中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 2350-2360.doi: 10.12307/2026.067
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
低频脉冲电磁场在肌肉修复与增长中的应用效果和作用机制
蒋祥龙1,厉中山2,车同同1
- 1青岛大学体育学院,山东省青岛市 266071;2东北大学体育部,辽宁省沈阳市 110819
-
收稿日期:2024-12-14接受日期:2025-03-01出版日期:2026-03-28发布日期:2025-09-29 -
通讯作者:Che Tongtong, Associate professor, School of Physical Education, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China -
作者简介:Jiang Xianglong, MS candidate, School of Physical Education, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China
Application effects and mechanisms of low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields in muscle repair and growth
Jiang Xianglong1, Li Zhongshan2, Che Tongtong1
- 1School of Physical Education, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Physical Education, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-14Accepted:2025-03-01Online:2026-03-28Published:2025-09-29 -
Contact:车同同,副教授,青岛大学体育学院,山东省青岛市 266071 -
About author:蒋祥龙,男,2000年生,安徽省黄山市人,汉族,在读硕士,主要从事身体运动功能训练和运动与健康促进的研究。
摘要:
文题释义:
低频脉冲电磁场:是一种通过特定频率和强度的脉冲电磁波进行治疗的非侵入性方法,通常采用低频(0-300 Hz)来治疗各种疾病,如骨质疏松和背痛等,其中低强度(小于100 mT)对改善身体功能有显著效果。摘要
背景:低频脉冲电磁场作为一种非侵入性治疗方法,不仅在骨折和关节炎的治疗中取得了显著效果,在促进肌肉修复与增长领域也显示出了巨大的潜力。
目的:旨在综述低频脉冲电磁场在促进肌肉修复与增长中的应用效果与作用机制。
方法:由第一作者检索CNKI和PubMed数据库2000-2024年相关文献,中文检索词为“低频脉冲电磁场,肌肉修复,肌肉增长,电磁生物效应”等,英文检索词为“Low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields,Muscle repair,Muscle growth,Electromagnetic biological effects”等,初步检索获得527篇文献,按纳入排除标准进行筛选,最终纳入89篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:近年来,有关低频脉冲电磁场的研究已经相对成熟,但它对肌肉修复与增长的效果和机制尚不清楚。尽管低频脉冲电磁场在增大肌肉质量和力量、提高有氧运动能力、预防失用性肌萎缩以及加速术后康复有积极作用,然而在作用机制、治疗参数的优化以及临床应用效果的广泛验证方面仍然存在挑战。此外,对低频脉冲电磁场作用机制的研究也能为肌肉修复与增长的生物学过程提供新的视角,有助于推进运动医学和再生医学领域的发展。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
蒋祥龙, 厉中山, 车同同. 低频脉冲电磁场在肌肉修复与增长中的应用效果和作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2350-2360.
Jiang Xianglong, Li Zhongshan, Che Tongtong. Application effects and mechanisms of low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields in muscle repair and growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2350-2360.
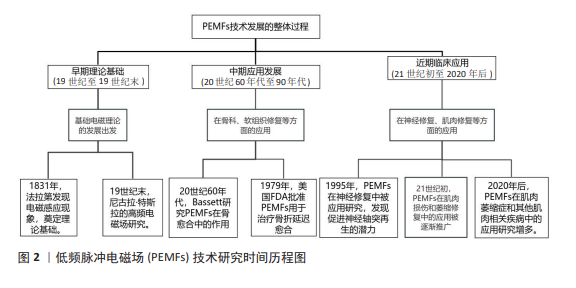
电磁场理论的发展可以追溯到19世纪,迈克尔·法拉第通过实验发现了电磁感应现象,并提出了“电紧张态”等概念,推动了电磁学理论的发展,为电磁场在生物医学中的应用奠定了科学基础[15]。19世纪末,尼古拉·特斯拉在高频电磁场研究方面进行了开创性的实验,探索了电磁场对人体的影响,成为最早将电磁场应用于人体治疗的先驱之一[16]。进入20世纪中叶,研究人员开始探索如何利用PEMFs促进组织的修复和再生。PEMFs作为一种非侵入性、低风险的治疗方法,最初主要被用于骨科治疗。20世纪60年代,BASSETT
等[17]首次系统研究了电磁场对骨愈合的促进作用,并通过动物实验发现低频低强度的PEMFs可以提高成骨细胞的活性、加速骨折的愈合,他们提出电磁场通过感应电流影响细胞膜电位,调节细胞功能,从而促进骨修复。随着基础研究的推进,PEMFs逐渐应用于临床,大量临床试验表明,PEMFs在治疗骨折延迟愈合和骨不连方面具有显著疗效,尤其是在非入侵性治疗中展现了明显优势[18]。1979年,美国食品和药物管理局(Food and Drug Administration,FDA)首次批准PEMFs用于治疗骨折延迟愈合和不愈合,这标志着PEMFs在骨科领域的应用得到了官方认可,推动了PEMFs在医学界的普及[19]。20世纪90年代初,研究人员开始关注PEMFs在软组织修复中的作用,实验显示PEMFs可以促进软骨细胞、肌腱细胞和韧带细胞的增殖和代谢活动[20]。这些发现使PEMFs的应用范围从骨组织扩展至软组织,为治疗关节炎、肌腱炎等疾病提供了新的治疗途径。同时,PEMFs在神经再生中的作用也引起了关注,研究显示PEMFs可以促进神经轴突的再生,为治疗神经损伤提供了潜在途径[21]。有关PEMFs技术发展的详细历程,参见图2。
随着PEMFs在骨科和软组织修复中的广泛应用,研究人员也逐步探索其在肌肉增长与修复中的潜力。肌肉损伤和萎缩一直是医学和运动康复中的关键问题,尤其对于运动员和老年人群体,如何有效促进肌肉再生与修复,已成为当前研究的重要方向之
一[22]。早期关于PEMFs在肌肉领域的研究主要集中在肌肉损伤的修复上,例如,高强度运动或创伤后常出现肌肉纤维撕裂或损伤,而传统的治疗手段(如物理治疗、药物治疗)虽有效,但恢复过程较为缓慢[23]。由于PEMFs具有非侵入性和低不良反应的特点,逐渐应用于肌肉损伤的康复中。许多研究表明,PEMFs治疗可以缩短运动员的恢复时间,改善肌肉功能[24];同时,PEMFs在治疗肌肉萎缩症等肌肉疾病中的应用也引起了广泛关注[25]。肌肉萎缩症患者通常由于神经退行性疾病或长时间不活动(如卧床)而导致肌肉组织的流失和功能下降[26],传统康复治疗方法在这一领域效果有限,而PEMFs作为一种新兴疗法,已在临床上初步展现出改善肌肉萎缩和增强肌肉质量的效果[27]。
尽管PEMFs在肌肉增长与修复领域的研究尚处于早期阶段,但现有的临床数据已为未来的深入研究奠定了坚实基础。随着越来越多的临床试验和科学研究的不断开展,PEMFs在肌肉疾病治疗中的应用前景愈加明朗。未来的研究将进一步验证PEMFs在不同类型的肌肉损伤和疾病中的疗效,并推动其在运动损伤、老年肌肉功能退化以及肌肉疾病中的广泛应用。
2.2 PEMFs在肌肉修复与增长中的应用效果
