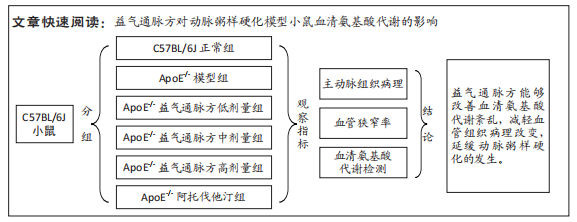
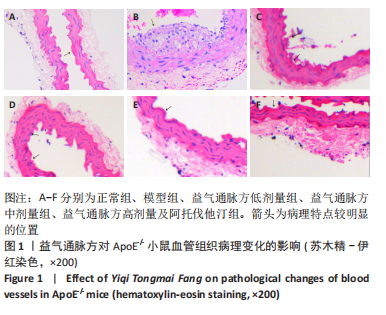
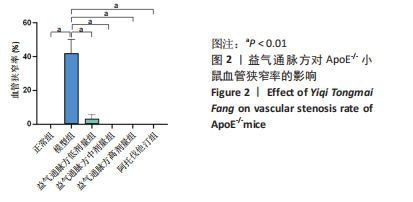
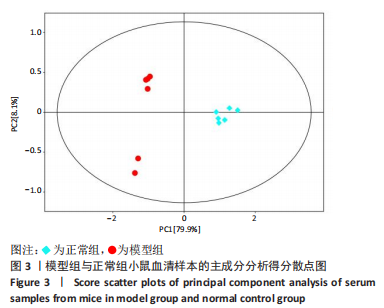
[1] PRASHER D, GREENWAY SC, SINGH RB. The impact of epigenetics on cardiovascular disease. Biochem Cell Biol. 2020;98(1):12-22.
[2] RAY S, SAWHNEY JPS, DAS MK, et al. Adaptation of 2016 European Society of Cardiology/ European Atherosclerosis Society guideline for lipid management to Indian patients –A consensus document. Indian Heart J. 2018;70(5):736-744.
[3] LI M, WANG X, LI X, et al. Statins for the Primary Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:4870350.
[4] DE JONG HJ, KLUNGEL OH, VAN DIJK L, et al. Use of statins is associated with an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; 71(5):648-654.
[5] PRASHER D, GREENWAY SC, SINGH RB. The impact of epigenetics on cardiovascular disease. Biochem Cell Biol. 2020;98(1):12-22.
[6] PAONE S, BAXTER AA, HULETT MD, et al. Endothelial cell apoptosis and the role of endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles in the progression of atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(6):1093-1106.
[7] WOLF D, LEY K. Immunity and Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2019;124(2):315-327.
[8] SAKAKURA K, NAKANO M, OTSUKA F, et al. Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis plaque progression. Heart Lung Circ. 2013;22(6):399-411.
[9] CHEN X, PANG S, LIN J, et al. Allicin prevents oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced endothelial cell injury by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016;16:133.
[10] YU XH, ZHANG DW, ZHENG XL, et al. Cholesterol transport system: An integrated cholesterol transport model involved in atherosclerosis. Prog Lipid Res. 2019;73:65-91.
[11] BONVALLOT N, TREMBLAY-FRANCO M, CHEVRIER C, et al. Potential input from metabolomics for exploring and understanding the links between environment and health. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2014;17(1):21-44.
[12] 张文涛,崔应麟,郑伟锋,等.康益胶囊联合常规治疗对缺血性中风急性期患者的临床疗效[J].中成药,2021,43(6):1676-1679.
[13] MEIR KS, LEITERSDORF E. Atherosclerosis in the apolipoprotein-Edefificient mouse: a decade of progress. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(6):1006-1014.
[14] 魏伟, 吴希美, 李元建. 药理实验方法学[M]. 4版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2010.
[15] WU M, YANG S, WANG S, et al. Effect of Berberine on Atherosclerosis and Gut Microbiota Modulation and Their Correlation in High-Fat Diet-Fed ApoE-/- Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:223.
[16] 李千会,葛卓望,田丁,等. 人参皂苷Rg1对心肌细胞缺氧/复氧损伤的保护作用及其机制研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2021,46(6):1460-1466.
[17] 叶劲涛,李锋涛,宋焕瑾,等.人参皂苷Rg1对氧糖剥夺/复氧复糖损伤PC12细胞的保护机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(7): 1090-1096.
[18] 聂忠富,孙小燕,张太平,等.人参皂苷Compound K对动脉粥样硬化大鼠氧化应激、炎症因子和血管活性物质的影响[J].河北中医,2019,41(7):1042-1047.
