[1] 张瀚月,马璐,孔振兴,等.2016—2020年我国学生超重、肥胖和营养不良状况的流行趋势与防控策略[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2023,46(11):118-131.
[2] LOB-CORZILIUS T. Overweight and obesity in childhood – A special challenge for public health. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2007; 210(5):585-589.
[3] DI CESARE M, SORIĆ M, BOVET P, et al. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: a worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med. 2019;17(1):212.
[4] 王军利,项立敏,张松奎,等.儿童青少年超重与肥胖的成因及社会网络干预[J].上海体育学院学报,2019,43(5):30-40.
[5] 蒋露芳,王莹莹,彭慧,等.学龄儿童肥胖与肠道菌群多样性及菌属丰度的关联研究[J].中华流行病学杂志,2022,43(2): 260-268.
[6] KOYUNCUOĞLU GÜNGÖR N. Overweight and obesity in children and adolescents. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2014;6(3):129-143.
[7] LEE EY, YOON KH. Epidemic obesity in children and adolescents: risk factors and prevention. Front Med. 2018;12(6):658-666.
[8] MAINIERI F, LA BELLA S, CHIARELLI F. Hyperlipidemia and cardiovascular risk in children and adolescents. Biomedicines. 2023;11(3):809.
[9] CAHILL PA, REDMOND EM. Vascular endothelium – gatekeeper of vessel health. Atherosclerosis. 2016;248:97-109.
[10] ALEXANDER Y, OSTO E, SCHMIDT-TRUCKSÄSS A, et al. Endothelial function in cardiovascular medicine: a consensus paper of the european society of cardiology working groups on atherosclerosis and vascular biology, aorta and peripheral vascular diseases, coronary pathophysiology and microcirculation, and thrombosis. Cardiovasc Res. 2021;117(1):29-42.
[11] GODO S, SHIMOKAWA H. Endothelial functions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017;37(9):e108-e114.
[12] STANHEWICZ AE, WENNER MM, STACHENFELD NS. Sex differences in endothelial function important to vascular health and overall cardiovascular disease risk across the lifespan. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018;315(6):H1569-H1588.
[13] JOO TURONI C, MARAÑÓN RO, FELIPE V,et al. Arterial stiffness and endothelial function in obese children and adolescents and its relationship with cardiovascular risk factors. Horm Res Paediatr. 2013;80(4):281-286.
[14] VINCZE M, DÉR H, KEREKES GY, et al. Decreased flow-mediated dilatation with increased arterial stiffness and thickness as early signs of atherosclerosis in polymyositis and dermatomyositis patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33(11):1635-1641.
[15] LO MH, LIN IC, LU PC, et al. Evaluation of endothelial dysfunction, endothelial plasma markers, and traditional metabolic parameters in children with adiposity. J Formos Med Assoc. 2019;118(1):83-91.
[16] HILL MA, YANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Insulin resistance, cardiovascular stiffening and cardiovascular disease. Metabolism. 2021; 119:154766.
[17] ZHANG X, GAO F. Exercise improves vascular health: Role of mitochondria . Free Radic Biol Med, 2021;177:347-359.
[18] GREEN DJ, THOMAS HJ, MARSH CE, et al.Impact of resistance and endurance exercise training on femoral artery function: sex differences in humans. J Physiol. 2025; 603(5):1045-1056.
[19] OTSUKI T, NAKAMURA F, ZEMPO-MIYAKI A. Nitric oxide and decreases in resistance exercise blood pressure with aerobic exercise training in older individuals. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1204.
[20] TSUKIYAMA Y, ITO T, NAGAOKA K, et al. Effects of exercise training on nitric oxide, blood pressure and antioxidant enzymes. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2017;60(3):180-186.
[21] EL ASSAR M, ÁLVAREZ-BUSTOS A, SOSA P, et al. Effect of Physical Activity/Exercise on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Muscle and Vascular Aging. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8713.
[22] PIERCE D R, DOMA K, RAIFF H, et al. Influence of exercise mode on post-exercise arterial stiffness and pressure wave measures in healthy adult males. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1468.
