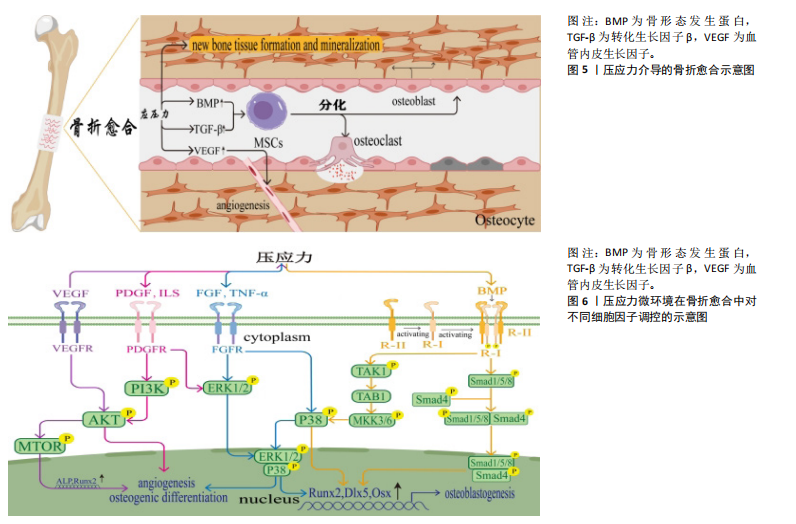
[1] 冯兴超,杨毅,金格勒.力学刺激在骨愈合中的作用及机制研究进展[J].四川解剖学杂志,2021,29(1):187-191.
[2] JIN SS, HE DQ, WANG Y, et al. Mechanical force modulates periodontal ligament stem cell characteristics during bone remodelling via TRPV4. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(10):e12912.
[3] EDAMOTO M, KURODA Y, YODA M, et al. Trans-pairing between osteoclasts and osteoblasts shapes the cranial base during development. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1956.
[4] ZHANG S, LU C, ZHENG S, et al. Hydrogel loaded with bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes promotes bone regeneration by inhibiting inflammatory responses and angiogenesis. World J Stem Cells. 2024;16(5):499-511.
[5] 胡建威,彭烨,张里程,等.骨折端力学环境研究进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2022,15(1):76-80.
[6] SHEEN JR, MABROUK A, GARLA VV. Fracture Healing Overview. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL); StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC. 2024.
[7] 王海锋,韩培彦,郝龙英,等.成骨细胞承受不同大小和不同时间压力后增殖变化的研究[J].北京口腔医学,2010,18(4):193-1955.
[8] 桂颖丽.静态张应力和压力刺激对大鼠成骨样细胞增殖及碱性磷酸酶表达影响的研究[D].成都:四川大学,2005.
[9] RATH B, NAM J, KNOBLOCH TJ, et al. Compressive forces induce osteogenic gene expression in calvarial osteoblasts. J Biomech. 2008; 41(5):1095-1103.
[10] YANG X, JIANG J, ZHOU L, et al. Osteogenic and angiogenic characterization of mandible and femur osteoblasts. J Mol Histol. 2019;50(2):105-117.
[11] ALFORD AI, KOZLOFF KM, HANKENSON KD. Extracellular matrix networks in bone remodeling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015;65:20-31.
[12] 刘奕斐.压力对小鼠成骨细胞增殖活性影响的基因表达谱差异分析[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2016.
[13] D’ANDREA CR, ALFRAIHAT A, SINGH A, et al. Part 2. Review and meta-analysis of studies on modulation of longitudinal bone growth and growth plate activity: A micro-scale perspective. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(5):919-928.
[14] LIU P, TU J, WANG W, et al. Effects of Mechanical Stress Stimulation on Function and Expression Mechanism of Osteoblasts. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:830722.
[15] 闫鹏安,蔡逸帆,闫振兴,等.体外实验中压应力对细胞的作用和影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(23):4993-5001.
[16] 陈涵纲,陈华,苏楠,等.FGFR1在骨骼发育、稳态维持和损伤修复中的作用研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(6):869-874.
[17] WANG L, YOU X, ZHANG L, et al. Mechanical regulation of bone remodeling. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):16.
[18] SUN X, MCLAMORE E, KISHORE V, et al. Mechanical stretch induced calcium efflux from bone matrix stimulates osteoblasts. Bone. 2012; 50(3):581-591.
[19] 林伟斌,朱聪,洪海森,等.体外周期性压应力对兔胫骨骨折愈合过程成骨与破骨细胞增殖分化能力的影响[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2021,16(4):289-300.
[20] LI X, KORDSMEIER J, XIONG J. New Advances in Osteocyte Mechanotransduction. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021;19(1):101-106.
[21] BUCK HV, STAINS JP. Osteocyte-mediated mechanical response controls osteoblast differentiation and function. Front Physiol. 2024; 15:1364694.
