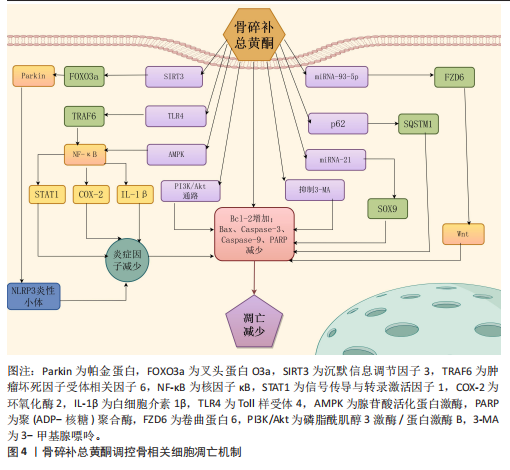
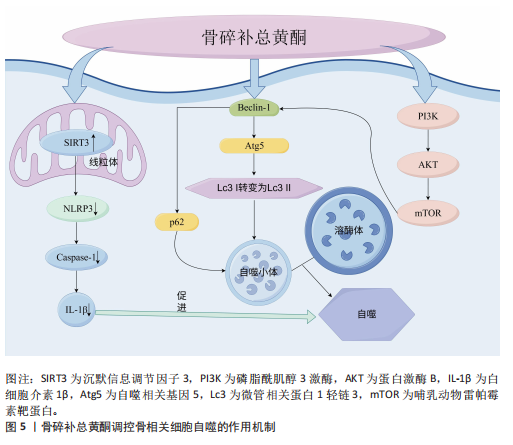
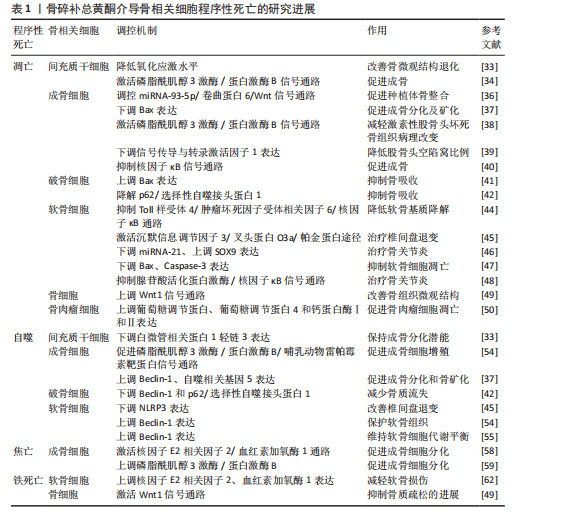
[1] WANG S, DENG Z, MA Y, et al. The Role of Autophagy and Mitophagy in Bone Metabolic Disorders. Int J Biol Sci. 2020; 16(14):2675-2691.
[2] TROMPET D, MELIS S, CHAGIN AS, et al. Skeletal stem and progenitor cells in bone development and repair. J Bone Miner Res. 2024;39(6):633-654.
[3] LI Y, LING J, JIANG Q. Inflammasomes in Alveolar Bone Loss. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:691013.
[4] STEGEN S, CARMELIET G. Metabolic regulation of skeletal cell fate and function. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2024;20(7):399-413.
[5] SUN Y, PENG ZL. Programmed cell death and cancer. Postgrad Med J. 2009;85(1001): 134-140.
[6] 梁松林,成文翔,张鹏,等.成骨细胞程序性死亡的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(3):385-390.
[7] CHEN L, YU C, XU W, et al. Dual-Targeted Nanodiscs Revealing the Cross-Talk between Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Macrophages. ACS Nano. 2023;17(3):3153-3167.
[8] XIA Y, GE G, XIAO H, et al. REPIN1 regulates iron metabolism and osteoblast apoptosis in osteoporosis. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(9):631.
[9] JIN Y, WU S, ZHANG L, et al. Artesunate inhibits osteoclast differentiation by inducing ferroptosis and prevents iron overload-induced bone loss. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023;132(2):144-153.
[10] XUE JF, SHI ZM, ZOU J, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:1252-1261.
[11] 谌顺清,梁伟,张雪妹,等.骨碎补化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2021,46(11):2737-2745.
[12] RAVETTI S, GARRO AG, GAITÁN A, et al. Naringin: Nanotechnological Strategies for Potential Pharmaceutical Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):863.
[13] MOTALLEBI M, BHIA M, RAJANI HF, et al. Naringenin: A potential flavonoid phytochemical for cancer therapy. Life Sci. 2022;305:120752.
[14] YAN Z, ZHAN J, QI W, et al. The Protective Effect of Luteolin in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1195.
[15] BANGAR SP, CHAUDHARY V, SHARMA N, et al. Kaempferol: A flavonoid with wider biological activities and its applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(28):9580-9604.