[23] KIM HB, SEO MW, JUNG HC. Effects of aerobic vs. Resistance exercise on vascular function and vascular endothelial growth factor in older women. Healthcare. 2023; 11(18):2479.
[24] DALL CH, GUSTAFSSON F, CHRISTENSEN SB, et al. Effect of moderate- versus high-intensity exercise on vascular function, biomarkers and quality of life in heart transplant recipients: a randomized, crossover trial. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015;34(8):1033-1041.
[25] BOIDIN M, ERSKINE RM, THIJSSEN DHJ, et al. Exercise modality, but not exercise training, alters the acute effect of exercise on endothelial function in healthy men. J Appl Physiol. 2021;130(6): 1716-1723.
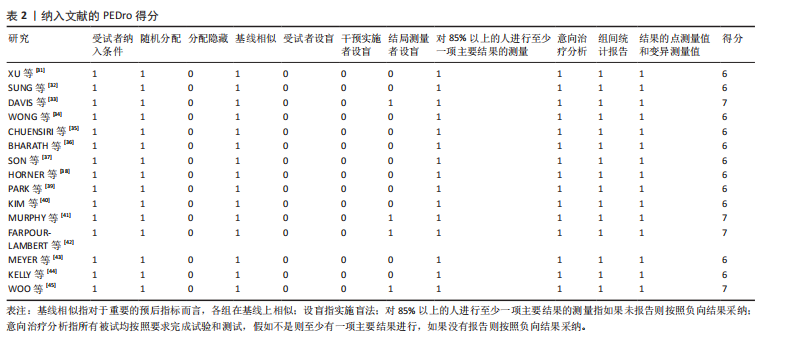
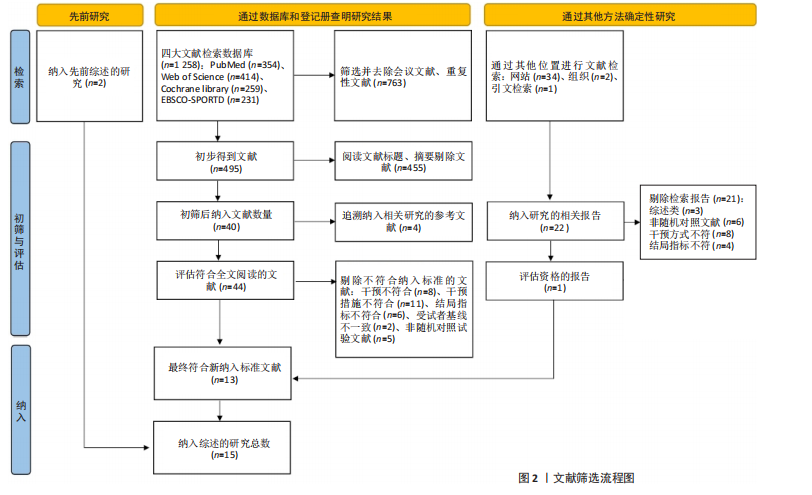
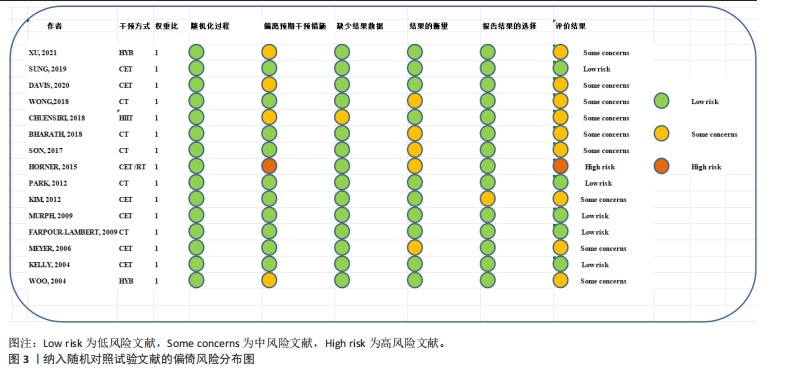
[26] CUMPSTON M, LI T, PAGE MJ, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;10(10):ED000142.
[27] FARRAH K, YOUNG K, TUNIS MC, et al. Risk of bias tools in systematic reviews of health interventions: an analysis of PROSPERO-registered protocols. Syst Rev, 2019;8(1):280.
