[1] BERGLUNDH T, ARMITAGE G, ARAUJO MG, et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(S20):S286-S291.
[2] ASTOLFI V, RÍOS-CARRASCO B, GIL-MUR FJ, et al. Incidence of Peri-Implantitis and Relationship with Different Conditions: A Retrospective Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(7):4147.
[3] RODRIGO D, SANZ-SÁNCHEZ I, FIGUERO E, et al. Prevalence and risk indicators of peri-implant diseases in Spain. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(12): 1510-1520.
[4] ROOS-JANSÅKER AM, LINDAHL C, RENVERT H, et al. Nine-to fourteen-year follow-up of implant treatment. Part II: presence of peri-implant lesions. J Clin Periodontol. 2006;33(4):290-295.
[5] DIAZ P, GONZALO E, VILLAGRA LJG, et al. What is the prevalence of peri-implantitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):449.
[6] BELIBASAKIS GN, MANOIL D. Microbial Community-Driven Etiopathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis. J Dent Res. 2021;100(1):21-28.
[7] MOMBELLI A. Maintenance therapy for teeth and implants. Periodontol 2000. 2019;79(1):190-199.
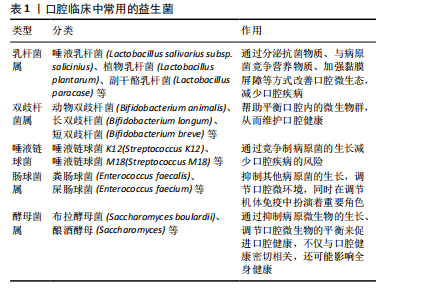
[8] AMATO M, DI SPIRITO F, D’AMBROSIO F, et al. Probiotics in Periodontal and Peri-Implant Health Management: Biofilm Control, Dysbiosis Reversal, and Host Modulation. Microorganisms. 2022;10(11):2289.
[9] CHUN GIOK K, MENON RK. The Microbiome of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review of Next-Generation Sequencing Studies. Antibiotics. 2023;12(11):1610.
[10] LAFAURIE GI, SABOGAL MA, CASTILLO DM, et al. Microbiome and Microbial Biofilm Profiles of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J Periodontol. 2017;88(10):1066-1089.
[11] LIÑARES A, SANZ-SÁNCHEZ I, DOPICO J, et al. Efficacy of adjunctive measures in the non‐surgical treatment of peri‐implantitis: A systematic review. J Clin Periodontol. 2023;50(S26):224-243.
[12] RAMS TE, DEGENER JE, VAN WINKELHOFF AJ. Antibiotic resistance in human chronic periodontitis microbiota. J Periodontol. 2014;85(1): 160-169.
[13] VAN WINKELHOFF AJ, HERRERA GONZALES D, WINKEL EG, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in the subgingival microflora in patients with adult periodontitis. A comparison between The Netherlands and Spain. J Clin Periodontol. 2000;27(2):79-86.
[14] HAFFAJEE AD, TELES RP, SOCRANSKY SS. The effect of periodontal therapy on the composition of the subgingival microbiota. Periodontol 2000. 2006;42:219-258.
[15] YADAV MK, KUMARI I, SINGH B, et al. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics: Safe options for next-generation therapeutics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022;106(2):505-521.
[16] REID G; FOOD AND AGRICULTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATION AND THE WHO. The importance of guidelines in the development and application of probiotics. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(1):11-16.
[17] FIJAN S. Microorganisms with claimed probiotic properties: an overview of recent literature. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;11(5): 4745-4767.
[18] SAVIANO A, PETRUZZIELLO C, CANCRO C, et al. The Efficacy of a Mix of Probiotics (Limosilactobacillus reuteri LMG P-27481 and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG ATCC 53103) in Preventing Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea and Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized Patients: Single-Center, Open-Label, Randomized Trial. Microorganisms. 2024;12(1):198.
[19] CHEN Z, LIANG W, LIANG J, et al. Probiotics: functional food ingredients with the potential to reduce hypertension. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023;13:1220877.