[22] WU Y, LI X, SUN Y, et al. Multiscale design of stiffening and ROS scavenging hydrogels for the augmentation of mandibular bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2023;20:111-125.
[23] GE YW, FAN ZH, KE QF, et al. SrFe(12)O(19)-doped nano-layered double hydroxide/chitosan layered scaffolds with a nacre-mimetic architecture guide in situ bone ingrowth and regulate bone homeostasis. Mater Today Bio. 2022;16:100362.
[24] NA NAN D, KLINCUMHOM N, TRACHOO V, et al. Periostin-integrin interaction regulates force-induced TGF-β1 and α-SMA expression by hPDLSCs. Oral Dis. 2024;30(4):2570-2579.
[25] WANG Y, ZHENG Y, LI W. Compression loading of osteoclasts attenuated microRNA-146a-5p expression, which promotes angiogenesis by targeting adiponectin. Sci China Life Sci. 2022;65(1):151-166.
[26] ZHAN JW, WANG SQ, FENG MS, et al. Constant compression decreases vascular bud and VEGFA expression in a rabbit vertebral endplate ex vivo culture model. PLoS One. 2020;15(6):e0234747.
[27] DAZZI C, MEHL J, BENAMAR M, et al. External mechanical loading overrules cell-cell mechanical communication in sprouting angiogenesis during early bone regeneration. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023; 19(11):e1011647.
[28] GANGULY K, LUTHFIKASARI R, RANDHAWA A, et al. Stimuli-Mediated Macrophage Switching, Unraveling the Dynamics at the Nanoplatforms-Macrophage Interface. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(20):e2400581.
[29] SU Y, YIN X. The Molecular Mechanism of Macrophages in Response to Mechanical Stress. Ann Biomed Eng. 2024 Oct 1. doi: 10.1007/s10439-024-03616-8.
[30] LIU Q, HU X, ZHANG X, et al. Effects of mechanical stress on chondrocyte phenotype and chondrocyte extracellular matrix expression. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37268.
[31] LIU Y, DZIDOTOR G, LE TT, et al. Exercise-induced piezoelectric stimulation for cartilage regeneration in rabbits. Sci Transl Med. 2022; 14(627):eabi7282.
[32] WU W, ZHAO Z, WANG Y, et al. Biomechanical Effects of Mechanical Stress on Cells Involved in Fracture Healing. Orthop Surg. 2024;16(4): 811-820.
[33] HUANG C, OGAWA R. Mechanotransduction in bone repair and regeneration. Faseb J. 2010;24(10):3625-3632.
[34] JOSEPHSON TO, MORGAN EF. Harnessing mechanical cues in the cellular microenvironment for bone regeneration. Front Physiol. 2023; 14:1232698.
[35] NAIR V, PATIL VS, TODKAR A, et al. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins: A Promising Approach for Enhancing Fracture Healing. Cureus. 2024; 16(8):e66619.
[36] MARIDAS DE, FEIGENSON M, RENTHAL NE, et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins. Principl Bone Biol. 2020:1189-1197.
[37] KODAMA N, MATSUBARA T, YOSHIMURA A, et al. BMP3b regulates bone mass by inhibiting BMP signaling. Bone. 2024;190:117303.
[38] BEGAM H, NANDI SK, KUNDU B, et al. Strategies for delivering bone morphogenetic protein for bone healing. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70(Pt 1):856-869.
[39] ROSEN V. BMP2 signaling in bone development and repair. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20(5-6):475-480.
[40] ZOU ML, CHEN ZH, TENG YY, et al. The Smad Dependent TGF-β and BMP Signaling Pathway in Bone Remodeling and Therapies. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:593310.
[41] CHEN G, DENG C, LI YP. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(2):272-288.
[42] WU M, WU S, CHEN W, et al. The roles and regulatory mechanisms of TGF-β and BMP signaling in bone and cartilage development, homeostasis and disease. Cell Res. 2024;34(2):101-123.
[43] MITSUI N, SUZUKI N, MAENO M, et al. Optimal compressive force induces bone formation via increasing bone morphogenetic proteins production and decreasing their antagonists production by Saos-2 cells. Life Sci. 2006;78(23):2697-706.
[44] DA SILVA MADALENO C, JATZLAU J, KNAUS P. BMP signalling in a mechanical context - Implications for bone biology. Bone. 2020;137: 115416.
[45] RATH B, NAM J, DESCHNER J, et al. Biomechanical forces exert anabolic effects on osteoblasts by activation of SMAD 1/5/8 through type 1 BMP receptor. Biorheology. 2011;48(1):37-48.
[46] SCHREIVOGEL S, KUCHIBHOTLA V, KNAUS P, et al. Load-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells is caused by mechano-regulated autocrine signaling. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(11):1992-2008.