[28] FATTAL R. Blue-noise point sampling using kernel density model//ACM SIGGRAPH 2011 papers. Vancouver British Columbia Canada: ACM, 2011:1-12.
[29] GABRY J, SIMPSON D, VEHTARI A, et al. Visualization in bayesian workflow. J R Stat Soc Ser A Stat Soc. 2019;182(2):389-402.
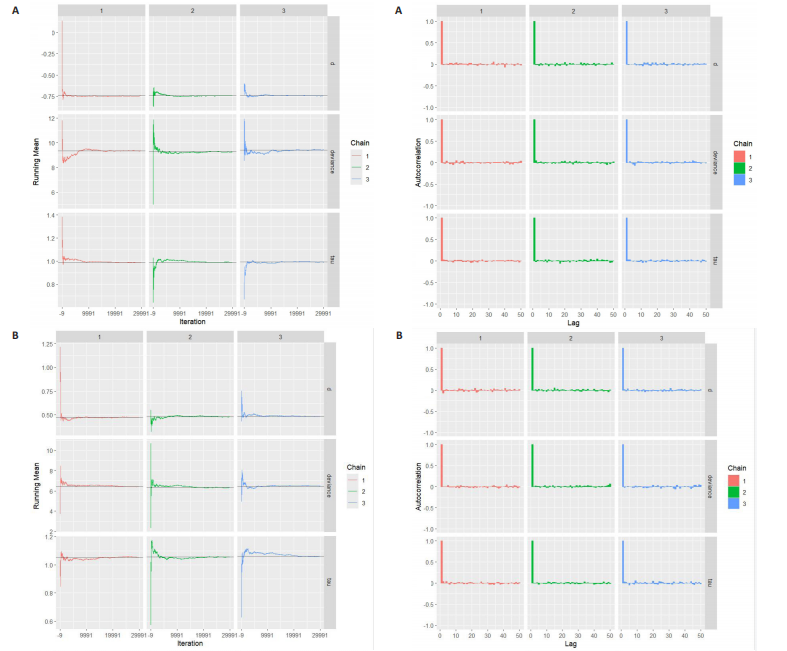
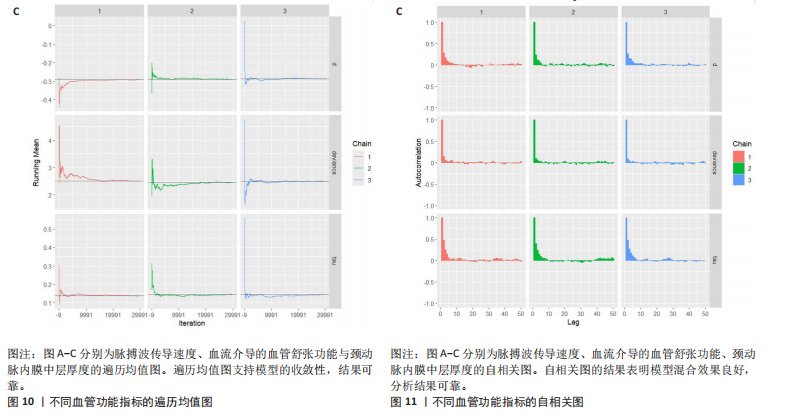
[30] DU H, KE Z, JIANG G, et al. The performances of gelman-rubin and geweke’s convergence diagnostics of monte carlo markov chains in bayesian analysis. J Behav Data Sci. 2022; 2(2):47-72.