2.2.1 肌肉组织的结构、修复与增长机制 肌肉组织是由肌纤维、结缔组织、血管和神经组成,是身体中主要负责产生运动和力量的结构[28]。每根肌纤维由数百到数千个肌原纤维组成,肌原纤维内部含有肌节,肌节由交替排列的肌动蛋白和肌球蛋白构成,它们通过滑动机制相互作用,导致肌纤维收缩并产生力量[29]。肌纤维被结缔组织包裹,这些组织不仅增强了肌纤维的结构稳定性,还促进了力量的有效传递[30]。肌肉中的血管网络为细胞提供氧气和营养,支持其活动,而神经网络控制肌肉的收缩与放松,确保运动的准确性和协调性[31]。
肌肉修复和增长是一个涉及多种细胞和分子机制的复杂生理过程,尤其在肌肉受到机械损伤或过度使用后显得更为重要[32]。肌肉损伤发生后,位于肌纤维外侧的卫星细胞被激活并增殖,它们可能分化为新的肌纤维或与现有肌纤维融合以修复损伤[33],这一过程不仅依赖于卫星细胞,还需要蛋白质合成的增加,以提升肌肉质量和力量[34]。HORNBERGER等[35]指出,哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路作为关键的调节通路,在运动或机械刺激下被激活,促进蛋白质合成和细胞增长。良好的血液循环能够确保氧气和营养物质供应,以及代谢废物的有效清除,从而进一步支持修复过程[36]。适度的炎症反应能够通过引入免疫细胞来清除损伤区域的细胞残骸,并释放生长因子,促进肌肉修复[37]。FERRARO等[38]和USHER‐SMITH等[39]的研究发现,肌肉细胞内外的离子流动和电位变化触发如磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(Protein
Kinase B,Akt)和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase,MAPK)等信号通路,能够调节细胞增殖、分化和代谢活动。此外,SCHIAFFINO等[40]指出,调节肌肉细胞的代谢活动也是维持和增加肌肉质量的重要因素。这些过程的协同作用,形成一个综合网络,调节肌肉的修复与增长。
2.2.2 PEMFs促进肌肉修复与增长的动物实验 多项动物实验表明,PEMFs对肌肉修复和增长具有促进作用,并涉及复杂的生物机制。SHIMADA等[41]在大鼠后肢悬挂模型中发现,PEMFs能够增加肌肉纤维的直径,尤其是1型、2A型和2B型纤维,这种增长主要由于肌肉内循环改善和细胞代谢活性的增强。STRAUCH等[42]进一步阐明,PEMFs通过促进组织修复过程中生长因子的级联反应,并增强钙离子的结合,提升了大鼠跟腱的生物力学强度。XU等[43]指出,PEMFs通过激活肌肉细胞的MAPK/细胞外信号调节激酶(Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase,ERK)信号通路,加速了肌肉损伤后的修复,并提高了新生肌纤维的数量和质量。在CICEK等[44]的研究中,40 Hz的PEMFs治疗不仅促进了肌肉修复,还通过提高肌纤维内的钙离子浓度来增强肌肉力量,从而也证实了PEMFs在运动医学领域的应用潜力。MAIULLARI等[22]从分子层面探讨了PEMFs通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路促进肌肉细胞的增殖和分化,进一步证明了PEMFs对肌肉再生的促进作用。此外,CHEING等[45]在糖尿病大鼠模型中发现,PEMFs能够加快伤口愈合,并通过增强肌纤维细胞中转化生长因子β1的表达,促进了组织的再生与修复。这些研究凸显了PEMFs在促进肌肉和跟腱组织修复与增长中的作用,展示了其在体育科学和运动医学中的潜在应用。
2.2.3 PEMFs促进肌肉修复与增长的细胞实验 细胞层面的研究充分表明,PEMFs在促进肌细胞增殖和分化方面具有显著效果,能够增加肌肉特异性蛋白质的合成,从而支持其在肌肉修复和增长中的应用潜力。LI等[46]研究发现,50 Hz PEMFs能够提升间充质干细胞的增殖率,并在细胞周期的G1期增加了细胞比例,表明PEMFs对细胞增殖的促进作用具有时间依赖性。HAN等[47]的研究为深入理解PEMFs在肌肉细胞层面的作用机制提供了重要证据,证明PEMFs提升了C2C12成肌细胞中的成肌因子5和成肌分化因子1基因的表达,促进了成肌细胞的分化。ZOU等[48]指出,PEMFs能够影响间充质干细胞的生长环境,虽然研究主要集中于炎症因子的调节,但结果间接支持了PEMFs对细胞增殖和分化的积极影响。GIROLAMO等[49]的研究显示,PEMFs影响了细胞形态和功能,进一步验证了其在细胞生物学研究中的广泛应用潜力。现有文献充分证明了PEMFs在促进成肌细胞增殖和分化中的重要作用,通过调节细胞周期、基因表达和生长环境,PEMFs展现了在肌肉增长与修复中潜在的应用潜力。
2.2.4 PEMFs促进肌肉修复与增长的临床实际应用 在实际应用中,PEMFs技术已被证实能够促进肌肉修复与增长,其机制主要包括改善血液微循环、增强肌细胞的代谢活性和调节细胞内钙离子通道的功能,这些机制的协同作用使PEMFs有着广泛的应用潜力。TROFè等[50]对半专业自行车运动员的研究表明,在无负载骑行的热身阶段,PEMFs提高了肌肉活性,使用PEMFs后,运动员在低负荷运动时血乳酸浓度显著增加(P < 0.001),表明PEMFs对肌纤维代谢活性具有显著影响。LEONARDO等[51]的研究凸显了PEMFs在治疗肌肉骨骼疾病中的潜在益处,揭示了该技术在促进血液微循环和组织再生中的广泛适用性。STEPHENSON等[52]深入探讨了PEMFs通过激活肌肉线粒体提升能量代谢和肌肉功能的机制,并指出PEMFs提高了运动员在高强度训练后肌肉的氧气供应和利用效率,加速了肌肉的恢复。PEMFs在一般人群中的应用,特别是在老年人中也显示出积极效果。例如,一项针对东南亚社区老年人的研究表明,PEMFs改善了参与者的运动能力和瘦体质量,证实了PEMFs在预防肌肉萎缩和提升生活质量方面的潜力[53]。
JEON等[54]的研究显示,PEMFs治疗能有效缓解运动引起的肌肉延迟性酸痛,包括感知的酸痛、收缩时的媒介频率以及电机械延迟的改善。厉中山等[55]的研究探讨了低频脉冲磁场通过激活经典瞬时感受器电位通道1(Classical Transient Receptor Potential Channel 1,TRPC1)钙离子通道如何促进肌肉生长和适应性重塑,发现特定参数下的PEMFs刺激提升了受试者的最大自主收缩力和耐力,且效果可维持数周,这表明在无需重负荷训练的情况下,PEMFs同样能有效增强肌肉的力量和耐力。
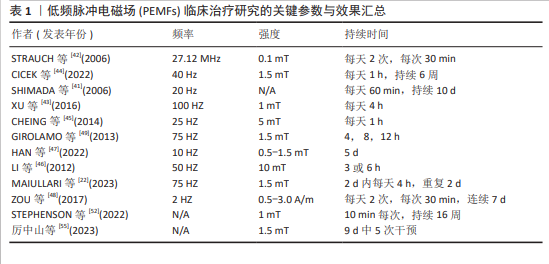
综上所述,PEMFs的独特生物效应在实验和临床研究中均显示出了对肌肉修复与增长的显著的促进作用。动物和细胞实验研究已证明,PEMFs能有效激活关键生物信号通路,加速肌肉细胞的增殖与分化,进而促进肌肉纤维的增长和修复。临床试验也表明,PEMFs对提高运动表现和加快术后恢复具有明显的效果。更详细的试验参数,如PEMFs治疗的频率、强度和持续时间等,详见表1。这些数据不仅反映了PEMFs在基础研究中的有效性,还凸显了其在医疗实践中的广泛应用潜力,证明了PEMFs在现代医学和运动科学中的重要价值。
2.3 PEMFs促进肌肉修复与增长的作用机制
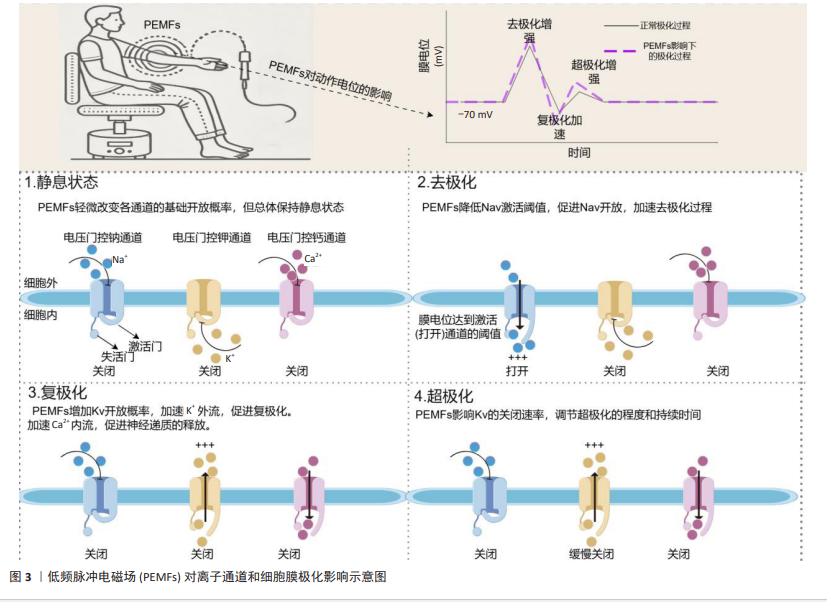
2.3.1 离子通道调节 离子通道在肌肉细胞的电生理活动和生化过程中起着关键作用,特别是Na+、K+和Ca2+离子通道,这些离子通道通过精确调控细胞内外的离子流动,维持电位平衡,从而影响细胞兴奋性、信号传递以及代谢调节[56-57]。Na+通道主要负责在肌肉细胞中促进动作电位的起始和传播,这对肌肉收缩至关重要[58]。K+通道通过调节复极化过程,帮助肌肉细胞在高频刺激下恢复电位,从而维持细胞兴奋性[59]。Ca2+通道促进钙离子流入,直接参与肌肉收缩和多种细胞内信号通路的激活,钙信号通路作为调节蛋白质激酶和磷酸化过程的关键介质,对细胞生长和分化至关重要[60]。
PEMFs通过诱导电场改变细胞内离子的动态,激活离子通道,进而调节细胞的跨膜电位,影响细胞功能和信号传递[61]。根据PANAGOPOULOS等[62]的理论模型,PEMFs通过诱导Na+、K+和Ca2+等离子在细胞膜上的强迫振动,调控电压依赖性离子通道的活动,影响细胞的电化学梯度和功能。FUNK[63]的综述详细探讨了PEMFs与细胞分子基础的联系,特别强调了PEMFs通过电磁场诱导的电压变化直接激活电压门控钙通道,这种激活引起了细胞内钙信号通路的变化,进一步调节一氧化氮和轻度自由基反应等生物效应,从而促进抗炎和细胞保护反应。此外,BAHMANPOUR等[64]发现,PEMFs通过改变细胞膜极化和跨膜电压,影响电压门控离子通道的活动,并在细胞增殖、分化和组织再生等关键过程中发挥重要作用(图3)。因此,通过调节离子通道活性,PEMFs为促进肌肉细胞生长和修复提供了理论支持,未来研究有望验证其在肌肉修复与增长方面的有效性。