[47] WANG D, WANG H, GAO F, et al. ClC-3 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation in MC3T3-E1 Cell After Dynamic Compression. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(6):1606-1613.
[48] PÉREZ-LOZANO ML, SUDRE L, VAN EEGHER S, et al. Gremlin-1 and BMP-4 Overexpressed in Osteoarthritis Drive an Osteochondral-Remodeling Program in Osteoblasts and Hypertrophic Chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(4):2084.
[49] WEI Q, HOLLE A, LI J, et al. BMP-2 Signaling and Mechanotransduction Synergize to Drive Osteogenic Differentiation via YAP/TAZ. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(15):1902931.
[50] MURUGAIYAN K, AMIRTHALINGAM S, HWANG NS, et al. Role of FGF-18 in Bone Regeneration. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(1):36.
[51] LI HZ, ZHANG JL, YUAN DL, et al. Role of signaling pathways in age-related orthopedic diseases: focus on the fibroblast growth factor family. Mil Med Res. 2024;11(1):40.
[52] ZHANG J, LIU Z, LI Y, et al. FGF2: a key regulator augmenting tendon-to-bone healing and cartilage repair. Regen Med. 2020;15(9):2129-42.
[53] ESWARAKUMAR V P, LAX I, SCHLESSINGER J. Cellular signaling by fibroblast growth factor receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005; 16(2):139-149.
[54] MURALI SK, ROSCHGER P, ZEITZ U, et al. FGF23 Regulates Bone Mineralization in a 1,25(OH)2 D3 and Klotho-Independent Manner. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(1):129-142.
[55] OGURA H, NAKAMURA T, ISHII T, et al. Mechanical stress-induced FGF-2 promotes proliferation and consequently induces osteoblast differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;684:149145.
[56] NAKAJIMA R, YAMAGUCHI M, KOJIMA T, et al. Effects of compression force on fibroblast growth factor-2 and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand production by periodontal ligament cells in vitro. J Periodontal Res. 2008;43(2):168-173.
[57] UDA Y, AZAB E, SUN N, et al. Osteocyte Mechanobiology. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017;15(4):318-25.
[58] 李亚洁,赵海英,荆蕾蕾,等.miR-29b、PTEN表达与胫骨干骨折延迟愈合的相关性分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(6):626-628.
[59] ZHANG M, YU W, NIIBE K, et al. The Effects of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB on Bone Marrow Stromal Cell-Mediated Vascularized Bone Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:3272098.
[60] 赵维维,杨大春,孙雄山.肌微管素相关蛋白7在小鼠血管平滑肌细胞增殖和迁移中的作用及机制[J].解放军医学杂志,2022,47(6): 545-554.
[61] WANG W, ZHUANG H, LEVITZ CL, et al. The increased level of PDGF-A contributes to the increased proliferation induced by mechanical stimulation in osteoblastic cells. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1997;43(2):339-346.
[62] GILLMAN CE, JAYASURIYA AC. FDA-approved bone grafts and bone graft substitute devices in bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;130:112466.
[63] CAPLAN AI, CORREA D. PDGF in bone formation and regeneration: new insights into a novel mechanism involving MSCs. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(12):1795-1803.
[64] SHAH P, KEPPLER L, RUTKOWSKI J. A review of platelet derived growth factor playing pivotal role in bone regeneration. J Oral Implantol. 2014;40(3):330-340.
[65] SHA L, ZHAO Y, LI S, et al. Insights to Ang/Tie signaling pathway: another rosy dawn for treating retinal and choroidal vascular diseases. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):898.
[66] 朱振华,左志城,周聚普,等.VEGF/Akt信号通路在骨折大鼠愈合中作用机制及对炎症因子IL-6、TNF-α的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2024,44(3):696-700.
[67] MENGER MM, LASCHKE MW, NUSSLER AK, et al. The vascularization paradox of non-union formation. Angiogenesis. 2022;25(3):279-290.
[68] MIYAGAWA A, CHIBA M, HAYASHI H, et al. Compressive force induces VEGF production in periodontal tissues. J Dent Res. 2009;88(8):752-756.
[69] ZHAN JW, WANG SQ, FENG MS, et al. Effects of Axial Compression and Distraction on Vascular Bud and VEGFA Expression in the Vertebral Endplate of an Ex Vivo Rabbit Spinal Motion Segment Culture Model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46(7):421-432.
[70] GUERRA A, BELINHA J, SALGADO C, et al. Computational Insights into the Interplay of Mechanical Forces in Angiogenesis. Biomedicines. 2024;12(5):1045.
[71] 芮泽,张喜善,张辉,等.持续性压力对VEGF分泌的影响[Z].第21届中国康协肢残康复学术年会暨第二届“泰山杯”全国骨科青年科技创新论坛论文集.山东泰安. 2012:218.