[19] 赵培,李永辉,高伟,等.三七总皂苷通过调节TLR4/SYK信号抑制ApoE 基因敲除小鼠动脉粥样硬化泡沫细胞的形成[J].天然产物研究与开发,2021,33(8):1267-1273.
[20] 江小萍,曾凡鹏,刘首明,等.三七总皂苷对动脉粥样硬化患者血管炎症因子及颈动脉内膜中层厚度和斑块的影响[J].中国中医急症,2015,24(10):1753-1754+1779.
[21] 陈丽,蔡惠铃,李影雄,等.注射用丹参多酚酸盐对动脉粥样硬化大鼠的作用和机制探讨[J].中医药导报,2021,27(3):4-8.
[22] 霍春青.土元提取物对脂多糖诱导血管内皮细胞一氧化氮合酶表达的调节作用[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2014.
[23] 刘孟楠,任维,罗钢,等.蛭龙活血通瘀胶囊对U937巨噬细胞焦亡的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2020,31(10):2371-2374.
[24] 李洋洋,杨乔,胡耀红.水蛭粉对动脉粥样硬化大鼠血管平滑肌细胞的影响[J].中成药,2016,38(4):894-898.
[25] 张翔,江兴林,周利玲,等.大黄素对氧化应激所致动脉粥样硬化模型大鼠的干预研究[J].中医药导报,2016,22(21):27-29.
[26] 赵剑锋. 大黄素抑制TLR4介导的动脉粥样硬化炎症的分子机制研究[D].济南:山东大学,2012.
[27] WU G. Amino acids: metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids. 2009;37(1):1-17.
[28] FU L, DONG SS, XIE YW, et al. Down-regulation of tyrosine aminotransferase at a frequently deleted region 16q22 contributes to the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010; 51(5): 1624-1634.
[29] WYPYCH TP, PATTARONI C, PERDIJK O, et al. Microbial metabolism of L-tyrosine protects against allergic airway inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(3):279-286.
[30] 郭天宇,温雨晴,金佰明,等. 酪氨酸对小鼠体内氧化应激机制的动态研究[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2017,38(19):2238-2239.
[31] WYPYCH TP, PATTARONI C, PERDIJK O, et al. Microbial metabolism of L-tyrosine protects against allergic airway inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(3):279-286.
[32] WÜRTZ P, RAIKO JR, MAGNUSSEN CG, et al. High-throughput quantification of circulating metabolites improves prediction of subclinical atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(18):2307-2316.
[33] BENJAMIN EJ, VIRANI SS, CALLAWAY CW, et al. American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137(12):e67-e492.
[34] DENNINGER JW, MARLETTA MA. Guanylate cyclase and the.NO/cGMP signaling pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1411:334-350.
[35] MORRIS SM JR. Enzymes of arginine metabolism. J Nutr. 2004;134(10 Suppl):2743S-2747S; discussion 2765S-2767S.
[36] WYSS M, KADDURAH-DAOUK R. Creatine and creatinine metabolism. Physiol Rev. 2000;80(3):1107-1213.
[37] 孟中华,尚莎莎,王建茹,等.巨噬细胞PI3K/Akt通路与动脉粥样硬化的研究进展[J].中国免疫学杂志,2022,38(1):102-106.
[38] YANNI AE, AGROGIANNIS G, NOMIKOS T, et al. Oral supplementation with L-aspartate and L-glutamate inhibits atherogenesis and fatty liver disease in cholesterol-fed rabbit. Amino Acids. 2010;38(5):1323-1331.
[39] MARTIN-LORENZO M, GONZALEZ-CALERO L, MAROTO AS, et al. Cytoskeleton deregulation and impairment in amino acids and energy metabolism in early atherosclerosis at aortic tissue with reflection in plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862(4):725-732.
[40] TZOULAKI I, CASTAGNÉ R, BOULANGÉ CL, et al. Serum metabolic signatures of coronary and carotid atherosclerosis and subsequent cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. 2019;40(34):2883-2896.
[41] YU D, RICHARDSON NE, GREEN CL, et al. The adverse metabolic effects of branched-chain amino acids are mediated by isoleucine and valine. Cell Metab. 2021;33(5):905-922.
[42] HE XD, GONG W, ZHANG JN, et al. Sensing and Transmitting Intracellular Amino Acid Signals through Reversible Lysine Aminoacylations. Cell Metab. 2018;27(1):151-166.
[43] 倪宇昕,章立群,谢安琪,等. L-缬氨酸对巨噬细胞raw264.7的作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(24):6069-6073.
|