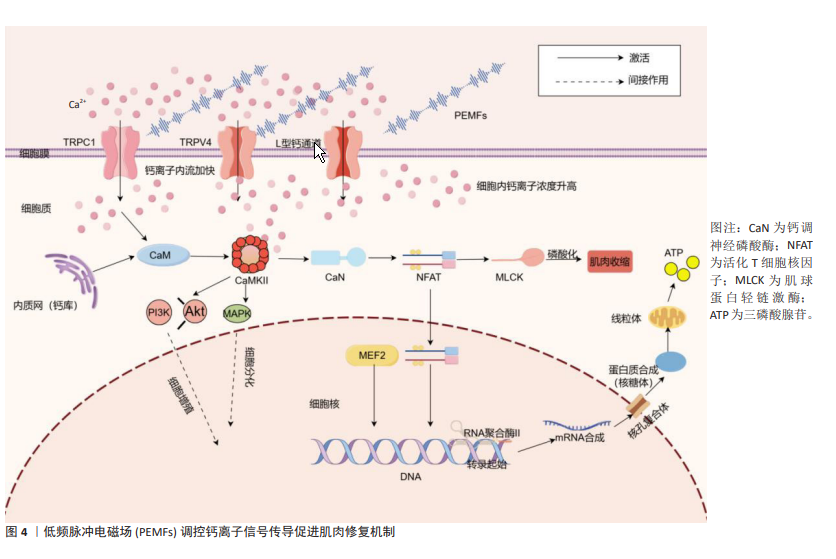
2.3.2 钙离子信号传导 钙离子信号传导在肌肉细胞的增长与修复中起着关键角色[65]。作为第二信使,钙离子的流动和浓度变化直接调控多种细胞功能,特别是在肌肉细胞的增殖、分化和再生过程中[66]。钙离子通过通道进入肌肉细胞后,激活钙调蛋白,而钙调蛋白进一步激活肌球蛋白轻链激酶,最后肌球蛋白轻链激酶通过磷酸化肌球蛋白轻链来调节肌肉收缩和其他的细胞功能,从而维持正常的肌肉活动和功能状态[60]。在肌肉再生过程中,钙离子通过TRPC1通道增强了PI3K/Akt信号通路的活性,从而促进肌肉细胞的迁移、增殖和分化,加速肌肉组织的增长[67]。此外,钙离子信号通过与钙调蛋白结合,激活依赖钙/钙调蛋白的激酶,这些激酶调节肌肉细胞中的基因表达,促进线粒体生物合成和肌纤维类型特异性蛋白的表达,增强肌肉的代谢功能和适应能力,对肌肉的生长和功能恢复至关重要[68]。
厉中山等[69]的研究表明,PEMFs通过激活TRPC1增加细胞内钙离子浓度,调控如钙调神经磷酸酶-核因子活化T细胞通路等关键信号通路,进而影响肌肉的生长与重塑。PEMFs通过增强L型钙通道的活性,导致细胞内钙水平升高,进而激活涉及肌肉收缩和神经递质释放等功能的信号通路,表明其对细胞功能调控的影响[70-71]。VARANI等[72]的研究显示,PEMFs通过激活特定的瞬变受体电位通道[如瞬时受体电位香草酸4通道(Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4,TRPV4)和TRPC1]促进钙离子从外部流入细胞内,增加细胞内钙浓度,这一升高激活了多个依赖钙离子的信号传导通路,这些通路在细胞分化过程中发挥了重要作用。LI等[73]的研究表明,PEMFs通过释放细胞内的钙离子并增加胞浆钙浓度,从而激活钙调蛋白,进而促进骨细胞的增殖。研究人员通过使用一些信号通路抑制剂来验证PEMFs的作用机制,结果发现PEMFs通过调节钙离子信号促进了细胞的活性和增殖。虽然PEMFs在肌肉修复和增长中的具体效应尚需进一步验证,但通过钙离子在细胞信号传导中的已知作用,可以推测PEMFs对钙离子动态的调节具有显著的生物学效应(图4)。这种效应可能在肌肉细胞的功能恢复和增强过程中起关键作用。通过优化钙离子信号传导,PEMFs能够提高肌肉细胞的反应效率和功能稳定性,为肌肉的修复和增长提供坚实的基础。
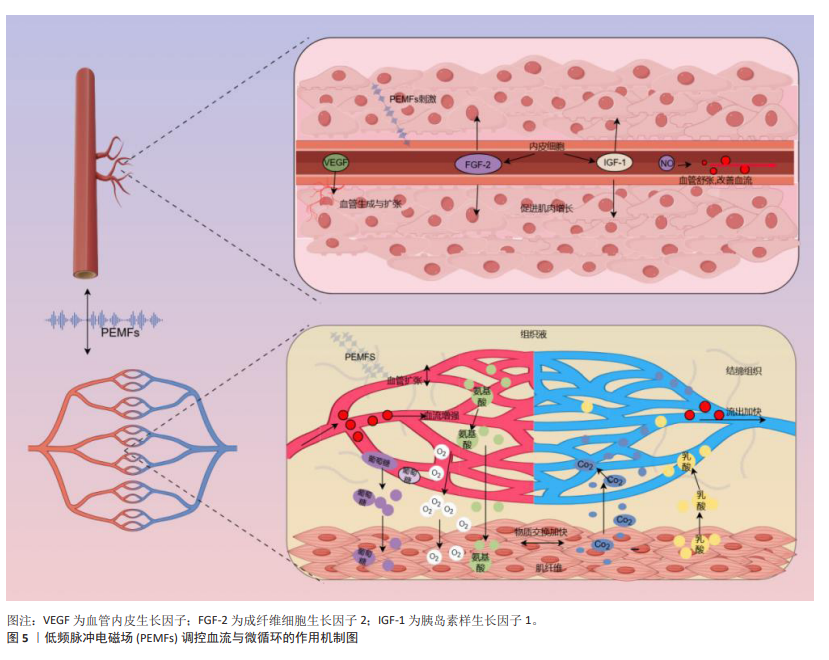
2.3.3 血流和微循环 肌肉组织损伤后,机体的自然反应之一是通过血管活性物质(如一氧化氮和前列腺素)引起的反应性血管扩张来增加受损区域的血流。增强的血流不仅快速将氧气和营养物质输送到所需要修复的区域,而且还带来了生长因子、细胞因子和关键的免疫细胞,这些都是启动和促进损伤后再生过程所必需的物质[74]。在运动中,增强的血流通过提高氧气和营养物质的供给,有助于细胞外基质重塑和肌肉纤维再生,这是功能恢复的关键[32]。而微循环,尤其是毛细血管网络,起着重要的作用。毛细血管作为微循环系统的核心,不仅负责输送氧气和营养物质,还负责移除二氧化碳和代谢废物[75]。毛细血管内皮细胞通过分泌血管内皮生长因子并调节基质金属蛋白酶的活性,重塑细胞外基质,促进细胞增殖和组织修复[76]。ARSIC等[77]的研究发现,血管内皮生长因子不仅促进新血管的形成,还通过与血管内皮生长因子受体2的相互作用在肌肉损伤后直接影响肌肉纤维,这包括促进肌肉细胞的生长并防止其凋亡,对肌肉组织的修复和再生具有关键作用。
PEMFs已被证实能够促进血管新生并改善血液微循环,该技术通过促进血管内皮细胞的增殖、迁移及管状结构的形成,并激活电压门控钙通道提高细胞内钙水平,从而刺激血管修复和生长,增强微循环和血管生成[78]。GOTO等[79]发现,PEMFs通过上调血管生成素2和成纤维细胞生长因子2的表达,诱导骨髓内有利于血管生成的环境,进而改善血液流动和微循环。TEPPER等[80]进一步展示了PEMFs通过促进内皮细胞释放并上调成纤维细胞生长因子2,通过旁分泌和自分泌机制促进血管新生,有效地调节血液流动和微循环。此外,TROFè等[50]观察到PEMFs通过增强毛细血管的血流速度和扩张直径,改善微循环,进一步促进了运动期间肌肉细胞的氧合和代谢。基于上述分析,可以推测PEMFs通过改善血流和微循环,对肌肉修复与增长具有潜在的积极作用。PEMFs通过增强血管内皮细胞的增殖和迁移,并提高血管内皮生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子2和血管生成素2等关键血管生成因子的表达,不仅促进新血管的形成,还可能通过改善毛细血管的血流速度和氧供,支持受损肌肉纤维的再生和功能恢复(图5)。尽管现有研究主要集中在PEMFs对血管生成和微循环的影响,但这些效应很可能间接促进了肌肉组织的修复与增长。
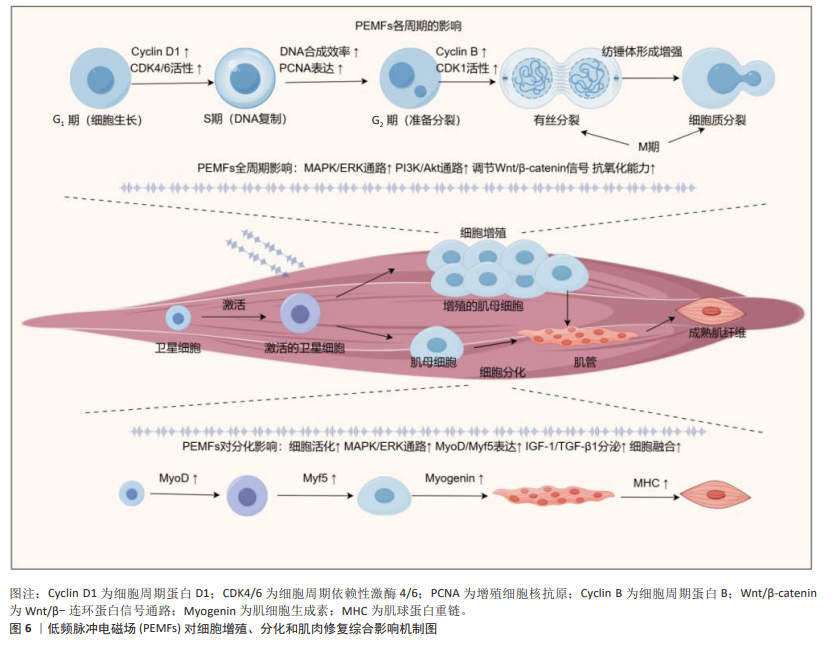
2.3.4 细胞的增殖与分化 肌肉的增长与修复是一个复杂的生物学过程,其核心在于细胞的增殖与分化[81]。肌肉损伤后,机体启动一系列生物反应来恢复受损组织的结构和功能。该过程首先涉及到肌肉卫星细胞的激活,这些位于肌纤维基底膜下的静止细胞在受到刺激后被激活,开始进入细胞周期并激活[82]。随后,这些细胞逐步产生或显示出一些特定的分化标志物(如肌动蛋白和肌调蛋白),这些转录因子直接调控肌肉特异性蛋白的表达,诱导细胞向成熟肌纤维转变[83]。成熟的肌肉细胞主要通过肌卫星细胞和肌母细胞的融合形成新肌纤维,或修复现有肌纤维,进而恢复肌肉组织的结构与功能[84]。该过程不仅受到局部环境因素(如生长因子和细胞因子)的调控,还可能受到全身性激素和代谢状态的影响[85]。而胰岛素生长因子1、成纤维细胞生长因子和血小板衍生生长因子等生长因子能够促进卫星细胞的增殖与分化,而肿瘤坏死因子α等炎症因子则可能参与节损伤后修复的调节[86]。
PEMFs通过促进细胞增殖与分化,在组织再生和愈合中发挥重要作用。FASSINA等[87]的研究表明,PEMFs 刺激增加了人类成骨细胞的增殖速度,并提高了Ⅰ型胶原、装饰蛋白和骨桥蛋白的表达。在VINHAS等[88]的研究发现,PEMFs 通过调节信号传递和基因表达,特别是控制MAPK/ERK信号通路和连接蛋白43的表达,调控人类肌腱细胞在炎症环境中的细胞通讯,影响炎症因子和抗炎因子的平衡,从而促进细胞的增殖与分化。LIU等[89]的研究也指出,PEMFs 在炎症条件下能增强人类肌腱细胞的基因表达,尤其是转化生长因子β1、血小板衍生生长因子β和骨形态发生蛋白12的表达,从而促进了细胞的增殖与分化。HAN等[47]发现,PEMFs能够增加C2C12细胞中肌原细胞的增殖与分化,特别是在1.5 mT磁场强度下,成肌分化因子 1和成肌因子5的表达在第5天显著增加,这表明PEMFs可以通过调节肌肉生成的关键因子来促进细胞分化(图6)。
2.4 脉冲电磁场促进肌肉修复与增长所面临的挑战 尽管PEMFs在细胞增殖、分化和修复方面有着积极影响,但在机制理解、治疗参数优化、临床证据积累以及长期安全性评估等方面仍面临多项挑战,这些问题限制了PEMFs的发展和应用,需要通过系统研究和技术创新加以解决。
(1)分子机制未完全明确:PEMFs虽在促进肌肉细胞增长、分化以及修复方面显示出潜力,但其具体分子机制尚未完全阐明。尤其是在如何调控肌肉细胞的信号通路及影响细胞行为方面,当前的研究主要集中在医学领域、体育科学中的探索仍显不足。
(2)参数缺乏标准化:PEMFs治疗的效果受到频率、强度、暴露时间等参数的影响,目前缺乏统一标准,导致治疗结果的可重复性和预测性不足,在运动康复领域,缺乏具体的治疗指南和标准化方案。
(3)临床证据不足:目前关于PEMFs在肌肉治疗中的有效性和安全性的临床证据仍然有限,尤其是在体育领域的研究较少,需要更多大规模、随机对照的临床试验来验证其在不同类型肌肉损伤中的应用效果。
(4)长期安全性不明确:对PEMFs长期使用效果和潜在风险的研究不足,尤其是其对人体健康的长期影响尚不明确,这在运动员长期康复和训练中的使用尤为重要。
