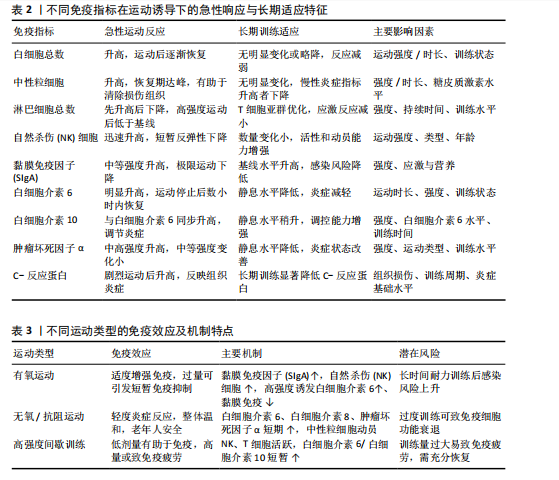
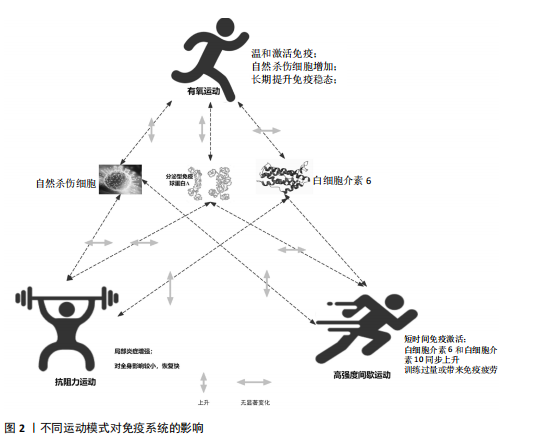
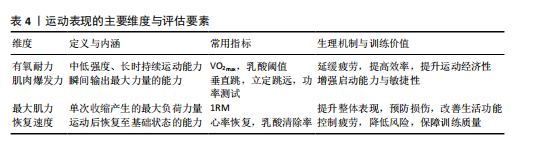
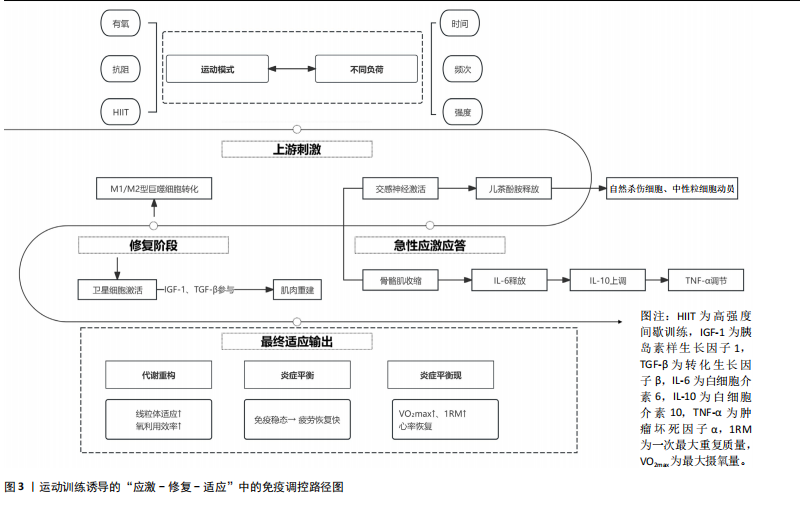
[1] SIMPSON RJ, CAMPBELL JP, GLEESON M, et al. Can exercise affect immune function to increase susceptibility to infection? Exerc Immunol Rev. 2020;26:8-22.
[2] SIMPSON RJ, KUNZ H, AGHA N, et al. Exercise and the Regulation of Immune Functions. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015; 135:355-380.
[3] NIEMAN DC, HOFFMAN-GOETZ L. Prolonged aerobic exercise, immune response, and risk of infection. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1996.
[4] CICCHELLA A, STEFANELLI C, MASSARO M. Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Sport and the Immune System Response. A Review. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(5):362.
[5] 张勉.赛前强化训练对我国田径短跨项目优秀运动员T淋巴细胞和唾液分泌型免疫球蛋白SIgA的影响[J].体育科学, 2002,22(4):91-94.
[6] KUROWSKI M, SEYS S, BONINI M, et al. Physical exercise, immune response, and susceptibility to infections-current knowledge and growing research areas. Allergy. 2022;77(9):2653-2664.
[7] SHAO T, VERMA HK, PANDE B, et al. Physical Activity and Nutritional Influence on Immune Function: An Important Strategy to Improve Immunity and Health Status. Front Physiol. 2021;12:751374.