[20] KALLASSY J, GAGNON E, ROSENBERG D, et al. Strains of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and its extracts reduce blood glucose levels, percent HbA1c, and improve glucose tolerance without causing hypoglycemic side effects in diabetic and prediabetic mice. BMJ Open Diab Res Care. 2023;11(3):e003101.
[21] LIU Y, WANG J, WU C. Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Immune System by Probiotics, Pre-biotics, and Post-biotics. Front Nutr. 2021;8: 634897.
[22] HOMAYOUNI RAD A, POURJAFAR H, MIRZAKHANI E. A comprehensive review of the application of probiotics and postbiotics in oral health. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023;13:1120995.
[23] 晏子衡.益生菌对Er:YAG激光治疗种植体周围炎疗效影响的临床观察[D].南京:南京医科大学,2018.
[24] Zaghloul SA, Hashem SN, El-Sayed SR, et al. Evaluation of the Cariogenic and Anti-Cariogenic Potential of Human Colostrum and Colostrum-Derived Probiotics: Impact on S. mutans Growth, Biofilm Formation, and L. rhamnosus Growth. Life. 2023;13(9):1869.
[25] ZIDAR A, KRISTL J, KOCBEK P, et al. Treatment challenges and delivery systems in immunomodulation and probiotic therapies for periodontitis. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021;18(9):1229-1244.
[26] SARMENTO ÉG, CESAR DE, MARTINS ML, et al. Effect of probiotic bacteria in composition of children’s saliva. Food Res Int. 2019;116: 1282-1288.
[27] INCHINGOLO F, MARTELLI FS, GARGIULO ISACCO C, et al. Chronic Periodontitis and Immunity, Towards the Implementation of a Personalized Medicine: A Translational Research on Gene Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Linked to Chronic Oral Dysbiosis in 96 Caucasian Patients. Biomedicines. 2020;8(5):115.
[28] SCHLAGENHAUF U, REHDER J, GELBRICH G, et al. Consumption of Lactobacillus reuteri-containing lozenges improves periodontal health in navy sailors at sea: A randomized controlled trial. J Periodontol. 2020;91(10):1328-1338.
[29] DARBY I. Risk factors for periodontitis & peri-implantitis. Periodontol 2000. 2022;90(1):9-12.
[30] ROCCUZZO A, IMBER JC, SALVI GE, et al. Peri-implantitis as the consequence of errors in implant therapy. Periodontology 2000. 2023; 92(1):350-361.
[31] CHALA M, ANAGNOSTAKI E, MYLONA V, et al. Adjunctive Use of Lasers in Peri-Implant Mucositis and Peri-Implantitis Treatment: A Systematic Review. Dent J (Basel). 2020;8(3):68.
[32] CAI R, LIU Y, WANG X, et al. Influences of standardized clinical probing on peri-implant soft tissue seal in a situation of peri-implant mucositis: A histomorphometric study in dogs. J Periodontol.2024;95(3):233-243.
[33] DI RAIMONDO R, SANZ-ESPORRIN J, MARTIN IS, et al. Hard tissue volumetric and soft tissue contour linear changes at implants with different surface characteristics after experimentally induced peri-implantitis: an experimental in vivo investigation. Clin Oral Invest. 2021;25(6):3905-3918.
[34] DI SPIRITO F, GIORDANO F, DI PALO MP, et al. Reliability and Accuracy of YouTube Peri-Implantitis Videos as an Educational Source for Patients in Population-Based Prevention Strategies. Healthcare. 2023;11(14):2094.
[35] DINI C, COSTA RC, BERTOLINI M, et al. In-vitro polymicrobial oral biofilm model represents clinical microbial profile and disease progression during implant-related infections. J Appl Microbiol. 2023;134(11):lxad265.
[36] DI SPIRITO F, GIORDANO F, DI PALO MP, et al. Microbiota of Peri-Implant Healthy Tissues, Peri-Implant Mucositis, and Peri-Implantitis: A Comprehensive Review. Microorganisms. 2024;12(6):1137.