[72] 石笑.周期性动态压力及富血小板纤维蛋白对牙周膜干细胞血管内皮向分化的影响及机制研究[D].西安:中国人民解放军空军军医大学,2020.
[73] 钟刚,裴福兴,黄富国,等.不同压力刺激耦合VEGF基因转染促进骨折愈合的试验研究[Z].中国康复医学会修复重建外科专业委员会第19次学术交流会暨中国医师协会烧伤科医师分会2012年年会论文集. 北京. 2012:69-70.
[74] TSENG HW, SAMUEL SG, SCHRODER K, et al. Inflammasomes and the IL-1 Family in Bone Homeostasis and Disease. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2022;20(3):170-185.
[75] SIMS NA. Influences of the IL-6 cytokine family on bone structure and function. Cytokine. 2021;146:155655.
[76] ZHANG Y, LI X, CHIHARA T, et al. Effect of TNF-α and IL-6 on Compact Bone-Derived Cells. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18(3):441-451.
[77] MCGREGOR NE, MURAT M, ELANGO J, et al. IL-6 exhibits both cis- and trans-signaling in osteocytes and osteoblasts, but only trans-signaling promotes bone formation and osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2019; 294(19):7850-7863.
[78] GADOMSKI S, FIELDING C, GARCíA-GARCíA A, et al. A cholinergic neuroskeletal interface promotes bone formation during postnatal growth and exercise. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29(4):528-544.e9.
[79] YANG A, LU Y, XING J, et al. IL-8 Enhances Therapeutic Effects of BMSCs on Bone Regeneration via CXCR2-Mediated PI3k/Akt Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(1):361-370.
[80] LIN D, CHAI Y, MA Y, et al. Rapid initiation of guided bone regeneration driven by spatiotemporal delivery of IL-8 and BMP-2 from hierarchical MBG-based scaffold. Biomaterials. 2019;196:122-137.
[81] MAHON OR, BROWE DC, GONZALEZ-FERNANDEZ T, et al. Nano-particle mediated M2 macrophage polarization enhances bone formation and MSC osteogenesis in an IL-10 dependent manner. Biomaterials. 2020;239:119833.
[82] CHEN X, WAN Z, YANG L, et al. Exosomes derived from reparative M2-like macrophages prevent bone loss in murine periodontitis models via IL-10 mRNA. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):110.
[83] JUNG YK, KIM GW, PARK HR, et al. Role of interleukin-10 in endochondral bone formation in mice: anabolic effect via the bone morphogenetic protein/Smad pathway. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(12): 3153-3164.
[84] YIN J, HAO Z, MA Y, et al. Concomitant activation of the PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signalling is involved in cyclic compressive force-induced IL-6 secretion in MLO-Y4 cells. Cell Biol Int. 2014;38(5):591-598.
[85] PROFF A, NAZET U, SCHRÖDER A, et al. Mechanical Stress Induces Sodium Entry and Osmoprotective Responses in Murine Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells. 2024;13(6):496.
[86] GARCíA-LóPEZ S, MEIKLE M C, VILLANUEVA RE, et al. Mechanical deformation inhibits IL-10 and stimulates IL-12 production by mouse calvarial osteoblasts in vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 2005;50(4):449-452.
[87] ZHANG F, WANG CL, KOYAMA Y, et al. Compressive force stimulates the gene expression of IL-17s and their receptors in MC3T3-E1 cells. Connect Tissue Res. 2010;51(5):359-369.
[88] FAHY N, MENZEL U, ALINI M, et al. Shear and Dynamic Compression Modulates the Inflammatory Phenotype of Human Monocytes in vitro. Front Immunol. 2019:10:383.
[89] CHATMAHAMONGKOL C, PRAVITHARANGUL A, SUTTAPREYASRI S, et al. The effect of compressive force combined with mechanical vibration on human alveolar bone osteoblasts. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2019;9(1):81-85.
[90] 王鑫,吾布力卡斯木•米吉提,黄金勇,等.肿瘤坏死因子α对骨组织细胞的调节[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(21):3400-3406.
[91] WU Y, JING Z, DENG D, et al. Dkk-1-TNF-α crosstalk regulates MC3T3E1 pre-osteoblast proliferation and differentiation under mechanical stress through the ERK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023; 478(10):2191-2206.
[92] KITAURA H, KIMURA K, ISHIDA M, et al. Effect of cytokines on osteoclast formation and bone resorption during mechanical force loading of the periodontal membrane. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:617032.
[93] ZHANG C, LIN S, LI T, et al. Mechanical force-mediated pathological cartilage thinning is regulated by necroptosis and apoptosis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(8):1324-1334.
[94] 杨青,吴磊,刘洋,等.开放性骨折感染患者病原菌分布及血清促炎细胞因子水平的变化[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2019,29(16): 2482-2485+2499. |