[8] PAŁKA T, AMBROŻY T, SADOWSKA-KRĘPA E, et al. The Levels of Markers of Muscle Damage, Inflammation, and Heat Shock Proteins in Judokas and the Extent of Their Changes during a Special Performance Test at Different Ambient Temperatures. Applied Sciences. 2023;13(16):9381.
[9] HOOIJMANS MT, SCHLAFFKE L, BOLSTERLEE B, et al. Compositional and Functional MRI of Skeletal Muscle: A Review. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024;60(3):860-877.
[10] FORNAZIERO AM, NOVACK LF, NASCIMENTO VB, et al. Acute Responses of Youth Elite Players to a Football Match in Terms of Blood Markers. Sports (Basel). 2023;11(12): 242.
[11] DOMÍNGUEZ-ANDRÉS J, DOS SANTOS JC, BEKKERING S, et al. Trained immunity: adaptation within innate immune mechanisms. Physiol Rev. 2023;103(1):313-346.
[12] GRAY JI, FARBER DL. Tissue-Resident Immune Cells in Humans. Annu Rev Immunol. 2022;40:195-220.
[13] CANNON JG. Exercise and the acute phase response. Exercise and Immune function. Boca Raton: CRC Press,2024.
[14] IMAI J, KATAGIRI H. Regulation of systemic metabolism by the autonomic nervous system consisting of afferent and efferent innervation. Int Immunol. 2022;34(2):67-79.
[15] QUINTANA-MENDIAS E, RODRÍGUEZ-VILLALOBOS JM, GASTELUM-ARELLANEZ A, et al. The Effect of Acute Physical Exercise on Natural Killer Cells Populations and Cytokine Levels in Healthy Women. Sports (Basel). 2023;11(10):189.
[16] GŁÓWKA N, DURKALEC-MICHALSKI K, WOŹNIEWICZ M. Immunological Outcomes of Bovine Colostrum Supplementation in Trained and Physically Active People: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2020;12(4):1023.
[17] TEODORO TH, COSTA KPM, PRESTES J, et al. The effects of acute and chronic exercise on immune markers of TH1/TH2 cells in older adults: a systematic review. Front Physiol. 2025;16:1453747.
[18] LIRA FS, DOS SANTOS T, CALDEIRA RS, et al. Short-Term High- and Moderate-Intensity Training Modifies Inflammatory and Metabolic Factors in Response to Acute Exercise. Front Physiol. 2017;8:856.
[19] SELLAMI M, BRAGAZZI NL, ABOGHABA B, et al. The Impact of Acute and Chronic Exercise on Immunoglobulins and Cytokines in Elderly: Insights From a Critical Review of the Literature. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 631873.
[20] FERREIRA-JÚNIOR JB, FREITAS EDS, CHAVES SFN. Exercise: A Protective Measure or an “Open Window” for COVID-19? A Mini Review. Front Sports Act Living. 2020;2:61.
[21] PROSCHINGER S, SCHENK A, WEßELS I, et al. Intensity- and time-matched acute interval and continuous endurance exercise similarly induce an anti-inflammatory environment in recreationally active runners: focus on PD-1 expression in Tregs and the IL-6/IL-10 axis. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2023;123(11):2575-2584.
[22] ROSE GL, SKINNER TL, MIELKE GI, et al. The effect of exercise intensity on chronic inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sci Med Sport. 2021;24(4): 345-351.
[23] ZAID NSN, MUHAMAD AS, JAWIS MN, et al. High-Intensity Interval Training Protocols Variation Response to Immune Parameters and Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Scoping Review. Springer: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Movement, Health and Exercise, 2003.
[24] NOURPETELIAN R. Effect of high-intensity interval training on the central and peripheral nervous system in females. Kaunas: Lietuvos Sporto Universitetas, 2022.
[25] MCDOUGLE JM, MANGINE GT, TOWNSEND JR, et al. Acute physiological outcomes of high-intensity functional training: a scoping review. PeerJ. 2023;11:e14493.
[26] WANG YH, TAN J, ZHOU HH, et al. Long-term exercise training and inflammatory biomarkers in healthy subjects: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Psychol. 2023;14:1253329.
[27] PADILHA CS, FIGUEIREDO C, MINUZZI LG, et al. Immunometabolic responses according to physical fitness status and lifelong exercise during aging: New roads for exercise immunology. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;68:101341.
[28] PAN H, MENG R, JIA Z, et al. Exercise: a non-drug strategy of NK cell activation. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024;57:e14144.
[29] GOMARASCA M, MICIELSKA K, FARALDI M, et al. Impact of 12-Week Moderate-Intensity Aerobic Training on Inflammasome Complex Activation in Elderly Women. Front Physiol. 2022;13:792859.