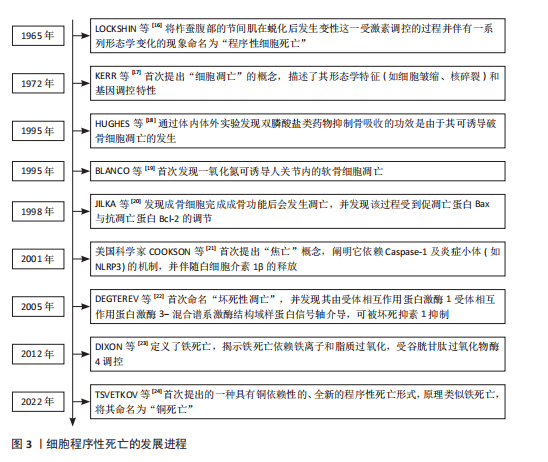
[16] LOCKSHIN RA, WILLIAMS CM. PROGRAMMED CELL DEATH--I. cytology of degeneration in the intersegmental muscles of the pernyi silkmoth. j insect physiol. 1965;11:123-133.
[17] KERR JF, WYLLIE AH, CURRIE AR. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972;26(4):239-257.
[18] HUGHES DE, WRIGHT KR, UY HL, et al. Bisphosphonates promote apoptosis in murine osteoclasts in vitro and in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 1995;10(10):1478-1487.
[19] BLANCO FJ, OCHS RL, SCHWARZ H, et al. Chondrocyte apoptosis induced by nitric oxide. Am J Pathol. 1995;146(1):75-85.
[20] JILKA RL, WEINSTEIN RS, BELLIDO T. Osteoblast programmed cell death (apoptosis): modulation by growth factors and cytokines. J Bone Miner Res. 1998;13(5):793-802.
[21] COOKSON BT, BRENNAN MA. Pro-inflammatory programmed cell death. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9(3):113-114.
[22] DEGTEREV A, HUANG Z, BOYCE M, et al. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 2005; 1(2):112-119.
[23] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012; 149(5):1060-1072.
[24] TSVETKOV P, COY S, PETROVA B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375(6586):1254-1261.
[25] BOCK FJ, RILEY JS. When cell death goes wrong: inflammatory outcomes of failed apoptosis and mitotic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30(2):293-303.
[26] Nagata S. Apoptosis and Clearance of Apoptotic Cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2018; 36:489-517.
[27] RODRÍGUEZ-GONZÁLEZ J, GUTIÉRREZ-KOBEH L. Apoptosis and its pathways as targets for intracellular pathogens to persist in cells. Parasitol Res. 2023;123(1):60.
[28] ABOLFATHI H, ARABI M, SHEIKHPOUR M. A literature review of microRNA and gene signaling pathways involved in the apoptosis pathway of lung cancer. Respir Res. 2023;24(1):55.
[29] LI W, JIANG WS, SU YR, et al. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy inhibits osteoblast apoptosis induced by advanced oxidation protein products. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(2):88.
[30] LIU CL, HO TL, FANG SY, et al. Ugonin L inhibits osteoclast formation and promotes osteoclast apoptosis by inhibiting the MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;166:115392.
[31] DING Y, WANG L, ZHAO Q, et al. MicroRNA 93 inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoarthritis by targeting the TLR4/NF κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(2):779-790.
[32] PITTENGER MF, MACKAY AM, BECK SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[33] 申意伟,李雪,张晓峰,等.柚皮苷对酒精诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞氧化应激、自噬、凋亡和成骨成脂分化的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2022,40(5):36-39,263-265.
[34] NAN LP, WANG F, RAN D, et al. Naringin alleviates H2O2-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Connect Tissue Res. 2020;61(6):554-567.
[35] 张艳杰,顾珊菱,赫子懿,等.治疗骨质疏松的药物对骨折愈合的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(18):4596-4599.
[36] 申晓靖,刘海蓉,厉华,等.骨碎补总黄酮对口腔种植骨整合中牙槽骨成骨细胞增殖和凋亡的影响研究[J].口腔医学, 2023,43(8):679-685.
[37] 吴泽钰.柚皮苷通过Akt/mTOR通路介导自噬促进牙槽骨成骨的作用及机制研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2023.
[38] LV W, YU M, YANG Q, et al. Total flavonoids of Rhizoma drynariae ameliorate steroid induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(5):345.
[39] YAN Z, ZHAN J, QI W, et al. The Protective Effect of Luteolin in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1195.
[40] PENG Z, ZHANG W, HONG H, et al. Effect of luteolin on oxidative stress and inflammation in the human osteoblast cell line hFOB1.19 in an inflammatory microenvironment. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024;25(1):40.
[41] 李风波,孙晓雷,马剑雄,等.柚皮苷对破骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(5):450-454.
[42] KIM CJ, SHIN SH, KIM BJ, et al. The Effects of Kaempferol-Inhibited Autophagy on Osteoclast Formation. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(1):125.
[43] AKARAPHUTIPORN E, SUNAGA T, BWALYA EC, et al. An Insight into the Role of Apoptosis and Autophagy in Nitric Oxide-Induced Articular Chondrocyte Cell Death. Cartilage. 2021;13(2_suppl):826S-838S.
[44] WANG Y, LI Z, WANG B, et alJ. Naringenin attenuates inflammation and apoptosis of osteoarthritic chondrocytes via the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway. PeerJ. 2023;11: e16307.
