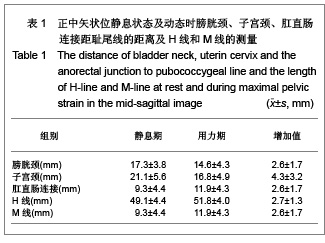
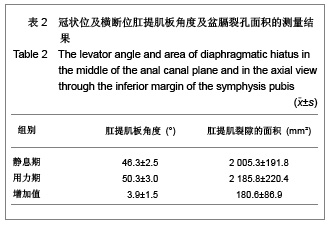
| [1] Boyadzhyan L,Raman SS,Raz S.Role of Static and Dynamic MR Imaging in Surgical Pelvic Floor Dysfunction.Radio Graphics. 2008;28(4):949-967.[2] Yang LL.Guowai Yixue: Fuchan Kexue Fence.2007; 34(2): 114-117. 杨玲玲.盆腔器官脱垂评估方法及特点分析[J].国外医学:妇产科学分册,2007, 34(2):114-117.[3] Yang X,Wang JL.Zhongguo Fuchan Kelin Chuangza Zhi.2007; 8(1):3-4. 杨欣,王建六. 盆腔器官脱垂治疗进展[J].中国妇产科临床杂志, 2007,8(1):3-4.[4] Handa VL,Lockhart ME,Kenton KS,et al.Magnetic Resonance Assessment of Pelvic Anatomy and Pelvic Floor Disorders after Childbirth.Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct.2009; 20(2):133-139.[5] Pannu HK.Dynamic MR imaging of female organ prolapse. Radiol Clin North Am. 2003;41(2):409-423.[6] Fielding JR,Dumanli H,Schreyer AG,et al.MR-based three-dimentional modeling of the normal pelvic floor.AJR. 2000;174(3):657-660.[7] Bump RC,Mattiasson A,Bo K,et al.The standardization of terminology of female pelvic organ prolapse and pelvic floor dysfunction. Am J Obstet Gynecol.1996; 175(1):10-17.[8] Larson KA,Hsu Y,Chen LY,et al.Magnetic resonance imaging-based three-dimensi-onal model of anterior vaginal wall position at rest and maximal strain in women with and without prolapse.Int Urogynecol J.2010;21(9): 1103-1109.[9] Bump RC, Mattiasson A, Bo K, et al. The standardization of terminology of female pelvic organ prolapse and pelvic floor dysfunction. Am J Obstet Gynecol.1996;175(1):10-17.[10] Yang A,Mostwin JL,Rosenshein NB,et al. Pelvic floor descent in women: Dymanic evaluation with fast MR imaging and cinematic display.Radiology.1991;179(1):25-33.[11] Wang Y,Gong SG,Zhang WG,et al.Disan Junyi Daxue Xunbao. 2004;6(12):1055-1057. 王毅,龚水根,张伟国,等.女性正常盆底与盆底脱垂性疾病MRI初步研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2004,6(12):1055-1057.[12] Ke GZ,Song YF.Zhongguo Fuyou Jiankang Yanjiu.2007;18(4): 316-317. 柯桂珠,宋岩峰.核磁共振在女性盆底功能障碍中的研究进展[J],中国妇幼健康研究,2007,18(4):316-317.[13] Yang X,Wang JL.Zhongguo Fuchan Kelin Chuangza Zhi. 2007;8(1):3-4. 杨欣,王建六.盆腔器官脱垂治疗进展[J].中国妇产科临床杂志, 2007,8(1):3-4.[14] Julia R F.Practical MR.Imaging of female pelvic floor weakness.Radio Graphics.2002;22:295-304.[15] Pannu HK.MRI of pelvic organ prolapse.Eur Radial.2004; 14(8):1456-1464.[16] Li GH,Tao T.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2009;13(16):3173-3176. 李光华,陶涛.生物补片在妇产科临床中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(16):3173-3176.[17] Zhao YH,Hu JP.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2010;14(16):2949-2952. 赵永红,胡金萍.盆底重建替代材料生物补片在妇产科临床中的应用特点[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(16): 2949-2952.[18] Cao XL,Xu HC,Liang ZQ,et al.Shiyong Fuchan Keza Zhi.2011;27(3):228-230. 曹晓兰,徐惠成,梁志清,等.盆底功能障碍性疾病盆底解剖学静动态磁共振成像研究[J].实用妇产科杂志,2011,27(3):228-230.[19] Gao X,Wang WY,You H,et al.Cigong Zhencheng Xiang.2010; 1(3):204-207. 高鑫,王文艳,有慧,等.动态MRI评价女性盆腔器官脱垂的初步研究[J].磁共振成像, 2010,1(3):204-207.[20] Li M,Jiang T.Yixue Zongshu.2010;16(11):1718-1721. 李敏,蒋涛.静态动态磁共振在盆底功能障碍性疾病中的应用[J].医学综述, 2010,16(11):1718-1721.[21] Wodfiel CA,Krishnamoorthy S,Hampton BS,et al.Imaging Pelvic Floor Disorders: Trend Toward Comprehensive MRI. CAJR.2010;194:1640-1649.[22] Wang Y,Gong SG,Zhang WG,Zhongguo Yixue Yingxiang Jishu.2003;19(12):1711-1714. 王毅,龚水根,张伟国,等,正常女性盆底解剖形态的动态MR研究[J].中国医学影像技术,2003,19(12):1711-1714.[23] Siegmann KC, Reisenauer C, Speck S, et al.Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging for assessment of minimally invasive pelvic floor reconstruction with polypropylene implant. Eur J Radiol. 2011;80(2):182-187. [24] Luo X.Zhongguo Shiyong Fuke yu Chanke Zazhi.2006;22(1): 78-80.罗新.女性盆底解剖结构的新概念[J].中国实用妇科与产科杂志. 2006;22(1):78-80.[25] Colaiacomo MC,Masselli G,Polettini E,e t al.Dynamic MR Imaging of the Pelvic Floor:a Pictorial Review. Radiographics. 2009;29(3):e35. |