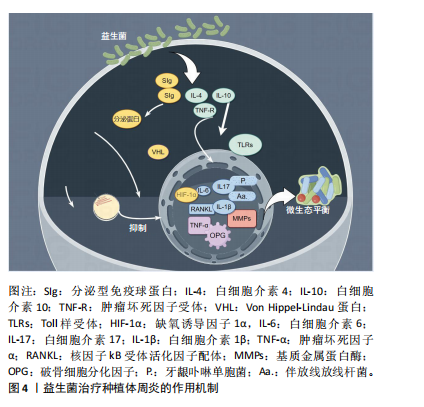
[37] ROUTIER A, BLAIZOT A, AGOSSA K, et al. What do we know about the mechanisms of action of probiotics on factors involved in the pathogenesis of periodontitis? A scoping review of in vitro studies. Arch Oral Biol. 2021;129:105196.
[38] BACA-CASTAÑÓN ML, DE LA GARZA-RAMOS MA, ALCÁZAR-PIZAÑA AG, et al. Antimicrobial Effect of Lactobacillus reuteri on Cariogenic Bacteria Streptococcus gordonii, Streptococcus mutans, and Periodontal Diseases Actinomyces naeslundii and Tannerella forsythia. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2015;7(1):1-8.
[39] NGUYEN T, BRODY H, RADAIC A, et al. Probiotics for periodontal health-Current molecular findings. Periodontol 2000. 2021;87(1):254-267.
[40] HAN N, JIA L, GUO L, et al. Balanced oral pathogenic bacteria and probiotics promoted wound healing via maintaining mesenchymal stem cell homeostasis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):61.
[41] SUN H, CHAN Y, LI X, et al. Multi-omics analysis of oral bacterial biofilm on titanium oxide nanostructure modified implant surface: In vivo sequencing-based pilot study in beagle dogs. Materials Today Bio. 2022;15:100275.
[42] LAFUENTE-IBÁÑEZ DE MENDOZA I, SETIEN-OLARRA A, GARCÍA-DE LA FUENTE AM, et al. Role of proinflammatory mutations in peri-implantitis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Implant Dent. 2022;8(1):2.
[43] JIA Q, LIU L, YU Y, et al. Inhibition of EGFR Pathway Suppresses M1 Macrophage Polarization and Osteoclastogenesis, Mitigating Titanium Particle-Induced Bone Resorption. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17: 9725-9742.
[44] VIRK MS, VIRK MA, HE Y, et al. The Anti-Inflammatory and Curative Exponent of Probiotics: A Comprehensive and Authentic Ingredient for the Sustained Functioning of Major Human Organs. Nutrients. 2024;16(4):546.
[45] MALKA O, MALISHEV R, BERSUDSKY M, et al. Tryptophol Acetate and Tyrosol Acetate, Small-Molecule Metabolites Identified in a Probiotic Mixture, Inhibit Hyperinflammation. J Innate Immun. 2023;15(1):531-547.
[46] VINCENZI A, GOETTERT MI, VOLKEN DE SOUZA CF. An evaluation of the effects of probiotics on tumoral necrosis factor (TNF-α) signaling and gene expression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021;57:27-38.
[47] HSU CY, MUSTAFA MA, MOATH OMAR T, et al. Gut instinct: harnessing the power of probiotics to tame pathogenic signaling pathways in ulcerative colitis. Front Med. 2024;11:1396789.
[48] RADAIC A, BRODY H, CONTRERAS F, et al. Nisin and Nisin Probiotic Disrupt Oral Pathogenic Biofilms and Restore Their Microbiome Composition towards Healthy Control Levels in a Peri-Implantitis Setting. Microorganisms. 2022;10(7):1336.
[49] KRASSE P, CARLSSON B, DAHL C, et al. Decreased gum bleeding and reduced gingivitis by the probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri. Swed Dent J. 2006;30(2):55-60.
[50] GRUNER D, PARIS S, SCHWENDICKE F. Probiotics for managing caries and periodontitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent. 2016; 48:16-25.
[51] QU R, CHEN X, HU J, et al. Ghrelin protects against contact dermatitis and psoriasiform skin inflammation by antagonizing TNF-α/NF-κB signaling pathways. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1348.
[52] LASSERRE JF, BRECX MC, TOMA S. Oral Microbes, Biofilms and Their Role in Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases. Materials (Basel). 2018;11(10):1802.