[45] WANG J, JING X, LIU X, et al. Naringin safeguards vertebral endplate chondrocytes from apoptosis and NLRP3 inflammasome activation through SIRT3-mediated mitophagy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024; 140:112801.
[46] 丘志河,谢卫勇,黄刚,等.山奈酚通过调控miR-21/SOX9对骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖、凋亡的影响[J].中国药师,2022, 25(12):2073-2078.
[47] 米倚林,易南星,许晓彤,等.山奈酚抑制软骨凋亡延缓小鼠膝骨关节炎的实验研究[J].海南医学院学报,2022,28(17): 1299-1306.
[48] CHEN GY, LIU XY, YAN XE, et al. Total Flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae Treat Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Arachidonic Acid Metabolites Through AMPK/NFκB Pathway. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:4123-4140.
[49] 兰双笠,向飞帆,邓光慧,等.柚皮苷抑制骨质疏松大鼠骨组织的铁沉积及细胞凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(5): 888-898.
[50] LEE CW, HUANG CC, CHI MC, et al. Naringenin Induces ROS-Mediated ER Stress, Autophagy, and Apoptosis in Human Osteosarcoma Cell Lines. Molecules. 2022; 27(2):373.
[51] LIU S, YAO S, YANG H, et al. Autophagy: Regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(10):648.
[52] TROJANI MC, SANTUCCI-DARMANIN S, BREUIL V, et al. Autophagy and bone diseases. Joint Bone Spine. 2022;89(3): 105301.
[53] LIU Y, ZHAO L, HE X, et al. Jintiange proteins promote osteogenesis and inhibit apoptosis of osteoblasts by enhancing autophagy via PI3K/AKT and ER stress pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;311:116399.
[54] GE X, ZHOU G. Protective effects of naringin on glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2021; 13(6):6330-6341.
[55] LI Y, DING Z, LIU F, et al. Luteolin regulating synthesis and catabolism of osteoarthritis chondrocytes via activating autophagy. Heliyon. 2024;10(11):e31028.
[56] HUANG Y, XU W, ZHOU R. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18(9):2114-2127.
[57] LI Z, LI D, CHEN R, et al. Cell death regulation: A new way for natural products to treat osteoporosis. Pharmacol Res. 2023; 187:106635.
[58] CAO S, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Naringenin can Inhibit the Pyroptosis of Osteoblasts by Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway and Alleviate the Differentiation Disorder of Osteoblasts Caused by Microgravity. J Agric Food Chem. 2024;72(46):25586-25600.
[59] CHAI S, YANG Y, WEI L, et al. Luteolin rescues postmenopausal osteoporosis elicited by OVX through alleviating osteoblast pyroptosis via activating PI3K-AKT signaling. Phytomedicine. 2024;128:155516.
[60] XIONG L, BIN ZHOU, YOUNG JL, et al. Exposure to low-dose cadmium induces testicular ferroptosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022;234:113373.
[61] SEIBT TM, PRONETH B, CONRAD M. Role of GPX4 in ferroptosis and its pharmacological implication. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133: 144-152.
[62] PAN Z, HE Q, ZENG J, et al. Naringenin protects against iron overload-induced osteoarthritis by suppressing oxidative stress. Phytomedicine. 2022;105:154330.
[63] ZHAO J, GUO S, SCHRODI SJ, et al. Cuproptosis and cuproptosis-related genes in rheumatoid arthritis: Implication, prospects, and perspectives. Front Immunol. 2022;13:930278.
[64] 王伟伟,欧志学,周毅,等.铜死亡基因在骨关节炎免疫浸润中的生物信息学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(11):1669-1676.
[65] TIAN Q, QIN B, GU Y, et al. ROS-Mediated Necroptosis Is Involved in Iron Overload-Induced Osteoblastic Cell Death. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:1295382.
[66] 冉栋成,王槐骏,杨城,等.坏死性凋亡与骨质疏松症机制研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(5):745-750.
[67] 余翔,黄志强,张鹏,等.骨碎补总黄酮干预骨质疏松性骨折愈合临床疗效机制研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2025,31(1):149-156.
[68] RAVETTI S, Garro AG, Gaitán A, et al. Naringin: Nanotechnological Strategies for Potential Pharmaceutical Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):863.
[69] 熊伟,袁灵梅,王梁霞,等.黄连素-柚皮苷双重载药复合微球的制备及其抗菌-成骨性能评估研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(12):1505-1513.
[70] MEHRANFARD N, GHASEMI M, RAJABIAN A, et al. Protective potential of naringenin and its nanoformulations in redox mechanisms of injury and disease. Heliyon. 2023;9(12):e22820.
[71] 曲扬,刘振红.复合凝聚法制备山奈酚微胶囊及对剧烈运动所致氧化应激损伤保护作用[J].食品科技,2025,50(1):275-283.
[72] 田莉,李伟宏,张付利.木犀草素磷脂复合物白蛋白纳米粒的制备及口服药动学评价[J].中草药,2024,55(10):3280-3290.
|