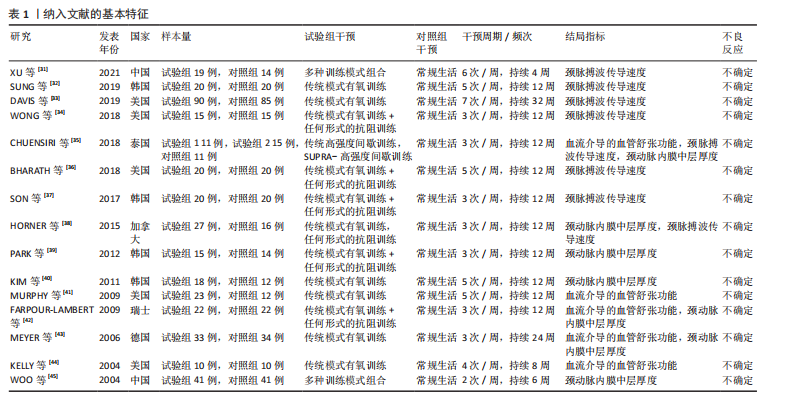
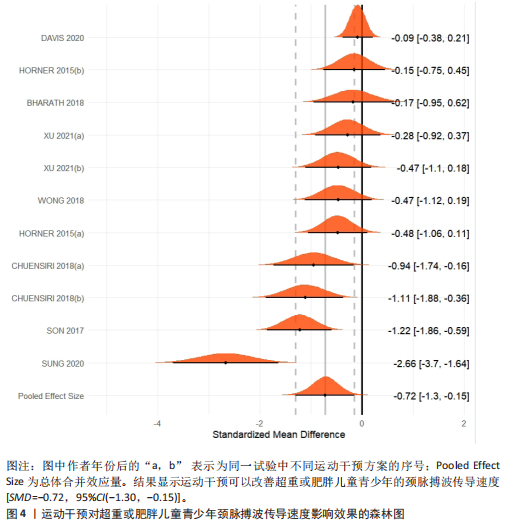
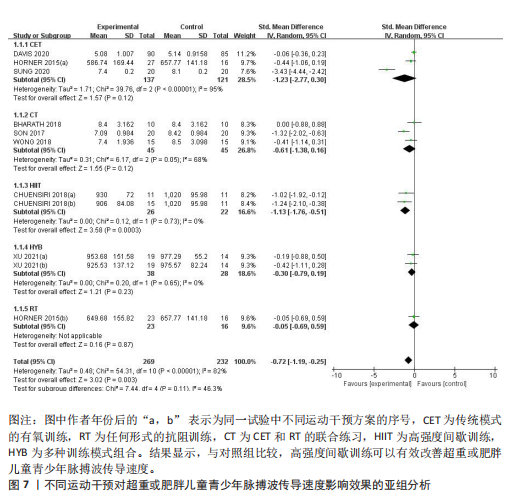
[31] XU L, ZOU X, GAO Z, et al. Improved fatty acid profile reduces body fat and arterial stiffness in obese adolescents upon combinatorial intervention with exercise and dietary restriction. J Exerc Sci Fitness. 2021;19(4):234-240.
[32] SUNG KD, PEKAS EJ, SCOTT SD, et al. The effects of a 12-week jump rope exercise program on abdominal adiposity, vasoactive substances, inflammation, and vascular function in adolescent girls with prehypertension. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019;119(2):577-585.
[33] DAVIS CL, LITWIN SE, POLLOCK NK, et al.Exercise effects on arterial stiffness and heart health in children with excess weight: the SMART RCT. Int J Obes (Lond). 2019;44(5):1152.
[34] WONG A, SANCHEZ-GONZALEZ MA, SON WM, et al. The Effects of a 12-Week Combined Exercise Training Program on Arterial Stiffness, Vasoactive Substances, Inflammatory Markers, Metabolic Profile, and Body Composition in Obese Adolescent Girls. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2018;30(4):480-486.
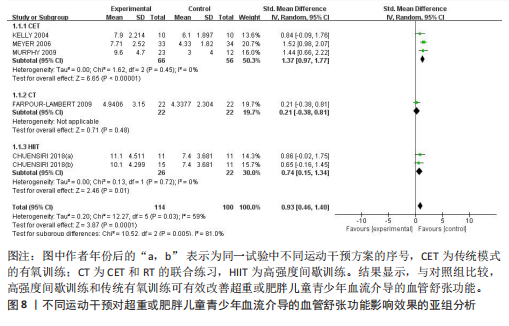
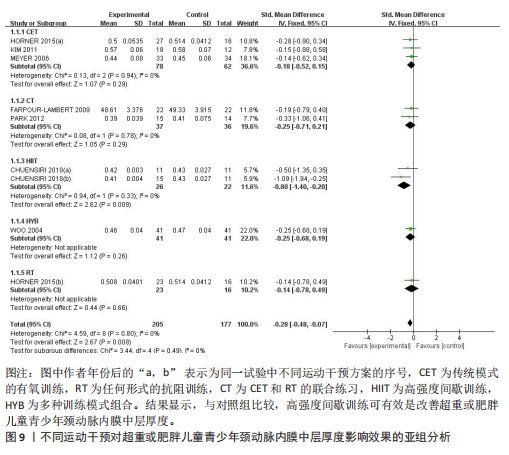
[35] CHUENSIRI N, SUKSOM D, TANAKA H. Effects of High-Intensity Intermittent Training on Vascular Function in Obese Preadolescent Boys. Child Obes. 2018;14(1):41-49.