[53] RIEDEL CU, FOATA F, PHILIPPE D, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of bifidobacteria by inhibition of LPS-induced NF-κB activation. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(23):3729-3735.
[54] LIU Y, YANG H, WANG P, et al. Correlation between short-chain fatty acids and peri-implant disease: A cross-sectional study. J Periodontol. 2024. doi: 10.1002/JPER.23-0682.
[55] FU Q, ZHOU S, YU M, et al. Portulaca oleracea Polysaccharides Modulate Intestinal Microflora in Aged Rats in vitro. Front Microbiol. 2022;13: 841397.
[56] JAMALPOOR Z, ASGARI A, LASHKARI MH, et al. Modulation of Macrophage Polarization for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;17(5):398-408.
[57] ZHU L, LIU X, NEMETH DP, et al. Interleukin-1 causes CNS inflammatory cytokine expression via endothelia-microglia bi-cellular signaling. Brain Behav Immun. 2019;81:292-304.
[58] LIU LR, LIU JC, BAO JS, et al. Interaction of Microglia and Astrocytes in the Neurovascular Unit. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1024.
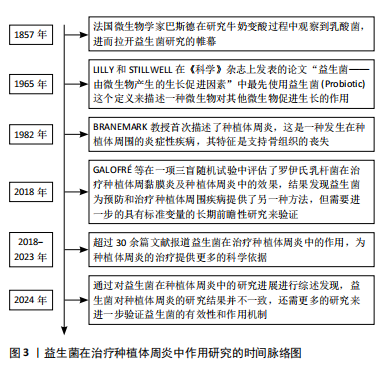
[59] GALOFRÉ M, PALAO D, VICARIO M, et al. Clinical and microbiological evaluation of the effect of Lactobacillus reuteri in the treatment of mucositis and peri-implantitis: A triple-blind randomized clinical trial. J Periodontal Res. 2018;53(3):378-390.
[60] CAI R, LIU Y, WANG X, et al. Influences of standardized clinical probing on peri-implant soft tissue seal in a situation of peri-implant mucositis: A histomorphometric study in dogs. J Periodontol. 2024;95(3):233-243.
[61] MATSUBARA VH, FAKHRUDDIN KS, NGO H, et al. Probiotic Bifidobacteria in Managing Periodontal Disease: A Systematic Review. Int Dent J. 2023;73(1):11-20.
[62] AL-HABSI N, AL-KHALILI M, HAQUE SA, et al. Health Benefits of Prebiotics, Probiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics. Nutrients. 2024; 16(22):3955.
[63] FULLER R. Probiotics in human medicine. Gut. 1991;32(4):439-442.
[64] ENGEVIK MA, RUAN W, ESPARZA M, et al. Immunomodulation of dendritic cells by Lactobacillus reuteri surface components and metabolites. Physiol Rep. 2021;9(2):e14719.
[65] MU Q, TAVELLA VJ, LUO XM. Role of Lactobacillus reuteri in Human Health and Diseases. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:757.
[66] ANTHONEY N, FOLDI I, HIDALGO A. Toll and Toll-like receptor signalling in development. Development. 2018;145(9):dev156018.
[67] INVERNICI MM, FURLANETO FAC, SALVADOR SL, et al. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp lactis HN019 presents antimicrobial potential against periodontopathogens and modulates the immunological response of oral mucosa in periodontitis patients. PLoS One. 2020;15(9): e0238425.
[68] KNACKSTEDT R, KNACKSTEDT T, GATHERWRIGHT J. The role of topical probiotics on wound healing: A review of animal and human studies. Int Wound J. 2020;17(6):1687-1694.
[69] OISHI Y, MANABE I. Macrophages in inflammation, repair and regeneration. Int Immunol. 2018; 30(11):511-528.
[70] GALARRAGA-VINUEZA ME, OBREJA K, RAMANAUSKAITE A, et al. Macrophage polarization in peri-implantitis lesions. Clin Oral Invest. 2021;25(4):2335-2344.
[71] JEONG S, KWON A, JEONG H, et al. Synergistic Immunostimulatory Activities of Probiotic Strains, Leuconostoc lactis and Weissella cibaria, and the Prebiotic Oligosaccharides They Produce. Microorganisms. 2023;11(5):1354.