[30] 石海旺,李婕,吴冲云,等.运动改善药物依赖者免疫功能障碍的研究进展[J].中国体育科技,2021,57(6):38-45.
[31] SIEDLIK J, DECKERT J, DUNBAR A, et al. Acute high-intensity exercise enhances T cell proliferation compared to moderate-intensity exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2025;50:1-12.
[32] YU X, PEI W, LI B, et al. Immunosenescence, Physical Exercise, and their Implications in Tumor Immunity and Immunotherapy. Int J Biol Sci. 2025;21(3):910-939.
[33] SÁNCHEZ MONTALVO A, GOHY S, ROMBAUX P, et al. The Role of IgA in Chronic Upper Airway Disease: Friend or Foe? Front Allergy. 2022;3:852546.
[34] KEAST D. Immune responses to overtraining and fatigue. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2024.
[35] KULLO IJ, KHALEGHI M, HENSRUD DD. Markers of inflammation are inversely associated with VO2 max in asymptomatic men. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007;102(4):1374-1379.
[36] FÄLDT J, WERNSTEDT I, FITZGERALD SM, et al. Reduced exercise endurance in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Endocrinology. 2004;145(6):2680-2686.
[37] BURZYN D, KUSWANTO W, KOLODIN D, et al. A special population of regulatory T cells potentiates muscle repair. Cell. 2013;155(6):1282-1295.
[38] KRÜGER K, ALACK K, RINGSEIS R, et al. Exercise induced modulation of natural killer cell function and sprint performance in trained athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020;120:1767-1779.
[39] NIEMAN DC. Exercise, infection, and immunity. Int J Sports Med. 1994;15 Suppl 3:S131-141.
[40] WALSH NP, GLEESON M, PYNE DB, et al. Position statement. Part two: Maintaining immune health. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2011; 17:64-103.
[41] KALÉN A, BISAGNO E, MUSCULUS L, et al. The role of domain-specific and domain-general cognitive functions and skills in sports performance: A meta-analysis. Psychol Bull. 2021;147(12):1290-1308.
[42] MALONE D. Cardiovascular and Pulmonary System. London: Routledge, 2024.
[43] JAMES LP, TALPEY SW, YOUNG WB, et al. Strength classification and diagnosis: not all strength is created equal. Strength Cond J. 2023;45(3):333-341.
[44] SANDFORD GN, LAURSEN PB, BUCHHEIT M. Anaerobic Speed/Power Reserve and Sport Performance: Scientific Basis, Current Applications and Future Directions. Sports Med. 2021;51(10):2017-2028.
[45] OLEKSANDRA B, YURIY F, SVITLANA S, et al. Adaptation of students with different body composition components to aerobic and anaerobic training. Sport Soc. 2021;21(1):1.
[46] SPRIET LL. Anaerobic metabolism during exercise. Berlin: Springer, 2022.
[47] ATTWATERS M, HUGHES SM. Cellular and molecular pathways controlling muscle size in response to exercise. FEBS J. 2022; 289(6):1428-1456.
[48] LÄHTEENMÄKI EI, KOSKI M, KOSKELA I, et al. Resistance exercise with different workloads have distinct effects on cellular respiration of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Physiol Rep. 2022;10(14):e15394.
[49] WU J, REN B, WANG D, et al. Regulatory T cells in skeletal muscle repair and regeneration: recent insights. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(8):680.
[50] EMERSON DM, CHEN SC, KELLY MR, et al. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on core body temperature during exercise: A systematic review. J Exerc Sci Fit. 2021; 19(2):127-133.
[51] WANG X, ZHOU L. The Many Roles of Macrophages in Skeletal Muscle Injury and Repair. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:952249.
[52] ARNOLD L, HENRY A, PORON F, et al. Inflammatory monocytes recruited after skeletal muscle injury switch into antiinflammatory macrophages to support myogenesis. J Exp Med. 2007;204(5):1057-1069.
[53] WEI W, RAUN SH, LONG JZ. Molecular Insights From Multiomics Studies of Physical Activity. Diabetes. 2024;73(2):162-168.
[54] KUSWANTO W, BURZYN D, PANDURO M, et al. Poor Repair of Skeletal Muscle in Aging Mice Reflects a Defect in Local, Interleukin-33-Dependent Accumulation of Regulatory T Cells. Immunity. 2016;44(2):355-367.
[55] CEBRIÁN‑SERRANO A, KHOSRAVI‑ MAHARLOOEI M, BUCHHOLZ VR, et al. CD103⁺ tissue‑resident memory T cells expedite recall responses during skeletal‑muscle regeneration. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1183671.