[36] BHARATH LP, CHOI WW, CHO JM, et al. Combined resistance and aerobic exercise training reduces insulin resistance and central adiposity in adolescent girls who are obese: randomized clinical trial. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018;118(8):1653-1660.
[37] SON WM, SUNG KD, BHARATH LP, et al. Combined exercise training reduces blood pressure, arterial stiffness, and insulin resistance in obese prehypertensive adolescent girls. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2017; 39(6):546-552.
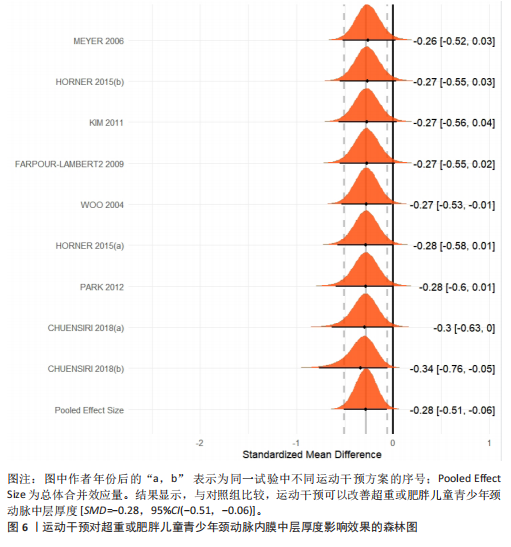
[38] HORNER K, BARINAS-MITCHELL E, DEGROFF C, et al. Effect of aerobic versus resistance exercise on pulse wave velocity, intima media thickness and left ventricular mass in obese adolescents. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2015;27(4):494-502.
[39] PARK JH, MIYASHITA M, KWON YC, et al. A 12-week after-school physical activity programme improves endothelial cell function in overweight and obese children: a randomised controlled study. BMC Pediatr. 2012;12:111.
[40] KIM JY, KIM ES, JEON JY, et al. Improved Insulin Resistance, Adiponectin and Liver Enzymes without Change in Plasma Vaspin Level after 12 Weeks of Exercise Training among Obese Male Adolescents. Korean J Obes. 2011;20(3):138.
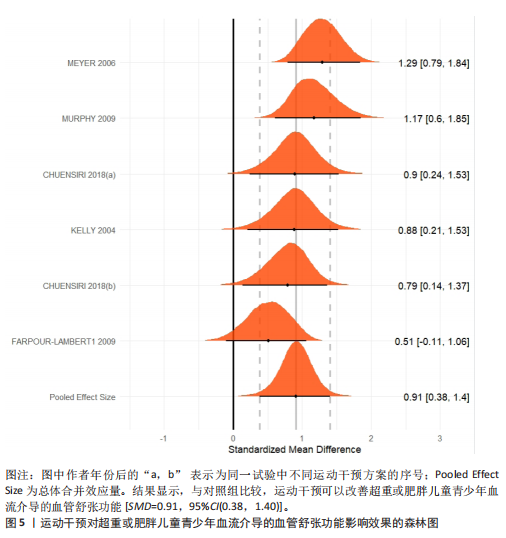
[41] MURPHY ECS, CARSON L, NEAL W, et al. Effects of an exercise intervention using Dance Dance Revolution on endothelial function and other risk factors in overweight children. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2009;4(4):205-214.
[42] FARPOUR-LAMBERT NJ, AGGOUN Y, MARCHAND LM, et al. Physical activity reduces systemic blood pressure and improves early markers of atherosclerosis in pre-pubertal obese children. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;4(25):2396-2406.