[72] MULLA M, MULLA M, HEGDE S, et al. In vitro assessment of the effect of probiotic lactobacillus reuteri on peri-implantitis microflora. BMC Oral Health. 2021;21(1):408.
[73] MULLA M, HEGDE S, KOSHY A, et al. Effect of Probiotic Lactobacillus salivarius on Peri-Implantitis Pathogenic Bacteria: An In Vitro Study. Cureus. 2021;13(12):e20808.
[74] VACCA C, CONTU MP, ROSSI C, et al. In vitro Interactions between Streptococcus intermedius and Streptococcus salivarius K12 on a Titanium Cylindrical Surface. Pathogens. 2020;9(12):1069.
[75] YANG Y, SONG X, WANG G, et al. Understanding Ligilactobacillus salivarius from Probiotic Properties to Omics Technology: A Review. Foods. 2024;13(6):895.
[76] PALLOS D, SOUSA V, FERES M, et al. Salivary Microbial Dysbiosis Is Associated With Peri-Implantitis: A Case-Control Study in a Brazilian Population. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;11: 696432.
[77] ZHU Y, XIAO L, SHEN D, et al. Competition between yogurt probiotics and periodontal pathogens in vitro. Acta Odontol Scand. 2010;68(5):261-268.
[78] GALOFRÉ M, PALAO D, VICARIO M, et al. Clinical and microbiological evaluation of the effect of Lactobacillus reuteri in the treatment of mucositis and peri-implantitis: A triple-blind randomized clinical trial. J Periodontal Res. 2018;53(3):378-390.
[79] KAZEMI N, KHORASGANI MR, NOORBAKHSHNIA M, et al. Protective effects of a lactobacilli mixture against Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology triggered by Porphyromonas gingivalis. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1): 27283.
[80] KÕLL-KLAIS P, MÄNDAR R, LEIBUR E, et al. Oral lactobacilli in chronic periodontitis and periodontal health: species composition and antimicrobial activity. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2005;20(6):354-361.
[81] TADA H, MASAKI C, TSUKA S, et al. The effects of Lactobacillus reuteri probiotics combined with azithromycin on peri-implantitis: A randomized placebo-controlled study. J Prosthodont Res. 2018;62(1): 89-96.
[82] ZHAN H, HE Y, WANG Q, et al. Evaluation of Probiotic Strains Isolated from Artemisia argyi Fermentation Liquor and the Antagonistic Effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum against Pathogens. Fermentation. 2023;9(6):536.
[83] SANCA FMM, BLANCO IR, DIAS M, et al. Antimicrobial Activity of Peptides Produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis on Swine Pathogens. Animals. 2023;13(15):2442.
[84] SAHIN T. Fermented foods and probiotic consumption frequency as protective indicators for peri-implant diseases – a cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):849.
[85] 张艺庭.在种植体周围疾病治疗中应用益生菌的临床疗效的Meta分析[D].济南:山东大学,2023.
[86] BUTERA A, MAIORANI C, GALLO S, et al. Evaluation of Adjuvant Systems in Non-Surgical Peri-Implant Treatment: A Literature Review. Healthcare. 2022;10(5):886.
[87] LÓPEZ-VALVERDE N, LÓPEZ-VALVERDE A, BLANCO RUEDA JA. The role of probiotic therapy on clinical parameters and human immune response in peri-implant diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical studies. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1371072.
[88] SAYARDOUST S, JOHANSSON A, JÖNSSON D. Do Probiotics Cause a Shift in the Microbiota of Dental Implants-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12:823985.
[89] EFSA PANEL ON BIOLOGICAL HAZARDS (BIOHAZ), RICCI A, ALLENDE A, et al. Update of the list of QPS-recommended biological agents intentionally added to food or feed as notified to EFSA 8: suitability of taxonomic units notified to EFSA until March 2018. EFSA J. 2018; 16(7):e05315.
[90] LIU X, ZHAO H, WONG A. Accounting for the health risk of probiotics. Heliyon. 2024;10(6):e27908. |