Cho KJ , Bridwell KH , Lenke LG, et al. Comparison of Smith-Petersen versus pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the correction of fixed sagittal imbalance. Spine. 2005; 30: 2030- 2037.
[24] Mcmaster MJ, Ohtsuka K. The natural history of congenital scoliosis. A study of two hundred and fifty-one patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(8): 1128-1147.
[25] Shufflebarger HL, Clark CE. Prevention of the crankshaft phenomenon. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1991;16(8 Suppl): S409-S411.
[26] Perdriolle R, Vidal J. Thoracic idiopathic scoliosis curve evolution and prognosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1985;10(9): 785-791.
[27] O'Leary PT, Sturm PF, Hammerberg KW, et al. Convex hemiepiphysiodesis: the limits of vertebral stapling. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(19):1579-1583.
[28] Thompson AG, Marks DS, Sayampanathan SR, et al. Long-term results of combined anterior and posterior convex epiphysiodesis for congenital scoliosis due to hemivertebrae. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(12):1380-1385.
[29] Thomasen E . Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis . Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;194: 142-152 .
[30] Winter RB, Lonstein JE, Denis F, et al. Convex growth arrest for progressive congenital scoliosis due to hemivertebrae. J Pediatr Orthop. 1988;8(6):633-638.
[31] Yaszay B, O'Brien M, Shufflebarger HL, et al. Efficacy of hemivertebra resection for congenital scoliosis: a multicenter retrospective comparison of three surgical techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(24):2052-2060.
[32] Jalanko T, Rintala R, Puisto V, et al. Hemivertebra resection for congenital scoliosis in young children: comparison of clinical, radiographic, and health-related quality of life outcomes between the anteroposterior and posterolateral approaches. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(1):41-49.
[33] Dimeglio A. Growth in pediatric orthopaedics. J Pediatr Orthop. 2001;21(4): 549-555.
[34] Ruf M, Harms J. Posterior hemivertebra resection with transpedicular instrumentation: early correction in children aged 1 to 6 years. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(18):2132- 2138.
[35] Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee SM, et al. Thoracic pedicle screw fi xation in spinal deformities: are they really safe ? Spine. 2001; 26:2049-2057 .
[36] Xu W, Yang S, Wu X, et al. Hemivertebra excision with short-segment spinal fusion through combined anterior and posterior approaches for congenital spinal deformities in children. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2010;19(6):545-550.
[37] Smith JT, Gollogly S, Dunn HK. Simultaneous anterior-posterior approach through a costotransversectomy for the treatment of congenital kyphosis and acquired kyphoscoliotic deformities. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(10):2281-2289.
[38] Mladenov K, Kunkel P, Stuecker R. Hemivertebra resection in children, results after single posterior approach and after combined anterior and posterior approach: a comparative study. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(3):506-513.
[39] Mehlman CT, Araghi A, Roy DR. Hyphenated history: the Hueter-Volkmann law. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 1997; 26(11):798-800.
[40] Kioschos HC, Asher MA, Lark RG, et al. Overpowering the crankshaft mechanism. The effect of posterior spinal fusion with and without stiff transpedicular fixation on anterior spinal column growth in immature canines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(10):1168-1173.
[41] Aydogan M, Ozturk C, Tezer M, et al. Posterior vertebrectomy in kyphosis, scoliosis and kyphoscoliosis due to hemivertebra. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2008;17(1): 33-37.
[42] Ruf M, Jensen R, Letko L, et al. Hemivertebra resection and osteotomies in congenital spine deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(17):1791-1799. |