| [1] 陈淑琴,刘刚,吴芮仁,等.运动员损伤的影响因素及康复策略研究[J].体育科学进展,2024,12(1):43-49. [2] 刘美含,吴雪萍,丁海勇,等.冬残奥运动项目损伤特征、风险因素及预防措施[J].武汉体育学院学报,2021,55(2): 93-100. [3] 何怡娴.运动生物化学检测与体育运动疲劳及过度训练的诊断:评《运动生物化学》 [J].化学学报,2024,82(3):378. [4] KRAEMER WJ, RATAMESS NA, FLANAGAN SD, et al. Understanding the science of resistance training: An evolutionary perspective. Sports Med. 2017;47(12):2415-2435. [5] PLUNCEVIC GLIGOROSKA J, MANCHEVSKA S, PETROVSKA S, et al. Physiological mechanisms of muscle hypertrophy. Res Phys Educ Sport Health. 2022;11(1):153-160. [6] 李海鹏,刘宇.肌肉衰减症的动态识解及对我国运动科学研究的启示[J].体育科学,2020,40(9):61-73. [7] HU H, YANG W, ZENG Q, et al. Promising application of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs) in musculoskeletal disorders. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110767. [8] SU D, ZHAO Z, YIN D, et al. Promising application of pulsed electromagnetic fields on tissue repair and regeneration. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2024;187:36-50. [9] CIOMBOR DM, AARON RK, WANG S, et al. Modification of osteoarthritis by pulsed electromagnetic field—A morphological study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003;11(6):455-462. [10] DAISH C, BLANCHARD R, FOX K, et al. The application of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs) for bone fracture repair: Past and perspective findings. Ann Biomed Eng. 2018;46(4):525-542. [11] ROSS CL, ZHOU Y, MCCALL CE, et al. The use of pulsed electromagnetic field to modulate inflammation and improve tissue regeneration: A review. Front Immunol. 2019;10:266. [12] GAYNOR JS, HAGBERG S, GURFEIN BT. Veterinary applications of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy. Res Vet Sci. 2018;119:1-8. [13] YANG X, HE H, YE W, et al. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy on pain, stiffness, physical function, and quality of life in patients with osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Phys Ther. 2020;100(7):1118-1131. [14] BACHL N, RUOFF G, WESSNER B, et al. Electromagnetic interventions in musculoskeletal disorders. Clin Sports Med. 2008;27(1):87-105. [15] 钱长炎.法拉第发现电磁感应现象及其思想转变过程[J].自然科学史研究,2019, 38(1):87-104. [16] MARINCIC A, CIVRIĆ Z, MILOVANOVIĆ B. Nikola Tesla’s contributions to radio development. Serbian J Electrical Eng. 2006;3(2):131-148. [17] BASSETT CAL, PAWLUK RJ, PILLA AA. Augmentation of bone repair by inductively coupled electromagnetic fields. Science. 1974;184(4136):575-577. [18] SHARRARD WJW. A double-blind trial of pulsed electromagnetic fields for delayed union of tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72(3):347-355. [19] CADOSSI R, MASSARI L, RACINE-AVILA J, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation of bone healing and joint preservation: Cellular mechanisms of skeletal response. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2020; 4(5):e1900155. [20] AARON RK, CIOMBOR DMK. Therapeutic effects of electromagnetic fields in the stimulation of connective tissue repair. J Cell Biochem. 1993;52(1):42-46. [21] SISKEN BF, WALKER J. Therapeutic aspects of electromagnetic fields for soft-tissue healing// BLANK M. Electromagnetic Fields. American Chemical Society, 1995: 277-281. [22] MAIULLARI S, CICIRELLI A, PICERNO A, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields induce skeletal muscle cell repair by sustaining the expression of proteins involved in the response to cellular damage and oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(23):16631. [23] JÄRVINEN TAH, JÄRVINEN TLN, KÄÄRIÄINEN M, et al. Muscle injuries: Biology and treatment. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(5):745-764. [24] GHOSHCHI SG, PETRONI ML, PIRAS A, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) stimulation as an adjunct to exercise: A brief review. Front Sports Act Living. 