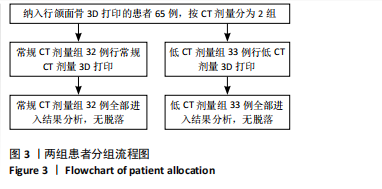
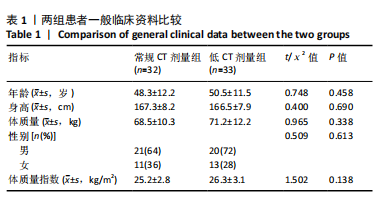
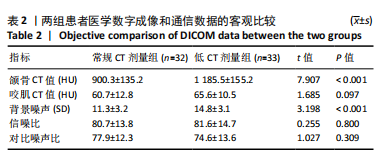
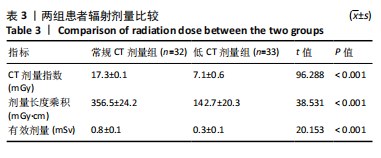
[1] WANG H, CHI Y, HUANG H, et al. Combined use of 3D printing and computer-assisted navigation in the clinical treatment of multiplemaxillofacial fractures. Asian J Surg. 2023;46(6):2284-2292.
[2] 何雪锋, 熊爱兵. 3D打印技术在整形外科的研究及应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(3):428-432.
[3] QIN HL, WEI YM, HAN JY, et al. 3D printed bioceramic scaffolds: Adjusting pore dimension is beneficial for mandibular bone defects repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;16(4):409-421.
[4] GOETZE E, ZELLER AN, PABST A. Approaching 3D printing in oral and maxillofacial surgery-suggestions for structured clinical standards. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024;28(2):795-802.
[5] WANG H, CHI Y, HUANG H, et al. Combined use of 3D printing and computer-assisted navigation in the clinical treatment of multiple maxillofacial fractures. Asian J Surg. 2023;46(6):2284-2292.
[6] LIU Z, ZHONG Y, LYU X, et al. Accuracy of the modified tooth-supported 3D printing surgical guides based on CT, CBCT, and intraoral scanning in maxillofacial region: A comparison study. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024;125(5S2):101853.
[7] MATTEO M, ADRIEN N, GUIDO MM, et al. 3D printed bone models in oral and cranio-maxillofacial surgery: a systematic review. 3D Print Med. 2020;6(1): 30.
[8] 郑坤, 许苑晶, 于文强, 等. 3D打印医工结合门诊在数字医学临床实践教学中的应用 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(15):2317-2322.
[9] HAN JJ, SODNOM-ISH B, EO MY, et al. Accurate mandible reconstruction by mixed reality, 3D printing, and robotic-assisted navigation integration. J Craniofac Surg. 2022;33(6):e701-e706.
[10] TAHERI OTAGHSARA SS, JODA T, THIERINGER FM. Accuracy of dental implant placement using static versus dynamic computer-assisted implant surgery: An in vitro study. J Dent. 2023;132:104487.
[11] HUANG YH, LEE B, CHUY JA, et al. 3D printing for surgical planning of canine oral and maxillofacial surgeries. 3D Print Med. 2022;8(1):17.
[12] GAO L, SUN M, LIU J, et al. Study on mechanical properties of dual-channel cryogenic 3D printing scaffold for mandibular defect repair. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024;62(8):2435-2448.
[13] ANTUNES D, MAYEUR O, MAUPRIVEZ C, et al. 3D-printed model for gingival flap surgery simulation: Development and pilot test. Eur J Dent Educ. 2024;28(2):698-706.
[14] JEDRZEJEK M, PESZEK-PRZYBYLA E, JADCZYK T, et al. 3D printing from transesophageal echocardiography for planning mitral paravalvular leak closure - feasibility study. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2023; 19(3):270-276.
[15] QUEIROZ-FONTES R, RIBEIRO P, NUNES T, et al. 3D printing and CBCT anatomical reproducibility assessment in forensic scenarios. J Forensic Leg Med. 2024;106:102719.
[16] WU W, LIU S, WANG L, et al. Application of 3D printing individualized guide plates in percutaneous needle biopsy of acetabular tumors. Front Genet. 2022;13:955643.
[17] PEKER OZTURK H, AYYILDIZ S. Comparison of different 3D printers in terms of dimensional stability by image data of a dry human mandible obtained from CBCT and CT. Int J Artif Organs. 2024;47(1):49-56.
[18] WANG L, CHEN XJ, LIANG JH, et al. Preliminary application of three-dimensional printing in congenital uterine anomalies based on three-dimensional transvaginal ultrasonographic data. BMC Womens Health. 2022;22(1):290.