[56] SHAH F, GIRI PS, BHARTI AH, et al. Compromised melanocyte survival due to decreased suppression of CD4+ & CD8+ resident memory T cells by impaired TRM-regulatory T cells in generalized vitiligo patients. Exp Dermatol. 2024;33(1):e14982.
[57] MAGNUSSON SP, LANGBERG H, KJAER M. The pathogenesis of tendinopathy: balancing the response to loading. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(5):262-268.
[58] SCHMITT EG, HARIBHAI D, WILLIAMS JB, et al. IL-10 produced by induced regulatory T cells (iTregs) controls colitis and pathogenic ex-iTregs during immunotherapy. J Immunol. 2012;189(12):5638-5648.
[59] LOUATI K, BERENBAUM F. Fatigue in chronic inflammation - a link to pain pathways. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:254.
[60] VANDERVEEN BN, FIX DK, MONTALVO RN, et al. The regulation of skeletal muscle fatigability and mitochondrial function by chronically elevated interleukin-6. Exp Physiol. 2019;104(3):385-397.
[61] NIEMAN DC, PENCE BD. Exercise immunology: Future directions. J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(5):432-445.
[62] DOCHERTY S, HARLEY R, MCAULEY JJ, et al. The effect of exercise on cytokines: implications for musculoskeletal health: a narrative review. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2022;14(1):5.
[63] YASEN A, SUN W, AINI A, et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals the Heterogeneity of Infiltrating Immune Cell Profiles in the Hepatic Cystic Echinococcosis Microenvironment. Infect Immun. 2021; 89(12):e0029721.
[64] GUO Q, JIN Y, CHEN X, et al. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: new insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):53.
[65] SU J, SONG Y, ZHU Z, et al. Cell-cell communication: new insights and clinical implications. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):196.
[66] MAUGHAN R. History of Exercise Physiology. J Sports Sci. 2015;33(15):1639-1640.
[67] RAMESSUR R, DAND N, LANGAN SM, et al. Defining disease severity in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis for the application to biomarker research: an interdisciplinary perspective. Br J Dermatol. 2024;191(1):14-23.
[68] NIEMAN DC. Risk of upper respiratory tract infection in athletes: an epidemiologic and immunologic perspective. J Athl Train. 1997;32(4):344-349.
[69] SHINKAI S, SHORE S, SHEK PN, et al. Acute exercise and immune function. Relationship between lymphocyte activity and changes in subset counts. Int J Sports Med. 1992; 13(6):452-461.
[70] OSTROWSKI K, ROHDE T, ASP S, et al. Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine balance in strenuous exercise in humans. J Physiol. 1999;515(Pt 1):287-291.
[71] STEENSBERG A, VAN HALL G, OSADA T, et al. Production of interleukin-6 in contracting human skeletal muscles can account for the exercise-induced increase in plasma interleukin-6. J Physiol. 2000;529 Pt 1(Pt 1): 237-242.
[72] ABRAMSON JL, VACCARINO V. Relationship between physical activity and inflammation among apparently healthy middle-aged and older US adults. Arch Intern Med. 2002; 162(11):1286-1292.
[73] PEDERSEN BK, FISCHER CP. Beneficial health effects of exercise--the role of IL-6 as a myokine. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007; 28(4):152-156.
[74] PERRY C, PICK M, BDOLACH N, et al. Endurance exercise diverts the balance between Th17 cells and regulatory T cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e74722.
[75] PEDERSEN L, IDORN M, OLOFSSON GH, et al. Voluntary Running Suppresses Tumor Growth through Epinephrine- and IL-6-Dependent NK Cell Mobilization and Redistribution. Cell Metab. 2016;23(3):554-562.
[76] CLIFFORD T, WOOD MJ, STOCKS P, et al. T-regulatory cells exhibit a biphasic response to prolonged endurance exercise in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017;117(8):1727-1737.
[77] CAMPBELL JP, TURNER JE. Debunking the Myth of Exercise-Induced Immune Suppression: Redefining the Impact of Exercise on Immunological Health Across the Lifespan. Front Immunol. 2018;9:648.
[78] HU X, XU J, GU Y. Inverted U-Shaped Association of Soluble Transferrin Receptor Concentrations with Risks of Cardiovascular Diseases in Overweight Individuals: A Cross-Sectional Study. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024; 25(12):439.
[79] NIE Y, MA Y, WU Y, et al. Association Between Physical Exercise and Mental Health During the COVID-19 Outbreak in China: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:722448.
[80] PETERSEN AM, PEDERSEN BK. The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005;98(4):1154-1162.
[81] CHEN Z, LAN H, LIAO Z, et al. Regulatory T cells-centered regulatory networks of skeletal muscle inflammation and regeneration. Cell Biosci. 2022;12(1):112.
|