2024: 6:1471087. [25] YANG J, SUN L, FAN X, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields alleviate streptozotocin-induced diabetic muscle atrophy. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(1): 1127-1133. [26] MOBACH T, BROOKS J, BREINER A, et al. Impact of disuse muscular atrophy on the compound muscle action potential. Muscle Nerve. 2020;61(1):58-62. [27] LEONARDO PS, CARDOSO KRDS, SILVA BO, et al. Evaluation of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy to improve muscle strength and functional aspects in the elderly: A pilot study. Manual Therapy Posturology Rehabil J. 2023;21:1293. [28] FRONTERA WR, OCHALA J. Skeletal muscle: A brief review of structure and function. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015;96(3): 183-195. [29] 赵倩,张学林.就离心收缩机制存在的问题探讨肌丝滑行理论的修正[J].生理学报,2021,73(1):143-147. [30] 王志柱.骨骼、肌肉和结缔组织对身体活动产生的适应[J].体育世界(学术版), 2019(7):147-148. [31] HORVATH SM. Review of energetics and blood flow in exercise. Diabetes. 1979; 28(Supplement_1):33-38. [32] KJAER M. Role of extracellular matrix in adaptation of tendon and skeletal muscle to mechanical loading. Physiol Rev. 2004; 84(2):649-698. [33] SIRABELLA D, DE ANGELIS L, BERGHELLA L, et al. Sources for skeletal muscle repair: From satellite cells to reprogramming. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2013;4(2):125-136. [34] PALLAFACCHINA G, BLAAUW B, SCHIAFFINO S, et al. Role of satellite cells in muscle growth and maintenance of muscle mass. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;23 Suppl 1: S12-518. [35] HORNBERGER TA, SUKHIJA KB, CHIEN S, et al. Regulation of mTOR by mechanically induced signaling events in skeletal muscle. Cell Cycle. 2006;5(13):1391-1396. [36] CLOSE GL, HAMILTON DL, PHILP A, et al. New strategies in sport nutrition to increase exercise performance. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;98:144-158. [37] SMITH C, KRUGER MJ, SMITH RM, et al. The inflammatory response to skeletal muscle injury: Illuminating complexities. Sports Med. 2008;38(11):947-969. [38] FERRARO E, GIAMMARIOLI AM, CHIANDOTTO S, et al. Exercise-induced skeletal muscle remodeling and metabolic adaptation: Redox signaling and role of autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014; 21(1):154-176. [39] USHER-SMITH JA, HUANG CL, FRASER JA. Control of cell volume in skeletal muscle. Biol Rev. 2009;84(1):143-159. [40] SCHIAFFINO S, DYAR K A, CICILIOT S, et al. Mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle growth and atrophy. FEBS J. 2013; 280(17):4294-4314. [41] SHIMADA Y, SAKURABA T, MATSUNAGA T, et al. Effects of therapeutic magnetic stimulation on acute muscle atrophy in rats after hindlimb suspension. Biomed Res. 2006;27(1):23-27. [42] STRAUCH B, PATEL MK, ROSEN DJ, et al. Pulsed magnetic field therapy increases tensile strength in a rat Achilles’ tendon repair model. J Hand Surg. 2006;31A(7): 1131-1135. [43] XU H, ZHANG J, LEI Y, et al. Low frequency pulsed electromagnetic field promotes C2C12 myoblasts proliferation via activation of MAPK/ERK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;479(1):97-102. [44] CICEK F, TASTEKIN B, BALDAN I, et al. Effect of 40 Hz magnetic field application in posttraumatic muscular atrophy development on muscle mass and contractions in rats. Bioelectromagnetics. 2022;43(8):453-461. [45] CHEING GLY, LI X, HUANG L, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) promote early wound healing and myofibroblast proliferation in diabetic rats. Bioelectromagnetics. 