[19] HAN MA, KIM JH. Diagnostic X-Ray Exposure and Thyroid Cancer Risk: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thyroid. 2018;28(2):220-228.
[20] ANSELMINO M, MARCANTONI L, AGRESTA A, et al. Interventional cardiology and X-ray exposure of the head: overview of clinical evidence and practical implications. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2022;23(6):353-358.
[21] GU Y, WANG J, WANG Y, et al. Association of low-dose ionising radiation wit site-specific solid cancers: Chinese medical X-ray workers cohort study, 1950-1995. Occup Environ Med. 2023;80(12):687-693.
[22] PEREZ JA, ROLDAN VS, GORDILLOordillo AK, et al. Mean glandular dose in the mammary gland and dose of radiation in the thyroid gland and lens in women with and without breast implants during different modalities of mammography. Radiologia (Engl Ed). 2022;64 Suppl 1: 11-19.
[23] ASMA’A AA, SARA AA, DANIA T, et al. Do Ultra-low multidetector computed tomography doses and iterative reconstruction techniques affect subjective classification of bone type at dental implant sites? Int J Prosthodont. 2018;31(5): 465-470.
[24] THONGVIGITMANEE SS, PONGNAPANG N, AOOTAPHAO S, et al. Radiation dose and accuracy analysis of newly developed cone-beam CT for dental and maxillofacial imaging. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013;2013:2356-2359.
[25] LI G, ZHANG L, LIU T, et al. Exploration of thoracoabdominalaortic mixed reality optimisation and its clinical application value in type A aortic dissection. Eur Radiol. 2023;33(6):4313-4322.
[26] BHANOT R, HAMEED ZBM, SHAH M, et al. ALARA in Urology: Steps to Minimise Radiation Exposure During All Parts of the Endourological Journey. Curr Urol Rep. 2022;23(10):255-259.
[27] LIPS M. ALARA in practice-4 decades of radiological protection at Goesgen NPP. J Radiol Prot. 2021;41(4). doi: 10.1088/1361-6498/ac1a82.
[28] HANNA P, MACIAS C, BUCH E. ALARA in Atrial Fibrillation: Redefining Ablation Success. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024;84(1):75-77.
[29] BAKER SI, KAMBOJ S. Applying ALARA Principles in the Design of New Radiological Facilities. Health Phys. 2022;122(3):452-462.
[30] YANG S, PU Q, LEI C, et al. Low-dose CT denoising with a high-level feature refinement and dynamic convolution network. Med Phys. 2023;50(6):3597-3611.
[31] NODA Y, KAGA T, KAWAI N, et al. Low-dose whole-body CT using deep learning image reconstruction: image quality and lesion detection. Br J Radiol. 2021;94(1121):20201329.
[32] GAN G, GONG W, JIA L, et al. Study of peripheral dose from low-dose CT to adaptive radiotherapy of postoperative prostate cancer.. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1227946.
[33] ARK S, YOON JH, JOO I, et al. Image quality in liver CT: low-dose deep learning vs standard-dose model-based iterative reconstructions. Eur Radiol. 2022;32(5):2865-2874.
[34] ZHANG J, SHANGGUAN Z, GONG W, et al. A novel denoising method for low-dose CT images based on transformer and CNN. Comput Biol Med. 2023;163:107162.
[35] LIU Y, WEI C, XU Q. Detector shifting and deep learning based ring artifact correction method for low-dose CT. Med Phys. 2023;50(7): 4308-4324.
[36] LI G, DONG J, CAO Z, et al. Application of low-dose CT to the creation of 3D-printed kidney and perinephric tissue models for laparoscopic nephrectomy. Cancer Med. 2021;10(9):3077-3084.
[37] LOIZOU L, ALBIIN N, LEIDNER B, et al. Multidetector CT of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Effect of tube voltage and iodine load on tumour conspicuity and image quality. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(11):4021-4029.
[38] LEE S, YOON SW, YOO SM, et al. Comparison of image quality and radiation dose between combined automatic tube current modulation and fixed tube current technique in CT of abdomen and pelvis. Acta Radiol. 2011;52(10):1101-1106.
[39] FAEZEH S, CECIL GW, RISHI A, et al. Feasibility of sub-second CT angiography of the abdomen and pelvis with very low volume of contrast media, low tube voltage, and high-pitch technique, on a third-generation dual-source CT scanner. Clin Imaging. 2022;82:15-20.
[40] WANG JJ, Chi XT, Wang WW, et al. Analysis of contrast-enhanced spectral chest CT optimal monochromatic imaging combined with ASIR and ASIR-V. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26(6):1930-1938.
[41] BIE Y, YANG S, LI X, et al. Impact of deep learning-based image reconstruction on image quality and lesion visibility in renal computed tomography at different doses. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023;13(4):2197-2207.
|