[43] MEYER AA, KUNDT G, LENSCHOW U, et al. Improvement of early vascular changes and cardiovascular risk factors in obese children after a six-month exercise program. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48(9):1865-1870.
[44] KELLY AS, WETZSTEON RJ, KAISER DR, et al.Inflammation, insulin, and endothelial function in overweight children and adolescents: the role of exercise. J Pediatr. 2004;145(6):731-736.
[45] WOO KS, CHOOK P, YU CW, et al. Effects of diet and exercise on obesity-related vascular dysfunction in children. Circulation. 2004;109(16):1981-1986.
[46] COLLINS AR, LYON CJ, XIA X, et al. Age-accelerated atherosclerosis correlates with failure to upregulate antioxidant genes. Circ Res. 2009;104(6):e42-e54.
[47] CERCATO C, FONSECA FA. Cardiovascular risk and obesity. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2019;11(1):74.
[48] GU C, YAN J, ZHAO L, et al. Regulation of mitochondrial dynamics by aerobic exercise in cardiovascular diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;8:788505.
[49] PINCKARD K, BASKIN KK, STANFORD KI. Effects of exercise to improve cardiovascular health. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019;6:69.
[50] XIAO H, PENG K, SUN L, et al. Effects of anaerobic exercise training on human function based on multiple linear regression. Front Phys. 2023;11:1168765.
[51] SCHJERVE IE, TYLDUM GA, TJØNNA AE, et al. Both aerobic endurance and strength training programmes improve cardiovascular health in obese adults. Clin Sci. 2008;115(9):283-293.
[52] BRAGA VA, COUTO GK, LAZZARIN MC, et al. Aerobic exercise training prevents the onset of endothelial dysfunction via increased nitric oxide bioavailability and reduced reactive oxygen species in an experimental model of menopause. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0125388.
[53] KOZAKOVA M, PALOMBO C. Vascular Ageing and Aerobic Exercise. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(20):10666.
[54] SHIMIZU R, HOTTA K, YAMAMOTO S, et al.Low-intensity resistance training with blood flow restriction improves vascular endothelial function and peripheral blood circulation in healthy elderly people. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016;116(4):749-757.
[55] DELGADO-FLOODY P, IZQUIERDO M, RAMÍREZ-VÉLEZ R, et al. Effect of high-intensity interval training on body composition, cardiorespiratory fitness, blood pressure, and substrate utilization during exercise among prehypertensive and hypertensive patients with excessive adiposity. Front Physiol. 2020;11:558910.
[56] DA SILVA MR, WACLAWOVSKY G, PERIN L,et al. Effects of high-intensity interval training on endothelial function, lipid profile, body composition and physical fitness in normal-weight and overweight-obese adolescents: a clinical trial. Physiol Behav. 2020;213:112728.
[57] PEDRALLI ML, MARSCHNER RA, KOLLET DP, et al. Different exercise training modalities produce similar endothelial function improvements in individuals with prehypertension or hypertension: a randomized clinical trial. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):7628.
[58] OTSUKI T, NAMATAME H, YOSHIKAWA T, et al. Combined aerobic and low-intensity resistance exercise training increases basal nitric oxide production and decreases arterial stiffness in healthy older adults. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020;66(1):62-66.
[59] ASHOR AW, LARA J, SIERVO M, et al. Effects of exercise modalities on arterial stiffness and wave reflection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e110034.
[60] LI Y, HANSSEN H, CORDES M, et al. Aerobic, resistance and combined exercise training on arterial stiffness in normotensive and hypertensive adults: a review. Eur J Sport Sci. 2015;15(5):443-457.
[61] SARDELI AV, GÁSPARI AF, CHACON-MIKAHIL MP. Acute, short-, and long-term effects of different types of exercise in central arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis . J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2018;58(6):923-932.
[62] BATRAKOULIS A, JAMURTAS AZ, DRAGANIDIS D, et al. Hybrid neuromuscular training improves cardiometabolic health and alters redox status in inactive overweight and obese women: a randomized controlled trial. Antioxidants. 2021;10(10):1601.
|