2014;35(6):426-437. [46] LI X, ZHANG M, BAI L, et al. Effects of 50 Hz pulsed electromagnetic fields on the growth and cell cycle arrest of mesenchymal stem cells: An in vitro study. Electromagn Biol Med. 2012;31(4):356-364. [47] HAN F, YIN S, WU H, et al. Effect on myoblast differentiation by extremely low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields. J Mech Med Biol. 2022;22(8):2240026. [48] ZOU J, CHEN Y, QIAN J, et al. Effect of a low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic field on expression and secretion of IL-1β and TNF-α in nucleus pulposus cells. J Int Med Res. 2017;45(2):462-470. [49] GIROLAMO L, STANCO D, GALLIERA E, et al. Low frequency pulsed electromagnetic field affects proliferation, tissue-specific gene expression, and cytokines release of human tendon cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;66(3):697-708. [50] TROFÈ A, PIRAS A, MUEHSAM D, et al. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs) on muscular activation during cycling: A single-blind controlled pilot study. Healthcare. 2023;11(6):922. [51] LEONARDO PS, CARDOSO KRDS, VIEIRA RDP, et al. Applications of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy in skeletal-muscle system: An integrative review. Man Ther Posturol Rehabil J. 2023;21:1-11. [52] STEPHENSON MC, KRISHNA L, PANNIR SELVAN RM, et al. Magnetic field therapy enhances muscle mitochondrial bioenergetics and attenuates systemic ceramide levels following ACL reconstruction: Southeast Asian randomized-controlled pilot trial. J Orthop Translat. 2022;35:99-112. [53] VENUGOBAL S, TAI YK, GOH J, et al. Short, weekly magnetic muscle therapy improves mobility and lean body mass in elderly: A Southeast Asian community case study. Aging. 2023;15(6):1768-1779. [54] JEON HS, KANG SY, PARK JH, et al. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy on delayed-onset muscle soreness in biceps brachii. Phys Ther Sport. 2015; 16(1):34-39. [55] 厉中山,白石,王春露,等.低频脉冲磁场诱导TRPC1技术对力量素质影响及训练应用展望[J].中国组织工程研究, 2023,27(11):1796-1804. [56] BALCAVAGE WX, ALVAGER T, SWEZ J, et al. A mechanism for action of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields on biological systems. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;222(2):374-378. [57] CHEN L, HASSANI NIA F, STAUBER T. Ion channels and transporters in muscle cell differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(24):13615. [58] RUBAIY HN. A short guide to electrophysiology and ion channels. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2017;20:48. [59] FAULER M, JURKAT-ROTT K, LEHMANN-HORN F. Membrane excitability and excitation–contraction uncoupling in muscle fatigue. Neuromuscul Disord. 2012:22 Suppl 3:S162-S167. [60] KUO IY, EHRLICH BE. Signaling in muscle contraction. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(2):a006023. [61] FLATSCHER J, PAVEZ LORIÈ E, MITTERMAYR R, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF)—Physiological response and its potential in trauma treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(14):11239. [62] PANAGOPOULOS DJ, KARABARBOUNIS A, MARGARITIS LH. Mechanism for action of electromagnetic fields on cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;298(1):95-102. [63] FUNK RHW. Coupling of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) therapy to molecular grounds of the cell. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(5):1260-1272. [64] BAHMANPOUR A, GHOREISHIAN SM, SEPAHVANDI A. Electromagnetic modulation of cell behavior: Unraveling the positive impacts in a comprehensive review. Ann Biomed Eng. 2024;52(8):1941-1954. [65] BENAVIDES DAMM T, EGLI M. Calcium’s role in mechanotransduction during muscle development. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33(2):249-272. [66] BERCHTOLD MW, BRINKMEIER H, MÜNTENER M. Calcium ion in skeletal muscle: Its crucial role for muscle function, plasticity, and disease. Physiol Rev. 2000; 80(3):1215-1265. [67] ZANOU N, SCHAKMAN O, LOUIS P, et al. Trpc1 ion channel modulates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway during myoblast differentiation and muscle regeneration. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287(18):14524-14534. [68] CHIN ER. Role of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinases in skeletal muscle plasticity. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005; 99(2):414-423. [69] 厉中山,白石,刘洁,等.短期低频脉冲磁场诱导经典瞬时感受器电位通道1对局部肌肉肌力提升后的保持与衰减变化轨迹[J].中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(23):3721-3727. [70] RAJALEKSHMI R, K AGRAWAL D. Energizing healing with electromagnetic field therapy in musculoskeletal disorders. J Orthop Sports Med. 2024; 6(2):89-106. [71] LIPSCOMBE D, HELTON TD, XU W. L-Type calcium channels: The low down. J Neurophysiol. 2004;92(5):2633-2641. [72] VARANI K, VINCENZI F, PASQUINI S, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation in osteogenesis and chondrogenesis: Signaling pathways and therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1116. [73] LI J KJ, LIN JCA, LIU HC, et al. Comparison of ultrasound and electromagnetic field effects on osteoblast growth. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2006;32(5):769-775. [74] STAMLER JS, MEISSNER G. Physiology of nitric oxide in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 2001;81(1):209-237. [75] MURRANT CL, FLETCHER NM. Capillary communication: The role of capillaries in sensing the tissue environment, coordinating the microvascular, and controlling blood flow. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022;323(5): H1019-H1036. [76] ARROYO AG, IRUELA-ARISPE ML. Extracellular matrix, inflammation, and the angiogenic response. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;86(2):226-235. [77] ARSIC N, ZACCHIGNA S, ZENTILIN L, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates skeletal muscle regeneration in vivo. Mol Ther. 2004;10(5):844-854. [78] PENG L, FU C, WANG L, et al. The effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields on angiogenesis. Bioelectromagnetics. 2021; 42(4):250-258. [79] GOTO T, FUJIOKA M, ISHIDA M, et al. Noninvasive up-regulation of angiopoietin-2 and fibroblast growth factor-2 in bone marrow by pulsed electromagnetic field therapy. J Orthop Sci. 2010;15(5):661-665. [80] TEPPER OM, CALLAGHAN MJ, CHANG EI, et al. Electromagnetic fields increase in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis through endothelial release of FGF-2. FASEB J. 2004;18(11):1231-1233. [81] SHADRACH JL, WAGERS AJ. Stem cells for skeletal muscle repair. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2011;366(2297): 2297-2306. [82] TIDBALL JG. Mechanisms of muscle injury, repair, and regeneration. Compr Physiol. 2011;1(4):2029-2062. [83] KARALAKI M, FILI S, PHILIPPOU A, et al. Muscle regeneration: Cellular and molecular events. In Vivo. 2009;23(5):779-796. [84] ZAMMIT PS. Function of the myogenic regulatory factors Myf5, MyoD, Myogenin, and MRF4 in skeletal muscle, satellite cells and regenerative myogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;72:19-32. [85] PEDERSEN BK, ÅKERSTRÖM TCA, NIELSEN AR, et al. Role of myokines in exercise and metabolism. J Appl Physiol. 2007;103(3):1093-1098. [86] TEN BROEK RW, GREFTE S, VON DEN HOFF JW. Regulatory factors and cell populations involved in skeletal muscle regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2010;224(1):7-16. [87] FASSINA L, SAINO E, VISAI L, et al. Electromagnetic enhancement of a culture of human SAOS-2 osteoblasts seeded onto titanium fiber-mesh scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;87(3):750-759. [88] VINHAS A, RODRIGUES MT, GONÇALVES AI, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic field modulates tendon cells response in IL-1β-conditioned environment. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(1):160-172. [89] LIU M, LEE C, LARON D, et al. Role of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) on tenocytes and myoblasts-potential application for treating rotator cuff tears: PEMF myoblast tenocyte. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(5): 956-964. |
| [1] | 陈秋函, 杨 龙, 袁代柱, 吴展羽, 邹梓豪, 叶 川. 膝关节周围截骨治疗膝骨关节炎:治疗策略的优化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2303-2312. |
| [2] | 赵非凡, 曹玉净. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折内固定失效的危险因素与应对策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2323-2333. |
| [3] | 刘金龙, 阿卜杜吾普尔•海比尔, 白 臻, 苏丹阳, 苗 鑫, 李 菲, 杨晓鹏. 不同非手术方法治疗青少年特发性脊柱侧凸效果的系统综述与网状Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2370-2379. |
| [4] | 曹 涌, 滕虹良, 邰鹏飞, 李骏达, 朱腾旗, 李兆进. 细胞因子和卫星细胞在肌肉再生中的相互作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1808-1817. |
| [5] | 管昱杰, 赵 彬 . 人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中的应用与展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 721-730. |
| [6] | 谭凤怡, 谢嘉敏, 潘振锋, 张新旭, 郑泽态, 曾祉莹, 周艳芳. 胶原蛋白联合微针治疗皮肤光老化的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 451-458. |
| [7] | 韩亚澎, 高 俊, 钮云伟, 邓恩甲. 骨碎补总黄酮介导骨相关细胞程序性死亡的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(12): 3091-3099. |
| [8] | 毛苏杰, 高 洁, 潘壮丽. 免疫细胞在训练诱导应激应答中协同调节炎症反应、肌肉再生和代谢稳态[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(10): 2671-2680. |
| [9] | 余 帅, 刘家伟, 朱 彬, 潘 檀, 李兴龙, 孙广峰, 于海洋, 丁 亚, 王宏亮. 小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的热点问题及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [10] | 周盼盼, 崔应麟, 张文涛, 王姝瑞, 陈佳慧, 杨 潼. 细胞自噬在脑缺血损伤中的作用及中药调控机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [11] | 于经邦, 吴亚云. 非编码RNA在肺纤维化过程中的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [12] | 王秋月, 靳 攀, 蒲 锐. 运动干预与细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [13] | 袁维勃, 刘 婵, 余丽梅. 肝脏类器官在肝脏疾病模型与移植治疗中的应用潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [14] | 彭洪成, 彭国璇, 雷安毅, 林 圆, 孙 红, 宁 旭, 尚显文, 邓 进, 黄明智. 血小板衍生生长因子BB参与生长板损伤修复的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
| [15] | 刘浩洋, 谢 强, 沈梦然, 任岩松, 马金辉, 王佰亮, 岳德波, 王卫国. 可降解锌基合金在骨缺损修复重建中的应用及研究热点和不足[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 839-845. |
近年来,低频脉冲电磁场(pulsed electromagnetic fields,PEMFs)作为一种新兴的非侵入性治疗技术,在促进肌肉修复与增长方面展现出巨大潜力[7]。
PEMFs通过产生的电磁场作用于生物组织,调节细胞膜电位和离子通道,促进细胞增殖、分化与组织再生[8],该技术不仅在骨折和关节炎的治疗中取得了显著效果[9-10],也逐渐在肌肉修复与增长领域中展现出了广阔的前景[11]。文章通过系统回顾现有文献,探讨PEMFs在调控细胞膜电位、钙离子信号传导和细胞内信号通路方面的作用,分析其在肌肉细胞的增殖、分化和修复中的机制,评估PEMFs在不同人群中的实际应用效果,旨在为科学地认识和应用PEMFs提供理论支撑和实践指导。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields,Muscle repair,Muscle growth,Electromagnetic biological effects”等,检索文献时限为2000-2024年,同时纳入少量远期经典文献。
1.2 文献入选标准
纳入标准:①纳入PEMFs发展历程及生物学效应相关研究;②纳入PEMFs促进肌肉修复与增长的机制研究;③纳入研究PEMFs促进肌肉修复与增长效果的文献,无论是细胞实验、动物实验还是临床研究;④纳入的文献需要设计合理、结果可靠,内容契合此文的主旨,且经过同行评审;⑤如果研究内容相似,则选择发表在近期及发表在核心权威杂志上的文章。
排除标准:①排除重复性研究;②排除文章质量差、设计不合理或发表在无同行评审的期刊者;③排除不能下载全文或数据不全的文章。
1.3 文献提取及筛选 初步检索获得527篇文献,其中来自PubMed数据库的英文文献480篇、来自CNKI的中文文献47篇,去重后由第一、二作者根据文题摘要进行初筛,获得153篇相关文献,之后查阅全文,按纳入排除标准进行筛选,纳入89篇文献进行综述,包括中文文献9篇、英文文献80篇。文献筛选流程图,见图1。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
文题释义:
低频脉冲电磁场:是一种通过特定频率和强度的脉冲电磁波进行治疗的非侵入性方法,通常采用低频(0-300 Hz)来治疗各种疾病,如骨质疏松和背痛等,其中低强度(小于100 mT)对改善身体功能有显著效果。#br# #br#文章亮点:(1)深入解析作用机制探讨了低频脉冲电磁场通过调节离子通道、钙离子信号传导及改善微循环,促进肌肉细胞增殖与分化的具体生物学路径。(2)综合实验证据汇总了动物实验、细胞研究及临床应用,证明低频脉冲电磁场显著提升新生肌纤维数量与质量,增强肌肉力量和功能恢复。
#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||